- Description and characteristics of bush roses
- The most beautiful varieties and hybrids
- Claire Austin
- Little White Pet
- Double Delight
- Versilia
- Niccolo Paganini
- Lili Marlene
- Flamingo
- Pros and cons of using in landscape design
- Growing rules
- Necessary conditions
- Site selection and preparation
- Preparing seedlings
- Planting dates and patterns
- Spring
- Summer
- Autumn
- Watering
- Fertilizing bushes
- Mulching and loosening the soil
- Peculiarities of rose pruning depending on the variety
- Long
- Average
- Short
- Wintering and shelter
- Transfer
- Preventive treatments
- Insects and other pests
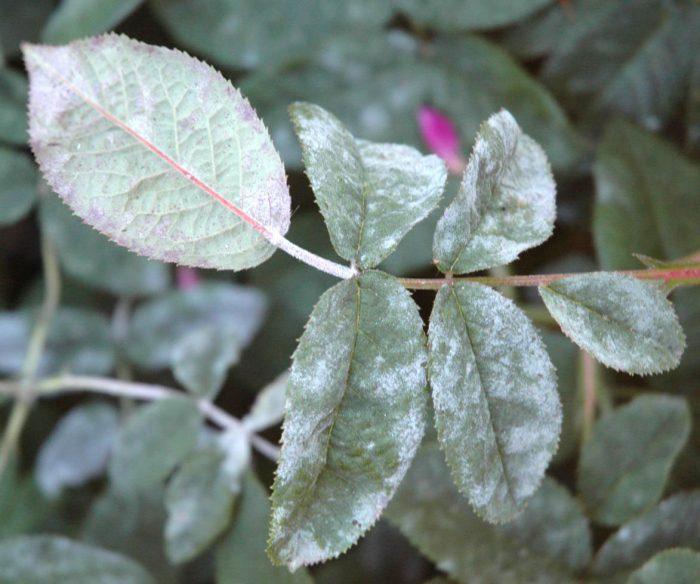
- Diseases
- Reproduction methods
- Difficulties encountered during cultivation
Shrub roses are traditionally planted in urban and country gardens. This flower boasts a surprising variety of bud colors, which appear from late spring to early fall. Roses are considered easy to grow, able to withstand both frost and heat. However, some varieties are sensitive to humidity and are susceptible to black spot. Therefore, to successfully cultivate shrub roses, it's important to know the basic techniques.
Description and characteristics of bush roses
The bush rose belongs to the Rosaceae genus and includes the following species: floribunda, grandiflora, polyanthus, park, and hybrid tea.
Botanical characteristics:
- the bush, depending on the variety, forms a pyramid, a cone, an ellipse;
- branches are divided into main perennial and annual;
- leaves with serrated edges are not arranged in pairs;
- leaf blades have two stipules;
- bush height - from 25 centimeters to 3 meters;
- peduncle length - from 10 to 80 centimeters;
- flower diameter: 2-18 centimeters;
- number of petals in a bud - 5-120 pieces;
- the shape of the buds depends on the variety - peony-shaped, spherical, pompom, cup, cone, flat, saucer-shaped;
- flowers are located singly or collected in inflorescences;
- inflorescences include from 3 to 300 buds.
Features of bush roses:
- bloom 1-3 times per season;
- frost-resistant, but in northern latitudes and humid climates they require winter shelter;
- require annual autumn pruning;
- Suitable for cutting and home growing.

Spiky plants are planted as hedges and in flowerbeds. English and Canadian varieties are the most cold-hardy.
The most beautiful varieties and hybrids
Among the two hundred thousand bush varieties, there are ancient, English, repeat-flowering, and new varieties. Among these, the most exotic flower bud shades stand out.
Claire Austin

Lemon-hued buds open to creamy white petals. The scent is reminiscent of myrrh, heliotrope, and vanilla.
The Claire Austin variety gains strength in the first two years after planting.
Little White Pet

