- The goals and objectives of rose transplantation
- When do planting operations take place?
- In the spring
- In summer
- In the fall
- Preparing for rose transplantation
- Choosing a location in the garden
- Hole for a rose
- Rules for digging up a bush and preparing for transplantation
- Rose transplantation technology
- With a lump of earth
- With bare roots
- Nuances and features of flower planting
- An old and large bush
- Replanting a rose during the flowering period
- Features of transshipment of climbing and twining varieties
- Further care
- Watering
- Loosening and mulching the soil
- Removing flowers
- Shelter for the winter
- Mistakes of novice gardeners
Roses decorate the garden in the spring and fall. Depending on the variety, they bloom once or twice per season. Even after blooming, with proper care, the bushes remain decorative. Sometimes, for various reasons, roses need to be repotted. To ensure the plant survives the process with minimal damage, it's important to learn how to do it correctly. Below is information on when and how to repot roses.
The goals and objectives of rose transplantation
The crop is replanted on the site for the following reasons:
- The bushes are planted in the wrong location. For example, water drips from the roof after rain, stagnating in the root zone. As a result, the rose is susceptible to fungal diseases.
- Trees have grown around the plant, creating shade. In such conditions, the rose's vines grow weak, and the flowers are small and inconspicuous.
- A gardener changed the landscape of the plot, and the plant ended up in an inappropriate location. Often, owners want to see the garden transformed, so the rose, as well as other plants, have to be dug up and replanted.
- The rose bush turned out to be larger than advertised, blocking the sun's rays intended for other beautiful plants.
- The soil is depleted, and fertilizing is ineffective. The rose's root system drains the soil of all its nutrients over the course of several years. The soil requires a rest period of several seasons.
For these and other reasons, roses need to be transplanted to a new location.
When do planting operations take place?
The best times for repotting are early spring and early fall. Summer repotting is only recommended if absolutely necessary. During this period, bare-root roses can be planted. They should be shaded during the hot midday sun. Bushes repotted in summer require special care.
In the spring
The procedure begins immediately after the danger of frost has passed. The sooner the bush is replanted, the faster it will adapt to its new location before the heat sets in. Moreover, the buds have not yet fully awakened. Consequently, the plant will focus all its energy on root development.
In summer
If a gardener didn't have time to replant a rose in the spring, they can do so in early or late summer. If there are buds on the bushes, they should be removed. Plants expend a lot of energy producing flowers, which is necessary for adaptation to the new location.

In June, it's best to plant roses with their root system closed. July is not the best time for replanting. In August, the heat subsides, and in northern regions, planting can begin by the end of the month. This procedure is carried out before cloudy weather sets in.
In the fall
This period is considered the most favorable for replanting roses. Plants planted in the winter will grow hardened and bloom the following year. In southern regions, the procedure can be carried out in October. The main condition is to replant a month before the onset of frost. In northern regions, roses are planted in September. Frosts arrive earlier there, and the plants need more time to adapt. Before replanting, inspect the bushes and prune out any dead, diseased, or dried-out shoots.
Preparing for rose transplantation
To ensure a rose's successful growth and bloom, the site must be chosen wisely, in accordance with the plant's specific needs. It should never be planted in a location prone to stagnant water due to melting snow or rainfall.
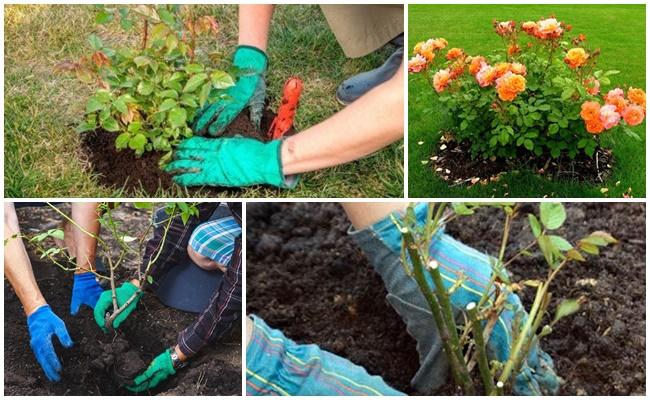

Choosing a location in the garden
Choose a sunny site for the plant. Ideally, it should be shaded during the hot midday sun. The buds of some rose varieties cannot withstand the scorching sun and will fade. Groundwater should not be too close to the soil surface. If the soil is heavy and clayey, add sand and peat.
