- Preparation and sowing procedure for zucchini seeds
- Soil preparation
- Crop rotation and compatibility with other crops
- Preparing zucchini seeds
- The procedure for sowing zucchini in open ground
- Agricultural technology for growing zucchini in open ground
- Caring for zucchini before flowering
- How to feed zucchini during flowering
- How to care for zucchini during fruiting
- Watering
- Caring for zucchini in open ground
- Diseases and pests, methods of protection and prevention
- Harvesting and storing zucchini
Growing and caring for zucchini outdoors requires following a number of rules. Despite the plant's low maintenance, only pre-treatment of the seeds and proper agricultural practices can ensure a good zucchini yield. Ripe zucchini are suitable for use in many culinary recipes due to their vitamin and mineral content.
Preparation and sowing procedure for zucchini seeds
To ensure proper crop growth, a number of preparatory measures are required, including the selection and processing of seed. Growing zucchini from pre-planted seeds allows you to grow large fruits with tender, juicy flesh. When planting directly, adherence to proper agricultural practices is essential.
Soil preparation
When choosing a suitable location for a garden bed, consider the crop's heat tolerance. It's best to grow zucchini outdoors in open areas with good natural light, away from dense trees and buildings that could block UV rays throughout the day. The local landscape should also be considered, as cold lowlands and areas with strong winds are unsuitable for vegetables.
The range of pre-planting work depends on the content of microelements in the soil.
To increase the zucchini harvest, you need to analyze the soil composition and adjust it by applying fertilizers.

The following types of soil are found:
- Peatlands. Before planting zucchini, apply compost or humus. After fertilizing, dig the soil to a depth of 20 centimeters and level the surface with a rake. After watering, cover the bed with plastic.
- Loam soils. To improve the soil composition, simply add a mixture of peat and sawdust as fertilizer.
- Sandy loam. To ensure a bountiful vegetable harvest, it's recommended to add peat, loam, humus, and ash to the soil.
- Fertile black soil. The beds should be loosened and treated with a mixture of superphosphate and sawdust.
- Undeveloped areas. The soil in such areas requires thorough loosening, removal of vegetation debris, and disinfection. Compost, nitrophoska, and ash are suitable as fertilizers.
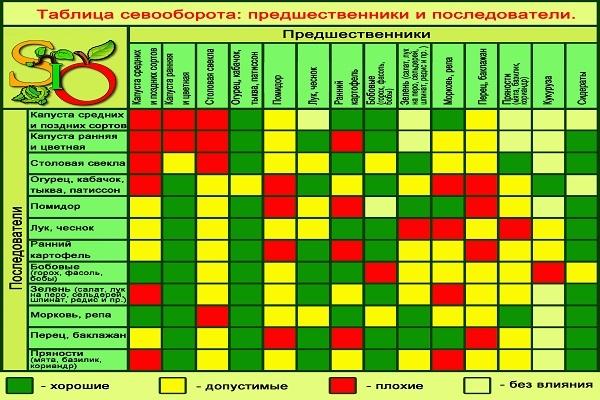
Crop rotation and compatibility with other crops
Selecting suitable preceding crops will promote accelerated growth and larger fruit production. Bush squash is best planted after cabbage, legumes, tomatoes, onions, and potatoes. It is not recommended to grow squash after pumpkins or any cucumber varieties.
The rules for growing zucchini also require crop rotation. It's prohibited to grow zucchini in the same soil for two consecutive seasons. Pumpkin crops should not be planted in the same bed with zucchini.
Zucchini can be grown in various parts of the garden, using small, unused plots. It's important that these plots be located in a sunny and warm spot.
Preparing zucchini seeds
Before sowing zucchini, the most important step is choosing the right seeds. These can be obtained from a previous planting or purchased from gardening stores. When using home-grown seeds, check their germination rate. To do this, dip the seeds in a weak solution of potassium permanganate, and soak any that sink to the bottom in a growth stimulant for 20 minutes. Then, rinse the selected seeds in water and wrap them in a damp cloth.
After the seeds have swollen and roots have formed, they should be kept in a cool place for two days. Then, the seeds, left in the cloth, should dry naturally. The seeds are ready for planting once root shoots have developed. Sowing typically begins in mid-July.
The procedure for sowing zucchini in open ground
Zucchini is considered an unpretentious vegetable that ripens quickly and produces its first shoots 7-10 days after planting. The crop can be planted using seedlings or directly into the ground. When growing in soil, follow these simple instructions:
- Dig holes in the ground 3-7 centimeters deep, spaced about 70 centimeters apart. There should be no more than three holes per square meter of soil for each zucchini.
- Place seed material (2-4 seeds) in each hole and cover with soil.
- When planting zucchini in the spring, cover the beds to protect them from potential frost. Once the temperature reaches the right temperature for zucchini, the covering can be removed.
- If several seeds sprout in one hole, it is necessary to leave the most developed zucchini shoot.
Early- and late-ripening vegetable varieties should be planted outdoors at different times. Early zucchini varieties can be sown from early May, while late varieties can be sown during the first 10 days of summer. Growing techniques for any zucchini variety allow for repeated plantings throughout the season, spaced 5-6 days apart.