White polyanthus rose variety with a delicate aroma.
This American bush variety is simple in appearance, but it survives snowy winters well and grows.
Double Delight
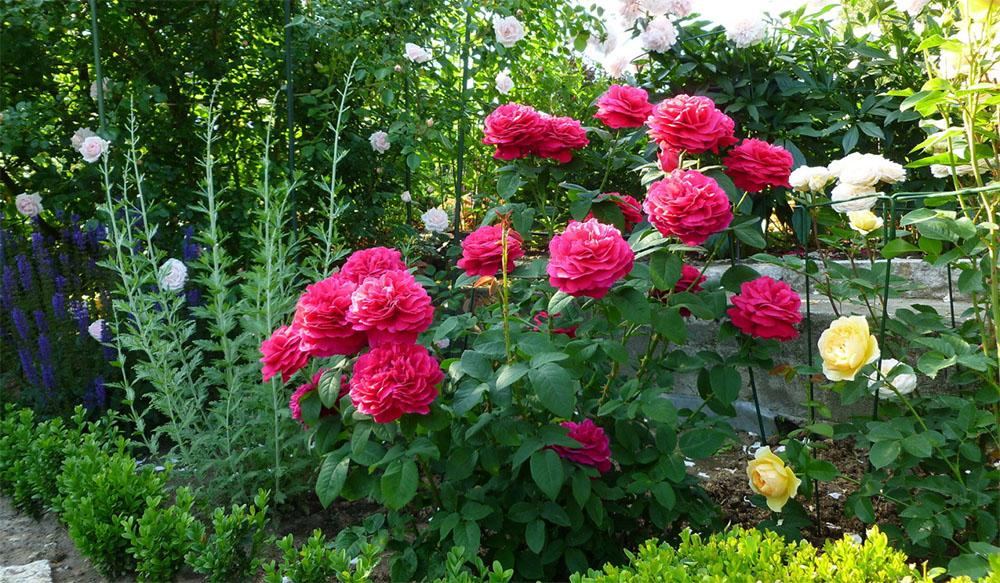

A classic bud with white petals in the center, turning to crimson at the edges.
The crimson edge of the roses is especially striking in sunny weather. If you cut a half-opened bud, its scent will intensify in the room.
Versilia
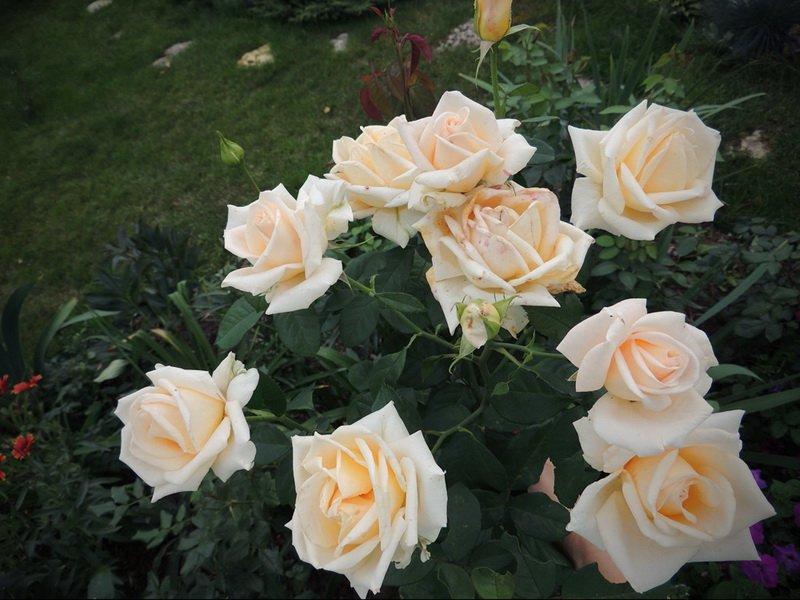

