- Appearance of the plant
- Smell and taste
- Aroma
- Types and varieties of basil
- Ararat
- Lime
- Oriental Breeze
- Blue Spice
- Anise Basil
- Thai Basil
- All Year
- African Blue
- Where it grows
- How spices are made
- How to choose it for seasoning
- Features and specifications
- Calorie content and nutritional value
- Chemical composition of basil
- Benefits and harms of the product
- Contraindications for use
- Application of culture
- In cooking
- In medicine
- In everyday life
- Features of growing basil
- Plant care
- Watering
- Fertilizers and dressings
- What can be planted after basil?
- Plant diseases
- Blackleg
- Fusarium
- Gray rot
- Pests of crops
- Aphid
- Meadow or field bug
- Propagation of basil
- Harvesting
- Procurement of raw materials
- Freezing
- Paste
- Pickling
Herbs have been a part of human life since ancient times. Every nation has its own favorite flavors, which make its national dishes unique. Knowledge of basil spread from Central Asia, the Caucasus, and France. Now everyone knows what basil is, how to use it, and the plant's benefits.
Appearance of the plant
Basil bushes are considered a garden ornament. Ovate leaves sit on petioles on tetrahedral stems. During the growing season, white or red flowers appear in the axils of the green or purple leaves. They are irregularly shaped and have a ligule. It's no wonder they are called two-lipped. Above the long lower lip are four stamens with hair-like appendages.
Breeders have developed ornamental varieties of the plant that are grown for landscaping. Annual basil is attractive, delightful with its aroma, and unique flavor.
Smell and taste
A favorite spice of the Caucasian peoples, basil has a wonderful aroma. Depending on the variety, it has a varied flavor. The green, juicy leaves are quite tender, making them excellent in desserts and cocktails. The purple, herbaceous basil has a slight tang and bitterness, making it suitable for meat, fish, and vegetable dishes.
Aroma
The spice varieties also differ in their aroma, which results from the presence of essential oils in the leaves. It's no wonder that the plants were used to produce camphor oil. The scent is stronger during the flowering period.

Green basil varieties are characterized by a subtle aroma. Bushes often have a delicate scent of cloves and pepper, mingled with the sweet aroma of vanilla and caramel. Purple varieties have a more pronounced aroma, with notes of pepper, cloves, cinnamon, lemon, and menthol more prominent.
Types and varieties of basil
Fragrant basil is a favorite among gardeners. It is grown as a spice for various dishes and drinks. There are varieties that are useful for treating illnesses. The plant's camphor-like scent repels harmful insects.
Ararat
The purple variety of basil has excellent taste. The anise-scented leaves enhance any dish and are also used in canning. Germination occurs in 70-75 days. The semi-spreading bush reaches a height of 40-60 centimeters. The harvest is in August-September.

Lime
The green variety of this herb has a vibrant lime aroma. The leaves are added as a seasoning to salads, desserts, soups, and rice dishes. The branched bush is compact, reaching a height of 15-60 centimeters. Its pointed, light green leaves. The flowers are white and borne in spikes.
Oriental Breeze
This red-flowered plant is considered an ornamental plant. However, the leaves of this mid-season herb can also be used in cooking.
Blue Spice
This hybrid has a delicate, fruity flavor and a pleasant aroma. The bushes reach half a meter in height. When in bloom, they are covered in numerous white spikelets. The plant prefers loamy soil and thrives at temperatures of 25°C.

Anise Basil
This purple-leaved plant makes a beautiful addition to your garden. Its anise-flavored leaves are perfect for use in seasonings and sauces.
Thai Basil
This is the best variety used in Thai cuisine. The bushes feature glossy green leaves and lilac flowers.
All Year
The hybrid has a distinctive clove aroma with a hint of resin. The green leaves are used in cooking. Flowers appear in July-August. They are white and gathered in spikes.
African Blue
The white flowers and purple foliage on tall basil bushes draw attention with their beauty. This ornamental variety produces enough aromatic herbs in August to last through the winter.

