- History of selection
- Description and characteristics of the variety
- Height of a mature tree
- Flowering and ripening period
- Productivity
- Transportability
- Drought resistance
- Frost resistance
- Applications of berries
- Pollinators
- Jealousy
- Tyutchevka
- Syubarovskaya
- Northern
- Ovstuzhenka
- Taste qualities of fruits
- Advantages and disadvantages
- How to plant
- Recommended timeframes
- Choosing a location
- Preparing the planting hole
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Requirements for neighbors
- Planting diagram
- Care Features
- Watering mode
- Top dressing and fertilization
- Crown formation
- First year
- Second
- Third
- Fourth
- Fifth
- Whitewash
- Sanitary pruning
- Spraying
- Protection from frost and rodents
- Weeding and loosening
- Prevention of diseases and pests
- Reproduction of culture
- Harvesting and storage
- Tips and recommendations
The main distinguishing feature of the Yantarnaya cherry variety is its large, sweet, bright yellow berries. This hybrid fruit variety tolerates subzero temperatures well, is resistant to fungal infections, and has become very popular among gardeners and farmers due to its high yield.
History of selection
The Yantarnaya cherry variety was developed by Ukrainian breeders in the early 2000s. To create this new fruit crop, the Goshe Chernaya cherry and the Drogana Yellow cherry were used.
A little later, specialists from the Russian Research Institute of Breeding refined this cherry variety and improved the characteristics of the berry crop.
The fruit crop is listed in state registers as the Orlovskaya Yantarnaya cherry variety.
Description and characteristics of the variety
Excellent frost and drought resistance characteristics allow this unpretentious cherry variety to be grown in virtually all climatic conditions.
Height of a mature tree
The cherry tree grows up to 4 meters, with a spreading, dense crown of an oval, slightly elongated shape. The skeletal branches are downward-facing, the shoots are strong, straight, and yellowish in color, and the bark of the trunk and branches is grayish and smooth.
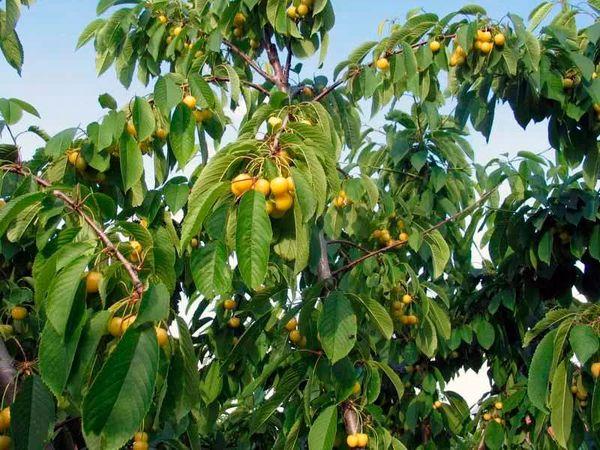

The leaf blades are elongated, with serrated edges and a pointed tip, and are bright green in color.
Flowering and ripening period
During the flowering period, clusters of large, white flowers appear on the bouquet branches. The first clusters open in mid-May, and the berries ripen by the end of June.
The fruits are a beautiful amber color with juicy, yet dense pulp and a sweet taste.
The berries are large, up to 6-6.5 g, with a small stone that easily separates from the pulp.
Fruiting of stone fruit crops begins in the 5th year of growth in open ground.
Important! To obtain a high-quality and abundant harvest, the Yantarnaya cherry variety requires the right pollinators.
Productivity
This hybrid cherry variety is highly productive. With proper and high-quality care, a single tree can yield up to 35 kg of ripe berries.
Ripe berries do not fall from the tree, which increases the chances of obtaining a high-quality fruit harvest.

Transportability
The skin of cherries is thin and delicate, so the berries quickly become bruised and spoil after picking. Yantarnaya cherries are not suitable for long-distance transportation; they lose their marketable appearance and flavor.
Drought resistance
A short-term drought won't harm a fruit tree. However, a prolonged lack of moisture has a negative impact on fruit yield and flavor. During the growing season, if there's no irrigation, cherry trees lose a large number of ovaries, which ultimately reduces fruit production.
Frost resistance
The Yantarnaya cherry variety easily survives winters in temperate and southern latitudes, with temperatures dropping to -30-32 degrees Celsius. In northern regions, trees require additional insulation.
Applications of berries
Ripe berries are best eaten fresh. Cherries are also dried, frozen, and canned. Ripe berries are used to make nectars, juices, compotes, jams, preserves, and are added to confectionery and dairy products.
Experienced housewives make homemade wine, tinctures, and liqueurs from cherries.