A hybrid tea variety with a strong fragrance, repeat blooming. The goblet-shaped buds are a peachy-cream color.
The color of the buds varies from apricot to champagne.
Niccolo Paganini
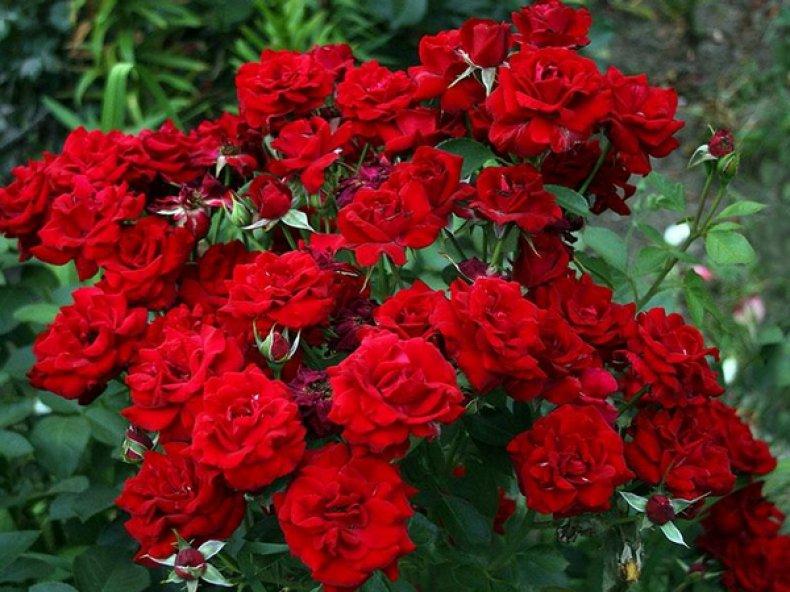

Floribunda rose with velvety red petals.
The Niccolo Paganini rose is considered the best floribunda due to its rich color and classic bud shape.
Lili Marlene

A continuously blooming variety of bush roses with deep burgundy-red buds.
The rose blooms profusely and vibrantly even when sick. The original hue of the buds can only be seen in person. Cameras distort the color.
Flamingo
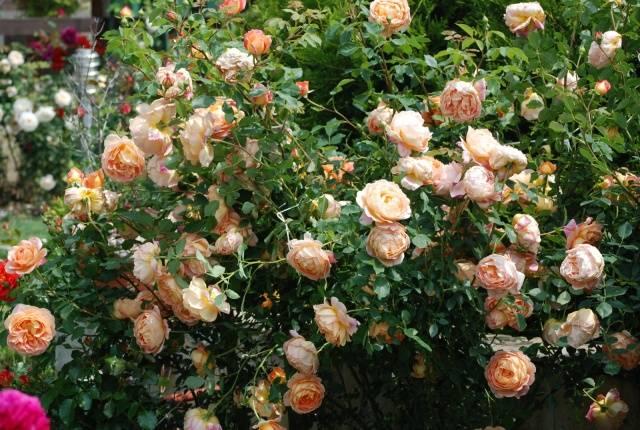

