- General description and purpose of fungicides
- Pros and cons
- How quickly does it work and how long does it last?
- Classification
- Depending on the effect on the pathogen
- Depending on chemical properties
- Depending on the nature of distribution within plant tissues
- By purpose of use
- Mechanism of action
- Biological drugs
- Chemical fungicides
- Instructions for use
- For plants
- For seeds
- For the soil
- List of funds
- Gliocladin
- Acrobat MC
- Maxim
- Kurzat
- Ridomil Gold
- Rovral
- Topsin-M
- Green soap
- Consento
- Ordan
- Bordeaux mixture
- Abiga Peak
- Previkur
- Trichodermin
- Fitosporin-M
- Profit Gold
- Bayleton
- Oxychom
- "Raek"
- Vitaros
- "Skor"
- "Hom"
- Gamair
- Horus
- Precautions for handling
Growing healthy plants and harvesting a bountiful crop is virtually impossible without the use of chemical pesticides. Almost every gardener and farmer faces fungal diseases that progress in rainy and damp weather. To prevent crop failure and crop loss, landowners choose the most appropriate fungicide from a wide selection of garden fungicides.
General description and purpose of fungicides
Fungicides are chemicals and biological agents whose primary purpose is to protect and treat crops from fungal diseases. They may contain one or more active ingredients.
Recently, gardeners have been turning to biofungicides, which are non-toxic to trees and shrubs. However, these products have a drawback: their protective properties take much longer to develop than those of chemical-based products.
Pros and cons
Preparations such as fungicides have their own strengths and weaknesses.
When using fungicides, it's important not to exceed the recommended dosages and avoid eating fruits and vegetables immediately after treatment. Each product has a withholding period after which fruits and vegetables will no longer pose a risk to human health.

How quickly does it work and how long does it last?
Each fungicide has its own timeframe for pathogen destruction. Generally, the active ingredient requires 3 days to a week to completely destroy pathogenic microorganisms.
As a rule, the protective effect lasts for 2 weeks, after which it is recommended to repeat the treatment.
Classification
All fungicidal preparations are divided into several classes.
Depending on the effect on the pathogen
Based on this parameter, products are divided into protective and therapeutic. The former category typically includes contact fungicides, while the latter includes systemic ones. These products are effective against anthracnose, powdery mildew, rust, gray mold, and other fungal diseases.
Depending on chemical properties
According to this parameter, fungicides are classified into organic and inorganic (copper-containing and sulfur-containing).

Depending on the nature of distribution within plant tissues
Based on their distribution, preparations are divided into systemic and contact. The former penetrate the plant tissue and are evenly distributed, destroying pathogens. The latter act locally, directly at the site of application, creating a protective film on the plant surface that prevents pathogens from penetrating.
By purpose of use
The primary purpose of fungicides is to combat fungal diseases. Some products are designed to target a specific disease, while others are effective against a wide range of harmful microorganisms.
Fungicides are typically used against the following fungal diseases:
- from powdery mildew and various types of spots;
- from rust and scab;
- from late blight and anthracnose.
Mechanism of action
The principle of action of fungicidal preparations depends on the active substance that they contain.

Biological drugs
Organic products contain a natural active ingredient, typically a strain of beneficial bacteria, which inhibits pathogen growth. These fungicides are more often used for prevention than treatment. Biofungicides offer advantages such as a short period of action, the ability to be used at any stage of the growing season, and the absence of heavy metal salts.
Chemical fungicides
The principle of action of chemical preparations is determined by the active ingredients they contain. They inhibit the vital processes of microorganisms, leading to their death. Their action stops spore formation and disrupts the pathogen's respiration and nutrition.
Instructions for use
Each fungicide comes with instructions that indicate the optimal dosage for plants, seed and soil treatment, and application instructions.

