- Advantages and disadvantages of greenhouse cultivation
- Basic requirements for growing the crop
- Soil acidity
- Illumination
- Temperature conditions
- Humidity level
- Ventilation
- Preparing for planting seedlings
- Disinfection of premises
- Preparing the beds
- Sowing seeds for seedlings
- Soil mixture for seedlings
- When and how to sow seeds
- Seedling planting technology
- Neighborhood with other cultures
- Optimal timing for planting seedlings
- Bush planting scheme
- Rules for caring for peppers in greenhouse conditions
- Regularity of irrigation
- Fertilizing
- The nuances of bush formation
- Shaping and pinching out side shoots
- Tying up the plant
- Stimulation of pollination
- Loosening and mulching the soil
- We protect plantings from diseases and pests
- Ways to speed up the ripening of peppers in a greenhouse
- How does the harvest proceed?
- The best pepper varieties for planting in a greenhouse
- Latino F1
- Gypsy F1
- Actor
- Montero
- Red Bull F1
Bell peppers are grown not only in open ground but also in greenhouses. Greenhouse care, from planting to harvest, is crucial. It determines whether the plants will produce a harvest. Without proper care, peppers take a long time to bloom, grow poorly, and yield little. The procedures are not much different from those for open ground care.
Advantages and disadvantages of greenhouse cultivation
Growing bell peppers in a polycarbonate greenhouse has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- In a greenhouse, plants bear fruit more often, and the harvest is collected even in the cold season.
- In the greenhouse, the bushes are protected from sudden frosts, hail and heavy rains.
- When growing in greenhouse conditions, it is easy to disinfect the soil and replace the soil.
- In closed ground, you can pay less attention to caring for the bushes.
- You can regulate the level of humidity and lighting.
The disadvantages of growing bell peppers under cover include the fact that the soil, unlike open ground, is less fertile. Also, when planted in a greenhouse, the fruits may not be as tasty as those grown in open ground during the fall and winter.
Basic requirements for growing the crop
Bell peppers won't produce a good harvest in a greenhouse if the plants aren't properly cared for. Sweet peppers prefer fertile soil and regular watering.
Soil acidity
Planting bell pepper seedlings in highly acidic soil is not recommended. If the soil is too acidic, lime it before planting. Light soil with a pH of 6.0-7.0 is considered most favorable.

Illumination
It's recommended to grow seedlings in a sunny location. Lighting issues most often arise when growing crops during the colder months, when the sun is less intense. To solve this problem, install additional lights in the greenhouse and turn them on as needed. Seedlings should be exposed to light for at least 14 hours a day.
Temperature conditions
What temperatures can peppers withstand when grown in a greenhouse?
- On sunny days the temperature should be between +23 and +27 degrees.
- In cloudy weather it fluctuates between + 20 and + 21 degrees.
- At night, the air temperature in the greenhouse should not be below +18 degrees.
The optimal soil temperature for normal crop growth is between 18 and 20 degrees Celsius. Low daytime temperatures in the greenhouse lead to deformed fruits. They also grow very small.

Humidity level
Bell peppers don't like excessive moisture. However, they also don't respond well to dry soil. The optimal humidity level in a greenhouse should be 60-75%.
Ventilation
The greenhouse needs to be ventilated regularly to ensure fresh air. During warmer months, windows and doors can be left open at all times. However, during colder months, you'll need to open them regularly. It's important to avoid drafts in the greenhouse, so if it's windy outside, ventilating the greenhouse isn't recommended. It's best to wait until the wind dies down.
Preparing for planting seedlings
To ensure a good harvest, you need to pay more attention to preparing bell pepper planting material for planting in a greenhouse.
Disinfection of premises
Greenhouse disinfection procedures should be completed at least two weeks before planting. The inside of the greenhouse should be thoroughly cleaned. Do not use chemicals to clean the glass. If dirt does not come off with water, a small amount of soap can be used.