A noble, graceful hybrid tea rose. The buds are goblet-shaped. The petals are creamy white or ivory. The center of the flower seems to glow with a pinkish glow.
The Flamingo scent is subtle and elegant, making it difficult to detect.
Pros and cons of using in landscape design
Benefits of working with bush roses:
- Early and late flowering varieties transform and fill the garden with different aromas throughout the year;
- By alternating compact and wide, low and tall bushes, you can create an original rose garden;
- Flowers of the same variety with unusually coloured buds, planted in geometrically shaped flower beds, serve as a single decoration.
Shrub roses are combined with deciduous and coniferous shrubs, creeping plants, and ferns.
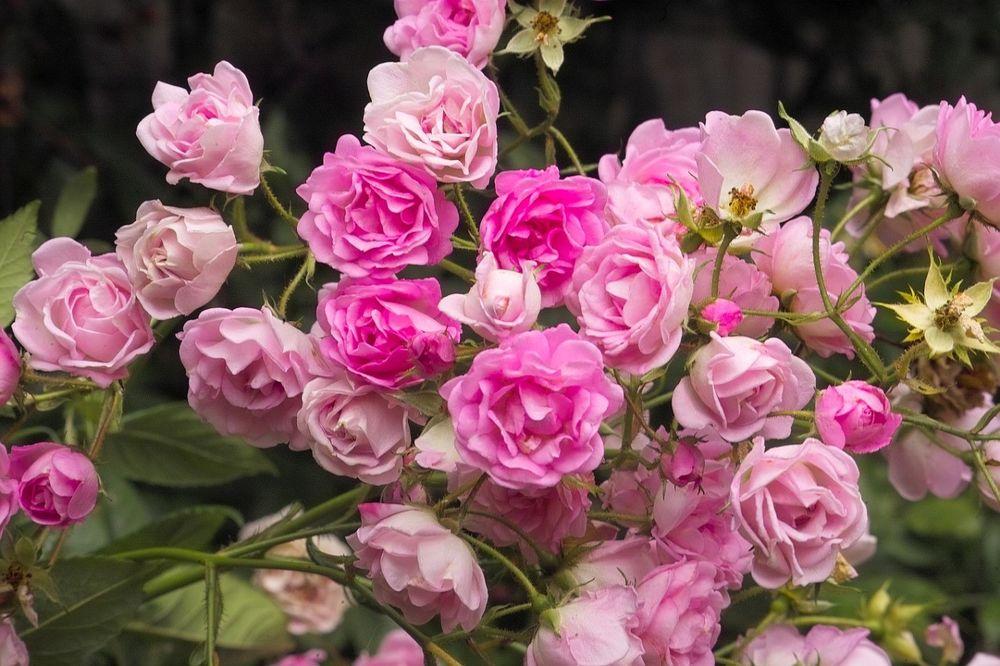

English rose bushes used as hedges are a classic landscape design. For lovers of traditional garden design, these are the first choice. Their drawback is that they cannot be given irregular shapes or used in patterns and imaginative compositions. The angles and curls are hidden beneath the green foliage.
Growing rules
Successfully growing shrub roses outdoors begins with choosing the right site. The foundation of garden care is watering, fertilizing, and pruning. Growing roses is easy, even for beginners, provided proper gardening practices are followed.
Necessary conditions
A dry, level site with deep groundwater is suitable for a rose garden. The soil pH should be 6-6.5. The soil should be well-drained and aerated, so sandy loam is preferred. Avoid planting shrub roses on the north side of the site, in the shade, or in the space of an old rose garden.
Site selection and preparation
A well-lit and draft-free location is ideal for roses in the garden, and there should be no bushes or trees within half a meter.

Two weeks before planting, the soil is dug up with peat, and planting holes are dug.
Preparing seedlings
Bare-root rose shoots are disinfected with a solution of Fundazol or copper sulfate. Young potted rose bushes are removed along with the root ball.
Planting dates and patterns
Shrub roses can be planted year-round. Adjustments are made only for climate. Planting density and arrangement depend on the design and width of the bushes. Young bushes that need replanting are planted more closely. The recommended spacing for hedges is 80 centimeters.
Spring
In temperate climates, the optimal time to plant shrub roses is early April. However, you need to be mindful of the weather. The soil should warm up to 10 degrees Celsius, and the warm, dry weather should last for 2-3 days.

Summer
From June to August, bare-root bushes are planted in any region. Ever-blooming rose varieties can open their buds as early as autumn.
Autumn
In southern regions, roses will have time to strengthen their roots before frost and devote all their energy to growth and flowering the following spring. Therefore, the best time to plant bush varieties in the south is September.
Watering
The basic care for bush roses consists of regular watering. Meltwater or rainwater at ambient temperature is ideal for these plants. Tap water should be allowed to settle for 24 hours beforehand, and cold water should be warmed in the sun.
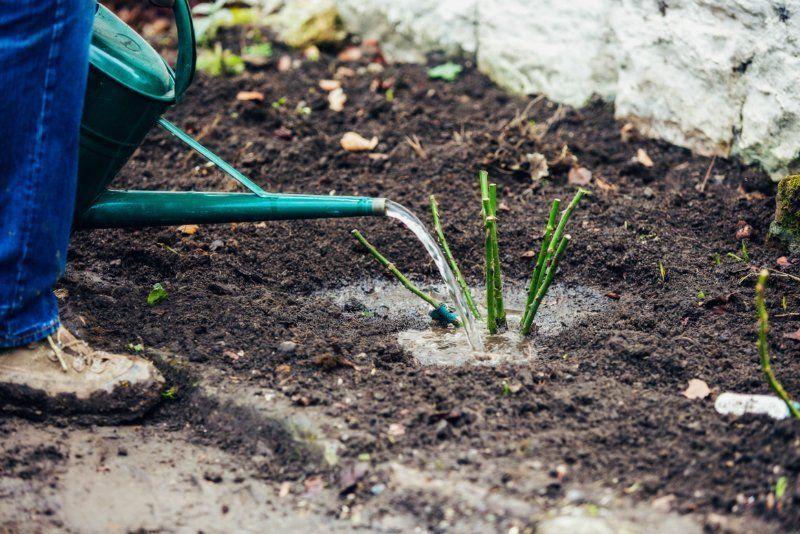

