- Composition, formulation and manufacturer
- Mechanism of operation and what it is used for
- Advantages and disadvantages
- Rules for use and preparation of working solution, dosage
- Berry bushes
- Seed treatment
- Flowers
- Grape
- Vegetables
- Fruit trees
- Roses
- Precautionary measures
- Is compatibility possible?
- How and how long can it be stored?
- What to replace it with
Without pesticides, crops will become diseased, which will not only reduce yields but also lead to soil contamination, which in turn will lead to the spread of fungal diseases. Modern triazole-based products are particularly effective. However, it is essential to follow the instructions for use of the fungicide "SKOR"—one of the best plant disease control products.
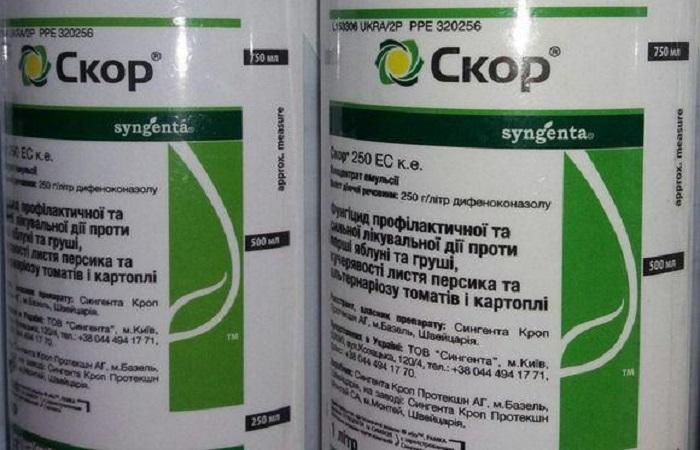
Composition, formulation and manufacturer
SKOR, a systemic fungicide produced by the Swiss company Syngenta, is an emulsifiable concentrate. It contains 250 grams of difenoconazole per liter.
Supplied in 1 liter canisters (12 canisters per package, containing one liter of emulsion concentrate).
Mechanism of operation and what it is used for
This product is used against a wide range of diseases, including powdery mildew, scab, Alternaria, and other diseases of fruit crops, grapes, potatoes, tomatoes, and carrots. SKOR can be combined and alternated with pest control products, and can also be used in compatible mixtures.
"SKOR" is fast-acting, penetrating plant cells through the vascular system within 2 hours of treatment. The active ingredient inhibits the growth of fungal mycelium, with only a minor effect on the number of spores produced. When applied to seed, the product penetrates the seed coat, persists throughout storage, and then spreads throughout the tissues of the sprouts that emerge after they are placed in the soil.

The drug "SKOR" is effective against the causative agents of the following fungal infections:
- Scab.
- Powdery mildew.
- Gray rot.
- Spotting.
- Leaf curl.
- Clusterosporiasis.
- Coccomycosis.
- Alternaria.
- Late blight.
- Septoria.
- Brown rust.
- Cercospora leaf spot of beet.
- Root rot.
- Seed mold.
On grapes, the product is aimed against the following diseases:
- Oidium.
- Phomopsis.
- Rubella.
- Black rot.
"SKOR" can be used in personal gardens and for treating indoor flowers and seedlings. Alternating the fungicide with insecticides and fertilizer will help maintain the health of your plants, making them stronger and more robust, and producing a full harvest.

Advantages and disadvantages
The pesticide "SKOR" has the following advantages:
- Rapid penetration into plant cells. The therapeutic effect lasts up to 96 hours, and the prophylactic effect lasts up to 8-10 days.
- The EC solution stimulates the natural immunity of plants. Plants develop shoots, increase leaf area, and the number of shoots is approximately one and a half times greater than in untreated plants.
- The yield of fruit and berry crops, and grapes, increases, as the green mass remains on the bushes longer after treatment with SKOR.
- On average, it accelerates seed germination by two days.
- When processing seed material, it increases the shelf life of seeds.
The product has no obvious drawbacks. The only caveat is that, although it's not weather-sensitive, SKOR performs significantly worse at temperatures below 12 degrees Celsius. The optimal temperature range for this fungicide is 14 to 25 degrees Celsius.