After the greenhouse has been washed, it is sprayed with a weak solution of Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate.
Preparing the beds
Once the soil and greenhouse have been disinfected, you can begin preparing the beds. To do this, dig the soil and remove all weeds. Then, add rotted manure and complex mineral fertilizer. Mix the soil and fertilizer thoroughly. Then, use a rake to create the beds in the most convenient way.
Sowing seeds for seedlings
When growing bell peppers in a greenhouse, it's not necessary to sow the seeds indoors. You can plant them directly in the soil in the greenhouse, and once the seedlings have grown, transplant them separately into a garden bed.
The process of sowing seeds in a greenhouse:
- Make furrows in the soil to a depth of 1-1.5 cm.
- Sow seeds individually, leaving enough space between seedlings for normal growth.
- Lightly cover with soil.
At the end of planting, water the beds generously with warm water and wait for the seedlings to emerge. You can also plant in containers indoors or place a box in a greenhouse.

Soil mixture for seedlings
It's best to buy ready-made soil mix for vegetable crops at a gardening store. Alternatively, you can use soil from your garden mixed with wood ash. If you're using soil from your garden, you should calcine it before sowing the seeds.
When and how to sow seeds
Any container is suitable for sowing seeds. The key is to use a spacious container. The choice of container doesn't depend on the material it's made of.
The best time to sow seeds is in late February or early March. This will ensure the seedlings receive sufficient light, eliminating the need for additional lighting. When growing in a greenhouse, there is no specific time for planting seedlings.
Seedling planting technology
If you follow agricultural practices when planting seedlings, they will take root faster in a new location and will be less susceptible to disease.
Neighborhood with other cultures
Like other agricultural crops, bell peppers don't tolerate certain plants. Conversely, there are a number of crops that are best planted next to bell peppers.

What crops are not recommended for planting bell peppers in a polycarbonate greenhouse?
- beans;
- kohlrabi;
- tomatoes;
- potato;
- eggplants;
- dill.
Favorable neighborhood:
- basil;
- nasturtium;
- tansy;
- carrot;
- cabbage;
- marigold;
- garlic;
- onion;
- coriander;
- catnip;
- spinach;
- zucchini;
- celery.
The proximity of crops that do not get along well with each other leads to them developing worse and may even get sick more often.
Optimal timing for planting seedlings
Pepper seedlings should be planted in a greenhouse after the soil warms up to 15 degrees Celsius. Seedlings can be planted in a greenhouse several weeks earlier than in open ground.

