- Basic rules
- Methods
- Breeding with seeds
- Selection and stratification
- Preparing the site
- Soak
- Sowing
- Green cuttings
- Description of the method
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Planting diagram
- Care after rooting
- Greenhouses for rooting at home
- Undergrowth
- Graft
- Preparation of planting material
- Preparation
- Storing cuttings
- How to graft
- Suitable varieties
- What can be vaccinated against?
- Deadlines
- Aftercare
- Air layering
- Common mistakes
- A few words about pollinators
- Tips and recommendations
There are many ways to propagate cherry trees. They differ in the materials used, the timing of the procedure, and the technology. This allows every gardener to choose the optimal method that will help them achieve the desired results. It's important to strictly follow the recommendations of experienced specialists and avoid common mistakes.
Basic rules
Cherry propagation can be done using various methods. Using seed will deprive the tree of its varietal characteristics. Its fruit will have a different flavor, yield will be reduced, and the berries will be smaller. Fruiting will only begin after five years. When carrying out such manipulation, it is worth going through the stratification procedure.
Grafting and cuttings are considered more effective methods of cherry propagation. With the latter method, gardeners can experiment with plant material. They can grow cherry trees without the use of complex equipment and preserve the tree's varietal characteristics.
Methods
Each cherry propagation method has its own unique characteristics. These nuances should be taken into account when performing the procedure.
Breeding with seeds
This is a simple and affordable method that allows you to grow a new fruit tree in your garden. The seed can be planted in spring or fall. Sometimes planting is also done in the summer. This is done immediately after removing the pulp.

Selection and stratification
To select high-quality planting material, it is worth focusing on the following features:
- Only the largest berries with excellent taste are suitable for extracting seeds and their subsequent sowing.
- It is recommended to use pits from berries that have been hand-picked. The trees should be grown in the same climate region where the cherry trees are planned to be planted.
- Avoid using seeds from fruits purchased at the market. Southern varieties are considered less frost-resistant and may not thrive in more northern regions.
Before sowing, the seeds are stratified. To obtain strong seedlings, follow these steps:
- place the bones in a container and sprinkle with moistened river sand;
- put it in any place with a temperature of 0 degrees;
- It is acceptable to bury the container in a snowdrift.

Preparing the site
To grow a tree this way, you need to pay attention to preparing the garden bed:
- First of all, choose the sunniest area. It should be well protected from cold winds.
- Clear the garden bed of weeds.
- Add 5 kilograms of rotted manure, 200 grams of wood ash and 1 large spoon of nitroammophoska per square meter.
Soak
Before planting, the seeds should be soaked. Any growth stimulant can be used for this purpose. It's important to strictly follow the instructions on the packaging. Planting can begin the following day.
Sowing
It's recommended to plant the seeds immediately after the snow melts and the soil warms to 0 degrees Celsius. To do this, follow these steps:
- Make furrows across the bed, spaced 35-40 centimeters apart.
- It's recommended to plant the seeds 15-20 centimeters apart. This will make caring for the seedlings easier. They will develop normally without interfering with each other.
- Add wood ash to the bottom of the furrow, making it 0.5 cm thick. Water the plantings.
- Cherry pits should be pitted a maximum of 2-3 centimeters deep.
- Sprinkle with a nutrient solution. This should include topsoil and compost. Mix these components in equal parts.
- After planting, the bed is fenced with pegs.

Autumn
Planting in the fall has its own specific requirements. First, the seeds should be thoroughly washed and soaked in a light solution of potassium permanganate, which helps disinfect the planting material.
Place the pits in a moist substrate. This should include sawdust and moss. After the preparatory work, the pits can be planted in the ground. This is done in early October. It is recommended to plant the cherries 5 centimeters deep, maintaining a distance of 20-25 centimeters from each other. Place 1-5 pits per bed.
In the spring, the seeds that survived the winter cold sprout. It's recommended to thin them out. The strongest seedlings are left for further development.
Spring
When planting cherry trees in the spring, it's important to ensure the pits are ripened after harvest. It's recommended to soak the seeds in moist sand for 2-3 months before planting. Wood sawdust is also suitable. Maintaining a temperature of 14-18 degrees Celsius is crucial.
Before planting, soak the seeds in cold water for 4 days. During storage, it's important to follow these guidelines:
- control the humidity of the material in which the seeds are stored;
- stir the soil from time to time to improve oxygen supply.
After three months, the seeds should be moved to a cellar and stored at a temperature no higher than 6 degrees Celsius. During this period, the seeds will germinate. It is recommended to move them to snow or ice. In the spring, the seeds are planted outdoors.