For plants
Fungicides for trees and shrubs are applied at the first signs of infection—discoloration of leaves, weakened growth, and stunted growth. They are also used as a preventative measure for garden flowers and ornamental plants.
If a gardener cannot accurately determine the specific disease symptoms appearing on a crop, it is recommended to use broad-spectrum fungicides effective against many pathogens. Copper-based fungicides are used against late blight; treatment with these fungicides is especially beneficial during adverse weather conditions to protect plants.
Fungicides are available in various formulations, and each gardener chooses the most convenient option. Liquid chemicals dissolve best in water, making them more popular among gardeners who don't have industrial sprayers with agitators.
The use of fungicides to protect crops is permitted throughout the entire growing season; the maximum permissible number of sprays is indicated in the instructions.

For seeds
Some fungicides are approved for use as a pre-plant treatment for seeds and tubers. The recommended amount of the solution is dissolved in water and added to the seed, left for several hours, and then dried before sowing. This treatment not only prevents infection but also promotes better germination.
For the soil
Both biological and chemical fungicides are used for soil intended for future crop cultivation. The former are less dangerous, but do not always completely destroy pathogenic microorganisms in the soil. The latter are much more effective, but if applied in excess, they also destroy beneficial natural microflora.
List of funds
In the process of using fungicides, gardeners have identified the best preparations that have proven their effectiveness in practice.
Gliocladin
This biological product is effective against anthracnose, various rots, late blight, and verticillium wilt. It contains a soil fungus that inhibits the growth of pathogenic microorganisms. Gardeners cite its advantages as being environmentally friendly, economical to use, and improving soil quality after application. To enhance the protective properties of Gliocladin, it is recommended to use it in combination with other chemicals.

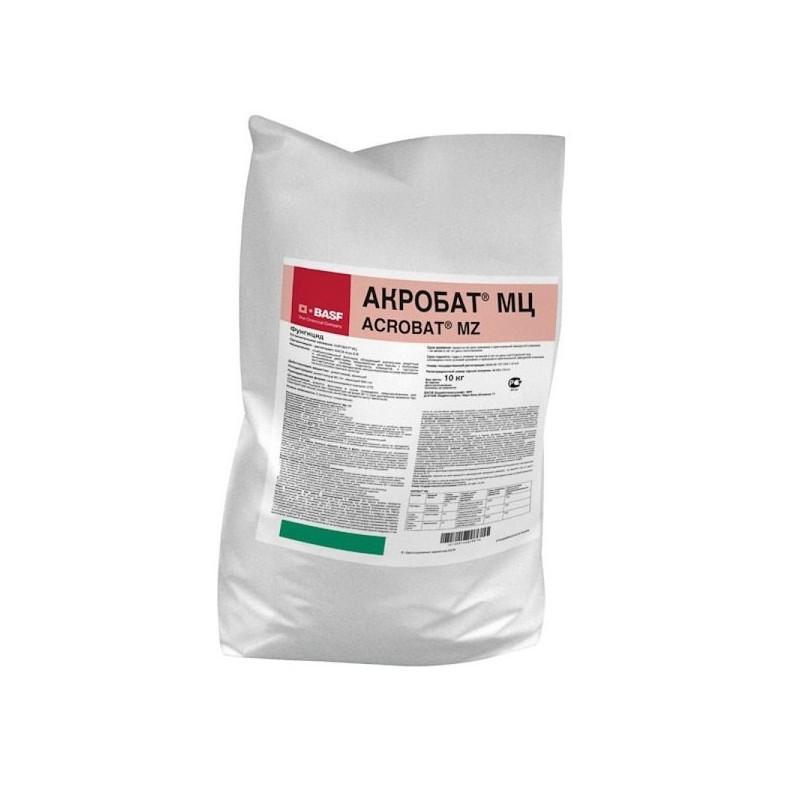
Acrobat MC
This two-component fungicide, manufactured in Germany, is designed to kill pathogens that cause diseases such as late blight, anthracnose, and downy mildew. Complete destruction of fungal mycelium is observed three days after plant treatment. It has both therapeutic and preventative properties, with the protective effect lasting for two weeks.