Where it grows
Although basil is native to the southern regions, it is grown everywhere. The plant does not tolerate low temperatures well, so it dies at the first frost. However, before then, a bountiful harvest of the spice can be harvested and stored for the winter. Common basil is widely used in Central Asia, where it is called raykhon, as well as in the Transcaucasus. There, the spicy shoots are eaten raw, dried, and added to soups and vegetable dishes. The French enjoy basil sauces, and Italians sprinkle the dried herb powder on pasta, jellied fish, and boiled fish.
How spices are made
You can cook with this spice, using it raw. Basil leaves are collected and used to garnish cocktails or desserts. Finely chopped green or purple basil is used to make a paste or added to cottage cheese. To prevent the spice from darkening and spoiling the appearance of the dish, tear the leaves into small pieces by hand.
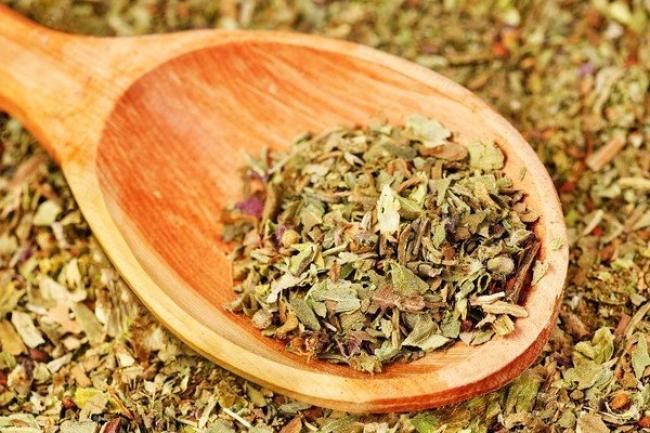

It's best to prepare a dry powder from the herb. To do this, dry the leaves in a well-ventilated area. Then grind them into a powder. Combined with pepper and cinnamon, this spice makes a wonderful addition to many dishes. A liquid seasoning is also available, which allows the basil flavor to be more fully expressed.
How to choose it for seasoning
When choosing a seasoning plant, you need to consider the dish you want to flavor:
- Green basil leaves are added to soups. They should be smooth and undamaged.
- You can mix finely chopped leaves of the purple and green varieties of the plant to decorate salads and vegetable dishes.
- Canning works best with whole plant parts. They should be brightly colored and juicy.
- Dry seasoning is prepared only from fresh basil.
Collect the grass in the morning or evening, carefully picking off the leaves.You don't need to store them for a long time, so they don't wilt.
Features and specifications
Before using basil, or the royal herb, in cooking, it's important to know if it's safe for everyone. This herb has many beneficial properties, but there are also some contraindications. Vegetable varieties are widely used as a spice. Interestingly, the common variety is more often used as food. Many cultivars have been bred purely for decorative purposes. The leaves of these species have no nutritional value.

Calorie content and nutritional value
The edible portion of the plant contains 23 kcal per 100 grams of product. Basil leaves are rich in vegetable protein (3.15 g) and carbohydrates (1.54 g). The amount of fat is minimal.
Chemical composition of basil
The leaves of the plant contain enough:
- B vitamins;
- ascorbic acid;
- vitamin E, K;
- potassium and calcium;
- magnesium;
- gland;
- manganese.

The plant contains a number of essential amino acids, as well as glycine and glutamic acid.
Benefits and harms of the product
For medicinal purposes, basil is harvested during its flowering period. The herb is used to prepare preparations effective for asthenia and circulatory disorders. It is also used to treat epilepsy and depression. The spice helps stop toothaches and vomiting. Those who include basil in their diet experience a calming effect and an improved appetite. It is also useful for relieving asthma and fever symptoms.
Infusions of the herb are used to rinse the mouth for stomatitis, and the leaves are applied to problem areas of the skin when allergic dermatitis is detected.
Pregnant women can take basil to improve fetal development, but only under a doctor's supervision. Nursing mothers can use basil to increase milk supply. However, it's important not to exceed the recommended dose, as it contains a high concentration of essential oils.
Contraindications for use
There are contraindications for indulging in this spice. Those who have had a myocardial infarction or suffer from poor blood clotting should not consume the herb. It is absolutely harmful to include basil in the diet of people with arterial hypertension, thrombophlebitis, and thrombosis of the veins of the lower extremities.

