- Description and characteristics of the plant
- Main varieties
- Petiolate
- Dwarf
- Petunnikova
- Ledebour
- Georgian
- Three-lobed
- Michurin
- Californian
- Popular varieties
- Dessert
- Foros
- Slovenia
- Victoria
- White Sail
- Nikitsky 62
- Dream
- Coastal
- Anyuta
- Dream
- Amaretto
- Volgograd
- Pink flamingo
- Antique
- Praline
- How to choose the right variety
- Regional features
- How to plant
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Requirements for the location
- Soil and site preparation
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Sanitary
- Formative
- Protection from diseases and pests
- Tips from experienced gardeners
Almond species and varieties vary widely. Each has its own unique characteristics. When choosing a specific variety, consider the region's climate, soil composition, and groundwater levels. To grow this crop yourself, it's crucial to properly plant it and provide it with comprehensive, all-inclusive care.
Description and characteristics of the plant
Almond is a perennial, heat-loving crop. It can grow as a bush or a small tree. The plant reaches 4-6 meters in height and is well-branched. The tree has lanceolate leaves with a pointed tip. There are also varieties with entire leaves and fine teeth.
The flowers are single and have five petals. They can be white or a soft pink. Flowering begins before the leaves emerge.
The fruit is a single oval drupe. The nut is also elongated and covered with small pits. It measures 2.5-3.5 centimeters in length and includes the shell and kernel.
The plant has taproots. Its main advantage is its ability to withstand drought and dehydration for long periods. It easily recovers under favorable conditions.
Main varieties
There are quite a few species of almonds. Some of them grow wild and are critically endangered, which is why they are listed in the Red Book.
Petiolate
This endangered perennial is native to Buryatia and Siberia. It grows as a bush reaching 1.8 meters in height. The plant is drought-resistant and characterized by narrow leaves and medium-sized nuts.

Dwarf
This plant, also known as laburnum, is a perennial shrub that reaches 1.5 meters in height. It has a dense, spherical crown and straight branches that produce numerous shoots.
Petunnikova
This deciduous perennial grows to a maximum height of 1 meter. It is characterized by a dense, rounded crown. The plant is considered heat-loving and easily tolerates dry weather. It will not thrive in temperate climates.
Ledebour
The plant is native to the Altai Mountains. It thrives in fertile soil. It is considered frost-hardy and reaches a height of 1.5 meters. It has a branched, rounded crown.
Georgian
This variety of almond grows on mountain slopes or in the forests of the Caucasus. The plant is a small shrub, reaching a maximum height of 1.2 meters. It thrives in neutral soil and easily tolerates higher temperatures. It is frost-resistant, making it suitable for cultivation in central Russia.

Three-lobed
This is an ornamental plant that is not intended for harvesting. Flowering begins before the leaves appear. The flowers come in a variety of shades, from soft pink to lilac. This variety of almond is characterized by resistance to disease, frost, and drought.
Michurin
This winter-hardy variety was developed by Michurin. It is a low shrub that produces edible drupes. However, its primary purpose is considered to be garden decoration. It blooms for several weeks and beautifies flower beds and hedges.
Californian
This is the most common nut crop in America. Today, there are many varieties that differ in ripening time. They are characterized by tasty, oily nuts that are large to medium in size.

Popular varieties
Almonds have many popular varieties, each with its own characteristics.
Dessert
This variety is characterized by a mid-season ripening period. This tall tree has a spreading crown. The fruit is best harvested in September. The nuts have a dessert-like flavor and a pleasant aroma.
Foros
This hybrid variety is known for its dessert qualities. It is considered a high-yielding cultivar, producing large fruits with a mid-season ripening period. The shells are easily peeled. The almond tree grows as a tree with a dense crown.
Slovenia
This is a new hybrid developed by Ukrainian scientists. The plant can be grown in temperate climates and is drought-resistant. The tree reaches 5.5 meters in height and has a dense crown. It is characterized by abundant flowering and large fruits.

Victoria
This high-yielding variety boasts excellent frost resistance. It's considered a heat-loving plant and easily tolerates dry weather. It produces large, tasty fruits, each weighing up to 6 grams.
White Sail
The plant is cultivated in southern regions. It tolerates dry weather well, but is not very frost-tolerant. This medium-sized bush grows up to 2 meters. It is characterized by a spreading crown with narrow leaves.
Nikitsky 62
This popular plant is grown in temperate climates. It is highly frost-resistant and characterized by a long winter dormancy period.
Dream
This ornamental plant grows to a maximum height of 1 meter. It is characterized by abundant flowering. It is frost-resistant and has a perfectly rounded crown.

Coastal
This tree reaches 2-3 meters in height and is characterized by high yields. Each plant can yield up to 13 kilograms of fruit. It can be grown in various regions and easily tolerates drought and low temperatures.
Anyuta
This low-growing plant is often used for ornamental purposes. It's ideal for creating a hedge, with shoots reaching 1.5 meters. It easily tolerates drought and frost.
Dream
The plant is characterized by spreading shoots up to 1 meter in length. The crown is rounded. The plant produces beautiful pink flowers and long, narrow leaves. The fruit ripens in July.
Amaretto
This variety can be grown in temperate climates. It can withstand temperatures down to -30°C. A mature plant reaches 3 meters in height and has a spreading crown.
With proper care, the tree produces 15 kilograms of fruit, each weighing 4 grams.