Green cuttings
Green cuttings are not considered the most effective method of cherry propagation. However, they are sometimes used.
Description of the method
For green cuttings, use young lateral shoots from this year. These should grow from the bottom of the crown. It's important to cut branches from the sunny side of the plant. Check the shoots for signs of fungal infection. The branches should be at least 30 centimeters long and contain large, high-quality buds.
To take cuttings, use a sharp knife. Secateurs are not recommended for this purpose, as they will crush the cut area. The shoots are cut into 8-12 cm long cuttings. These should be placed in water or a container filled with damp moss.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
It's recommended to take green cuttings in June. If your region has a short summer, do this in July. It's best to harvest the planting material early in the morning, during cooler times of the day. This can also be done on cloudy days.
Planting diagram
Once the cuttings are harvested, they are prepared for planting in the greenhouse. First, the lower cut should be soaked in a growth stimulant solution. Kornevin or Heteroauxin are used for this purpose. The process lasts 15-20 hours. Afterwards, the cuttings are planted in nutrient-rich soil and covered with plastic wrap.

The soil must be regularly moistened. Maintaining an optimal temperature of 25-27 degrees Celsius is also crucial. The greenhouse should be regularly ventilated. Avoid exposing the cuttings to direct sunlight. With proper care, the plant will root in 3-4 weeks.
Care after rooting
To ensure the plant thrives, proper care is recommended. This requires a number of procedures.
Watering mode
In hot weather, water the plant at least 5 times a day. On cloudy days, reduce the frequency to 3. Using too much water is not recommended.
When the first signs of rot appear, reduce the amount of water. However, maintain the same frequency of watering.
Top dressing
Without timely fertilization, the crop will not develop normally. Proper feeding promotes the development of strong roots and a robust plant base, laying the foundation for a future harvest.

If planted correctly, cherry trees do not require mineral fertilizers in the first year. Organic fertilizers are recommended for use during planting. They are mixed with the soil.
It is recommended to apply organic fertilizers several more times afterward. When choosing the amount and composition of fertilizers, consider the appearance of the plant.
It is recommended to apply nutrients during watering or 24 hours after. Foliar feeding is done by spraying. This procedure should be done in the evening or on cloudy days. It should not be performed until the plant is two years old.
When applying foliar fertilizer, exercise caution. It is recommended to wear gloves, protective clothing, and goggles.
Crown formation
Cherry trees require proper crown formation. To ensure a tree with developed roots, pruning is performed from the first year of life. The specific technique used depends on the variety. However, there are some general guidelines.
Pruning is done to increase fruiting, prevent diseases, and improve berry quality. In cold climates, it's best to train the plant as a bush. This will make it easier to survive the winter.
It's recommended to begin shaping the tree when it's young, when the shoots bend easily. Start by removing the lower, non-skeletal branches. The central shoot should be shortened as well. This is necessary to shape the lateral branches.

