- Why do plants get sick?
- Characteristic signs of seedling wilting
- Causes associated with bush damage by infections and fungi
- Blackleg
- Verticillium wilt
- Septoria
- Alternaria
- Cladosporiosis
- White rot
- Fusarium wilt
- Gray rot
- Phytophthora disease
- Chlorosis
- Marsupial fungus
- Powdery mildew
- Methods of combating diseases
- Alirin B
- Bordeaux mixture
- Quadris SK
- Trichodermin
- Prevention of disease occurrence
- In the greenhouse
- In open ground
- Reasons related to violation of agricultural technology in cultivation
- How to properly care for peppers
- What to feed
- Proper watering
- Caring for the beds after planting
Bell peppers are a popular vegetable used in a variety of dishes. During growth and development, the plant suffers from diseases that cause white spots to appear on the leaves. To understand why bell pepper leaves turn white, it's important to recognize the symptoms of each disease.
Why do plants get sick?
Regardless of where they're grown—open ground, a greenhouse, or a hothouse—certain symptoms indicate pest infestation. Bell peppers suffer from improper care, insect infestations, and diseases. Both mature pepper plants and seedlings are susceptible.
Characteristic signs of seedling wilting
Plants grown from seed tend to grow poorly and stunt over time. This is most often noticeable by the appearance of the leaf blades. The leaf edges curl inward, and the central vein bulges upward. The veins on the leaf become pale, and the areas between them become convex. The green part of the plant loses color and appears lifeless. This process typically begins at the top of the stem.
If no action is taken, the leaves fall off and the young plant dies.
Causes associated with bush damage by infections and fungi
When growing bell peppers, vegetable growers encounter a number of diseases.

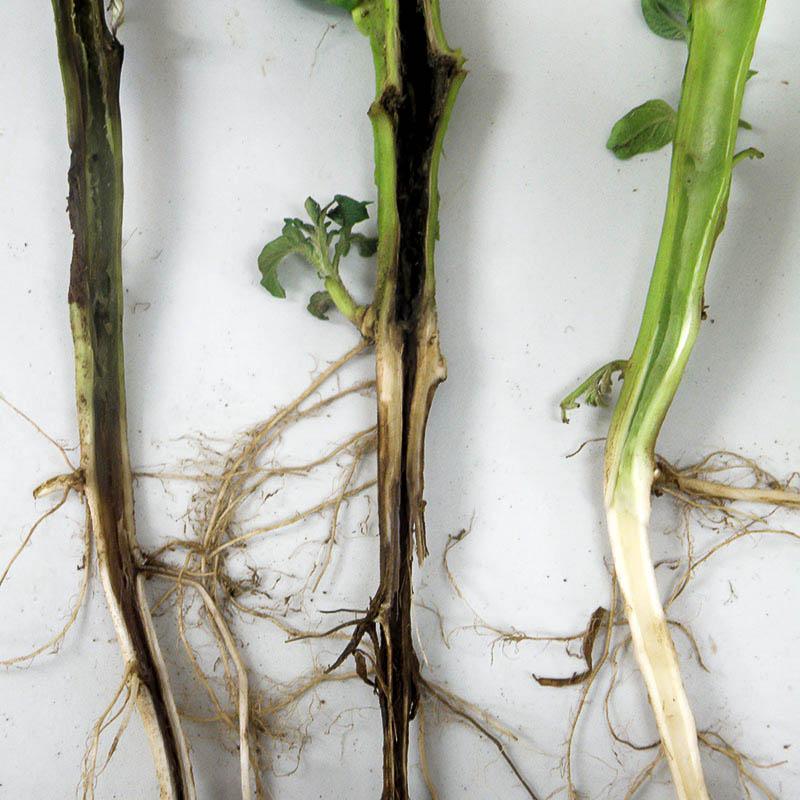
Blackleg
The disease develops when young shoots are infected with rot. It attacks not only seedlings but also mature pepper plants. It lives in the soil and spreads to the plant after planting. Black leg is transmitted by seed material or remains from the old crop.
Signs indicating the presence of pathology:
- darkening of the root collar;
- the leaves on the bushes turn pale green;
- The plant's stem is rotting.
The name of the pathology makes it clear what a diseased plant looks like.