Water the bushes in the morning or evening. During dry periods, moisten the soil 2-3 times a week, pouring half a bucket of water under the bush. In normal weather, one bucket per bush once a week is sufficient.
Fertilizing bushes
From April until flowering, roses are fed with nitrogen—urea, manure, and nitroammophos. A universal fertilizer or mullein solution is applied under faded bushes. In August and September, the flowers are fertilized with phosphorus and potassium, and before wintering, with superphosphate.
During the first season after planting, the plants do not need to be fed, as enough nutrients have already been added to the hole.
Mulching and loosening the soil
To reduce the risk of black spot in roses, cover the soil with peat or compost after watering. Freshly cut grass is also used for covering. Apply mulch to a depth of 8 centimeters. Without mulch, the soil will require more careful maintenance, including loosening and weeding. Own-rooted bushes have roots close to the surface, so loosening the soil to a depth of 3 centimeters is necessary.

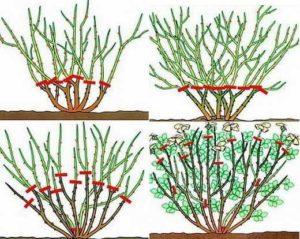
Peculiarities of rose pruning depending on the variety
During the first year, the roses are pinched to encourage abundant blooming. In subsequent years, the shoots require pruning in the fall and spring.
Long
The tops of well-growing shoots are pruned, counting 8-10 buds from the bottom. After light pruning, floribunda roses bloom a week earlier. The shoots of one-year-old bushes are also lightly pruned.
Average
To define the bush's shape, the shoots should be pruned by half, leaving 4-6 buds and making the cut. Medium pruning is optimal for hybrid tea roses.

Short
Shoots that are not growing well are severely shortened. Stimulating pruning of roses is done in the spring: two buds are removed from the base of the bush and the rest of the crown is trimmed. After a short pruning, hybrid tea roses will bloom 1.5 months later, and the smaller number of buds is compensated for by their larger size. Therefore, it is better to severely shorten roses intended for cut flowers.
After pruning, bush roses should be sprayed with a 0.5% copper sulfate solution. For any type of pruning, make an angled cut 6 millimeters above a dormant, outward-facing bud.
Wintering and shelter
To prepare roses for winter, stop watering in August and September. In October, trim dead and overgrown branches. Treat the cuts with garden pitch.
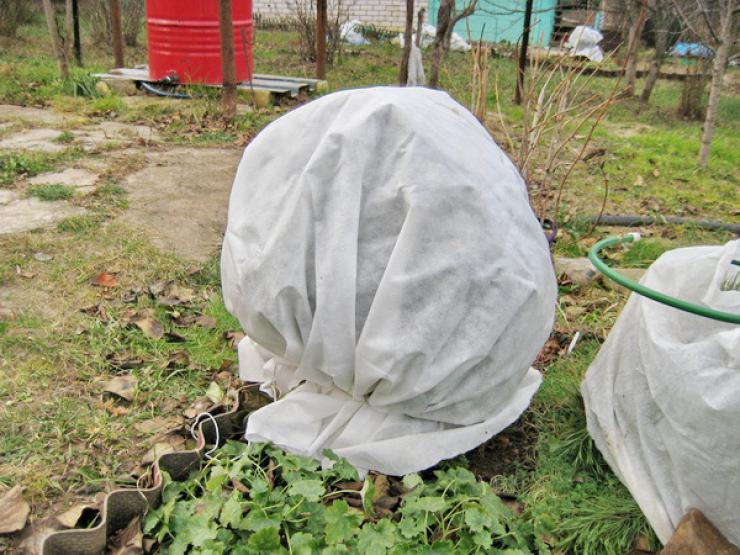

