- History of selection
- Description and characteristics of the variety
- Height of a mature tree
- Flowering and ripening period
- Productivity
- Transportability
- Drought resistance
- Frost resistance
- Applications of berries
- Pollinators
- Taste qualities of fruits
- Advantages and disadvantages
- How to plant
- Recommended timeframes
- Choosing a location
- Preparing the planting hole
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Requirements for neighbors
- Planting diagram
- Care Features
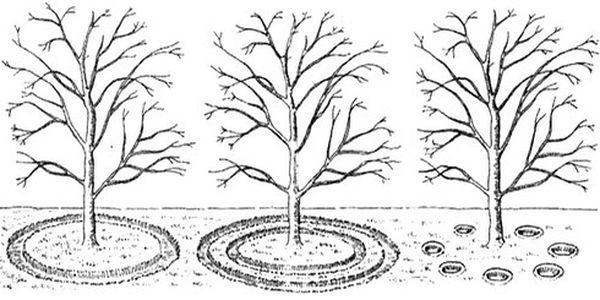
- Watering
- Ditch
- Hose with sprayer
- Drip method
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Formative
- Sanitary
- Thinning
- Preparing for winter
- Diseases and pests
- Monilial burn
- Coccomycosis
- Cherry aphid
- Cherry fly
- Clusterosporiasis
- Powdery mildew
- Weevil
- Reproduction of culture
- Harvesting and storage
Gardeners growing cherries are eager to harvest their crops as early as possible. Therefore, they are drawn to the earliest ripening varieties. One of the fastest-growing is the Veda cherry variety.
History of selection
I. V. Michurin began working on frost-resistant cherry varieties in the late 19th century. By the 1930s, 13 such varieties had been developed. They shared common drawbacks: low yields and very small fruits. Subsequent breeding efforts continued.
In Russia, M.V. Kanshina is currently the recognized leader in cherry breeding. She has developed 14 winter-hardy cherry varieties, one of which is Veda. This work continues at the All-Russian Lupine Institute.
Veda was included in the State Register in 2009. It was zoned for the Central Region.
Description and characteristics of the variety
This tree is known for its rapid growth. The shoots are olive-green, straight, and hairless. The large green leaves are ovate with serrated edges. Their surface is matte and smooth, appearing leathery and slightly sheen. The petiole is thick.
The heart-shaped berries are medium in size. Their skin is thin and smooth, with barely noticeable dark spots underneath.
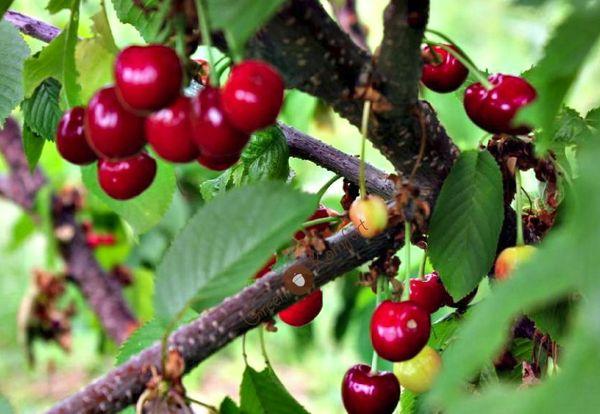

Height of a mature tree
The Veda cherry tree has a compact, dense crown. The tree reaches a height of 2.5 meters. Its low stature allows for harvesting not only from the lower parts but also from the top. The main branches are positioned at right angles to the trunk.
Flowering and ripening period
Veda blooms in May or June. These dates are for central Russia. This helps prevent the effects of spring frosts, such as freezing of the inflorescences.
Veda ripens late, in July. In some areas, this fruiting time is considered an advantage. Heavy rainfall often occurs in late June or early July. This may result in cracking of the berries. This variety begins to produce crops after the end of the rainy season.
Productivity
The Veda cherry tree begins to bear fruit starting from the fourth year after planting.
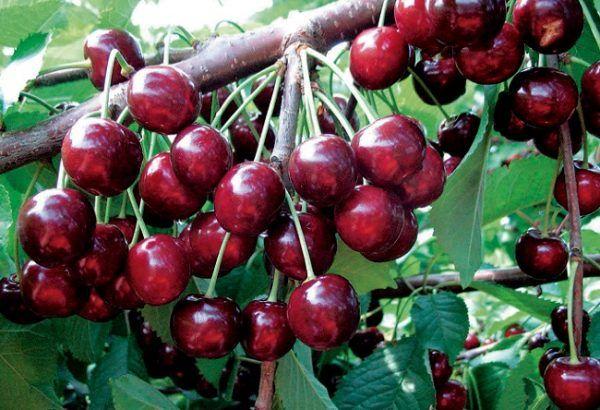