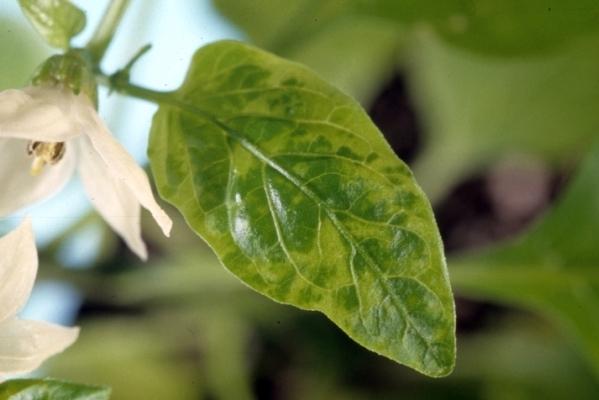
Verticillium wilt
The symptoms of this disease are often confused with those of cucumber mosaic disease. The similarity lies in the disruption of the plant's vascular system. Verticillium wilt symptoms include:
- reduction of leaf blade, slow growth of pepper;
- the lower leaves on the stem become lighter;
- As a result of infection, young bushes do not produce ovaries.
If an adult bell pepper is infected, the number of leaves on the branches decreases every day.
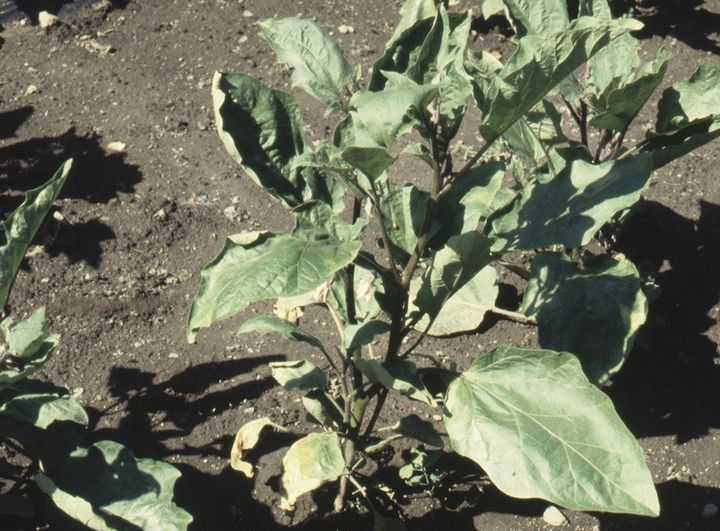

Septoria
The disease is characterized by the appearance of white spots with a grayish tint on the leaves. Initially, they are small and irregular in shape. Without adequate treatment, they rapidly expand and cover all parts of the leaves.
The number of whitened leaves is increasing. A fungal infection is destroying half the crop. It's equally dangerous for peppers grown in greenhouses and outdoors.
Alternaria
The disease also has another name: dry spot. It is identified by the appearance of white spots on the leaves, which gradually darken. The disease is caused by a fungus that reproduces by spores. It is caused by temperature fluctuations.
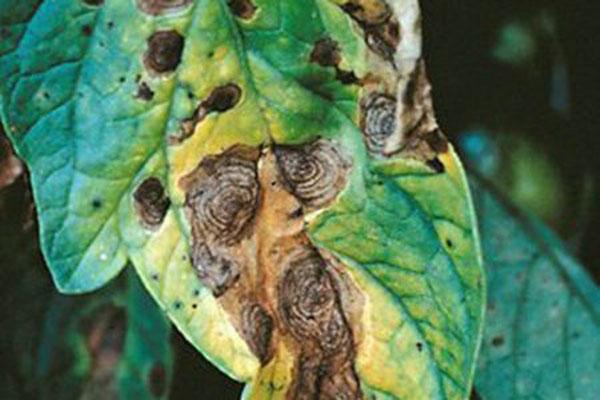
Cladosporiosis
Pepper bushes are affected by the disease, affecting the stalks, ovaries, leaves, and petioles. Cladosporiosis is distinguished by the following symptoms:
- rapid spread of pathology from the lower part of the plant to the upper part;
- leaves become covered with pale green spots;
- a fungal coating accumulates on the outer side of the leaf blade;
- After transplanting the seedlings, the leaves wither and dry out.
The disease originates from crop residues infected with Cladosporiosis. Infection also occurs through soil and gardening tools. The main characteristic of this disease is that it is not transmitted through seed.

White rot
If numerous white leaves appear on seedlings, this could be due to white rot. White rot is characterized by the appearance of light-colored areas. The plant retains this appearance for an extended period. Over time, the bell pepper dies.
The cause of white rot is considered to be increased soil moisture, inappropriate acidity levels, and bush density.
Fusarium wilt
In the early stages of the disease, it's difficult to notice that the leaves appear unhealthy. Vegetable growers recognize Fusarium wilt when the crop bears its first fruit. Foliage curls, changes color, and eventually wilts. Unfortunately, the disease is incurable. Infected bushes will die regardless. Diseased bushes are removed by digging them up and burning them.

Gray rot
The right conditions for the disease to develop are humidity combined with temperatures above 20°C. Gray mold covers the entire plant, leaving no area untouched. Signs of infection are visible on the pods, stems, and foliage. The rot appears gray. It is possible to prevent the disease from developing. To prevent this, it is recommended to avoid planting vegetables too close together.
Phytophthora disease
It all starts with white spots, which gradually lead to the drying out of the leaf blades. The dried leaves don't stay on the branches for long and fall off. After some time, the plant itself dies.
Chlorosis
Chlorosis is a leaf disease that affects more than just bell peppers. It also affects herbaceous crops, trees, and even shrubs. Chlorosis is characterized by a deficiency of chlorophyll.

