- First symptoms
- Causes and factors influencing color change
- Parasites and insects: methods of control and prevention
- Aphid
- Currant glasshouse
- Kidney mite
- Spider mite
- If disease is to blame: how to treat currant bushes?
- Spheroteka
- Columnar rust
- Anthracnose
- Nutrient and water deficiency
- Unsuitable climatic conditions
- What to do?
- How to prevent currants from turning yellow
- Agricultural technology rules
- Timely fertilizing of bushes
- Seasonal treatments against insects and pests
Blackcurrant is considered a resilient plant with low maintenance requirements. Thanks to its long history of cultivation, the bush has strong immunity and resilience. Therefore, when blackcurrant leaves turn yellow, it can be difficult to know what to do to save the plant. There are a number of reasons that can trigger a negative reaction and require prompt solutions.
First symptoms
Over the years of breeding, many blackcurrant varieties have been developed, each with its own distinct biological characteristics. However, when plant leaves turn yellow, the cause of the problem is not dependent on the variety. A healthy bush of any variety is characterized by:
- strong shoots;
- uniform bark of a brownish hue;
- juicy green leaf blades.
The first signs of health problems with black currants can be the following symptoms:
- the leaves gradually turn pale;
- the edges of the leaf blades dry out;
- the crown thins out until autumn;
- shoots develop more slowly;
- the bush grows poorly overall.
Causes and factors influencing color change
Possible causes of yellowing on currant bushes can be divided into groups depending on the factors causing them:
1. External factors:
- the variety is not suitable for the climate;
- poor soil;
- poorly developed root system;
- lack of heat and light.
2. Growing mistakes:
- incorrect landing location;
- early planting in spring;
- incorrect application of fertilizers;
- lack or excess of moisture;
- thickening of plantings.
3. Insects:
- gall aphid;
- currant glasshouse;
- kidney mite;
- spider mite.
4. Diseases:
- spheroteka;
- columnar rust;
- anthracnose.
Each factor, individually or in combination, causes damage to the bush and can lead to the death of the blackcurrant plant. It is important to quickly identify and eliminate the negative factor.

Parasites and insects: methods of control and prevention
Attacks by parasites and insects are most often the cause of the appearance yellow currant leavesThe source of pests may be:
- waterlogged soil with signs of rot;
- weeds;
- closely spaced garden crops.
Aphid
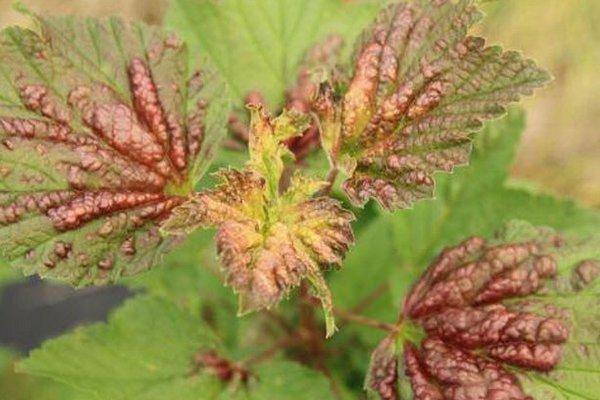
Blackcurrant gall aphids deprive the plant of its ability to properly distribute nutrients. These parasitic insects feed on the sap of blackcurrant leaves. The pests infest the undersides of leaf blades. Blisters appear at the bite sites, and the leaf itself gradually turns yellow or reddish. If the aphids are not eliminated promptly, they will quickly spread not only to the currant plant but throughout the entire garden.
 To combat gall aphids, it is necessary to use chemicals, but do not use pesticides after the bushes have flowered; it is better to use gentle products that do not spoil the quality of the fruit.
To combat gall aphids, it is necessary to use chemicals, but do not use pesticides after the bushes have flowered; it is better to use gentle products that do not spoil the quality of the fruit.
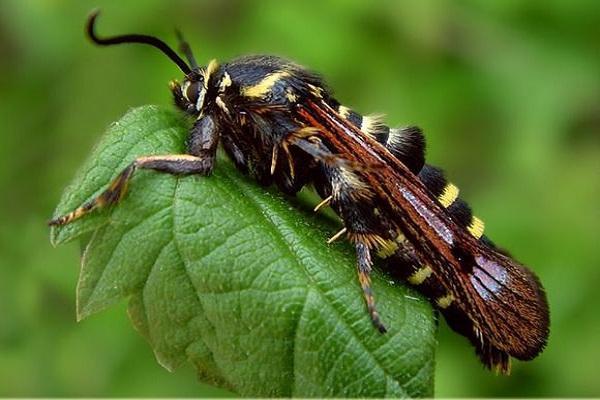
Currant glasshouse
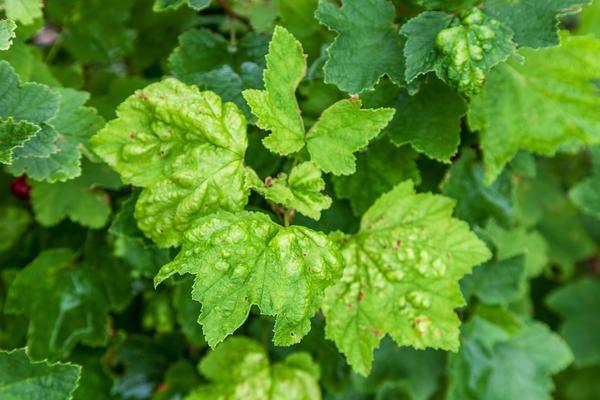
The glasswing butterfly itself is harmless, but the same cannot be said for its caterpillars. The larvae develop inside the plant's bark, and the pest can only be detected after cutting off a branch or section of bark. Under the influence of toxins and a lack of nutrients, the foliage black currants turn yellow and dry out.
The difficulty in controlling glasswort is that chemical insecticides do not kill the pests. Only sanitary pruning of damaged shoots and their complete destruction can help the plant. To reduce the risk of infestation, it is recommended to till the soil around the shrub in spring or summer.