The yield is 77 centners per hectare.
Transportability
Veda fruits are characterized by high transportability.
Drought resistance
The plant does not tolerate prolonged drought and requires watering.
Frost resistance
Veda has above-average frost resistance, making it well-suited for growing in Russia's climate.
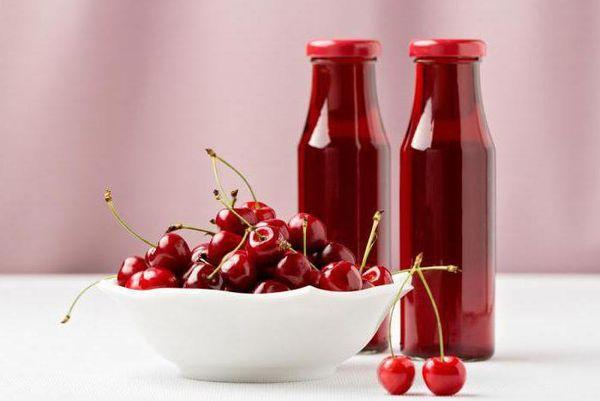
Applications of berries
The Veda cherry is considered a versatile berry. It's perfect for eating fresh, making preserves, or juicing.
One of the characteristics of this variety is the ability to easily separate the pit and pulp. This makes these berries suitable for use as pie filling.

Pollinators
This tree is not self-pollinating. To ensure Veda can delight the gardener with a bountiful harvest, pollinator plants must be planted nearby. The following varieties can be used for this purpose:
- Michurinka;
- Iput;
- Tyutchevka;
- Leningrad black;
- Bryanochka;
- Jealous.
Veda produces the highest yields when using the varieties from this list. Pollination can occur with or without insects, driven by wind.
Taste qualities of fruits
According to experts, the taste of the berries deserves a rating of 4.6 out of 5.
Veda berries have the following characteristics:
- the weight of one berry, on average, is 5.1 grams;
- the largest fruits can weigh up to 7 grams;
- the color is uniform, dark red;
- the berry skin is tender and smooth;
- Veda cherry produces dark red juice;
- The fruits contain 11.5% sugar.
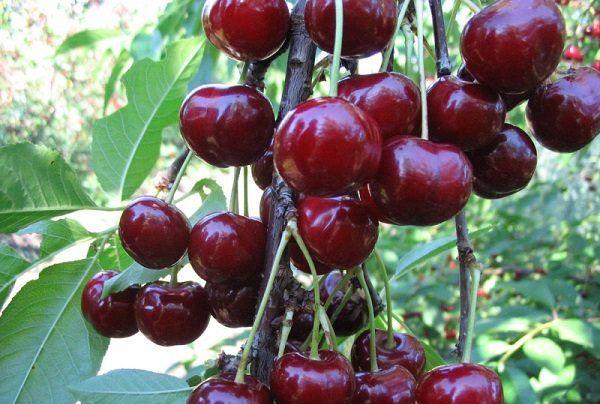

Veda's peduncle is medium-length. When harvested, it easily separates from the branch and the berry. The break remains dry. Veda berries are undamaged during harvesting, which facilitates their high-quality storage.
Advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of this variety are:
- Abundant harvest.
- Excellent taste of fruits.
- Early ripeness of the Veda.
- Late ripening of berries allows for a higher quality harvest.
- Frost resistance allows Veda cherry to be grown in central Russia.
The disadvantage is the self-sterility of this cherry variety. Since the solution requires planting one or more additional trees, this will take up some of the garden space and may create a surplus of fruit if the berries are grown for home use.
How to plant
When planting, water the Veda seedlings generously. Each one will require two buckets of water.
The root collar should be located at a height of 5 centimeters from the ground.
A peg is driven in nearby and the seedling is tied to it.

Recommended timeframes
Cherry trees can be planted in spring or fall. Both periods represent a dormant period for the cherry tree's root system. However, spring planting of the Veda cherry tree is considered more effective. This is because the seedlings may not have enough time to establish roots in the fall.
In the southern regions of the country, planting of Veda seedlings is permitted no later than mid-October.
Choosing a location
A cherry orchard is built to last for many years. Therefore, the location must be chosen carefully. Low-lying areas where moisture will accumulate are unsuitable for the Veda cherry tree.
The best relief for the landing site is gentle slopes with good sunlight.
When choosing a site for planting the Veda cherry tree, consider the groundwater level. It shouldn't be deeper than one and a half meters.
If high humidity conditions cannot be avoided, drainage ditches can be used to drain moisture.
The best soil composition for the site is loose, sandy loam. Heavy clay or acidic soils are not suitable for the Veda cherry tree. It's best to add the required amount of sand to the former, and lime to the latter (500 grams per square meter).
Preparing the planting hole
Site preparation begins no later than three weeks in advance.

