- The history of red currant breeding
- Cultivation areas
- Main advantages and disadvantages
- Composition of berries
- Taste and medicinal properties of fruits
- Application
- Botanical information and characteristics of the variety
- Bush and root system
- Leaf blades
- Flowering and pollination
- Fruit ripening time and yield
- Resistance to subzero temperatures and drought
- Immunity to diseases and pests
- Septoria or white spot
- Anthracnose
- Currant glasshouse
- Gall aphid
- How to plant red currants in a garden
- Deadlines
- Required soil composition
- Selecting and preparing a site
- Distance between bushes
- Seedling preparation and work procedure
- Further care of currants
- Watering mode
- Loosening and mulching the soil
- Fertilization
- Pruning: formative, sanitary, rejuvenating
- Pouring and hardening of bushes
- Preventive seasonal treatments
- How to cover plantings for the winter
- Methods of reproduction
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
- Reviews of the variety
Red currant variety Rovada is distinguished by its good It is productive and has excellent flavor. This crop is easy to grow and is resistant to many diseases. To achieve successful cultivation, it is necessary to water the bushes regularly, prune, and fertilize. In regions with harsh climates, it is important to ensure proper winter preparation.
The history of red currant breeding
This variety was developed in 1980 by staff at the Institute for Agricultural Breeding in the small Dutch town of Wageningen. It was created by crossing Heinemann Rote Spätlese and Faiz Prolific.
Cultivation areas
This currant variety is not suitable for growing in areas with a harsh continental climate. This climate is characterized by a combination of intense summer heat and very cold winter temperatures. Therefore, it should not be planted in the Urals, northeastern Ukraine, or northwestern Russia.

Main advantages and disadvantages
The key benefits of the plant include the following:
- high yield – 14 kilograms of fruit can be obtained from 1 bush;
- tasty large berries – they weigh up to 1.5 grams;
- high resistance to diseases and pests;
- frost resistance – currants can withstand temperatures down to -34 degrees;
- resistance to short-term drought and bright sunlight.
The only drawback of this crop is its poor tolerance to prolonged heat. Therefore, the variety is not grown in the southern regions of Russia, the Volga region, and other regions with such a climate.
Composition of berries
The fruits contain many valuable elements, including vitamins B, P, A, E, and C. The berries also contain coumarin substances and pectins. Currants of this variety also contain micro- and macroelements, including magnesium, phosphorus, iron, selenium, and iodine.
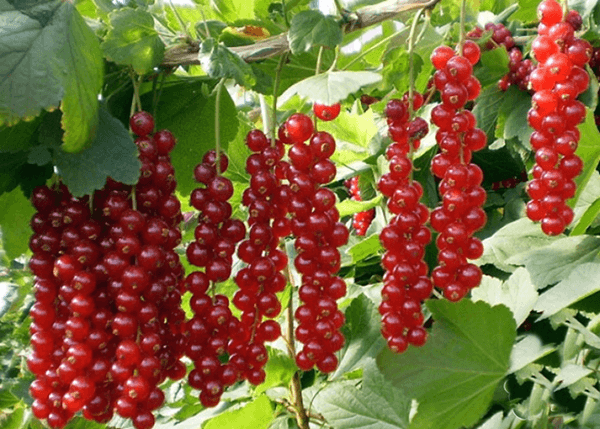
Taste and medicinal properties of fruits
The fruits have a characteristic sweet and sour taste. They have a therapeutic effect on the body. Consuming the berries can achieve the following results:
- normalize cholesterol levels, reduce blood clotting, strengthen blood vessel walls;
- reduce elevated temperature, relieve inflammation;
- achieve a pronounced antioxidant effect, neutralize the action of free radicals;
- improve intestinal peristalsis and normalize digestion;
- remove excess fluid from the body;
- cleanse the body of uric acid salts;
- suppress the synthesis of histamine and serotonin;
- improve hematopoiesis, reduce sugar levels;
- cleanse and tighten skin, strengthen hair;
- stimulate metabolism.
Application
The berries can be used to make juices, preserves, jellies, compotes, and jellies. Currants are also used in sauces.
Leaves, branches and buds are used to make tea, decoctions and preserves.
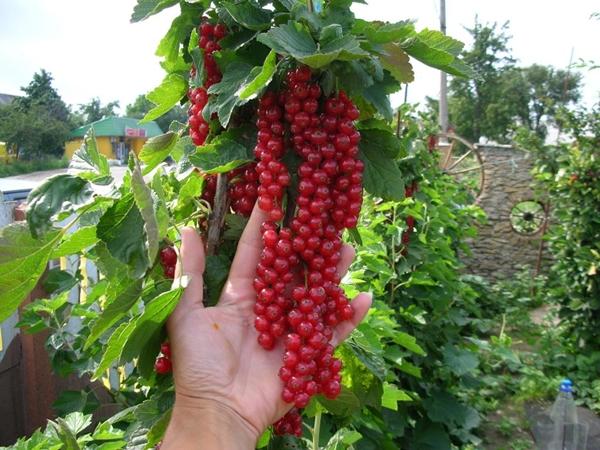