Pollinators
To produce a large and high-quality harvest of berries, the Yantarnaya cherry tree requires pollinators with similar flowering times. Trees are planted 5 to 30 meters apart.
Jealousy
This variety, bred at the Bryansk nursery of the Lupine Institute, is capable of partial self-pollination. It bears fruit in the fifth year of growth. The berries are large, up to 8 g, dark red, with dense, juicy flesh and a sweet-tart flavor.
The variety is resistant to low temperatures, fungal diseases and pests.
One tree produces 10 to 15 kg of ripe berries.
Tyutchevka
The Tyutchevka cherry is considered the best variety. Suitable for growing in temperate climates. This fruit crop tolerates winters well, is rarely susceptible to fungal infections and pest attacks, and produces high yields. A single tree produces up to 40 kg of ripe berries.
The fruits are large, up to 7 g, dark red in color with juicy pulp of a dessert taste.
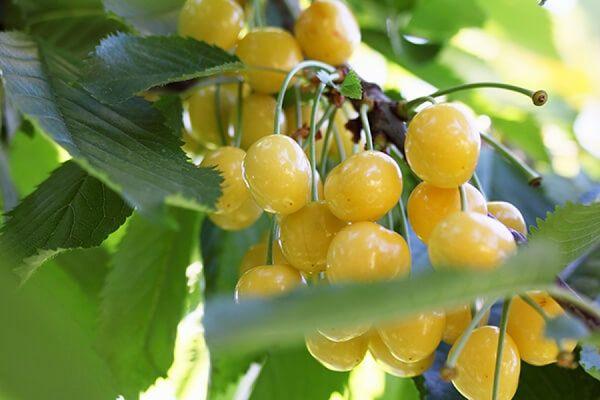

The berries withstand long-distance transportation well, so the variety is often grown in industrial quantities.
Syubarovskaya
The variety was developed by Belarusian breeders in 2005. The variety is distinguished by tall trees, reaching 20 m in adulthood.
The berries are medium-sized, weighing up to 6 g, dark red in color with juicy pulp and a dessert taste.
The fruit crop takes root and grows well in southern and temperate climates.
Northern
A frost-resistant berry variety recommended for cultivation in regions with different climatic conditions.
Small berries weighing up to 4 g are pink-orange in color, with firm, juicy flesh and a sweet flavor. Flowering begins in the second half of May, and the first berries are harvested in late June or early July.
Fruiting begins in the 4th year of growth in open ground.
Ovstuzhenka
The variety is partially self-pollinating. Fruiting is early, with berries already harvested in the fourth year of growth. The fruits are medium-sized, up to 5 g, dark red in color, with juicy, sweet flesh.
With proper care, a single tree can yield up to 15 kg of ripe berries. The variety is resistant to fungal diseases and easily survives winters in temperate and southern latitudes.
Taste qualities of fruits
Ripe berries rarely exceed 5 grams in weight and are bright amber in color, sometimes with a pink blush. The flesh is light, juicy, and sweet, with a slight hint of acidity. The pit is small and easily separated from the flesh.
Important! Cherries contain a large amount of vitamins, minerals, and amino acids that promote healthy body function and support the immune system.
Advantages and disadvantages
Before planting a hybrid cherry variety, you should understand all the advantages and disadvantages of the fruit crop.
Pros:
- Resistance to low temperatures, which allows the cherry variety to be grown in different climatic conditions.
- Early ripening. The first berries ripen in late June.
- Stable, annual fruiting.
- Ripe berries do not crack.
- The variety is unpretentious in care.
- Resistance to some diseases and pests.
Also, the advantages include the universal use of ripe berries.
Cons:
- The variety is not capable of self-pollination; other cherry varieties are required for fruiting.
- Impossibility of long-term transportation of ripe berries.
Important! In harsh winters, fruit buds can freeze, so the tree needs additional protection and insulation.
How to plant
To grow a healthy, fruit-bearing tree, you need to select high-quality seedlings and choose the right location and timing for planting the fruit crop.
Recommended timeframes
Cherry tree saplings are planted according to climate conditions. In the south, planting is recommended in the fall. In temperate regions, trees are planted in early spring, before the growing season begins.

