- When should roses be planted?
- Spring
- Autumn
- Summer planting: all the subtleties and nuances
- How to select and prepare seedlings
- A place for a rose: selection and preparation
- Step-by-step instructions for planting
- Planting patterns and distances for bushes
- We dig planting holes
- Planting Features of Different Types of Roses
- Park roses
- Bushy
- Climbing
- Floribunda
- Hybrid tea
- Groundcover
- Standard and cascading
- Further care
- Watering
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Protection from diseases and pests
- Shelter for the winter
- Mistakes of novice gardeners
Roses can grow and bloom in the same spot for many years. Therefore, planting them requires careful consideration. Otherwise, the plant will not be able to fully express the characteristics intended by the breeder. Each variety requires an individual approach. Below is information on the specifics of planting different types of roses, their subsequent care, and the mistakes made by novice gardeners.
When should roses be planted?
Each gardener decides for themselves when to plant their shrubs. This decision is based on factors such as the climate region and the variety and cultivar being planted. The warmer the region, the longer the planting season.
Spring
This period is good for planting roses in northern regions. Before the cold weather sets in, the plants will have time to take root well and produce several strong shoots. If planted in the fall, the branches may not have time to mature and will die in the harsh winter. Roses are planted outdoors after the onset of stable warmth.
Autumn
In the south, bushes can be planted in the fall. The advantage of planting before winter is that the gardener can see the blooms on the chosen rose variety, and that careful care is not required until spring. Fall planting begins in September. To speed up the establishment of the bushes, the flowers are cut back.
If new shoots begin to grow after rooting, they should be removed. An immature rose may die in winter. To ensure the rose survives the winter, plant it a month before the onset of sustained frost. If the bush is planted in October, the root zone should be thoroughly mulched.
Summer planting: all the subtleties and nuances
It's best not to plant roses during hot summers. This procedure is only performed when necessary. For example, if an ordered seedling was delivered late, or a gardener unexpectedly purchased a favorite rose variety. If planting is necessary, it's best to do so in August or June. In some regions, frosts can persist until the end of May, so June planting is even recommended. Experts advise against planting in summer, particularly in July, as the survival rate will be minimal due to the intense heat.
How to select and prepare seedlings
Rose bushes should be purchased from reputable sellers at nurseries or garden centers. Seedlings should be carefully inspected to ensure they have a developed root system and 1-3 shoots. Two-year-old bushes are most likely to thrive and bloom the following year.
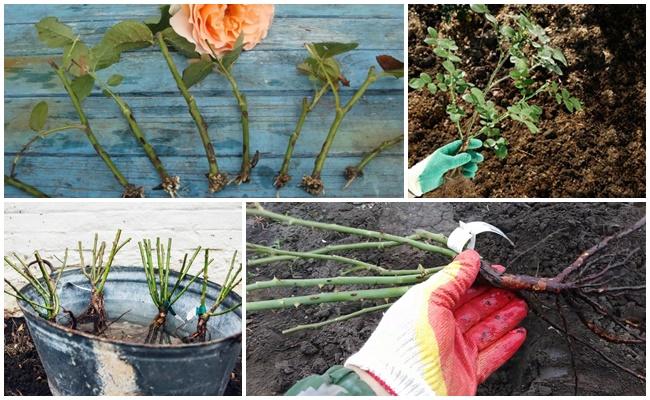

The stems of the selected plants should be free of dents and signs of disease. The root system dries out slightly during transportation, so place it in a bucket of water for 3-4 hours. Add a small amount of potassium permanganate for disinfection.
A place for a rose: selection and preparation
A well-lit area should be selected for planting. The blooms of some rose varieties are prone to fading, so the area should be shaded during hot midday hours. The groundwater level should not be closer than 1 meter to the soil surface.
The rose planting site at the dacha is prepared in advance. The area is dug over and fertilized if necessary. The soil should be moderately loose. If the soil in the garden is too heavy, waterlogging will occur. Therefore, compost and humus are added to loosen the soil and increase fertility.