Botanical information and characteristics of the variety
This red currant variety has certain characteristics that should be taken into account before planting.
Bush and root system
Bushes average 1.75 meters. This height is typically achieved five years after planting. The plant tends to become dense. It has a spreading root system without a taproot. Basal shoots appear at 4-5 years and reach 0.5-1 meter.
Leaf blades
The leaves are large and 5-lobed. They are characterized by an elongated shape. The foliage is dark green and has a wrinkled texture. The underside is downy.
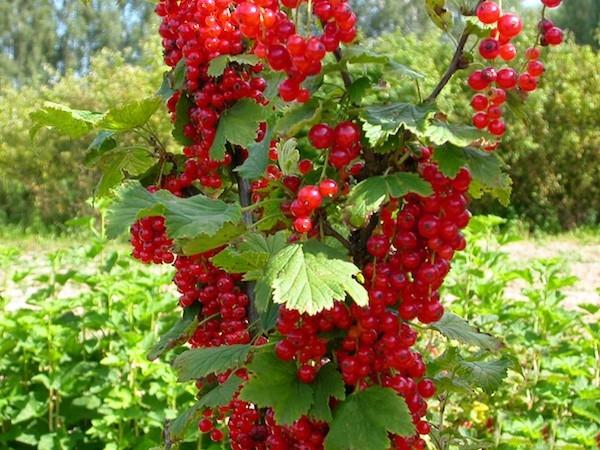

Flowering and pollination
The flower clusters are long and dense, adorned with 10-16 bell-shaped flowers. The petals have a yellow-green hue. The flowers emerge late and are highly self-pollinating.
Fruit ripening time and yield
The harvest can be done from mid-June to mid-July. The exact timing depends on the climate. On average, the bushes bear fruit for 1.5 months.
This variety is considered high-yielding. With proper care, a single bush can yield 7-10 kilograms of fruit. These yields last for 20 years.
Resistance to subzero temperatures and drought
The plant can withstand temperatures down to -34 degrees Celsius and is drought-resistant.
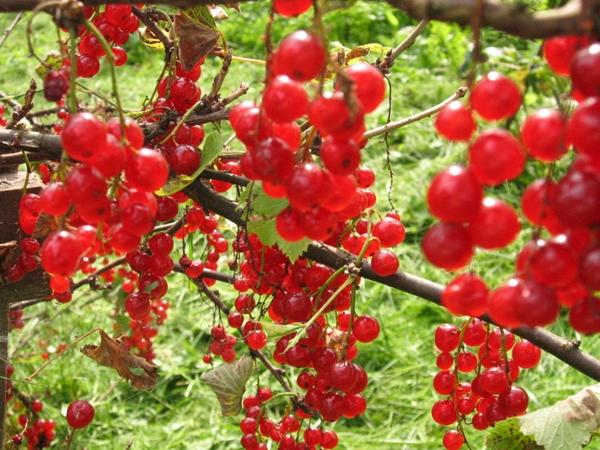

Immunity to diseases and pests
Fungal infections pose a particular threat to the crop. It is also susceptible to pest attacks.
Septoria or white spot
This is a parasitic fungal infection that causes spots to appear on the leaves. These spots gradually enlarge, eventually causing the foliage to fall off. Nitrafen helps prevent the disease from progressing. Bordeaux mixture can be applied before flowering.
Anthracnose
This is the most dangerous problem. Fungal infection causes leaf drop and rotting. To prevent the disease, it's important to use a Bordeaux mixture solution promptly.
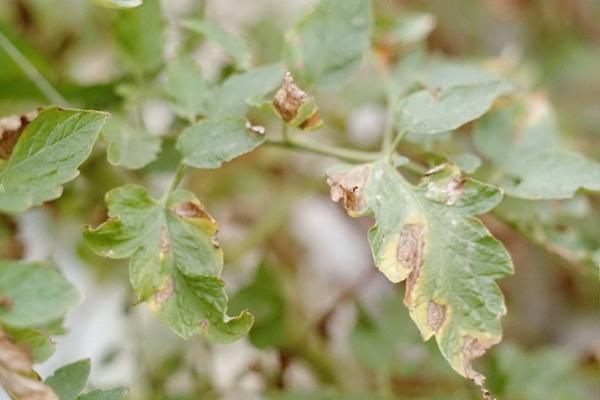