In addition, sanitary pruning is performed. This helps prevent disease and plant death. During this procedure, it is recommended to remove diseased and crooked branches. Damaged areas are coated with garden pitch.
Protection from diseases and pests
Young trees should be treated for pests and infections. Gardeners should regularly monitor the condition of the seedlings to identify problems early.
Chemical treatments are used to prevent diseases. They are recommended before flowering. Afterwards, only folk remedies are acceptable.
To control insects, set a trap filled with a special mixture. This attracts the pests and kills them. In severe cases, insecticides are used.
Greenhouses for rooting at home
To root green seedlings, it's best to use plastic greenhouses. They maintain normal temperature and humidity levels. In hot weather, the structure should be shaded using tarps or branches.
Undergrowth
Cherry trees are easily propagated by suckers. This method is simple and accessible. First, it's important to select the right planting material. Young shoots are used for this purpose. They must be sufficiently strong. Weak or crooked branches will not take root. Two-year-old shoots are best.
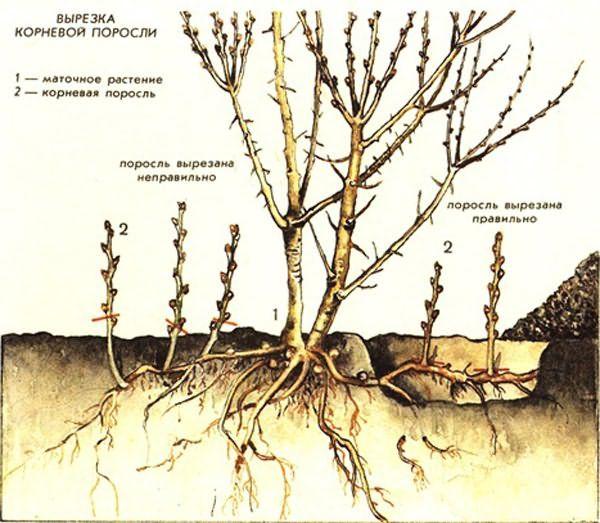
Saplings that are sufficiently distant from the main tree are suitable for propagation. The shoots should grow throughout the summer. By autumn, they will be ready for transplanting. The planting material is separated along with a small fragment of the parent root. This will improve its survival rate. The advantage of this method is the rapid rooting and development of the tree.
Graft
To perform grafting, you'll need cuttings. These can be used to propagate any tree, ensuring high-quality results.
Preparation of planting material
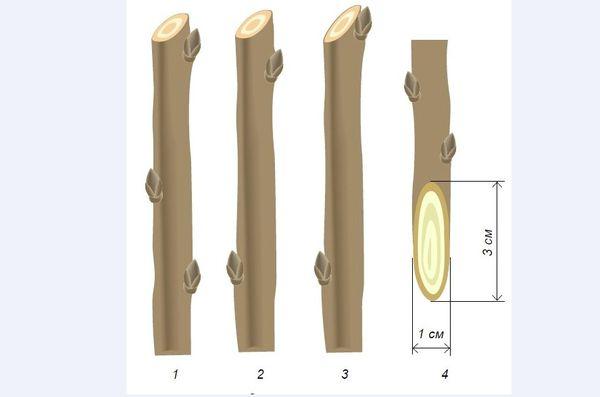
To ensure high-quality fruiting, it's recommended to pay close attention to the selection of cuttings. Here are some considerations:
- Planting material should be taken from trees that bear fruit well.
- Mature shoots aged 1 year are suitable for propagation.
- It is better to take branches from the sunny side of the tree.
- Suitable stems should be taken from the middle part of the cherry tree. The upper shoots may be too thick, and the lower ones may bear fruit poorly.
- The length of the blanks should be 60-70 centimeters.
- Young trees that do not have a large number of flower buds are suitable for propagation.

Preparation
It's acceptable to prepare shoots for grafting twice a year. The first time, this is done in mid- to late fall. The procedure is then repeated in early spring. Autumn preparation can be carried out after the leaves have fallen and the first frosts have set in. This method has several advantages:
- Cuttings taken in the fall or early winter will be more cold-hardy, able to withstand even significant temperature drops.
- The blanks will remain dormant until the grafting is performed.
If pruning a branch in the fall fails, it can be postponed until spring. However, it's important to determine the viability of the shoots.
Storing cuttings
It is recommended to store cuttings properly. It is important to ensure that the branches do not dry out or freeze. The grafting material should not be damaged by rodents. Otherwise, good results will not be achieved.
Experts advise against keeping different varieties of cuttings together. It's better to separate them into groups and tie them together beforehand. To avoid mixing up varieties, it's a good idea to label them.