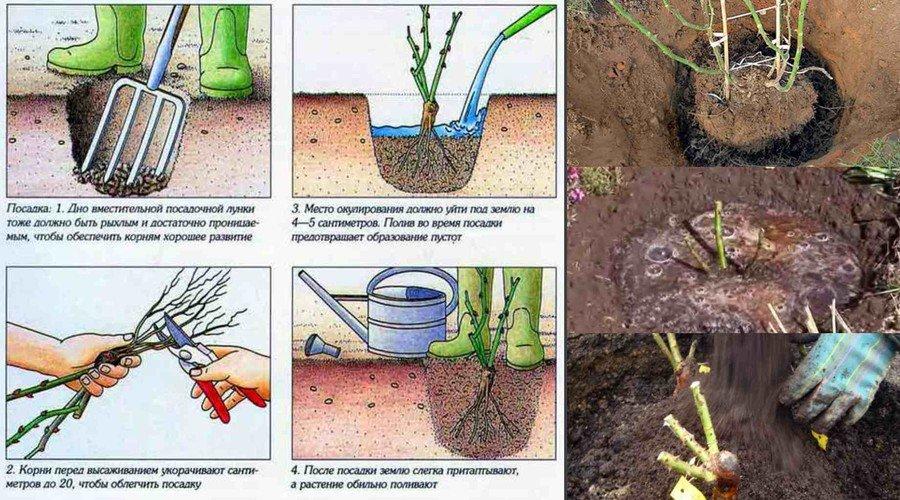
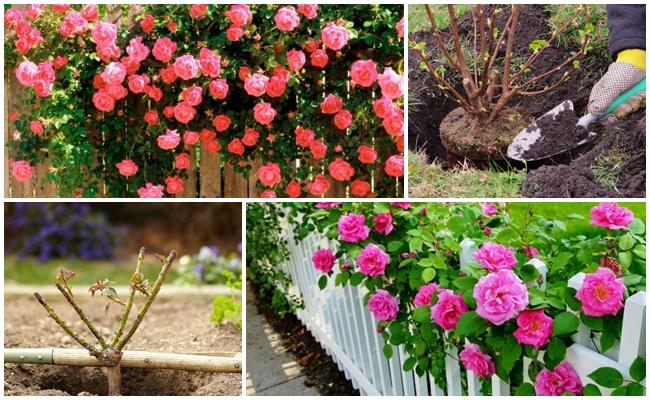
Step-by-step instructions for planting
The further development of the crop depends on correctly implemented agricultural measures.
Planting patterns and distances for bushes
The spacing between bushes depends on the variety. Climbing roses require the greatest distance: 2 to 3 meters. If spaced too closely, plants will compete with each other for nutrients and sunlight. Miniature varieties require 30 centimeters. Hybrid tea roses, depending on the variety, require 50-100 centimeters between each other. Low-growing roses are planted along the edge of the flowerbed, while taller ones are planted in the center. A staggered pattern is common.
Important! If the bushes are planted too densely, there is no air circulation between them. This can lead to diseases and pests.
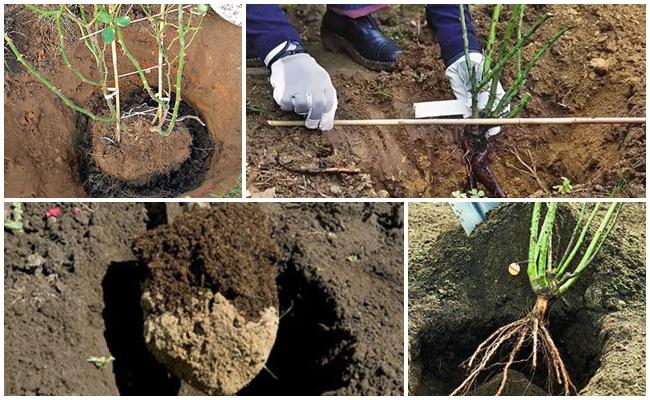
We dig planting holes
A hole 50-70 centimeters deep and about 40 centimeters in diameter is dug two weeks before planting the roses. This is necessary to prevent the root collar from sinking over time due to settling of the hole. The size of the planting hole depends on the variety and cultivar. If the soil is heavy, a drainage layer of small stones or expanded clay is placed at the bottom.