Application of culture
The plant is widely used not only in cooking and medicine, but also in other areas of life. Essential oils are needed for the perfume industry. Dried herbs are used in the preparation of sausages, liqueurs, and smoking.
In cooking
Basil leaves are added to all dishes, both first and second courses. They are chopped by hand and sprinkled before serving. The herb's flavor and aroma complement tomatoes, peppers, eggplant, and beans. You can sprinkle it over boiled spaghetti. Italians can't imagine pasta or pesto sauce without the aroma of this herb. In Central Asia, this herb, with its delicate lemon aroma and flavor, is a favorite addition to all dishes of their national cuisine.

In medicine
The herb is added to medications used by patients with:
- bronchial asthma;
- epilepsy;
- depression;
- colds.
Fresh leaves should be consumed to relieve headache symptoms.
In everyday life
The essential oils in basil serve as a good repellent against flies and other insects. Hanging a bunch of sprigs in the kitchen can improve the room's aroma and disinfect the air. Wiping down household utensils with water and basil essential oil, along with other herbs, can eliminate unpleasant odors.

Features of growing basil
To plant herbs, prepare beds with fertile, well-drained soil. The planting site must be well-lit. Seeds should be sown when the temperature reaches 10 degrees Celsius (50 degrees Fahrenheit). Spring frosts can ruin the crop. Plants should be spaced 30-40 centimeters apart.
Basil grows best at temperatures of 18-25 degrees.Therefore, at first it is necessary to cover the beds with plastic film.
Plant care
Basil is easy to care for, but it does require specific soil moisture, air temperature, and light. It requires the same attention as other vegetable crops.
Watering
Basil sprouts require constant watering. During dry summers, water up to twice a week. Use room-temperature water. The plant dislikes cold watering and will look depressed. Before watering and after rain, be sure to loosen the soil around the basil bed.

Fertilizers and dressings
The grass yield depends on the soil's nutritional value. Fertilizing should begin 10 days after planting. Then, apply fertilizer every two weeks, alternating mineral and organic fertilizers. Nitrophoska is optimal. Dissolve two tablespoons in a bucket of water, then water the plants. Use 4 liters of nutrient solution per square meter.
What can be planted after basil?
Basil should be planted in the same spot for 2-3 seasons. Then, move to another location. After basil, you can plant tomatoes, squash, zucchini, cucumbers, and carrots. Basil should be planted in areas previously occupied by tomatoes, cabbage, and onions.