It plays a vital role in photosynthesis. A deficiency of this nutrient prevents this process from functioning properly. The presence of white and yellow leaves instead of the usual green ones indicates that the plant is not developing normally. The edges turn yellow, and the leaf blade itself becomes mottled.
Marsupial fungus
Many gardeners don't immediately understand what they're talking about when they hear the name sclerotinia. Commonly known as "sac fungus," this disease affects the entire plant. However, the root zone is particularly affected. The plant itself gives clues to the presence of this fungus. It's time to sound the alarm if the leaves turn white. Large black spots can be seen in the center of each leaf.

Powdery mildew
Peppers grown in greenhouses are susceptible to this disease. Powdery mildew appears as large, chlorotic spots of irregular shape. Powdery mildew does not cause serious damage to plants. Restoring photosynthesis returns the crop to a healthy state. To prevent powdery mildew, peppers need plenty of light.
Methods of combating diseases
Treatment for bell peppers begins only after the underlying cause has been determined, and this is a crucial step. Starting with medications intended for other conditions will have no positive effect. A wide range of products are available on the market for treating various bell pepper conditions.

Alirin B
This is a biological product designed to treat Cladosporiosis, Septoria leaf spot, late blight, and Alternaria leaf spot. The product is diluted with water just before application. One tablet per 5 liters of water is sufficient for treating 5 square meters of land.
The medicine is sprayed onto the soil before planting the seedlings. The solution is poured into each hole and the soil is stirred. It is also added dry to the holes during planting.
Gardeners share their experiences using the product during the active growth period of bell peppers. The plants are fertilized with the product twice a month, with at least a week between applications.

Bordeaux mixture
It has a negative effect on fungi and bacteria. Add copper sulfate to 240 g of quicklime, and then pour a bucket of water over the mixture. For a more effective solution, reduce the amount of liquid to 7 liters.
Before pouring the solution into the sprayer, filter it using a double-layered gauze cloth. The effectiveness of the spray depends on the correct preparation of the solution. If the dosage is not met, the copper content in the liquid will be excessive.
Quadris SK
Treatment is carried out after the seedlings have been transplanted to their permanent location. Spraying is done early in the morning or after sunset. Quadris SK is applied to the leaf blade and penetrates deep into the tissue, protecting it from infectious diseases.

It's used to prepare a solution that's diluted with plain water. It's recommended to use the mixture within 24 hours. Do not use it if it's been sitting for several days.
Trichodermin
Protects bell pepper plants from fungal infections. This product contains Trichoderma. It is safe for humans, animals, and the environment. The prepared mixture can be stored in the refrigerator or any cool place for up to a month.
Prevention of disease occurrence
Before starting treatment, gardeners should review their plant care. These signs usually indicate improper human care. To ensure the plant grows and produces a productive harvest, more time is needed.

In the greenhouse
Caring for the plant indoors and outdoors is virtually the same, with a few exceptions. Here are some guidelines to follow:
- Control of indoor air temperature and humidity levels.
- Daily inspection of leaves and other parts of the crop.
- The diseased bush is immediately removed from the garden bed and burned.
Fertilizers must be applied on time and growing conditions must be maintained. Watering also plays a major role. Weeds must be removed from the beds promptly.

In open ground
Pepper care:
- Planting seedlings in a specific manner and sowing seeds at the right time influences the subsequent development of the pepper. If everything is done correctly at this stage, the mature plant will have good immunity.
- Timely loosening of the soil and application of fertilizers.
- Before planting seedlings, the soil must be prepared.
- Constant monitoring of bush development.
If the bushes grow in unprotected soil, there is no need to control the humidity level and air temperature.

Reasons related to violation of agricultural technology in cultivation
When investigating the causes of white spots on leaves, it's important to follow proper agricultural practices. Whitening of leaves occurs when watering is delayed. The plant should not be transplanted to a permanent location without first hardening it off.
How to properly care for peppers
This requires systematic approach. If a novice gardener doesn't know what to do, it's best to start small.

What to feed
Peppers appreciate fertilizers of various origins. These can include mineral fertilizers, organic matter, and even everyday foods. Their appearance will tell you what fertilizer your bell pepper needs at any given time.
Proper watering
Peppers are watered once a day, either in the morning or evening. Avoid watering during the day in the scorching sun. The water should not be cold. If there is precipitation, watering should be postponed for a while.

Caring for the beds after planting
Transplanted peppers require the most care. After transplanting, care must be taken to ensure they adapt to their new location and thrive. When planting young peppers, care should be taken not to damage their root system. Other garden crops should be planted near peppers, ensuring they are close to each other.
The beds are loosened and weeds are removed regularly. These steps are part of pepper planting care.
White spots on pepper leaves can be removed using various treatments and care adjustments. To save your plants, it's important to identify the disease early and begin treating it. Preventative measures will prevent the development of many diseases.