Planting roses is done as follows:
- dig a hole of the required size;
- if necessary, place drainage material on the bottom;
- filled with fertile substrate consisting of garden soil, compost, peat, sand;
- a seedling is placed in the middle;
- fill with substrate and water generously.
Make sure the root collar is buried no more than 5-6 centimeters deep. To retain moisture in the soil, sprinkle the root area with straw, sawdust, or peat.
Planting Features of Different Types of Roses
The principles for planting roses are roughly the same for all varieties. However, there are some differences.
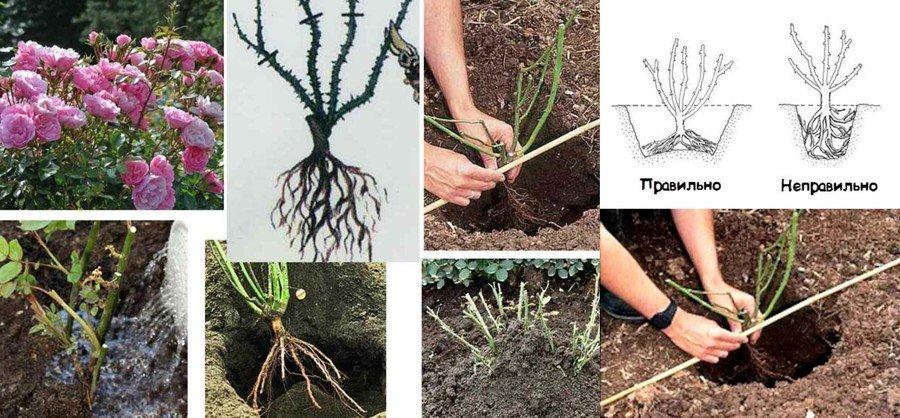
Park roses
If planted correctly, the bushes will boast beautiful, long-lasting blooms. The petals come in a variety of colors. Park roses are resilient and can easily withstand harsh winters. They are planted using a standard pattern, without burying the root collar.

Bushy
Plant heights range from 25 to 300 centimeters. Bush roses can have a narrow pyramidal or spreading crown. Planting holes are dug depending on the height and spreading habit of the plant. Sufficient space should be left between bushes to allow for ventilation.
Climbing
This rose variety produces large vines. They are planted near supports, arbors, and even arches. If several bushes are planted close together, leave at least two meters between them. Before planting, lightly prune the roots of climbing roses. The shoots are not shortened.

Floribunda
Floribunda bushes produce flowers almost continuously from late spring until frost. The petals are a variety of colors. The shoots reach a height of 1.5 meters. Bushes are planted in spring or fall. After planting, two to three buds are left on the shoots. Anything higher is cut off.
Hybrid tea
The bushes grow 50-90 centimeters tall. The petals are cream, yellow, red, and pink. Hybrid tea roses are planted in flowerbeds, along borders, and in raised beds. Depending on the variety, the spacing between plants should be between 50 centimeters and 1 meter.
Groundcover
These roses can have either short or long stems. They are planted on a slight mound, allowing the branches to cascade gracefully downwards. One to three plants are planted per square meter. When planting in the fall, the stems are only lightly pruned.
Standard and cascading
The plant is grown by grafting onto the standard of climbing, groundcover, and hybrid tea roses. The bushes look beautiful when planted individually. If several plants are to be planted side by side, space them at least 1 meter apart. When planting, a stake is driven into the hole for support, and the trunk is tied to it.
Tip! If for some reason the gardener didn't have time to plant roses in the ground in the fall, they can dig them into a trench 40 centimeters deep. When the frost sets in, cover the plants with peat moss and spruce branches.