Kidney mite
If blackcurrant buds have become significantly larger and the leaves have begun to turn yellow, it's likely a sign of a bud mite infestation. These tiny white insects infest the plants during the winter, and with the onset of the growing season, they begin feeding on the sap and destroying the core of the shoots. Their rapid reproduction rate and large egg clutches make this pest very dangerous. Spreading rapidly throughout the garden, the mites can destroy entire blackcurrant bushes in a single season.
Treatment is only possible at an early stage of development. To do this, the bushes must be generously doused with boiling water in the spring, before the sap begins to flow. In summer and fall, getting rid of the bud mite is almost impossible: the plants must be dug up and destroyed.
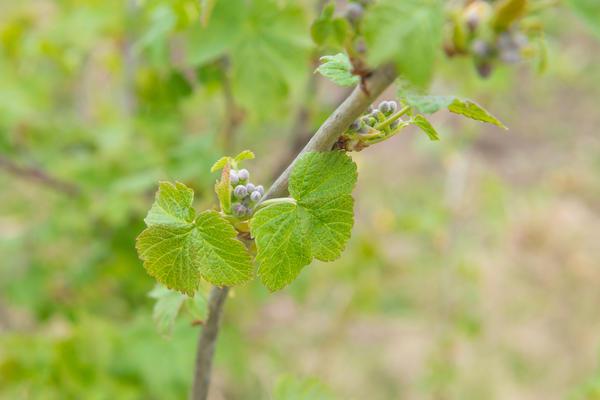

Spider mite
If currant leaves turn yellow, pay attention to the accompanying symptoms. If thin webs and reddish, moving dots are visible on the plants, this indicates the presence of spider mites. These insects are most attracted to young, succulent shoots with an active supply of nutrients.
If spider mites are found on bushes, the shoots should be cleared of cobwebs and sprayed with insecticides. Timely prevention will protect against insects: before flowering, black currants should be treated with Actellic or Nitrafen.
If disease is to blame: how to treat currant bushes?
Yellowing foliage can be caused by infections in garden crops. Fungal diseases, which develop more rapidly under unfavorable weather conditions and poor agricultural practices, are particularly dangerous.
Spheroteka
Symptoms of the disease:
- the fruits are covered with a white coating;
- over time, the affected berries fall off;
- the leaves dry out and turn yellow.
If the disease is not treated immediately, the affected parts will become covered with black spots, after which the bush will have to be dug up and burned.
Columnar rust
The disease is typical for cereal crops, but if crops aren't treated with chemicals promptly, the rust will spread to neighboring plants. Signs of blackcurrant damage include:
- the lower leaves on the bushes acquire a reddish tint;
- the edge of the leaf blade turns yellow and dries out;
- the affected greenery falls off.
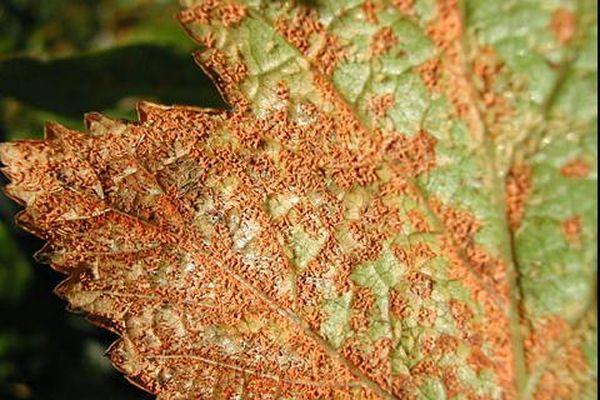