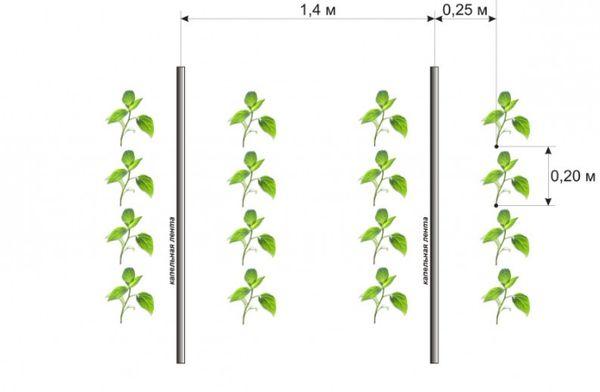
Bush planting scheme
When planting seedlings, the distance between them should be at least 40 cm. Bushes can be located opposite each other, or they can be planted in a checkerboard pattern.
Rules for caring for peppers in greenhouse conditions
How to properly care for bell peppers to ensure they produce the largest possible harvest.
Regularity of irrigation
Peppers love well-moistened soil, especially seedlings. You can water them every other day or every day. You can also water them as the soil dries out. Mature plants can be watered less frequently, every three days.
Fertilizing
In the first half of the season, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are added to the soil. During the flowering and ovary formation period, the soil is fertilized with phosphorus and potassium. After harvesting, the soil is mixed with manure or chicken droppings.
The nuances of bush formation
Bell pepper bushes are generally not pruned or shaped. You can only pinch the tops to make the plant bushier.
Shaping and pinching out side shoots
As the pepper grows, the lower leaves - stepsons - are torn off.
Tying up the plant
Most varieties of bell peppers don't require staking. Staking should be done if the fruit begins to break under the weight of the plant.
Stimulation of pollination
Bell pepper flowers are pollinated by bees, so beehives are placed in the greenhouse during flowering. However, self-pollinating varieties are best.
Loosening and mulching the soil
Weed control is also a challenge in the greenhouse. The soil should be loosened several times a week before watering. Weeds should be removed from the beds as needed.
We protect plantings from diseases and pests
To prevent diseases and pests, spray with Bordeaux mixture or copper sulfate. Treating with a soap solution helps against insects. This method is used once the fruit has already appeared.
After harvesting, the soil is always dug to a depth of 10-15 cm to remove insects that overwinter in the soil. It's also important not to overwater the beds or plant the seedlings too close together. Water with warm water. Moisturizing with cold water leads to the development of fungal diseases.
Ways to speed up the ripening of peppers in a greenhouse
A good harvest can be obtained by growing peppers in a greenhouse, and not only in open ground.
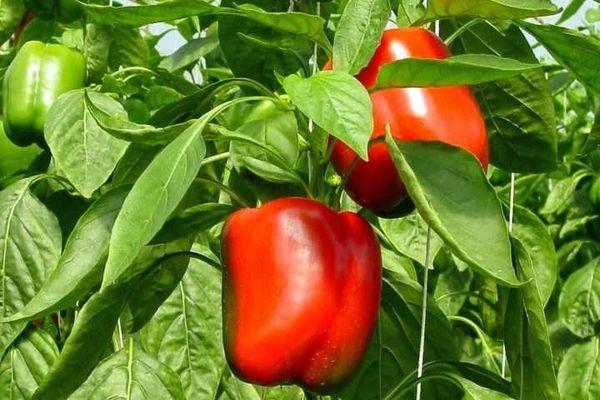

How to speed up fruit ripening:
- The soil needs to be loosened regularly so that the roots are saturated with oxygen.
- Make a longitudinal cut on the highest stem of the bush and insert a wooden stick into it. This will ensure that the nutrients are directed to the fruit, not the stems and leaves.
- Dilute 2 tablespoons of wood ash in water and spray the bushes with the resulting solution.
Another way to speed up the ripening of fruits is to pick unripe vegetables and place them in a dark place. They will ripen in a few days.
How does the harvest proceed?
Greenhouse peppers are harvested several times per season. The fruits can be picked at any time. Unlike many crops, bell peppers don't reach a specific point of maturity. The fruits are harvested as soon as they reach a large size. You can wait until the skin turns a reddish-orange color, or you can harvest the peppers when the skin is green.

The best pepper varieties for planting in a greenhouse
For greenhouse planting, it's best to choose self-pollinating pepper varieties. When planting these varieties, you won't have to worry about artificial pollination.
Latino F1
The Latino F1 variety is an early-ripening variety. The first fruits ripen within 100-110 days after sowing. A productive hybrid, a single bush yields up to 8 kg of fruit. The fruits are large and cube-shaped.
Gypsy F1
The peppers are conical in shape with thick, fleshy walls. They are small in size, weighing approximately 100-120 g. As they ripen, they acquire a rich red hue.

Actor
The peppers are elongated. The vegetables are large, with fleshy, juicy walls. The flesh is sweet. When ripe, the vegetables turn a deep red.
Montero
The bush is medium-sized and the variety is considered a productive one. The peppers turn red as they ripen. The peppers are cube-shaped, with a smooth, glossy skin. The average fruit weight is 170 g.
Red Bull F1
A mid-early hybrid with large fruits, fully ripening, weighing up to 250 g. The skin is red, the flesh is juicy and sweet. The pepper is very aromatic.












I grow peppers exclusively in a greenhouse; the yield is much higher and the fruits grow significantly larger. It's easier to create optimal conditions for seedling growth in a greenhouse, and I use only mineral fertilizers.