Veda cherry tree seedlings are smaller and have a weaker root system than other cherry varieties. To plant the bush, prepare a hole 50 centimeters deep. The width and depth should also be 50 centimeters.
Before planting, you need to apply fertilizer. The composition of the fertilizer depends on the soil type. If you're planting the Veda cherry tree in black soil, mix humus with soil in a ratio of 1:10. If you're planting in less fertile soil, you can make a more concentrated fertilizer: 1 part humus to 7 parts soil.
Add 150 grams of double superphosphate, 50 grams of potassium sulfate and 0.4 kilograms of ash to each hole.
Fertilized soil is poured into the bottom of the hole to form a small cone. When planting the Veda cherry tree, the roots are spread out and covered with soil.
How to select and prepare planting material
Seedlings should be purchased from nurseries or botanical gardens. These will provide a certificate with detailed plant information. Upon purchase, inspect the seedlings to ensure they are free of diseased or damaged plants. It's best to choose 1-2-year-old Veda cherry seedlings.
Each tree must have at least three skeletal roots. The crown must have three skeletal branches at least half a meter long. There is a bend 10 centimeters from the root collar. This is where the plant was grafted.
Veda cherry tree seedlings should be soaked in water for 6-8 hours before planting. It's best to soak them overnight and then plant them in the ground in the morning. Adding a growth stimulant to the water ensures 100% survival.

It is recommended to renew the root system. To do this, trim the roots. Leave the thick parts, and remove any shoots 1 centimeter away from them.
Requirements for neighbors
It's helpful to plant sage, marigolds, dill, and calendula nearby. These plants can repel insect pests from the Veda cherry tree.
Avoid planting corn or sunflowers nearby. They can deplete the soil. Furthermore, by casting shade, they steal sunlight from the bird cherry.
This plant is self-sterile. Fruit will not set without the presence of other varieties. It is necessary to plant the Veda cherry tree alongside Tyutchevka, Michurinka, Leningradskaya Chernaya, and other varieties.
Sometimes there's no room in the plot for planting pollinators. In this case, you can use the Veda cherry as a rootstock for the varieties listed above. Pollination will then occur normally. However, it's important to keep in mind that this method is only successful for young trees. For established trees, it's impossible to ensure the scion's survival.
Planting diagram
These trees are not tall, but their crown is spreading, formed by horizontal branches. Therefore, when planting, sufficient space between plants should be provided to allow for the neighboring trees to grow freely. Therefore, Veda cherry tree seedlings should be spaced 2.6-3 meters apart. This will ensure that the fruit ripens evenly across the branches throughout the tree's height.
Care Features
The plant needs quality care.
Watering
After planting, water weekly. Each young tree will require 30 liters of water.
An adult Veda cherry tree that has reached the fruiting age needs to be watered three times during the season:
- in the green cone phase;
- when the ovary occurs;
- at the end of fruiting.
Each time, one plant will need 5 liters of water.
Ditch
These grooves are dug in a circle, running along the perimeter of the tree's crown. Their depth should be 15 centimeters.
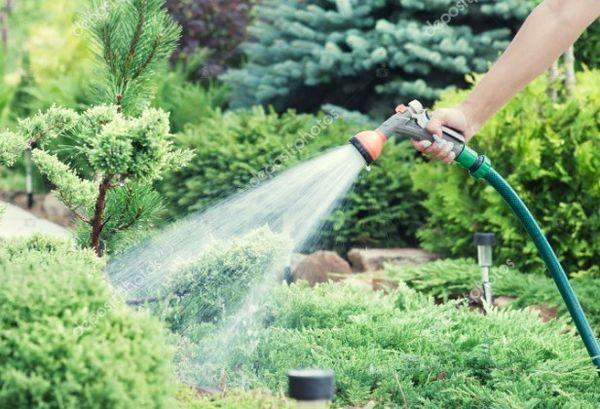
Hose with sprayer
Using these hoses ensures water is distributed evenly across the soil, trunk, and various parts of the cherry tree's crown. Watering is recommended in the evening.