In the south, frost-hardy varieties often don't need to be covered for the winter. A mound of sawdust is sufficient for young bushes. In central and northern regions, roses will need to be covered with several layers of spunbond, leaving a gap at the bottom for ventilation.
Transfer
Bush roses are replanted in spring, at the end of April. To determine if a bush is suitable for replanting, try separating a thorn from the stem. If the thorn breaks off easily, the plant is ready for replanting. Dig up the bush with a lump of soil, lay it on a cloth, and transfer it to a new, prepared location. Moisten the hole before planting.
Preventive treatments
Rose disease prevention involves proper agronomic practices, including proper watering, fertilization, loosening the soil, and pruning. Bushes that receive sufficient nutrients, oxygen, and light have a strong immune system. However, adverse weather conditions weaken their defenses. Seasonal treatments can help protect roses from fungal diseases and pests.

Insects and other pests
The following parasites inhabit bush roses:
- Rose aphids are small green or pink insects that suck the sap from plant leaves. To prevent them, spray roses with Fitoverm and Aktara in early spring and before flowering.
- Spider mites feed on leaf sap and entangle stems with thin, white web-like threads. Preventative measures include Iskra and Inta-Vir.
- Leafhoppers—their presence is recognizable by the white marbled pattern on rose leaves. Actara is effective against these insects.
A simple way to protect plants from pests is to collect and burn fallen leaves.

Diseases
Types of rot that affect bush roses and how to protect against them:
- Black spot – leaves become covered with dark spots, dry out, and fall off. Before bud break and flowering, roses are sprayed with Gammar, Topaz, and Vectra. During the growing season, bushes are treated with a solution of Kuprozan, and before wintering, with Bordeaux mixture.
- Rust—orange spores cover the petioles, stems, and root collar of the bush. Spraying with Bordeaux mixture in spring and late fall, as well as Topaz, Vectra, and Cuprozan, can prevent this disease.
- Powdery mildew is recognizable by the white coating on the leaves, followed by drying of the bush. Fundazol is used against the fungus throughout the growing season;
- Downy mildew manifests as brown spots on the surface and a gray coating on the underside of the leaves. To protect roses, spray them with Bordeaux mixture before bud break and before wintering. During the active growth period, Fundazol, Topaz, and Baktofit are also used.
Due to a lack of nutrients, chlorosis develops on the leaves—they turn yellow or white. Petioles remain green or also become discolored. To prevent the disease, follow a regular fertilization schedule.