To prevent damage to the grafting material, it is not recommended to store it at too low a temperature. Sometimes cuttings dry out. This usually occurs after exposure to cold.
Monitoring humidity levels is crucial. Cuttings can rot, leading to mold. If mold appears, it's recommended to treat the material with an alcohol-based iodine solution.
If the branches have sprouted, they cannot be propagated. This usually occurs when the temperature rises to +5°C (41°F). In any case, the cuttings should be checked every two weeks. If necessary, moisten the sand or sawdust.
Sawdust
For storing cuttings, you can use damp sawdust. Place the cuttings in the sawdust and sprinkle the same material on top. Move to a cool place. If the temperature drops to -20 degrees Celsius, add an additional layer of sawdust, 30-40 centimeters thick.
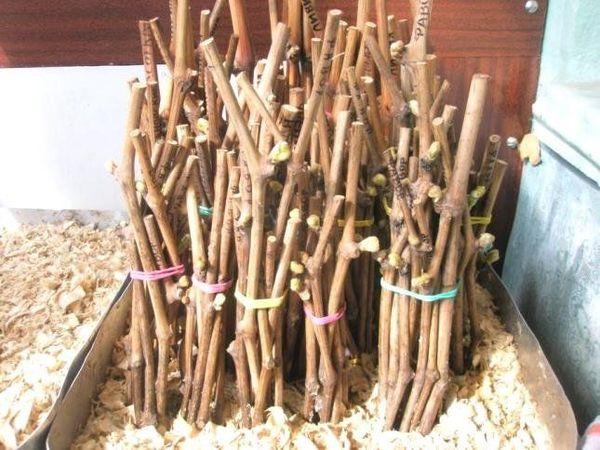

A few days before grafting, the planting material is moved to a warm room. This will allow it to thaw.
Cellar
Any substrate is suitable for this method. Cuttings can be placed in peat or moss. Sawdust or sand are also suitable. Sand is ideal. It is recommended to place the branches in moist substrate. The container should have holes to allow air to enter. The temperature should be 0 degrees Celsius, with a maximum of 2 degrees Celsius.
Fridge
This method is used for small quantities of food. Wrap the food in several layers of film. The optimal temperature is +2 degrees Celsius.
How to graft
Vaccination is performed in various ways, each with its own advantages.
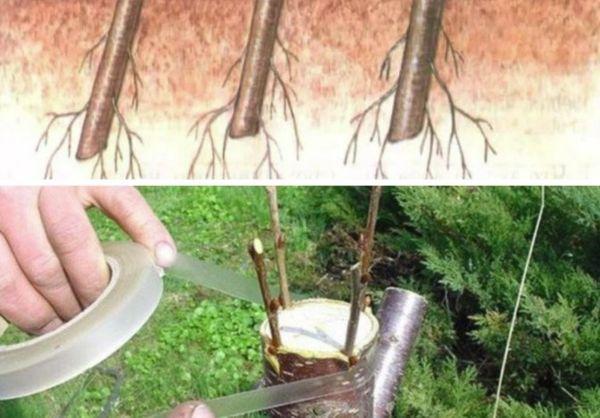

Copulation
To propagate cherries using this method, neat, diagonal cuts of equal size are made on the rootstock and scion. They are then aligned and secured with film.
Into the cleft
This method is suitable for trees in the dormant phase. To do this, the branch is carefully cut off, then a split is made with an axe. The branches are placed in this split. They should have 2-4 buds, with the lowest bud located at the level of the cut.
For the bark
This method is used if the bark peels off easily. For propagation, make a longitudinal cut on the scion and peel off the bark. Then insert the stem into the cut.
In the butt
To implement this method, it is recommended to make a cut on the rootstock and remove a section of bark. Apply the graft to this area. Immediately after grafting, the butt area should be bandaged.
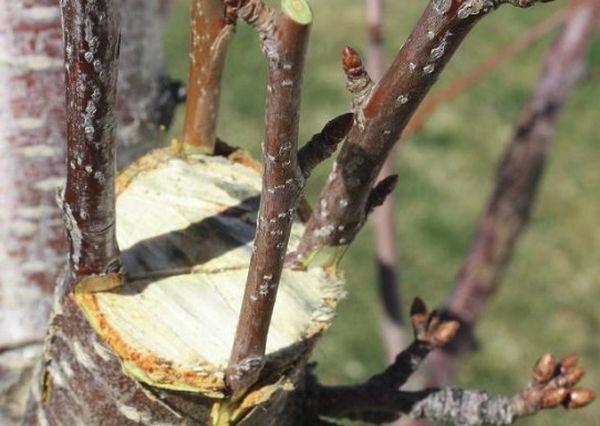