Drip method
To do this, wrap a sprinkler tape in a spiral around the tree trunk. This watering method thoroughly moistens the cherry tree's root zone, preventing the soil from sticking together when it dries.
Top dressing
During the first year, cherry trees don't require additional feeding. Each spring, water with a saltpeter solution (60 g per 10 liters of water). Two weeks later, water with a urea solution (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water). In the fall, fertilize with a phosphorus-potassium solution (2 tablespoons per 10 liters of water).
Trimming
As the tree grows, it's important to take steps to shape the cherry tree's crown and ensure abundant and uniform berry growth. Pruning can affect the berry's flavor, eliminating bitterness and ensuring high sugar content.
Removing branches ensures better ventilation and uniform sunlight exposure of the cherry berries.
For fruit-bearing trees, fertilizing is done 5 times during the year:
- At the end of March, saltpeter is used.
- Before flowering - superphosphate, after it - nitrophoska.
- After harvesting, superphosphate and potassium sulfate are used.
Before the onset of winter, cherry trees are fertilized with humus.
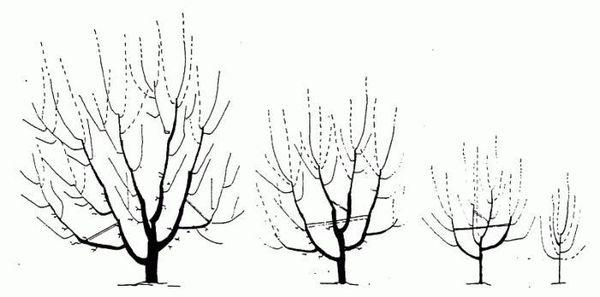
Formative
The purpose of pruning is to form a three-tiered crown.
First year
The distance between cherry tree tiers should be at least half a meter.
Second
The three strongest branches are left on the bottom row. The central shoot is removed at a distance of one meter from the bottom tier.
Third
A second tier of three shoots is formed. The trunk is cut at a height of one meter from it.
Fourth
During this season, the third tier is formed, leaving the three strongest cherry branches.
Fifth
4-5 year old branches are pruned, using young lateral shoots instead.
Sanitary
Cherry tree pruning for health begins in mid-March and continues until the sap begins to actively flow. This involves first trimming back any major branches that have grown excessively. It is important to pay attention to cherry tree branches that prevent uniform illumination of ripening berries.
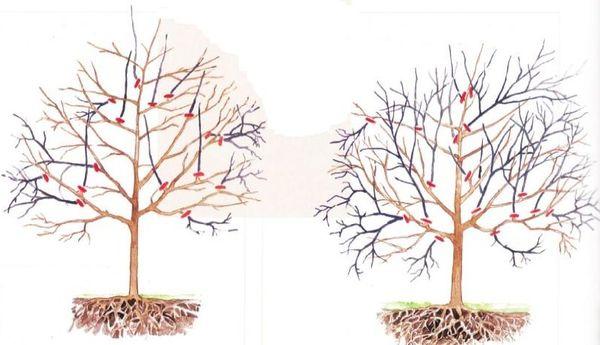
When buds begin to grow, you can see which branches have been frostbitten. These should be removed, but the cut area should be coated with garden pitch to help them heal faster.
Thinning
Remove old, diseased cherry tree branches.
Preparing for winter
In winter, it is recommended to cover young plants with agrofibre or spray them with a Novosil solution, which increases the plant's immunity.
When the leaves fall, pre-winter watering is carried out, which is necessary to help the cherry tree survive the winter.
Diseases and pests
The following means are used to combat diseases and pests.
Monilial burn
With this disease, buds, leaves, and ovaries gradually turn brown. After some time, they dry up. Diseased branches should be pruned and burned. HOM or Horus are effective treatments. All trees in the garden should be treated, not just the diseased ones.
To prevent the occurrence of the disease, it is recommended to carry out preventive spraying with fungicides.

This type of spraying is carried out before flowering and in the fall, after harvest. Bordeaux mixture, Mikosan-V, Skor, and other similar products can be used.
If a shoot has been cut, the cut should be disinfected. This will reduce the risk of infection.
Coccomycosis
At the green cone stage, spray with copper sulfate. After flowering, use Bordeaux mixture.
Cherry aphid
Before and after flowering, use Aktara and Actellic.
Cherry fly
After flowering, use Iskra or Aktara. Repeat the treatment after a week.

Clusterosporiasis
For treatment, it is necessary to remove diseased branches, treat with Bordeaux mixture before and after flowering and again after two weeks.
Powdery mildew
In this case, treat with Skor or Topaz before flowering. After flowering, use Hom. In the fall, spray with Bordeaux mixture.
Weevil
Spray with Fufanon at the green cone stage.
Reproduction of culture
When growing, seedlings are used, which are sold in nurseries or botanical gardens.
Harvesting and storage
The harvest takes place in late July. Veda cherries store well and retain their marketable appearance for a long time.