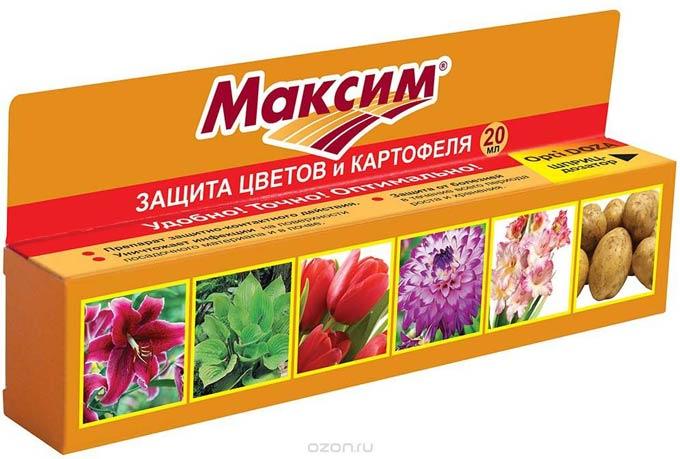
Maxim
This Italian-made product is intended for pre-sowing treatment of seeds and tubers. Its active ingredient acts like an antibiotic, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic fungi. Furthermore, it forms a protective film on the plant surface, preventing harmful microorganisms from penetrating the crop. Gardeners have highlighted the fungicide's versatility, allowing it to be used on both fruit and grain crops, its ease of use, and its high effectiveness.

Kurzat
This copper-containing fungicide is a systemic and locally active product. It is used to treat diseases of potatoes, grapes, and vegetable crops. It has a three-pronged effect—curative, protective, and preventative. The active ingredient immediately penetrates plant tissue and begins destroying pathogens, with the therapeutic effect lasting for two days after application.

Ridomil Gold
This fungicide is a combination fungicide containing two active ingredients. The instructions state that it is suitable for treating diseases of vegetable crops and grapes. It is also used preventatively. Among the advantages of Ridomil Gold are its lack of resistance and phytotoxicity when applied at the recommended dosage.

Rovral
The product is approved for use not only for plant treatment but also for disinfecting planting holes before planting seedlings. It is effective against various types of rot, downy mildew, and ascochyta blight. The active ingredient slows spore germination and inhibits mycelial growth. It is recommended to alternate Rovral with other chemicals to prevent the development of resistance. Phytotoxicity occurs only when the dosage is significantly exceeded.

Topsin-M
This product is used to protect fruit and berry crops from fungal pathogens. Topsin can be used throughout the growing season, but is most effective before the disease develops or when the first symptoms appear. Due to its systemic action, it quickly spreads throughout the crop and begins to have a detrimental effect on pathogens. Gardeners consider this fungicide's ability to be used on plants with mechanical damage a positive feature.

Green soap
Green soap is based on potassium salts of fatty acids. It has a contact effect and is used to combat insect pests on both garden plants and indoor flowers.

Consento
The product, available as an emulsifiable concentrate, contains two active ingredients with different effects on pathogens. Gardeners cite Consento's advantages as being suitable for both treatment and prevention, as well as its long protective period, even in adverse weather conditions.

Ordan
This fungicide has a local and systemic effect and is effective against late blight and downy mildew pathogens. It is approved for use on houseplants.
Bordeaux mixture
Bordeaux mixture is based on copper sulfate dissolved in slaked lime. It effectively kills most pathogenic microorganisms that damage garden crops. Spraying with Bordeaux mixture begins in the spring as a preventative measure.

Abiga Peak
The advantage of this fungicide is that it is effective against not only fungal diseases but also some bacterial ones. It can be used on both fruit and ornamental crops.

Previkur
The German company's chemical not only effectively protects crops from pathogens but also stimulates their growth and development. After applying Previkur, plants also experience increased immunity and resistance to pathogens. The plant penetrates through the root system.

Trichodermin
Trichodermin is a biological fungicide and does not harm soil microflora or treated plants. It is used both for treating already planted crops and for seed treatment.