Suitable varieties
There are many varieties that can be used for grafting, and each has its own specific characteristics.
Fatezh
This variety is characterized by a medium-sized tree with a spreading crown of medium density. It is distinguished by excellent frost resistance. It produces red fruits that ripen mid-early. The fruit contains light-colored flesh.
Franz Joseph
This is a large tree with a pyramidal crown. It is characterized by excellent frost resistance. The fruits are amber-colored and ripen early. The flesh has a sweet, slightly tart flavor.
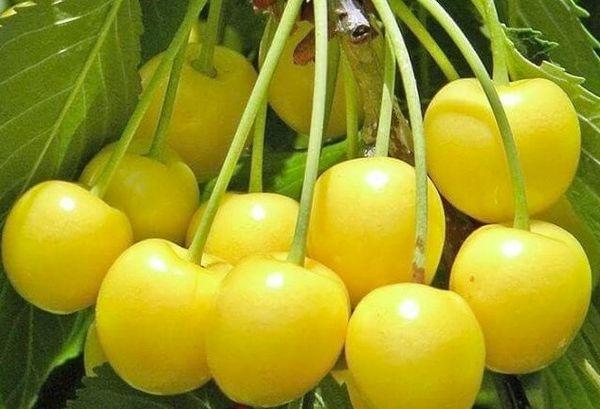
Homestead yellow
This is a large, medium-density tree. It is frost-resistant and drought-resistant. The fruit is yellow and contains firm, sweet-tart flesh.

Beauty of Kuban
This medium-sized tree has a dense, rounded crown. The variety is frost- and drought-resistant. The fruit is characterized by excellent flavor, with a light cream color and juicy flesh.
General's
This is a large tree with a spherical crown. The cultivar is frost-resistant. The fruit ripens mid-season. They are yellow with a blush. The flesh inside is dense and tasty.
Dagestani
This variety was bred from Drogana zheltaya and Aprelka chernaya. It is characterized by large trees and a rounded crown. The fruits are heart-shaped and have thick red skin.
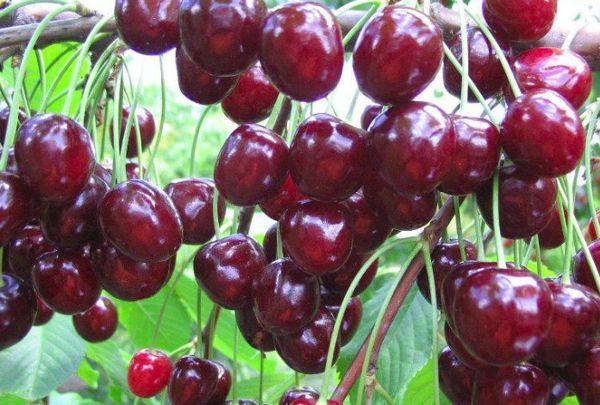
Tyutchevka
The tree is medium-sized and has a rounded crown. The berries ripen mid-late. They are dark red and have firm flesh. The stalk separates easily. This variety is noted for its excellent transportability.

Colt
This tree is small in size and has a pyramidal crown. It produces fruit early, producing tasty and sweet fruits. However, the variety is characterized by low frost resistance and high susceptibility to disease.
Maksma Delbar 14
This French variety has gained widespread popularity. Its cherries boast excellent flavor and are easy to transport.
Piku
This medium-sized plant is frost-resistant. The tree produces a bountiful and consistent harvest.
Gisela
This German variety easily tolerates severe temperature drops. The berries are characterized by excellent flavor.
What can be vaccinated against?
Cherry trees can be grafted onto another variety. This allows for the creation of several varieties on a single tree. This method saves space and eliminates the need for pollinator trees. Other crops can also be used for grafting.
Plum
This combination helps produce tastier fruits and increase yields. Cleft grafting is best. It's important to note that this is a fairly complex procedure and doesn't always yield results.
Bird cherry
This method is quite controversial, as it's impossible to predict the outcome of such an experiment. Even if the scion adapts to the bird cherry rootstock, such a hybrid will require constant monitoring.
Cherry plum
This type of grafting takes root well, which is why it's performed so often. This procedure increases the plant's hardiness. It can thrive even in areas with high groundwater levels.

