- What is tomato picking: how does it affect plants?
- Advantages and disadvantages of the method
- Methods of picking
- The classic way
- From film to diapers
- How to transplant tomatoes planted in tablets
- When to transplant tomatoes after germination
- Optimal timing in 2025
- Favorable dates according to the lunar calendar
- Preparing tomatoes for picking
- Preparing tomatoes for picking
- Preparing containers
- What kind of soil is needed for transplanting tomatoes?
- We determine where the 2 true leaves are on tomatoes
- The principle of root pinching
- Technological process of picking
- Caring for tomatoes after
- Picking out elongated tomato seedlings
- What problems may arise and how to deal with them
- The seedlings are not growing
- Plants are dying
- The seedlings are falling
- Is it possible to grow seedlings without picking?
Pricking out is considered one of the most important agricultural practices in tomato cultivation. It is performed to obtain plants with developed lateral roots. Pricking out promotes proper seedling development and improves the quality of the harvest. To achieve the best results, consider the timing of the procedure and adhere to the requirements for container and soil selection.
What is tomato picking: how does it affect plants?
Pricking out isn't necessary for all plants, but tomatoes are one vegetable crop that requires it. This term refers to the procedure of shortening the main taproot to stimulate the development of lateral roots.
A simplified explanation of this term: picking is the transplanting of seedlings into separate, larger containers.
This is carried out even if the seedlings were initially planted individually - then a container 2-3 centimeters larger is selected for further procedures.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
Experts in growing different varieties of tomatoes highlight the pros and cons of the procedure.
| Pros | Cons |
| Providing optimal conditions for growing seedlings | Stress for the sprout |
| Separating strong and weak plants from each other | Loss of a third of seedlings due to selection |
| Formation of a developed root system | |
| Preventing the development of an emerging disease | |
| Stopping the growth of overgrown seedlings | |
| Plant development |
Methods of picking
Gardeners distinguish several methods for transplanting tomatoes. Each has its own distinct technology and equipment requirements.

The classic way
This method involves transplanting seedlings individually using cups. Cups are small, specialized containers. Many gardeners purchase disposable plastic cups, such as those found in grocery stores, or cardboard dairy cartons with the tops cut off. After transplanting, the seedlings are placed in the shade and, after a while, brought into the light. Transplanting stimulates root development and also helps strengthen the stems.
From film to diapers
For this method, prepare a plastic sheet. Spread the potting mix on it, then place the seedling, sprinkle the potting mix on top, and wrap it in the plastic sheet. These bags are placed in five-liter plastic bottles, positioned vertically.

A layer of sawdust is spread along the bottom, providing an additional source of moisture for tomatoes after watering. This method is suitable for those who grow seedlings on apartment windowsills and then transport them to their garden plot. This method prevents damage to the seedlings during transportation.
How to transplant tomatoes planted in tablets
Pricking out seedlings planted in a peat tablet is ideal. These seedlings are transplanted when the third or fourth leaf appears. Make small holes in the bottom of the cup to allow water to drain, then fill it with soil. Take the peat tablet with the cutting, remove the bottom mesh, place the cutting in the cup, cover with soil, and place it in a shaded window for two days.
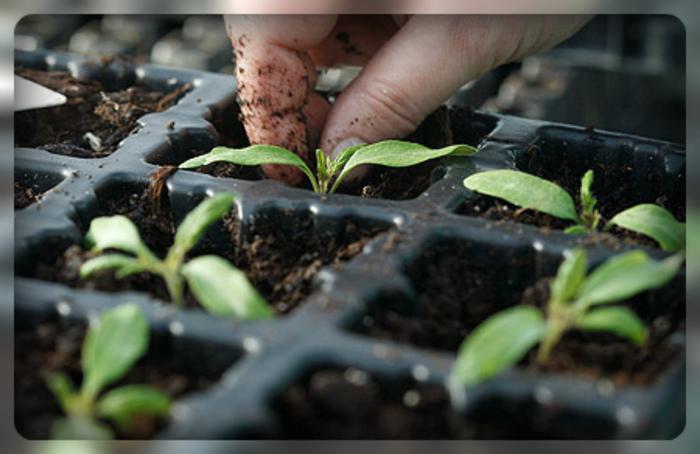

When to transplant tomatoes after germination
Beginning gardeners often wonder about the timing of the procedure.
This is carried out two weeks after the seedlings emerge, although the timing may vary depending on the region and circumstances. You can accurately determine the seedlings' readiness by their appearance:
- number of leaves on a shoot – 2 or more;
- the height of the shoot is 6-7 centimeters.
Optimal timing in 2025
A key factor in growing any tomato variety is timely sowing of seeds for seedlings and subsequent care. This depends on several factors:
- from the region, its climatic conditions;
- depending on the tomato variety;
- from the conditions of seedling development.