Choosing a location
The Yantarnaya cherry variety is planted in well-lit, level areas or small hills, protected from cold winds and drafts.
The groundwater level should not exceed 2-2.5 m. Otherwise, the tree's rhizome will quickly rot and the seedling will die.
The fruit crop is grown in fertile, loose soils with neutral acidity and humidity levels.
Heavy, clayey soil is mixed with river sand and humus or compost. Acidic soil is limed.
Preparing the planting hole
Preparation of the planting hole begins 3-4 weeks before planting the seedlings.
- The selected area is dug deeply, cleared of weeds and loosened.
- Humus, mineral and organic fertilizers are added to the soil.
- Planting holes are dug in the prepared soil.
- The depth and width of the hole is from 70 to 90 cm, the distance between plantings is from 1.5 to 2 m, between rows 4-5 m.
- A thick drainage layer of sand and small stones is placed at the bottom of the hole.
- Add fertile soil mixture on top and water.
Important! Place a stake in the center of the hole to support the seedling.

How to select and prepare planting material
Seedlings of varietal and hybrid cherries are purchased in nurseries or specialized stores.
- 2-3 year old plants take root and establish themselves best.
- The trunk of the seedling has no obvious damage or fungal infections, is smooth and uniform in color, with numerous branches.
- Each branch must have buds or green leaves.
- When examining the rhizome, pay special attention to moisture. The roots should not be overdried.
- The roots are free of any damage, plaque, signs of rot or fungus.
There should be a graft mark at the bottom of the tree, which can be used to determine whether the cherry tree belongs to a cultivar. The absence of a graft mark indicates that the plant is wild.
Requirements for neighbors
The Yantarnaya cherry variety does not tolerate the proximity of other trees, with the exception of varieties of fruit crop pollinators, or cherries.
Berry bushes, flower beds, garden strawberries, rowan or hawthorn are planted next to the cherry trees.

It is not recommended to grow raspberries, gooseberries, or any plants from the nightshade family next to cherries.
Important! Only by following proper crop rotation can you grow healthy, disease- and pest-resistant fruit crops.
Planting diagram
Before planting, seedlings are placed in a container with warm, settled water for 10-15 hours and treated with preventative measures to prevent the spread of fungi and viruses.
- The plant is placed into the prepared planting hole.
- The roots are evenly distributed throughout the hole and covered with fertile soil, leaving no voids between the roots and the soil.
- The soil under the plant is compacted and watered generously.
- The seedling is attached to a support peg and trimmed.
After planting, the tree trunk circle is mulched with humus or dry grass.

Care Features
This fruit-producing crop requires careful watering, fertilizing, and pruning. Only then will the cherry tree impress with its high-quality yields.
Watering mode
Cherry trees don't tolerate excess moisture well. In temperate climates, fruit trees need to be watered no more than 3-4 times per season, and if there's frequent rainfall, watering is stopped altogether.
In southern, arid latitudes, irrigation work is carried out more frequently, as the top layer of soil dries out.
Top dressing and fertilization
If the seedlings are planted correctly in fertile soil, fertilizing and feeding the cherry tree begins in the 3rd or 4th year of growth.
At the beginning of the growing season, trees are fed with nitrogen fertilizers. When fruit set and fruiting begin, berries require potassium and phosphorus. In the fall, cherries are fertilized with organic matter and a balanced mineral complex.