Cherry
This tree is considered an excellent scion. The adapted scion thrives. However, after a few years, the cherry tree thickens significantly at the junction. It exhibits pronounced sap flow. To prevent branches from breaking under the weight of the fruit, the junction is furrowed.
Deadlines
To ensure successful crop grafting, it is recommended to strictly adhere to the procedure timing.
In summer
When propagating a plant during hot weather, it's recommended to perform the procedure very quickly. Otherwise, there's a risk of damaging the cuttings. Grafting is recommended by copulation. Performing this procedure in August typically yields excellent results. The stem has time to establish itself by autumn and grows well the following year.
Most gardeners recommend choosing this time of year for propagation. Grafting should be done in cool, cloudy weather. However, it's important to keep in mind that there shouldn't be any rain.
In the spring
This season is excellent for grafting. In spring, the scion and rootstock usually fuse well.

It's important to keep in mind that cherries are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. Therefore, it's best to graft during sap flow. The temperature shouldn't drop below 0 degrees Celsius.
Aftercare
The results of this procedure directly depend on the care provided to the plant. To ensure rapid adaptation, it's important to follow certain rules.
Maintaining moisture
It's important to ensure there are no drops of liquid between the rootstock and scion. However, excessive dryness is also unacceptable, as it will cause the graft to fail.
Temperature control
Direct sunlight should not fall on the grafted area. This area should be protected by other branches. It's also acceptable to create your own protection.
Growth control
Nutrients have difficulty reaching the scion. Excessive buds can impair plant development.

Fractures
It's recommended to tie young branches to a support. Otherwise, other shoots, wind, or birds may break them.
Air layering
New crops can be grown from air layering. This method is rarely used due to its increased complexity and significant time consuming nature.
To implement this method, it's recommended to make cuts on the fruiting branch. Then, take a bag of soil and wrap it around the cut sections. The soil should be watered.
This method is used only on high-yielding crops. It's time-consuming, so it's only used when grafting or cuttings are not possible.
Common mistakes
To ensure a high-quality plant, it's recommended to strictly follow all necessary rules. When propagating cherries, inexperienced gardeners face various difficulties:
- The plant isn't producing growth. The problem is usually caused by a lack of moisture or fertilizer.
- The seedling isn't rooting. First, it's important to make sure it truly hasn't rooted. After that, it's recommended to take action. To do this, treat the cuttings with a beneficial mixture or use mineral supplements.
- The cherry tree isn't blooming. This is due to errors during planting, excessive root collar planting, and other factors.
If problems arise, don't give up. First, it's recommended to identify the underlying causes and try to eliminate the trigger.
A few words about pollinators
Most cherry varieties are considered self-sterile. This means that to produce a large harvest, the plant requires pollinators. To achieve this, it's best to plant two or three cherry varieties in the same plot. It's important that their flowering times coincide roughly.

Tips and recommendations
To grow cherries, you need to provide them with the best possible conditions. To do this, follow these basic guidelines:
- Loosen the soil around the tree trunk regularly. This will provide the plant with oxygen and nutrients.
- Monitor the amount of watering. It's recommended to moisten the soil regularly. However, avoid over-wetting the soil.
- Prune. It's important to pay attention to crown formation. Sanitary pruning, which aims to remove diseased, dry, and deformed shoots, is also important.
- Inspect the crop for diseases and pests. If problems arise, prompt treatment with fungicides or insecticides is recommended.
- Apply fertilizer promptly. Young plants 1-2 years old don't need additional feeding, as they are planted in fertile soil. Later, the plant requires nitrogen fertilizer. The tree also requires mineral supplements.
Cherry trees can be propagated in a variety of ways. Seeds, grafting, and cuttings are all used. Sometimes, the tree is propagated by suckers or air layering.
In any case, good care for the young plant will help ensure good results and a bountiful harvest. It needs to be watered, loosened, and fertilized regularly. Protecting the tree from diseases and pests is also crucial.











