Fertilizers are substances used to enrich soil with nutrients and improve its fertility. These products work by providing plants with one or more deficient chemical elements they require for proper growth and development. To achieve the desired effect, it's important to strictly follow the instructions.
What is fertilizer?
This term refers to all substances added to the soil or used as foliar sprays. They can be natural or chemically synthesized. Plants absorb these substances through their roots from the soil or through their foliage when sprayed. Once absorbed by the plant, these substances participate in essential life processes. They are required for development, flowering, and fruiting.
Fertilizers are absorbed by crops as individual mineral elements. If the soil is deficient in certain nutrients, single-component fertilizers can be used. However, in most cases, combined formulations are used. These are considered more convenient from a preventative standpoint and should be applied according to a specific schedule.
Types of fertilizers for plants
Mineral and organic fertilizers are classified by origin, application method, aggregate state, and other parameters. All of these factors must be taken into account to select the right fertilizer.
By mode of action
Depending on the specific effects of fertilizers, they are divided into the following types:
- Direct fertilizers are used to saturate plants with nutrients. They include various elements, such as iron, magnesium, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, and others. These fertilizers are divided into simple and combined.
- Indirect fertilizers are used to influence the soil to improve the conditions for fertilizer application. For example, ground limestone or dolomite can help make the soil less acidic. Sodium hydrosulfite is suitable for acidifying the soil.
By method of application to soil
Depending on the method of introducing the substance into the soil, the following types of fertilizers are distinguished:
- The main ones are those that saturate the soil with nutrients required for a particular crop.
- Pre-sowing – involves treating seeds before planting.
- Top dressing – replenish the deficiency of specific substances.
- Intrasoil – embedded in the root zone.
- Surface - in this case, the fertilizer is distributed over the surface of the beds.
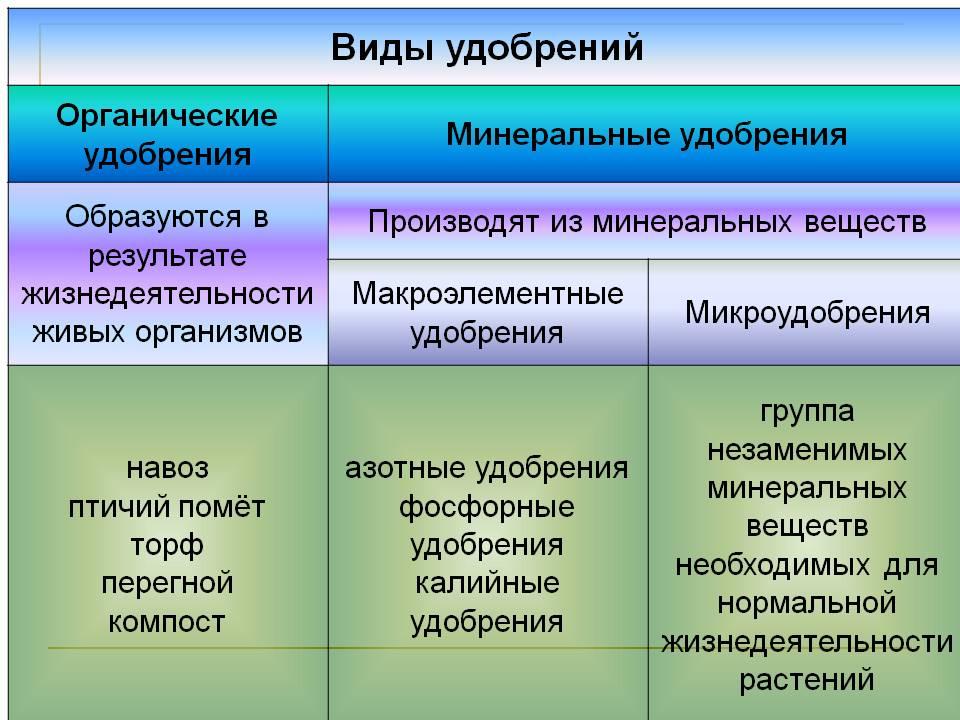
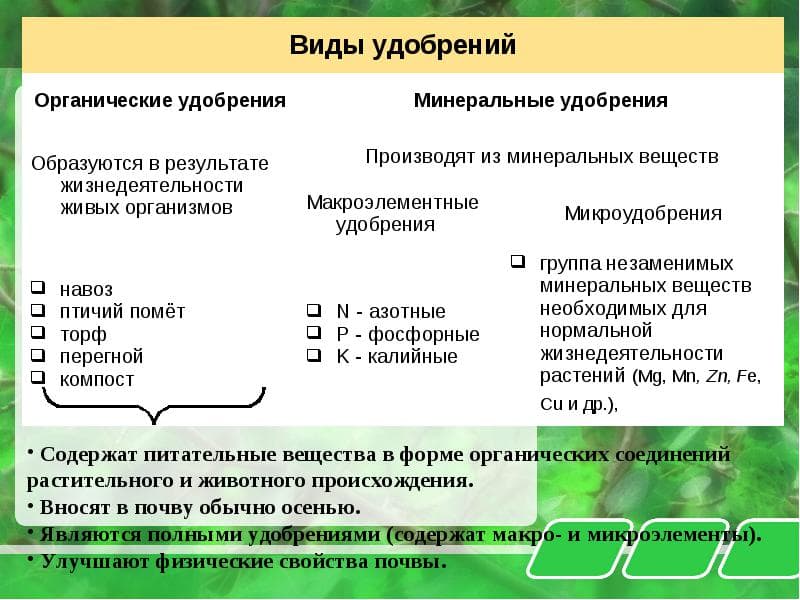
By origin
All fertilizers are classified by composition. Based on their origin, substances can be divided into two major groups:
- Minerals – include microelements that are easily absorbed by plants.
- Organic waste is the byproduct of animal and plant life. This group also includes decayed waste. It breaks down into its individual components and is readily absorbed by crops.
Mineral fertilizers may contain a single active ingredient or a combination of them. In the former case, the product is used to replenish specific element deficiencies. Combined fertilizers must be applied according to a schedule. This helps prevent problems.
By state of aggregation
