Tomatoes need to be grown from seedlings to reach maturity. The future harvest depends on the condition of the tomato seedlings before planting them in open ground. Growing tomato seedlings presents many challenges. It's crucial to identify the cause of yellowing tomato seedlings and eliminate the underlying causes.
Why do tomato seedlings turn yellow?
Growing tomato seedlings on a windowsill requires proper care. Watering and soil composition play a role in the proper development of tomato seedlings. It's important to ensure the growing crops have enough space in the container. After transplanting, the plants thrive; they receive sufficient moisture, nutrition, and light. Cotyledon leaves dry out when seedlings become diseased or when planting is too dense.
Deficiency or excess of micronutrients
Growing tomatoes successfully requires sufficient micronutrients in the soil. A deficiency or excess of these micronutrients causes the seedlings to dry out. Deficiencies can be seen in:
- nitrogen - in yellowing of the lower leaves, red veins on the plates;
- potassium - the tips of the leaves dry out;
- zinc - in the curling of leaves and brown spots on them;
- iron - white spots on greenery.
Excessive amounts of nitrogen and potassium fertilizers also lead to yellowing of tomato leaves.
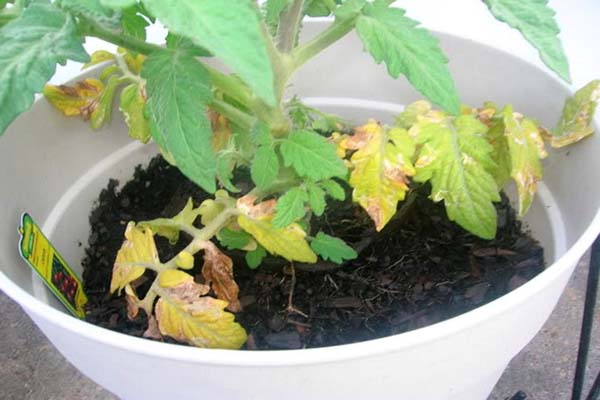

Insufficient lighting
Tomatoes require a maximum of 12 hours of daylight for growth. During winter and cloudy weather, seedlings receive little light. Without this light, healthy seedlings will not grow. The best solution is to install phytolamps over the tomato boxes. It is not recommended to keep them on for more than 12 hours. Otherwise, a pathological condition called chlorosis, associated with iron deficiency, cannot be avoided.
Consequences of close planting of seedlings
Tomato seeds are first planted in boxes. If the distance between them is less than 1-2 centimeters, the seedlings will soon lack nutrients and become crowded. They will begin to stretch. Taller plants will overwhelm the weaker ones. They will wither, turn yellow, and die.
When the seedlings have two true leaves, they are pricked out. When replanting, each plant should be given its own pot.
Too many plants in a container leads to waterlogging. A lot of moisture accumulates because light and air are blocked. This contributes to root rot and tomato diseases.
Soil
Before planting vegetables, select the soil mixture. It should contain sufficient nitrogen, potassium, zinc, and manganese. Pay attention to the looseness of the soil. Dense soil will prevent moisture and air from reaching the tomato roots, causing the leaves to turn yellow.
Tomatoes won't grow well if the soil's acidity isn't checked. Use litmus paper to determine the soil's pH. It should be between 6 and 6.5. You can reduce the acidity by adding slaked lime or dolomite powder.
Soil salinity causes the seedlings' leaves to become covered in yellowish spots. A whitish coating is visible on the soil surface in the boxes. In this case, the seedlings need to be replanted.
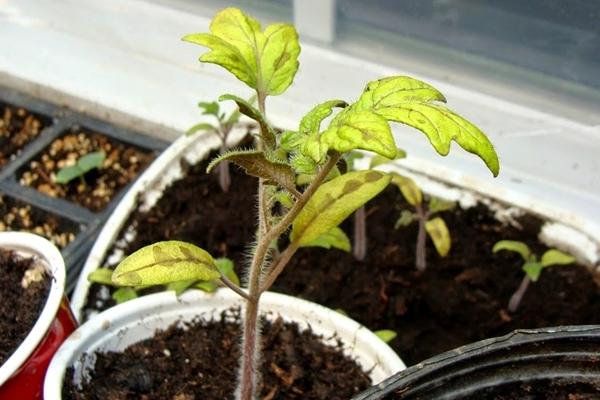