Rules for use and preparation of working solution, dosage
It is recommended to dilute the product in a separate container with clean, warm water at approximately 25 degrees Celsius. First, fill the container a quarter full, then add the fungicide, previously mixed in the canister.
Pour the required amount of the solution into a container and stir. Add water until the desired consistency is achieved. The prepared working solution should be used within 1-2 hours of preparation.
Berry bushes
To prevent fungal diseases, spray dormant buds and green shoots with the product. Treating the tree trunks is also recommended. Currants, raspberries, gooseberries, blackberries, and other berry plants are severely affected by powdery mildew and various spotting diseases.
The treatment can be repeated before and after flowering. Spraying fungicide on flowering berry bushes is prohibited. The maximum number of treatments is three, with an interval of no more than two weeks between treatments.

Seed treatment
Before sowing, soak the seeds in a pesticide solution for 6-36 hours. The solution is prepared immediately before treatment using 1.6 milliliters of the solution per 1 liter of water.
After treatment, the seeds are washed, lightly dried until free-flowing, and immediately sown into the soil or seedlings. Since the treatment remains in the seed tissue, it prevents disease in young plants even during the seedling stage.
Flowers
To protect the garden from powdery mildew, two treatments are used, with the application rate being 2 milliliters per 10 liters of water. To protect against gray mold, a solution twice as concentrated is used.
To prevent and treat spots, take 5 milliliters of concentrate per equal amount of liquid.

Grape
To combat powdery mildew and other grape diseases, use a 5 milliliter solution of emulsion diluted in a 10-liter bucket of water. Apply four sprays: during bud formation or during the first flowering stage, before the berries form clusters, then twice more, 10 days apart. It is recommended to alternate with other fungicides, such as Topaz.
Vegetables
"SKOR" is used on vegetable crops such as tomatoes and potatoes, beets and carrots, against late blight and early blight. Three treatments are used on tomatoes, and two on potatoes and other vegetables. The waiting period after spraying is 14 days. The application rate in both cases is 0.5 kilograms per hectare.
For 10 square meters of plantings you will need to prepare 10 liters of working solution.

Fruit trees
"SKOR" is used in gardening in the spring, twice before and twice after flowering. It helps combat scab and powdery mildew on apple and pear trees, as well as leaf curl on peaches. The application rate is 0.5-2 kilograms per hectare.
Roses
The queen of flowers is especially susceptible to fungal diseases in cool and damp weather. During such periods, treatment is essential to protect these garden beauties.
Apply 2-4 sprays per season at the first signs of infestation, at two-week intervals. Apply to the foliage, avoiding open flowers. This may leave spots on light-colored petals, which can detract from the beauty of the plant.

Precautionary measures
"SKOR" is classified as hazard class 3, with a soil stability rating of 2. It is low-toxic to humans, birds, and beneficial earthworms. Use in fish protection zones is prohibited.
When using a pesticide, the following personal protective equipment must be used:
- Closed clothing and footwear.
- Mask or respirator.
- Special glasses.
- Rubber gloves.
- It is recommended to cover your head with a hat or bandage.
If the solution comes into contact with skin or mucous membranes, rinse with plenty of running water. If swallowed, induce vomiting by drinking clean water and seek medical attention.

Is compatibility possible?
The product is compatible with most existing pesticides and can be used in tank mixes provided there are no adverse reactions. If compatibility is in doubt, it is recommended to conduct a test mix in small quantities.
How and how long can it be stored?
The emulsion concentrate has a shelf life of 36 months. It is not recommended to use the product after this period or if it has been stored in improper conditions.

The prepared solution cannot be stored; it must be used within 2 hours. This applies to both the "pure" EC fungicide solution and tank mixes prepared with it.
What to replace it with
The following fungicides operate on similar principles as SKOR:
- "Discor".
- "Battleship".
- Boxwood.
- "Strobie".
- Split.
- "Guardian".
- "Revus Top" and many others.

When using substitutes, it is necessary to carefully study the instructions for a specific fungicide, because dilution proportions, frequency of treatment, and waiting periods may differ from those in SKOR.
The pesticide is widely used in agriculture, home gardening, and indoor floriculture. Its advantages include affordability, non-phytotoxicity, and low hazard rating for humans, bees, fish, and other animals.