To achieve the best results, consider the seedlings' location near windowsills and their access to natural light. Typically, seeds are sown in late February or early March. Further transplanting is done 14-16 days later.
Favorable dates according to the lunar calendar
Gardeners use the lunar calendar to calculate seed planting dates and plan seedling care. Favorable days for transplanting in 2025: March 13 and 14.
Preparing tomatoes for picking
Before beginning the transplanting process, the tomatoes need to be prepared. Choose a clear day for transplanting.

Preparing tomatoes for picking
The seedlings are watered generously the day before transplanting. This ensures the soil is properly structured, neither too wet nor too dry, allowing the roots to be pulled out without damaging them.
Information! For indeterminate (tall) tomato varieties, it is recommended to transplant twice.
Preparing containers
The choice of container depends on the variety of tomatoes:
- Use a container with a capacity of at least 100 milliliters and a height of at least 15 centimeters; pierce the bottom to provide the seedlings with air access;
- The containers are filled with soil, a hole is made, water is added, and then the seedling is placed in.
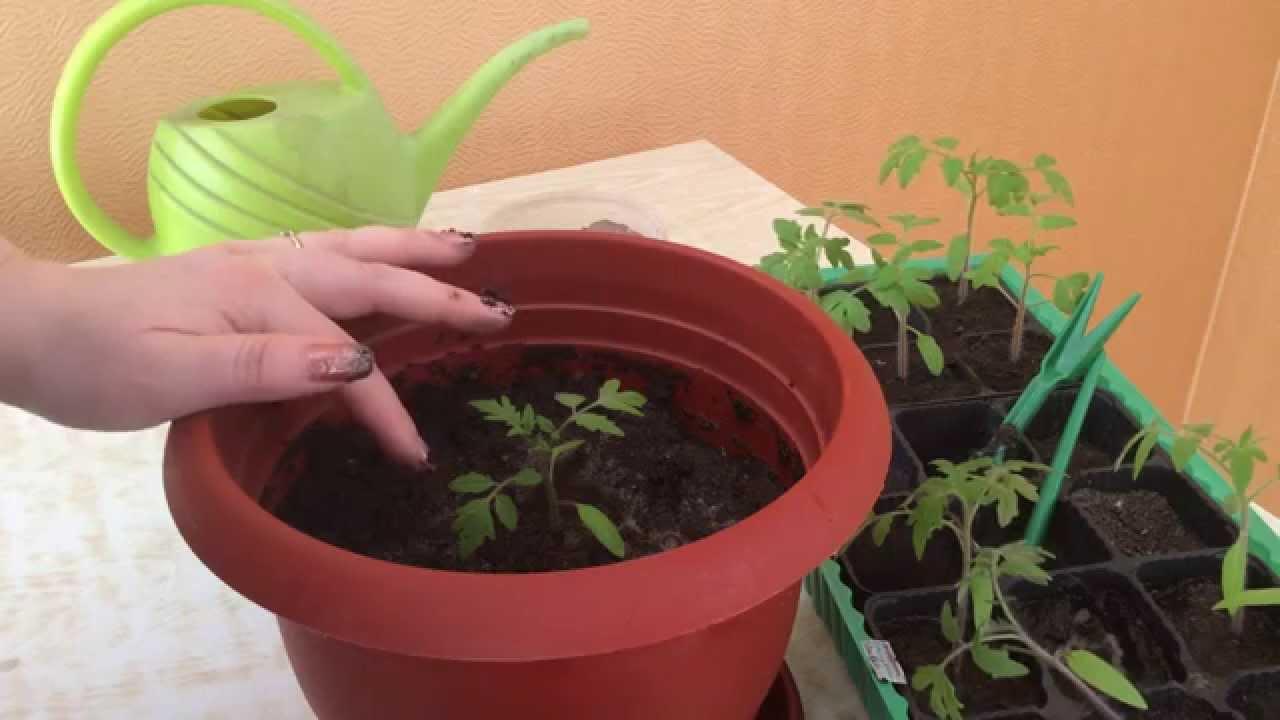