Plant diseases
The plant rarely gets sick. Most often, diseases arise due to improper care and poor growing conditions. Young plants are susceptible to fungal infections in humid and hot weather. Planting density provokes the development of pathologies.
Blackleg
Gets a fungal infection basil at the seedling stagePathogenic microorganisms thrive in an acidic environment, in dense soil without air access. The blood vessels in the root collar become clogged, and the plant dies. The disease can be identified by thinning and blackening of the stem base. Immediately treat affected plants with a potassium permanganate solution. Plants affected by blackleg are best destroyed. Fitosporin is a fungicide that can combat the infection and its spread.
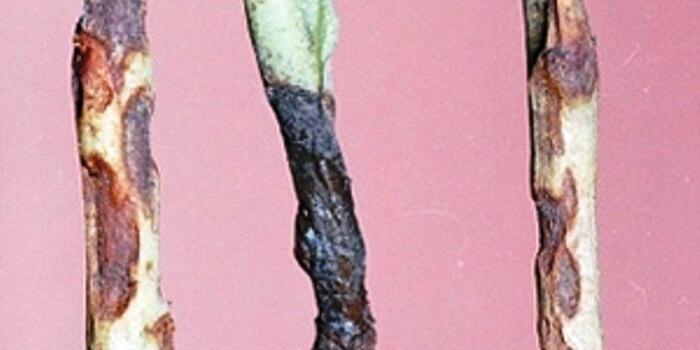
Fusarium
Fusarium disease of basil is characterized by:
- drying out of the top;
- thinning of young shoots;
- coloring the bushes brown.
Fungal toxins enter the plant's blood vessels, eventually infecting all basil plantings. Preventing the disease involves dusting the basil beds with wood ash.
Gray rot
Spice bushes grown indoors are susceptible to the disease. The infection begins with the drying of the lower leaves. Brownish spots then appear across the entire foliage. Over time, the leaves become covered with water-soaked spots and a gray fuzz.
At the initial stage of the disease, you can spray basil plantings with an infusion of onion peels.
Pests of crops
This herb is resistant to garden pests. However, under unfavorable conditions, basil is also susceptible to insect attack.
Aphid
One dangerous pest is almost invisible to the naked eye, but its activity causes leaf curling. Colonies of aphids are visible on the undersides of the leaves. The sweet, sticky secretions attract pathogens to the basil, infecting it. You can fight aphids by spraying with decoctions of wormwood and tansy.Treatment should be done with a tar soap solution, 100 grams per 10 liters of water. Insecticides such as "Karbofos" and "Aktellik" are considered effective against aphids.
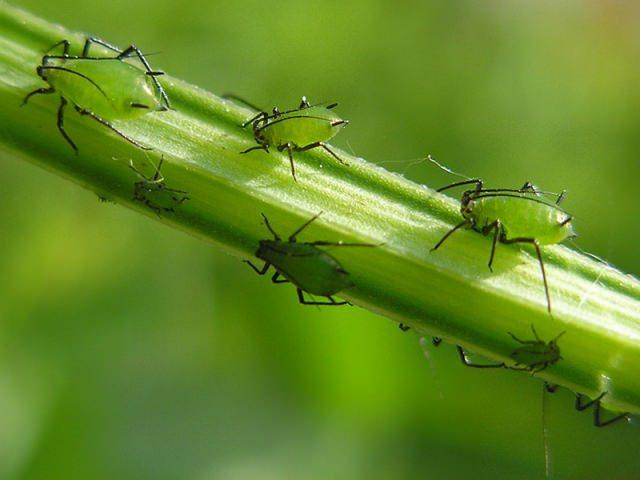

Meadow or field bug
This sucking insect feeds on the sap of basil leaves. The pest's presence can be identified by whitish spots on the leaves and deformed blades. As a result, basil plants are left bare. The best way to control the bug is with insecticides and wood ash solutions.
Propagation of basil
Since the plant is an annual, seeds are used for propagation. This preserves the varietal characteristics of the grass, unless different species are planted nearby. Cross-pollination can cause the characteristics to blend.
Seeds are planted directly into the soil or grown using seedlings.
Harvesting
Basil leaves are cut before the plants bloom. The first cut is made at the top of the plant. After this, the plants begin to branch, increasing the amount of foliage. The next time, the tops are left uncut, leaving the flower stalks.

After the first harvest in July, water the beds to ensure the foliage is lush. Harvesting should be done in dry weather, finishing before frost.
Procurement of raw materials
The herb is stored by drying. Bundles of the herb are hung in a dark, ventilated room. The dried plant retains the same beneficial properties as the fresh one. It is better to grind the dried leaves into powder, pour it into glass jars, and close them with a tight lid.
Freezing
Freeze whole basil leaves. Place them in bags or containers and place them in the freezer. It's best to freeze in small batches.
Paste
You can prepare basil for the winter like this:
- Place a layer of leaves tightly.
- Sprinkle with salt.
- Then the layers are laid out, mixing with salt.
- Fill the container with spices with olive oil.
- Cover with a lid and store in a cool place.
Oil and herbs are used to make pesto sauce.
Pickling
The collected leaves and stems are crushed by hand, sprinkled with salt. The ratio of herbs to salt is 5:1. Tamp the herbs down firmly, filling the container completely. Store the mixture in a cool place under ordinary lids.