Otherwise, moisture will stagnate in the root zone, which can lead to disease. Clay is added to soil that is too light.
Hole for a rose
The hole is dug two weeks before replanting. Its diameter should be 50-60 centimeters. The depth of the hole depends on the soil composition. If the soil is heavy, a drainage layer of stones or expanded clay is placed at the bottom. Then, a layer of fertilizer mixed with soil is added. Only then is the soil filled in, where the rose root system will be placed.
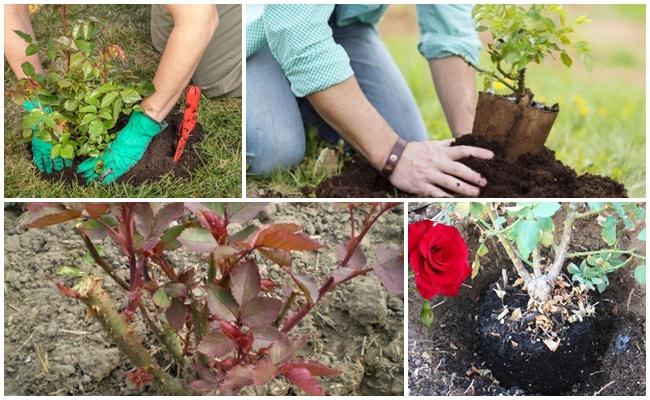
Rules for digging up a bush and preparing for transplantation
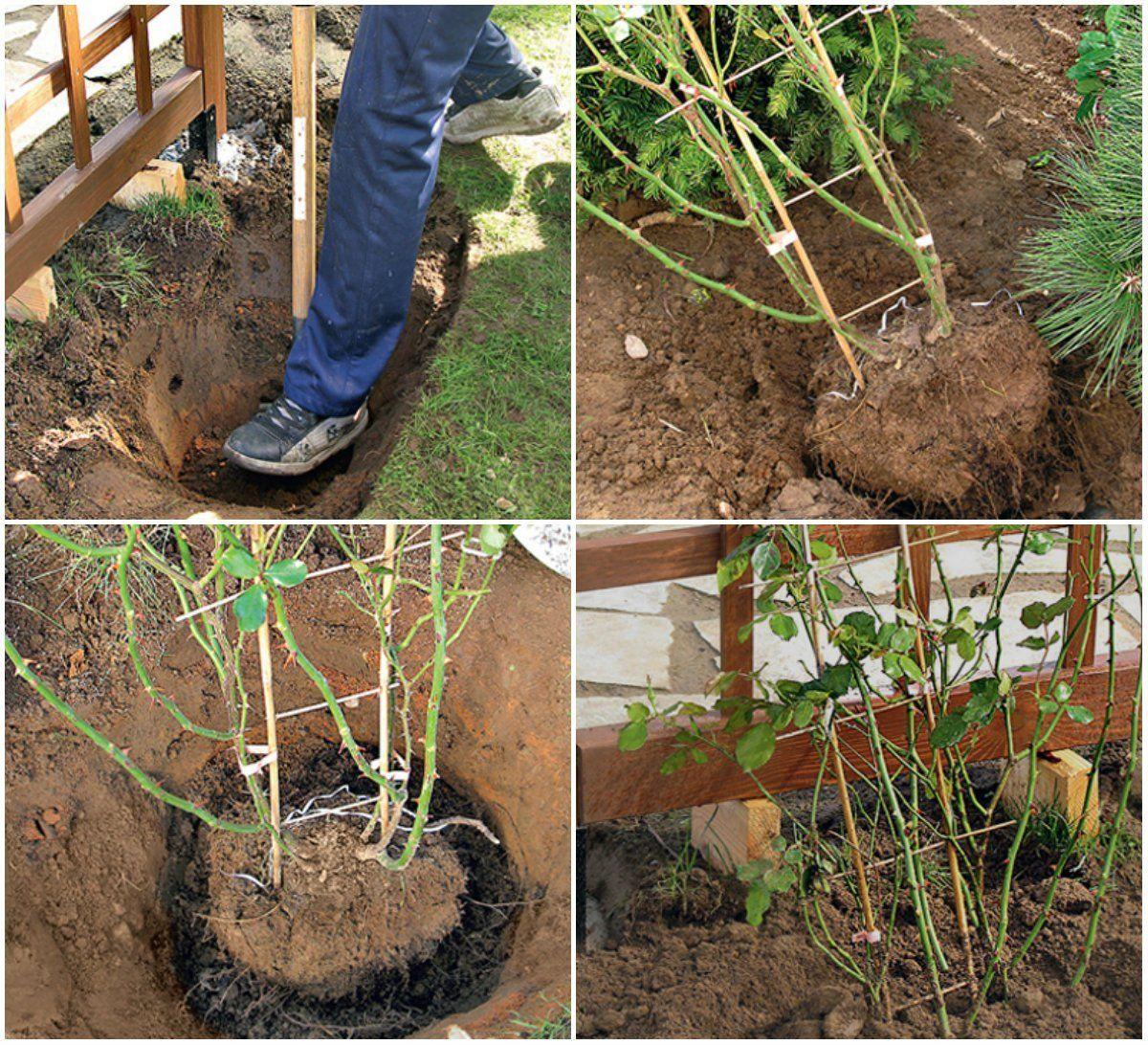
The more carefully you dig up the bush, the easier it will be to establish itself in its new location. To prevent the root ball from disintegrating, water the plant before replanting. Once the soil has dried slightly, begin digging. To do this, step back at least 25 centimeters from the outermost shoots and carefully dig around the bush on all sides.
Then it's lifted and removed from the ground. If the bush is too large, it's divided. The central stem is long and impossible to remove without damage. However, the rose won't be harmed; the main thing is to avoid damaging the small lateral roots.
Please note: When digging up the bush, use a disinfected, sharp shovel or pitchfork.
Rose transplantation technology
Plants can be transplanted with a lump of earth or with bare roots.
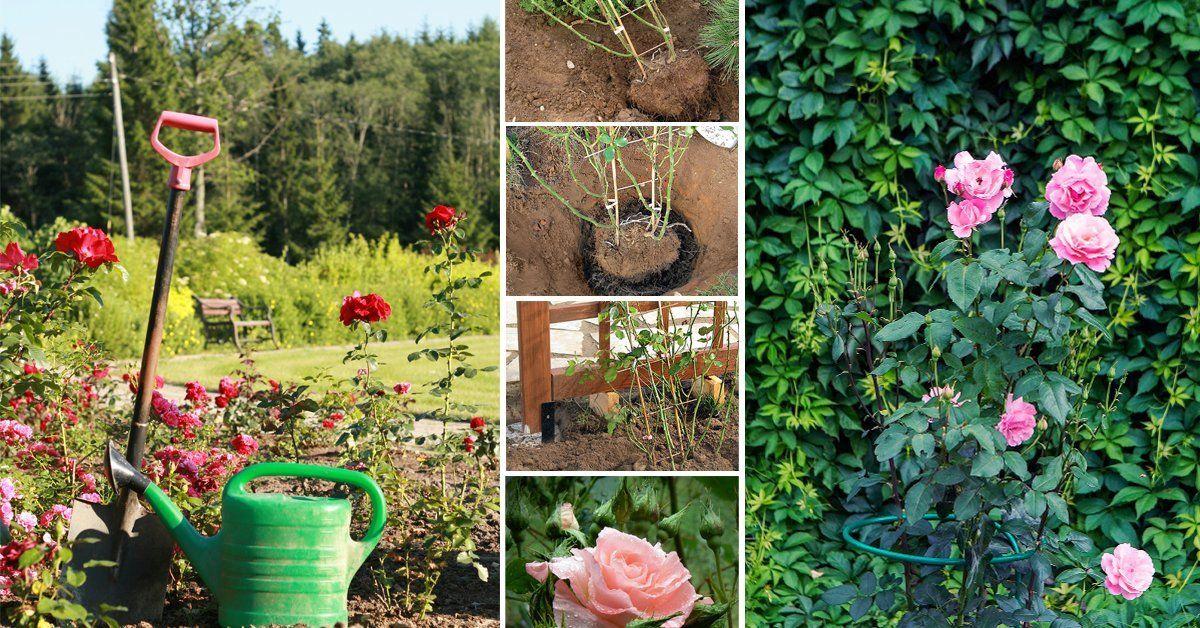

With a lump of earth
The procedure is performed as follows:
- Irrigate the root circle several hours before the procedure.
- They dig around the bush, pry it up with a shovel, and remove it from the soil. To prevent the root ball from falling apart, they wrap it in burlap.
- The rose is planted in a prepared hole in a new location and the voids are filled with fertile soil.
- Water generously. If the soil has settled slightly after watering, add more.
- To conserve moisture, the root zone is mulched with straw, peat, or grass clippings. The layer of mulch should not exceed 5 centimeters.
When planting, the root collar should be buried 4-5 centimeters deep. Otherwise, the rose may stunt its growth.
With bare roots
If dividing a bush during replanting is necessary, it's difficult to do without breaking up the root ball. Each division should contain several shoots and a root system. The cut sites are treated with a fungicide for disinfection. The rest of the process is similar to planting with a root ball.
Nuances and features of flower planting
You can repot not only young bushes but also older ones. It's important to remember that the younger the plant, the easier it adapts to a new location. Therefore, roses older than 4-5 years are repotted only if absolutely necessary. The procedure is performed early in the morning or evening.
An old and large bush
An old bush has typically developed many shoots over the years. Therefore, it can be not only replanted but also divided. This way, the gardener gains several beautifully blooming plants. Replanting a mature rose requires several people. The procedure is as follows:
- water the ground around the bush;
- tie the shoots with twine;
- dig around the bush from all sides;
- removed from the ground and placed in burlap;
- transferred to a new planting site;
- if necessary, divide into parts;
- planted in a pre-prepared hole;
- fill the voids with soil, water, and mulch.

Important! The new hole should be larger than the root ball. The bush should be planted at the same level as it was in its previous location.
Replanting a rose during the flowering period
When plants are in bloom, it's best not to disturb them. During this period, the bushes devote all their energy to forming and opening buds. If necessary, a blooming rose can be repotted. However, all buds will need to be removed. The flowers that form immediately after repotting should also be cut off with sharp, disinfected pruning shears.
Features of transshipment of climbing and twining varieties
First, the vines are removed from their supports. Then they are trimmed, depending on the type of climbing rose they belong to.
For example, ramblers bloom on the previous year's growth. Therefore, the stems of once-blooming climbing and rambling roses are only slightly pruned. Diseased and dry stems are always pruned at the root.
Climbing roses and climbers form buds on shoots from both the previous and current years. These roses bloom twice a year. The shoots of these plants can be pruned by half. If the bush is mature, all old branches are cut back to the stump.