Further care
To ensure rapid growth and abundant blooms, plants require proper care. This includes timely watering, fertilizing, and treating plants for diseases and pests. To stimulate reblooming, buds that begin to dry out, along with stem fragments, are cut off. If left unattended, roses will turn into wild roses.
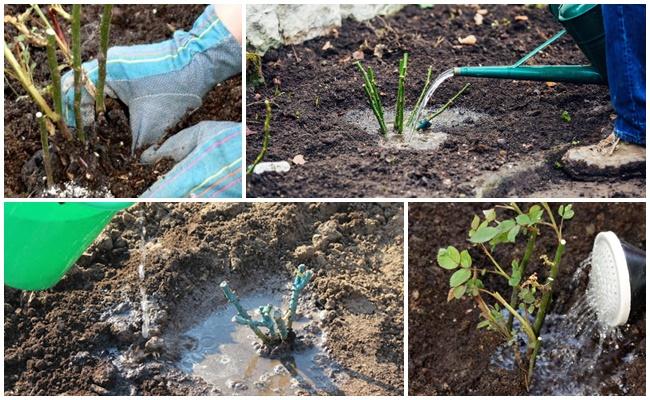
Watering
Water the soil under the bushes as needed. The top layer of soil must dry out, otherwise the root system can be damaged by pathogens. Water the rose in the morning or evening at the base. Overhead watering, especially in hot weather, can cause leaf burn.

Top dressing
In spring, nitrogen fertilizers are applied to the root zone of plants. This promotes rapid growth. Potassium and phosphorus are added during budding. After the first flush of flowering, complex mineral fertilizers are used. Nutrients are added to pre-moistened soil.
Trimming
Throughout the season, the bushes are inspected, removing dead, diseased, and broken branches. Depending on the rose variety, formative pruning is performed. Some varieties have shoots pruned back to 2-4 buds, while others only have slightly shorter stems. Buds that begin to dry out are cut off along with part of the shoot.
Protection from diseases and pests
In early spring, the bushes are treated with copper-containing preparations. These will prevent fungal diseases. Fungicide treatments are applied several times throughout the season for prevention and treatment. If harmful insects appear, an insecticide solution is used.

Shelter for the winter
Most rose varieties tolerate winter well. When frost sets in, simply add peat or compost to the root zone and cover with spruce branches. If a harsh winter is expected, build a frame over the roses. Cover it with agrofibre or spunbond. As soon as spring warmth arrives, remove the covering.
Please note! To ensure the rose survives the winter, water it generously in mid-autumn. Moist soil will reduce the root system's exposure to the cold's negative effects.
Mistakes of novice gardeners
Inexperienced rose growers can make certain mistakes, resulting in poorly established bushes and poor blooms. The most common mistakes made by novice gardeners are:
- Roses are being planted too late. To ensure the plants take root well and survive the winter safely, they need to be planted a month before the expected frost.
- Don't hill up the bushes for the winter. When steady frosts arrive, add a layer of soil to the root zone. Under this layer of soil, the root system will survive the cold weather.
- Water the rose frequently, but with small amounts. In hot weather, irrigate the soil once a week, pouring at least 15 liters of water under the bush.
- Avoid treating the plant for diseases and pests. Some rose varieties have weak immunity. Starting in early spring, the bushes should be sprayed with antifungal agents and insecticides.
- Leave dried inflorescences on the shoots. After the first flush of flowering, cut off the dried buds. If they are left on the stems, they may not bloom again.
- Bushes are planted too close to each other and outbuildings. If there's insufficient space between plants, they may be susceptible to diseases and pests due to stagnant air.
- The root collar is buried deep. The grafting site should be 5-6 centimeters below ground level. If the grafting is too deep, the bushes may grow poorly, and flowering may not occur at all.
Roses are beautiful garden plants. They produce buds almost continuously from late May until the first frost. The development and flowering of these ornamental shrubs depends on proper planting and subsequent care.

