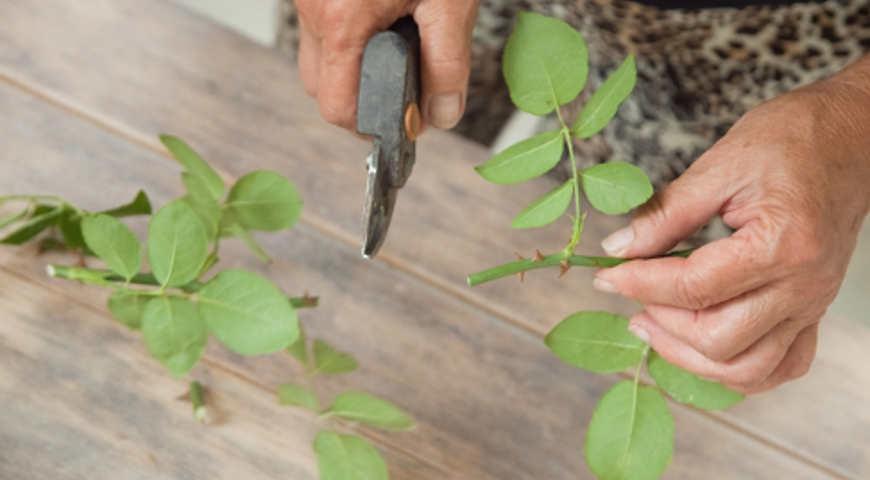
Reproduction methods
Vegetative propagation methods for bush roses:
- Cuttings: During flowering, select a young shoot and cut it into 8-centimeter-long pieces. Make a straight upper cut, and an oblique lower cut just below a bud. Remove thorns, and trim the top two leaves in half. Dip the lower cut of the cuttings into a root stimulator solution, plant them in a sandy bed, and cover with perforated plastic. Cover the rose seedlings with insulation for the winter, and remove the plastic in the spring. The young bushes will be ready for transplanting in their second year.
- Dividing the bush is a method suitable for bushes with their own roots. They are dug up in early spring or fall, the sections with shoots and roots on each are marked, and cut with a sterile knife. The cuts are sprinkled with wood ash or crushed activated charcoal. The divisions, planted in the spring, will bloom the same year. Polyanthus and floribunda roses thrive better after division.
- Layering: Select a basal shoot, make a cut on the outer bark, and bend it to the ground. Dig a trench under the shoot and lower the cut into it. Cover the top with damp soil and secure with a staple. Leave the tip of the shoot exposed. Roses are propagated by layering in the spring. The new plant is replanted the following year. This method is suitable for grafted bushes and those with their own roots.
To propagate a hybrid rose variety, its bud is grafted onto a rootstock:
- a T-shaped cut is made in the bark of the rootstock's root collar;
- a layer of bark with a 3-centimeter-long bud is cut from the cutting;
- the scion is inserted into the cut of the rootstock so that the bud remains outside;
- The grafting site above and below the bud is secured with polyethylene tape.

After 3 weeks, the rooted bud will swell.
Grafting is done in July and August. Rose hips and wild rose varieties are suitable for rootstock. For the winter, the plant is earthed up so that the scion is covered with a 5-centimeter layer of soil. By the following fall, a young bush will have formed, ready for transplanting.
Difficulties encountered during cultivation
Features of the growth and development of bush roses that need to be taken into account when caring for them:
- Faded buds don't always fall off—they need to be pruned to prevent the plant from wasting energy on seed production. Faded flowers spoil the appearance of the bush. Pruning old buds stimulates the formation of new ones;
- Shoots without flowers appear on the bushes—thick, long shoots called blind or fattening shoots. They appear in the spring and can reach a length of 1.2 meters. Sometimes blind shoots bloom. Therefore, experienced gardeners recommend leaving them until the next spring pruning.

Difficulties associated with agricultural technology:
- Grafting depth: It's recommended to lower the junction of the scion and rootstock 3-5 centimeters below the soil surface. If the graft is above the soil surface, new shoots will grow on the rootstock's root collar, and the scion will not develop. Moisture is retained in the deep soil layer, so if the graft is too deep, rot will occur on the scion.
- Surface irrigation—water poured onto a flat surface doesn't reach the roots. Therefore, before watering, dig a 15-centimeter-deep trench around the trunk of the bush and pour water into it. Once the moisture has been absorbed, fill the trench and mulch it.
- Nutrient imbalance—nitrogen deficiency leads to slow growth and early flowering, while excess nitrogen leads to a lack of flowers. If the leaves are yellow with green petioles, the roses are potassium deficient. Their tips curl and turn brown when there's too much potassium. It's important to fertilize the bushes at the right time and carefully measure the doses.
- Premature release from winter cover—roses are uncovered after the snow has completely melted. Unstable weather and night frosts can cause plants to freeze, and shoots can turn black. Young bushes can also become sunburned.
It's best not to rush to remove the covering, but to ensure air reaches the stems. Otherwise, another problem will arise: damping off, when the roses suffocate from lack of oxygen.