Further care
A transplanted rose requires careful care. It needs to be watered, the soil around it loosened, and weeds removed. Forming buds should be pruned. Fertilizing is not necessary in the year of planting. To prevent diseases and pests, the bushes are treated with special preparations.
Watering
Roses need to be watered generously immediately after planting, especially if they were repotted in the spring. This should be done in the morning or evening using warm, settled water. Make sure there's no standing water in the root zone. Otherwise, there's a risk of fungal infection of the root system.
Loosening and mulching the soil
After watering, loosen the soil around the roses. This procedure promotes air and moisture penetration to the root system. If a crust forms, root respiration will be restricted, slowing the growth of the bushes. While loosening the soil, weeding is also performed. Weeds can carry pathogens and harmful insects.
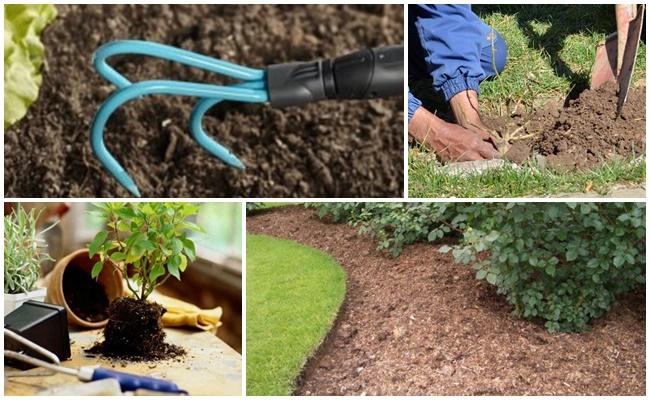

The root zone can be mulched. By covering the soil with straw, peat, compost, or grass clippings, the gardener prevents premature moisture evaporation. Furthermore, mulch makes it harder for weeds to grow to the surface.
Removing flowers
A replanted rose can begin to form buds immediately. However, the bushes need energy to thrive. Bud formation and flowering take a lot of energy from the plant. Therefore, any flowers that form immediately after replanting should be removed.
Shelter for the winter
A plant transplanted in the spring has time to adapt before frost sets in. Therefore, it's sufficient to earth up the bushes when a steady frost sets in. If the plant was planted in late fall, a structure can be erected over it and covered with agrofibre.
Important! Since the rose has been transplanted into fertile soil, there is no need to fertilize it this year.
Mistakes of novice gardeners
Inexperienced rose growers make mistakes that result in poorly established plants and poor blooms. Some plants may even die. The most common mistakes made by novice gardeners are:
- Don't remove the flowers. Roses require a lot of energy to establish themselves. Forming buds also takes a lot of energy from the plants. Therefore, it's necessary to remove the flowers.
- Roses are planted too close to walls. These conditions provide poor ventilation. Furthermore, rooftops shed a lot of water during rainfall, which can be detrimental to the roses.
- Don't put drainage material at the bottom of the hole. This is necessary if the rose is planted in heavy soil or if the groundwater level is close to the surface. Otherwise, the root system may be attacked by fungus.
- When replanting in summer, avoid shading the bushes. The sun is too hot at this time of year. If the plant is left uncovered, moisture will evaporate quickly, causing the leaves to wilt.
- Roses are planted too deep or too high. If they are planted too deep, the plants will develop poorly. If they are planted too high, the root system can freeze in a harsh winter.
- Don't treat the bushes with special products. After transplanting, the plants are weakened and have poor resistance to diseases and pests. Therefore, they need to be periodically sprayed with special products according to the instructions.
Sometimes, for various reasons, it may be necessary to replant roses. The best time to do this is early spring or fall. In summer, replanting is only done if absolutely necessary. If the gardener properly cares for the roses after replanting, they will enjoy beautiful blooms for many years to come.








![TOP 50 best new rose varieties of [year] with descriptions and characteristics](https://harvesthub.decorexpro.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/big-perpl-300x200.jpg)