Fitosporin-M
This product, which contains a biological component, is used to prevent powdery mildew, late blight, and root rot. It is approved for use on both garden crops and houseplants, as it has no adverse effects on human health.
Profit Gold
This product is intended for preventative treatments. It has demonstrated positive results in combating late blight of potatoes and tomatoes. Up to four applications per season are acceptable.

Bayleton
The product has a broad spectrum of action. It is used to protect vegetable crops, grains, and berry bushes. After penetrating plant tissue, it inhibits the development of mycelium and prevents further sporulation.

Oxychom
This two-component product is classified as a contact-systemic fungicide. "Oxychom" is recommended for the prevention and treatment of major diseases of potatoes, tomatoes, and grapes. A significant advantage is its long post-treatment protection period.

"Raek"
The systemic fungicide "Raek" is used to control scab and cercospora leaf spot pathogens affecting grain crops, sugar beets, and fruit trees. It is characterized by rapid penetration into plant tissue and long-lasting protective action. No more than four sprayings are permitted per season.

Vitaros
This product is designed to protect bulbous plants from soil-borne infections. Before planting, the soil is treated with it by adding 2 ml of fungicide to a liter of water.

"Skor"
The chemical is used for garden plants and indoor flowers. Its active ingredient quickly destroys pathogens that cause diseases such as powdery mildew and scab, early blight, and late blight.
"Hom"
This contact fungicide combats scab on pears and apples, leaf curl, and mildew on grapes. It is also used to disinfect soil before planting seedlings.

Gamair
The preparation belongs to biological fungicides and not only protects plants from pathogens, but also helps increase crop yields.

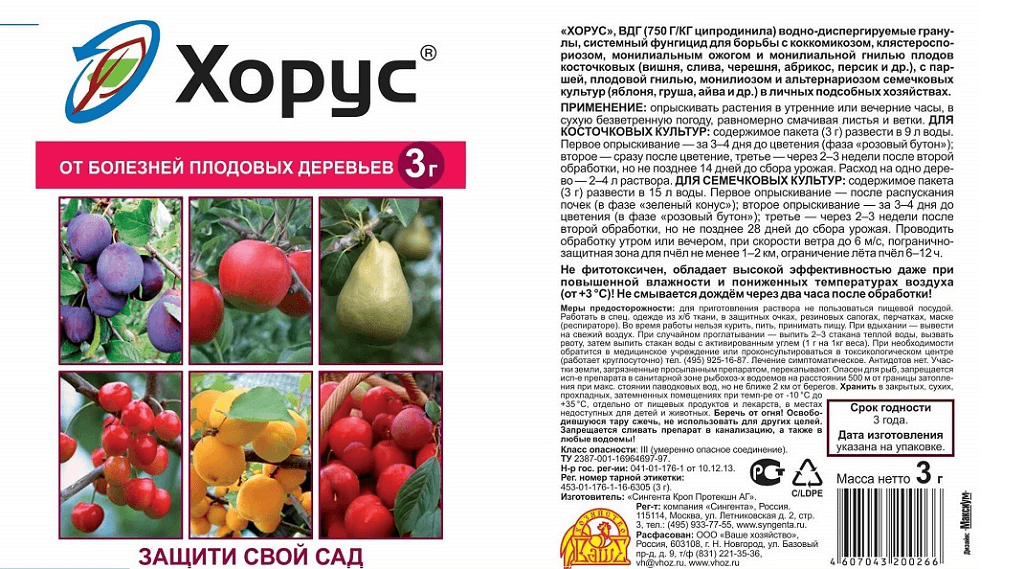
Horus
The fungicide has a wide range of applications, from stone fruit trees to berry bushes. Horus can be used even at low temperatures, as these do not affect its performance.
Precautions for handling
When working with fungicidal preparations, certain rules are followed:
- Use protective clothing.
- Do not prepare the solution in copper containers to avoid oxidation.
- Do not use seed dressings to treat fungal diseases.
- Do not consume processed vegetables before the expiration date indicated in the instructions.
By following simple recommendations, you can quickly overcome fungal diseases of cultivated plants.