Crown formation
Crown shaping begins immediately after planting. This significantly increases the yield and flavor of the berries.
First year
Immediately after planting, the main stem of the seedling is cut back to the level of 5-6 buds. The cut area is treated with garden pitch.
Second
In the second year of growth, the tree develops many branches, of which 3-5 of the strongest and healthiest are selected, the rest are pruned.
Third
In the third year of growth, the first lower tier of the cherry tree is formed, and the formation of skeletal branches of the second level is initiated.
Fourth
Now the tree has grown and requires a fully formed second tier of skeletal branches and the establishment of a third level of branches.
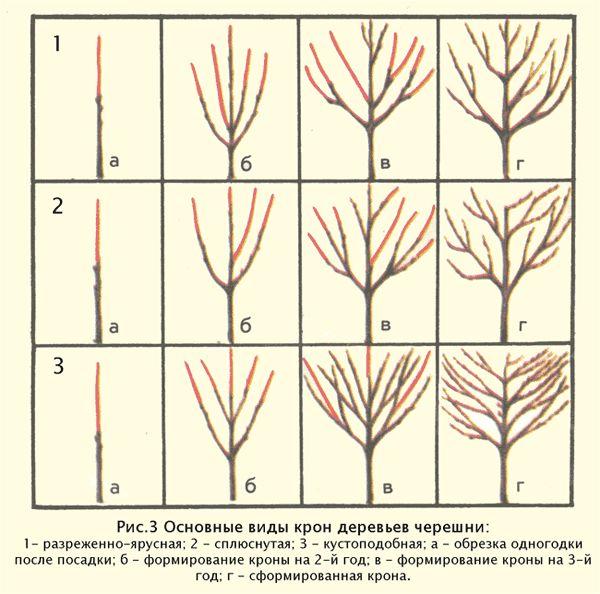
Fifth
The cherry tree is fully formed, only sanitary and thinning pruning is carried out.
Whitewash
Trees are whitewashed in early spring and late fall. Spring whitewashing helps prevent bark burns, while fall whitewashing protects plants from fungal and viral infections.
Sanitary pruning
During sanitary pruning, broken, dry, damaged, and frozen branches and shoots are removed. Also, cherry tree branches that are growing incorrectly and those that have stopped bearing fruit should be pruned.

Tip! To prevent diseases and pests, treat cut surfaces with special products or garden pitch.
Spraying
Before the start of the growing season, trees are treated with fungicide and insecticide-based preparations for preventive purposes.
The same treatment of fruit crops is carried out in late autumn, before the plant’s winter dormancy.

Protection from frost and rodents
With the onset of autumn, the Yantarnaya cherry variety is prepared for winter.
- The tree is watered generously.
- The tree trunk circle is dug up and mulched with a thick layer of humus, and covered with dry grass or spruce branches on top.
- To protect the tree from small rodents, the trunk is covered with a net or a layer of roofing felt.
- A large snowdrift is raked from the first snow under the tree.
It is recommended to insulate young seedlings with burlap or special material before wintering.
Weeding and loosening
During the growing season, the soil around the tree trunk is weeded and loosened, which allows the root system to receive additional nutrition, moisture, and oxygen.
Prevention of diseases and pests
To protect trees from diseases and pests, it is necessary to properly and timely fertilize, prune, weed, and mulch the tree trunk area.

In early spring, carry out preventative treatment of fruit crops with professional preparations or folk remedies.
Reproduction of culture
The easiest way to propagate the Yantarnaya cherry variety is by cuttings.
The procedure is carried out in early summer. A strong, healthy shoot is cut from a mature tree and divided into equal sections of 25-30 cm. Each cutting must have buds or leaves. The cutting is treated with a growth stimulant, rooted in a container with fertile soil, and covered with plastic wrap.
As soon as the seedling takes root, the plant is planted in open ground.
Also, for propagation they use the grafting method or grow cherries from seeds.
Harvesting and storage
The Yantarnaya cherry harvest begins in mid-July, when all the berries are ripe. The fruits are removed from the branches along with the stalks, which helps extend the berries' shelf life.

The harvested fruit is carefully laid out on a flat surface and sorted. Any bruised or damaged berries are sent for processing, while whole fruits are placed in containers or bins and stored in the refrigerator.
The shelf life of fresh berries is up to 5 days.
To extend the berry season, cherries are frozen, dried or canned.
Tips and recommendations
Growing the Yantarnaya cherry variety requires no special knowledge or conditions. This fruit tree is easy to grow, thrives, and thrives in any climate. Even novice gardeners can easily grow it.