Fertilizers are categorized by release form. When choosing the optimal formulation, consider convenience and the area being treated. For indoor plants, it's best to use sticks or liquid fertilizers. For larger areas, powders or solutions are recommended. These are applied using specialized equipment.
Depending on the form of release, fertilizers are divided into the following groups:
- Liquid – used for application to soil or foliar treatment.
- Solid fertilizers are available in granules, sticks, tablets, or powder form. They should be applied dry to the soil or used to prepare solutions.
Beginners are better off using fertilizers designed for specific crop types. Manufacturers of these products take into account the specific characteristics of the crops and use nutrients in the right proportions.

How to choose the right one
Any substances must be applied to the soil strictly according to the instructions. It's important to select the right combination of nutrients and consider a number of factors. Primarily, consider the soil's acidity.
Normal pH values are 6-6.5. Crops thrive in this range. General-purpose fertilizers are acceptable. If pH values exceed 7, the soil is considered alkaline. Nitrate fertilizers are needed in this situation. If soil pH is less than 5.5, there's a risk of decreased potassium, sulfur, and magnesium absorption. In this situation, ammonium-based fertilizers are more suitable.
When choosing a fertilizer, it's important to consider the type of plant. Plants can be indoor, ornamental, or garden. Each type has specific nutrient requirements, which dictates the type of fertilizer used. Excessive amounts of certain substances can cause unpredictable consequences.
The need of crops for certain resources can be determined by their appearance:
- A lack of nitrogen causes foliage to become smaller and duller. It can also turn yellow and fall off. This can also cause the plant to lag behind in development.
- Phosphorus deficiency causes dull spots to form on the foliage. These spots have a red or purple tint. There is also a risk of delayed flowering and crop ripening.
- A potassium deficiency causes the foliage to turn pale and bluish. There's also a risk of shoot thinning.
- Potassium deficiency leads to the formation of whitish leaves and the death of shoots.
- Magnesium deficiency causes plant leaves to drop, turning yellow or reddish.
Top manufacturers
Currently, many brands produce fertilizers. Among the most well-known companies are EuroChem, PhosAgro, and Acron.
Instructions for using garden fertilizers
When applying fertilizers, be sure to follow the instructions for use. They specify the rules for preparing aqueous solutions and the frequency of their use for crops.
When applying fertilizer, it's important to do so only at the stages where it's needed. Fertilizing plants should only be done during the growing season—from March to October. In winter, plant life slows down. Fertilizing at this time of year disrupts the natural cycle of crops. Furthermore, the soil freezes in winter, so applying fertilizer to the garden is ineffective.
Fertilizers are essential tools often used in plant cultivation. They come in a variety of categories and have a complex effect on crops. To ensure effective application, it's important to strictly follow the instructions.