Volgograd
This variety is considered ornamental. It grows well in steppe regions and is undemanding. Pink buds appear on the bush in late April. Fruiting begins in late summer.
Pink flamingo
This low-growing plant produces rich pink flowers. They densely cover the shoots, making the bushes often used for ornamental purposes.
Antique
This tree grows up to 3 meters tall and has a wide crown. The fruits are harvested in September or October. The drupes weigh up to 4 grams. The kernel separates easily from the shell.
Praline
This almond variety blooms quite late. The tree is medium-sized and has a broad, oval crown. The fruits are large, weighing 3-6 grams. They are characterized by a sweet taste and a pleasant aroma.
How to choose the right variety
When choosing a variety, consider the region's climate. In the south, almonds are planted outdoors. Therefore, it's best to choose larger varieties.

In the north, almonds are grown in tubs. Therefore, dwarf varieties are recommended. Steppe almonds are suitable for container growing. They are low-growing bushes with beautiful inflorescences. However, eating their fruits is prohibited, as they are poisonous.
Various varieties can be grown in the ground, including Yaltinsky and Foros. Most varieties are adapted to specific climate conditions.
Regional features
Initially, almonds were considered a heat-loving plant, grown only in the south. However, through the efforts of breeders, many frost-resistant varieties have been developed that can be grown in other regions. However, choosing the right variety is important.
How to plant
When planting, it's important to follow basic agricultural guidelines. This will help you achieve good results.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
Almonds can be planted in the fall, after the leaves have fallen, or in the spring, once warm weather sets in. It's important to avoid the risk of recurrent frosts. However, fall planting is considered preferable.

Requirements for the location
The plant thrives in a sunny location that is well protected from drafts and wind. It prefers well-drained soil. Black soil, loamy soil, or sandy soil rich in lime are ideal. Acidic or salty soils are not recommended.
Soil and site preparation
It's recommended to dig a hole at least 30 centimeters deep in the area. Fill the bottom with broken brick or crushed stone, top with sand, and install a long pole in the center. It's important that the pole extends at least 50 centimeters above the ground.
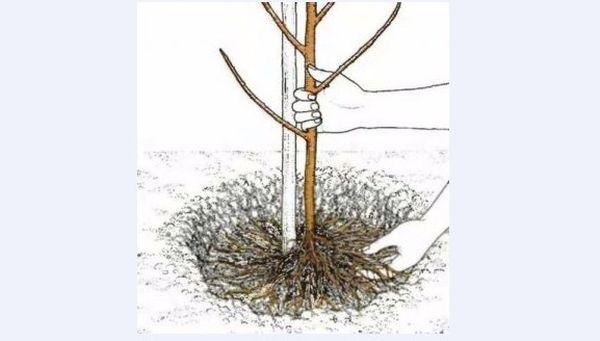
Planting diagram
It's recommended to plant the plant early in the morning or in the evening. First, soak one-year-old seedlings in a clay slurry. Then, lower them into the hole. The root collar should be a few centimeters above the soil surface.
After this, the hole should be filled with a mixture of topsoil, leaf mold, sand, and humus. If the soil is acidic, a little lime can be added.
After planting, compact the soil around the plant, then pour 1-1.5 buckets of water under it. Once the moisture has been absorbed, tie the seedling to the support and cover the area around the trunk with peat.
Care instructions
To ensure proper care for the plant, it is important to water, feed, and prune it properly.
Watering
To ensure good fruiting, the almond tree requires regular soil moisture. Young trees should be watered at two-week intervals. Mature plants should be watered every 20-25 days.
Top dressing
Almond trees require timely fertilization. Starting in their second year, in late April or early May, apply a urea or ammonium nitrate solution to the tree's trunk. 20 grams of urea or ammonium nitrate are needed per tree.
In the fall, it is worth adding a composition based on 40 grams of superphosphate, 1 kilogram of manure, and 20 grams of potassium sulfide to the soil.
Trimming
In early spring, it's a good idea to remove broken, frozen, twisted, or diseased branches. This should be done before the buds open.
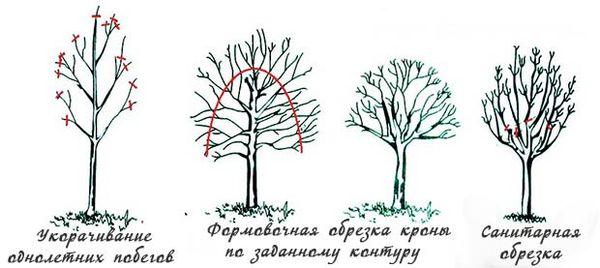
Sanitary
After the leaves fall, sanitary and rejuvenating pruning is performed. This is aimed at removing dry and broken branches. It's also worth cutting off shoots that are growing in the wrong direction or that are crowding the crown.
Formative
After flowering has finished, you can begin formative pruning. This should result in three levels of skeletal branches:
- At the first year, select three shoots spaced 15-20 centimeters apart. Prune them back to 15 centimeters.
- Over the next 2-3 years, three tiers should be formed on the main conductor. They should be spaced 20-30 centimeters apart.
- Several times during the summer it is worth pinching small shoots.
- Shorten the remaining branches to a length of 50-60 centimeters.
- Shorten the central conductor. This will leave a distance of 55-60 centimeters between it and the upper tier.
Protection from diseases and pests
The plant can be susceptible to dangerous diseases, such as cercospora leaf spot, scab, and rust. Almonds are also susceptible to gray mold and holey spot. Fungicides such as Champion and Horus can help eliminate these diseases. Affected plant parts should be cut off and burned.

Almonds are susceptible to pests such as leaf rollers, spider mites, and aphids. Insecticides can help combat this problem. These include Fufanon, Tagor, and Actellic.
Tips from experienced gardeners
To achieve results when growing almonds, it is worth following these rules:
- choose a variety taking into account the regional climate;
- water the plant on time;
- apply fertilizers;
- carry out sanitary and formative pruning;
- carry out treatment against diseases and pests.
Almonds are a popular plant with many species and varieties. To choose the best option for your garden, consider your region's climate.