Agricultural technology for growing zucchini in open ground
A prerequisite for growing a large harvest is adherence to proper agricultural practices throughout all stages of the crop's development. Proper agricultural practices directly impact the number of fruits ripening by harvest time. Plant care requires no special approach and consists of regular watering, weeding, and fertilization. Care is necessary before and during flowering, as well as when the first ripe zucchini appear.
Caring for zucchini before flowering
To ensure that zucchini plants produce numerous ovaries, fertilize the seedlings before they begin flowering. After the seedlings emerge, apply a mineral fertilizer to the beds by mixing one tablespoon of nitrogen supplement with 10 liters of settled water. Apply one liter of the solution per plant.
Caring for zucchini plants with organic fertilizers also has a positive effect on the subsequent development of the root system and above-ground parts of the plants. Nettle infusion or a solution of fresh manure and water are suitable organic fertilizers. Water the zucchini plants with organic fertilizers at the roots, preventing any contact with the leaves. For maximum effectiveness, alternate between mineral- and organic-based fertilizers.
How to feed zucchini during flowering
During the intense flowering period, it's important to attract harmless insects that will pollinate the bushes. This requires foliar feeding with a sweetened solution. You can prepare the fertilizer by mixing one tablespoon of honey or refined sugar in a glass of warm water and adding two tablespoons of superphosphate. This attracts bees and other pollinating insects.
The solution is used to spray the above-ground portion of zucchini plants. This procedure promotes the formation of numerous ovaries. Before treating the seedlings during flowering, it is recommended to remove a couple of large leaves from the center of the plant to ensure additional ventilation and clear the way for insects to reach the inflorescences.

How to care for zucchini during fruiting
When the crop begins to bear fruit, additional agricultural techniques for growing zucchini are required. Specifically, it is necessary:
- visually inspect the beds daily to promptly remove weeds;
- remove diseased plants to prevent the infection from spreading to the fruit;
- manually remove large insects from the fruit.
The procedure for caring for zucchini to increase fruiting during fruiting also involves the use of special fertilizers. Fertilizing zucchini Organic fertilizers help increase yields. During the fruiting period, the crop requires a growth stimulant, which should be applied 10-12 days after the previous fertilization at a ratio of 2 liters of solution per 10 square meters of soil. A urea solution is also suitable for fertilization, prepared at a ratio of 1 tablespoon per 10 liters of water, with the calculation of using 1 liter per plant.
Watering
Maintaining soil moisture is one of the conditions for proper crop growth and growing a large harvest. Zucchini needs systematic watering. Warm solution. Water at the roots, as liquid coming into contact with the leaves can cause sunburn. It's recommended to water the beds once a week until flower buds appear, and double the frequency once buds have formed. Each plant should receive 5-10 liters of water, depending on the soil conditions. When watering plants, keep the following points in mind:
- Water for the beds should be collected in advance so it has time to settle. Using unsettled water can cause the seedlings to rot.
- Although zucchini like to absorb large amounts of water when growing, overwatering can damage the root system.
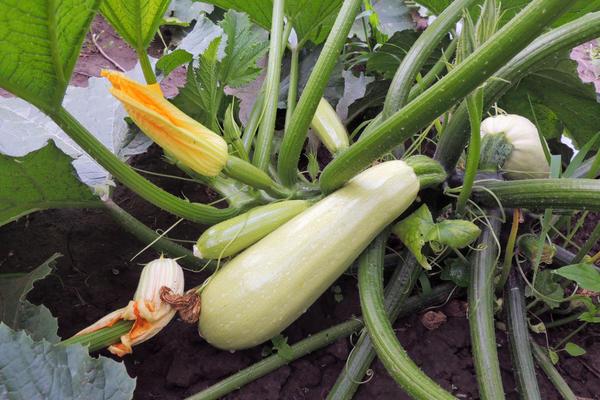