Incorrect watering
When caring for vegetable crops, always follow the norm. Although plants need moisture, it should be within the norm. If yellowing appears on the cotyledon leaves, pay attention to the soil condition. The appearance of mold indicates waterlogging. Watering the seedlings should be stopped and the soil should be brought back to normal.
Plants also do not tolerate drought well. Infrequent watering leads to the roots drying out and the death of young tomatoes. When the soil dries out to a depth of 3-5 centimeters, it is dangerous for seedlings.
Diseases that cause yellowing
Tomato seedlings are susceptible to diseases caused by improper care. Pathogenic fungi become active when the soil becomes waterlogged. Plants become infected more quickly when their containers are crowded. Diseases can be detected by the condition of the leaves, which turn yellow and become spotted.
A common disease is black leg.
Tomato seedling death is usually caused by crown rot, or blackleg. When 2-3 true leaves appear, the lower part of the stem becomes thinner. The seedlings then fall over and die. The disease is caused by:
- the soil is contaminated with fungus;
- tomatoes are planted densely;
- there is not enough air for the crops;
- water the seedlings generously;
- the room temperature jumps sharply.
To prevent fungal diseases, it's important to take soil and seed disinfection seriously. Plants should be provided with sufficient light and nutrients to strengthen their immune system.
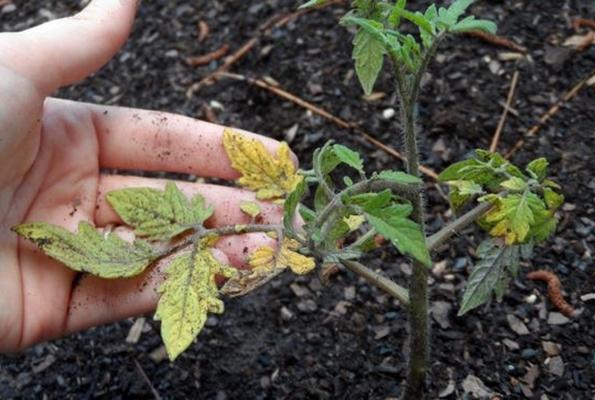

Fungal disease fusarium
Fusarium wilt is caused by a soil-dwelling fungus. It invades green tomato seedlings and causes their death. The fungus is active when:
- tomatoes are densely planted;
- there is no stability in temperature conditions;
- a lot of chlorine in the soil;
- increased air and soil humidity.
The fungus attacks the lower leaves of seedlings, then spreads upward. Brown spots are visible on the stems, where fungal spores have accumulated.
Diseased plants are immediately removed and the soil is watered with a solution of potassium permanganate.
How to help tomato seedlings
The leaves of the tomato seedlings have turned yellow – urgent action is needed:
- You should dig up the plant, carefully examine the roots and transplant the seedling into another pot.
- Before repotting, the soil and container must be disinfected. Solutions of potassium permanganate or boric acid are used for this purpose. Boiling water will also work.
- Dense plantings are thinned by picking seedlings. They are planted 3-5 centimeters apart.
- Monitor the air temperature. It should not be above 25 degrees Celsius or below 18 degrees Celsius.
- If the soil is wet and covered with mold, then remove the top layer of soil, stopping watering for a while.
- The small amount of light is compensated by installing phytolamps or fluorescent devices.
- You can cope with seedling diseases by treating them with Fitosporin.
Yellowing of plant leaves is prevented by proper tomato cultivation techniques.
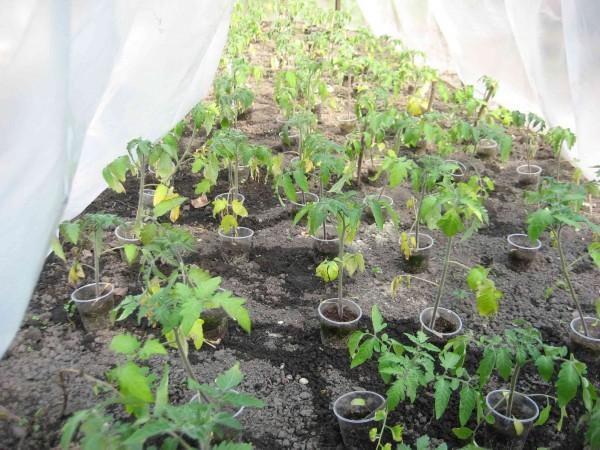

Preventive measures
Preventing yellowing on tomato leaves involves feeding the seedlings properly. Young plants need nitrogen to increase their foliage. Apply urea every two weeks, diluting 20-30 grams of the fertilizer in a bucket of water.
Potassium permanganate is used not only for disinfection but also as a fertilizer. The solution will replenish manganese in the soil. You can simply spray the leaves of seedlings with the pinkish liquid.
Wood ash contains many useful elements necessary for the development of tomatoes. One cup of ash is enough for 10 liters of water. After two hours of preparation, water the tomato seedlings with the solution.
Potassium nitrate contains important substances that promote healthy tomato seedling growth. However, when using this fertilizer, it's important to follow the instructions. High concentrations of the fertilizer can cause leaf and stem burns.
Tomato seedlings are cared for so that they don't suffer from a lack of nutrition, moisture, or light. However, over-watering and over-fertilizing can also cause the seedlings to turn yellow.