Fungicides are used for treatment, and proper planting planning and selection of adjacent crops will help protect bushes from disease.
Anthracnose
Signs of a fungal infection:
- the appearance of brown spots on leaf blades;
- yellowing of greenery;
- falling of diseased leaves.
It's important to begin treating the disease in its early stages to prevent the death of the plant or part of it. Chemical fungicides or folk remedies can be used.
Nutrient and water deficiency
A mineral deficiency can cause yellowing of the foliage. To apply the necessary supplements, you need to determine the mineral your blackcurrant bush is deficient in:
- Low levels of nitrogen compounds result in skeletal paleness of the leaves, while the veins remain rich green.
- Calcium deficiency is expressed by the lightening of the lower surface of the plates, while the upper surface takes on a red tint.
- Lack of boron in the soil causes yellowing of veins and falling of affected leaves.
- Iron deficiency causes foliage to lose its richness and yellow edges to gradually fall off.
To replenish the nutrients in the soil, you need to prepare a solution of the necessary fertilizers and water the bushes, loosening the soil afterwards.
Blackcurrants are moisture-loving plants that require watering several times a season, especially during hot summers. If the plants don't get enough moisture, the root system dries out, small branches die, and the bush can't receive adequate nutrition, which leads to yellowing of the leaves.

Unsuitable climatic conditions
Unfavorable weather, especially for heat-loving varieties, causes leaves to turn yellow, become deformed, and fall off:
- During rainy early summer, the problem can arise from overwatering. In this case, the top of the bush turns yellow, and the lower part is susceptible to rot.
- Leaf edges may turn yellow, drying out and losing their elasticity as they approach the ground. This indicates overheating and drought. Dry, hot weather often sets in in August or July, which causes the entire plant to wilt and lose its green color.
- Rains in June can cause more than just waterlogging. When currants are planted in light soil, too much water quickly leaches nutrients from the soil that are essential for the formation of green mass.
- In spring, leaves on bushes dry out due to late frosts. Temperature fluctuations negatively impact plants that have already begun growing.
What to do?
To prevent black currants from drying out completely after the yellow leaves appear, the following steps should be taken:
- treat the bushes against pests;
- in dry weather, increase watering;
- in case of heavy rains, arrange drainage;
- apply the necessary fertilizers.
You can use folk remedies against pests and fungi:
- spraying with a soap solution with an infusion of garlic, dandelion, tobacco or onion peel;
- watering with tomato leaf decoction;
- sprinkling the bushes with dry mustard.

How to prevent currants from turning yellow
Preventative measures will help reduce the risk of leaf yellowing and keep blackcurrant bushes healthy:
- Follow the rules for planting and caring for currants.
- Apply the required amount of fertilizer.
- Treat bushes against pests and diseases.
Agricultural technology rules
Correct growing black and red currants assumes:
- observe the planting deadlines for seedlings;
- plant bushes in a sunny area without waterlogging or drafts;
- select high-quality planting material;
- use fertile soil with a light structure;
- observe the watering regime;
- protect young bushes from frost.

Timely fertilizing of bushes
For full development, blackcurrant bushes need to be fertilized several times per season:
- In autumn, the soil should be mixed with rotted grass, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers.
- Applying wood ash at the beginning of the growing season stimulates root growth and plant immunity.
- In summer, after picking berries, it is recommended to water the bushes with a solution of potassium fertilizers with the addition of phosphates.
Seasonal treatments against insects and pests
Currant treatment should begin in the spring before budding begins. Clear the soil of last year's leaves and plant debris. It is recommended to water the plants with a watering can, using water heated to 80°C. After this, prune the shoots for sanitary purposes, preferably burning them immediately after cutting. After the air warms to 20°C, spray the blackcurrants and the surrounding soil with a solution of "Karbofos" or Bordeaux mixture, as well as fungicides.
In the fall, remove excess shoots to shape the bush's crown and ensure proper sanitation. Treat the plantings and soil with a solution of Karbofos or colloidal sulfur. Bordeaux mixture, Topaz, or Fundazol can also be used.