- By regularly checking the condition of the soil, you can determine the seedlings' need for watering.
- If the leaves on the bushes close up due to improper watering, a soil mixture of compost and peat should be added to the soil, pouring a layer up to 5 centimeters high.
- If the leaves turn yellow and start to fall off, it is necessary to increase the amount of watering.
- Cold water should not be used for watering, as the root system begins to rot when exposed to liquid at low temperatures.
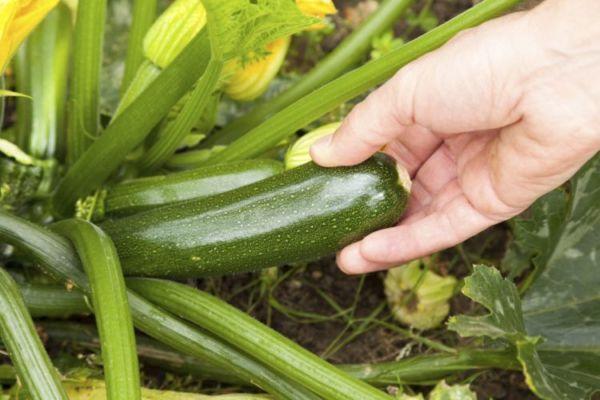
Caring for zucchini in open ground
Any vegetable crop requires healthy soil. Caring for vegetables planted outdoors involves not only watering and regular inspection, but also loosening the soil. This must be done with extreme care, as the root system of vegetables is located in the upper soil layer, and careless handling can damage it.
The quality of the harvest also depends greatly on the presence of weeds in the beds. If weeds grow near the bushes, the crop will not be able to fully develop and produce fruit. When tending to the crops, it's important not only to remove unwanted vegetation from the beds but also to till the space between the rows with a hoe.

Diseases and pests, methods of protection and prevention
Negative external influences, unsuitable climate, or improper care of zucchini can lead to the development of diseases and insect infestations. Common plant diseases include:
- Powdery mildew. This fungal disease spreads from other plants to zucchini through the air or rainwater. When affected by the fungus, the leaves of affected plants turn yellow, wilt, and dry out. The formation of powdery mildew on the leaves inhibits photosynthesis.
- Root rot. This disease causes the plant's roots to darken and gradually rot. As the fungus progresses, the zucchini's development is completely stunted. Root rot is caused by overwatering and poor sterilization of the planting material.
- Anthracnose. If dark yellow spots appear on zucchini leaves during the growing season, gradually spreading to the entire above-ground portion, there is a risk of infection with this disease. If left untreated, the fruit will wrinkle, develop a bitter taste, and lose its firmness.
Common pests that can damage zucchini seedlings include melon aphids, spider mites, flies, and other insects. Larger pests can be detected by inspecting the beds, while smaller ones are indicated by chewed holes in the leaves and the appearance of larvae.
To protect against diseases and pests, it is recommended to treat zucchini beds with insecticidal and fungicidal fertilizers. Large pests should be removed manually before treatment. When using a variety of pesticides, it is important to follow the manufacturer's recommendations and the decomposition period of the active ingredients. If insects remain in the beds after spraying, apply the fertilizer twice.
For preventative purposes, it is necessary to adhere to crop rotation rules and correctly select preceding crops, observe basic care rules, and regularly inspect plantings for pests and signs of disease.

Harvesting and storing zucchini
There's no set time for harvesting zucchini, as the fruits can be picked as they ripen throughout the season. The first vegetables ripen within 1.5 to 2 months after planting. Young zucchini, up to 20 centimeters in size, can be used in cooking, but only fully ripened zucchini are suitable for long-term storage. A distinctive feature of ripe zucchini is its dense, hard rind.
It's best to harvest zucchini with a sharp knife. Picking the fruit by hand can accidentally damage the stem, which will prevent growth. Young zucchini should be cut off at the base, while ripe ones should be cut off with the stem attached.
Store your zucchini harvest in a cool place. If you store young zucchini in the refrigerator, keep in mind that they will only last for about two weeks without losing their nutritional value. You can also leave early zucchini on the balcony, wrapped in plastic wrap first. Fully ripened zucchini can be stored for up to six months.
The storage area for the fruits should be well-ventilated and have low humidity. The harvest should be packaged in wooden boxes, lined with pine sawdust at the bottom. Vegetables should not come into contact with each other during the entire storage period. To prevent disease and bacterial growth, it is recommended to dip the stems of the vegetables in hot paraffin.
It's not advisable to exceed the recommended storage period for zucchini, as the vegetables lose their flavor over time. Furthermore, with the onset of spring, the seeds begin to sprout. By following basic storage guidelines, you can have fresh vegetables for a long time for various uses.