Currant glasshouse
Caterpillars damage buds and shoots, leading to wilting of the crop. Affected parts should be immediately cut off and burned. As a preventative measure, treat the crop with a solution of Malathion (Karbofos) two weeks after flowering.
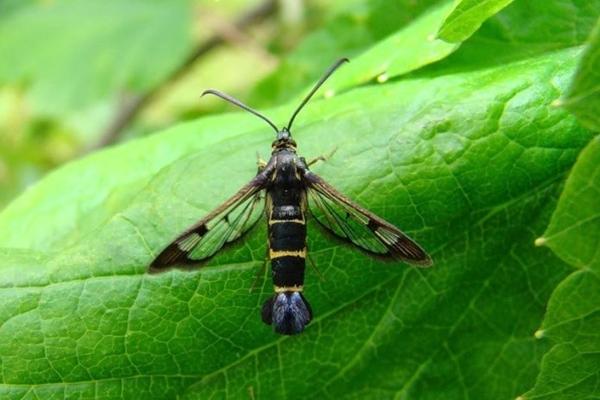

Gall aphid
Insects consume currant leaves. They pose a particular threat in early summer. A solution of Nitrafen helps control aphids.

How to plant red currants in a garden
To achieve good results and reap a bountiful harvest, it is necessary to carry out planting work correctly.
Deadlines
It's recommended to plant bushes in late summer or early fall. However, many gardeners begin planting as early as the first half of spring.
Required soil composition
Red currants require fertile black soil, sandy loam, or loamy clay. The soil should have a neutral pH.

Selecting and preparing a site
Currants should be planted on the south side of the plot. The location should be well-lit and protected from strong winds. Before planting, remove weeds and loosen the soil.
It's recommended to prepare the hole 2-3 weeks before planting. It should be 50 centimeters wide, 60 centimeters in diameter, and 40 centimeters deep. If the groundwater table is high, plant the bushes on a raised bed.
Ensure good drainage in the hole. If necessary, it's recommended to use acid neutralizers.

Distance between bushes
The distance between bushes should be 1.5 meters. The width between rows should be 2.5-3 meters.
Seedling preparation and work procedure
The seedling must meet the following criteria:
- have an elastic and branched top;
- have lush roots without any spots or signs of rot;
- the bark should not peel or have cracks;
- be 1-2 years old.
When planting, it is recommended to position the plant at a 45-degree angle. The root collar should be planted 5-7 centimeters deep.

Further care of currants
To ensure the plant's normal development, it is recommended to provide it with high-quality care. This care should be comprehensive.
Watering mode
Soil moisture depends on temperature. It's best to water the plant in the morning or evening. In spring, the soil should be moistened every 7 days. Add 10 liters of water to each plant. In summer, the frequency of watering depends on temperature. The last time the plant should be watered is in the fall.
Loosening and mulching the soil
Regardless of the temperature, the bed should be mulched. Use agrofibre or sawdust. This helps reduce the frequency of watering. Loosening the soil is also important, as it provides oxygen to the roots.

Fertilization
Organic and mineral fertilizers are applied before planting. They are used during flowering and fruit formation. It's best to apply them every two years. In the spring, nitrogen-rich substances should be used in combination with organic fertilizers. Foliar spraying is used in the summer, and potassium and phosphorus-based fertilizers are applied in the fall.
Pruning: formative, sanitary, rejuvenating
The variety requires the following types of pruning:
- Formative pruning is carried out in the fall, starting in the third year of growth. It's important to leave 5-6 strong shoots. On young shoots, 5-7 buds are left.
- Sanitary pruning is performed in the spring. This involves removing shoots damaged by frost, broken branches, and branches growing inward.
- Rejuvenation involves removing the thickest branches and cutting them back to the root. This procedure is mandatory in the 8th or 9th year of life.
Pouring and hardening of bushes
In spring, before the buds open, pour boiling water over the currant bushes. This will help kill harmful insects that have overwintered in the bark and soil and harden off the plants.

Preventive seasonal treatments
The plant can be susceptible to fungal infections and pest attacks. As a preventative measure, treat the bushes with Bordeaux mixture.
How to cover plantings for the winter
To prepare the crop for winter in regions where temperatures drop below -35 degrees Celsius, dig trenches 10 centimeters deep, insert the branches, and cover them with soil. Then cover them with mineral wool insulation.
Methods of reproduction
Currants are propagated by cuttings, layering, or division. Cuttings are taken in the fall, three years after the plant is first grown. For layering, strong branches should be dug in. The bush begins to develop independently after the layering is moved to its permanent location.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
To successfully grow currants, you should follow these recommendations:
- carry out planting operations correctly;
- water the crop on time;
- carry out pruning;
- apply fertilizers;
- treat bushes against diseases and pests.

Reviews of the variety
Numerous reviews confirm the popularity of the culture:
- Anna: "I've been growing Rovada currants for several years. They produce large, juicy fruits with a noticeable tartness. I harvest up to 3 kilograms of fruit per bush."
- Alexander: "I really like this variety. It produces large clusters and delicious fruit. I can say that Rovada is versatile and easy to care for."
The Rovada redcurrant is highly productive and produces large, tasty fruits. To achieve successful cultivation, proper planting and proper care are essential.