What kind of soil is needed for transplanting tomatoes?
To prepare seedlings, choose a store-bought mixture or prepare it yourself.
Components of the mixture:
- garden soil;
- washed river sand;
- humus;
- moss;
- wood ash;
- peat with acidity levels not exceeding 6.5.
Organic fertilizers are not added to the seedling mixture. They can damage the seeds due to the increased heat they produce, burning them before germination. Clay or similar additives are not used, as they make the mixture heavy. It is recommended to transplant the seedlings into disinfected soil.
 Important! The soil for seedlings should not be acidic.
Important! The soil for seedlings should not be acidic.
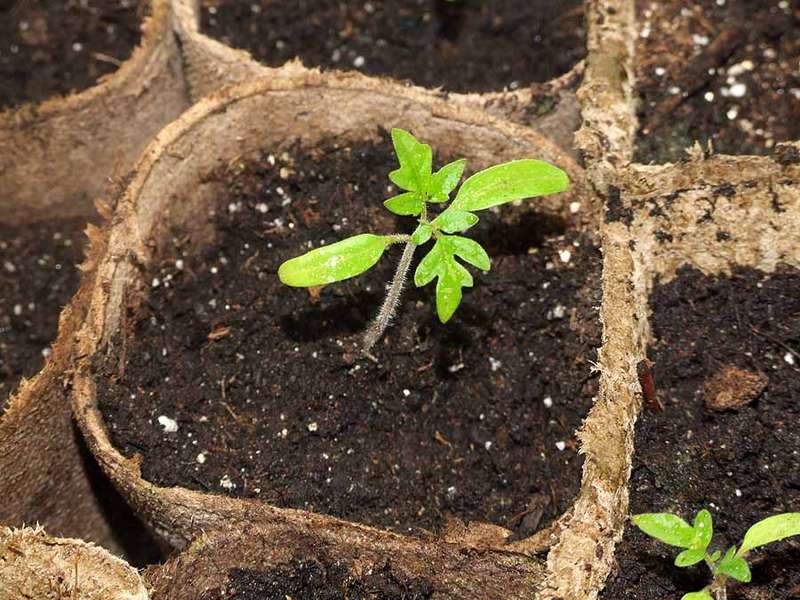
We determine where the 2 true leaves are on tomatoes
Many novice gardeners confuse the two true leaves and the two first leaves of a tomato plant. The cotyledons appear first, but they don't play a significant role in the subsequent development of the seedling. Therefore, when determining the right time to transplant, it's important to wait until the true leaves appear. In tomatoes, these leaves are slightly serrated and have a different shape from the cotyledons.
To avoid making a mistake in your choice, you should look at the photo to see what cotyledon and true tomato leaves look like.
The principle of root pinching
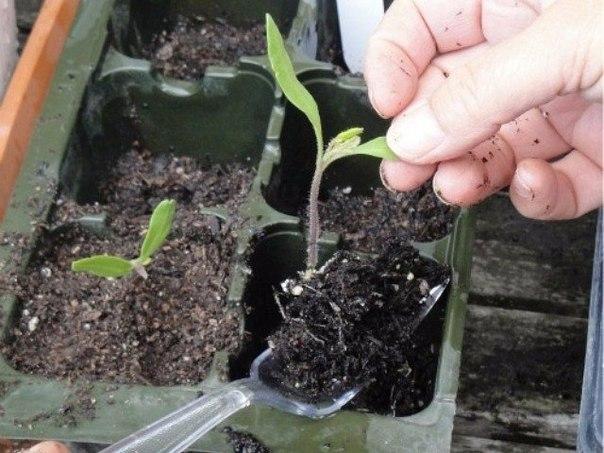
To pinch off the seedling, remove it from the container and inspect the root. To pinch off the root, locate the central root. Pinch it off by a third. This approach stimulates the formation of lateral roots, preventing the seedling from stretching upward and promoting full stem development.

Technological process of picking
After the first two leaves appear, the tomato is prepared for transplanting.
- The container with seedlings is watered generously with warm water the day before the procedure.
- Prepare containers and soil.
- Fill the cups one-third full and make a depression.
- Strong, viable shoots are removed from the soil using a small wooden tool.
- They examine the root system and pinch off the main root.
- The shoot is transferred along with the soil and placed in the hole.
- The seedling is planted deep, then the soil around the transplanted shoot is lightly compacted.
To avoid mistakes, follow step-by-step instructions. One option is a video master class on transplantation.

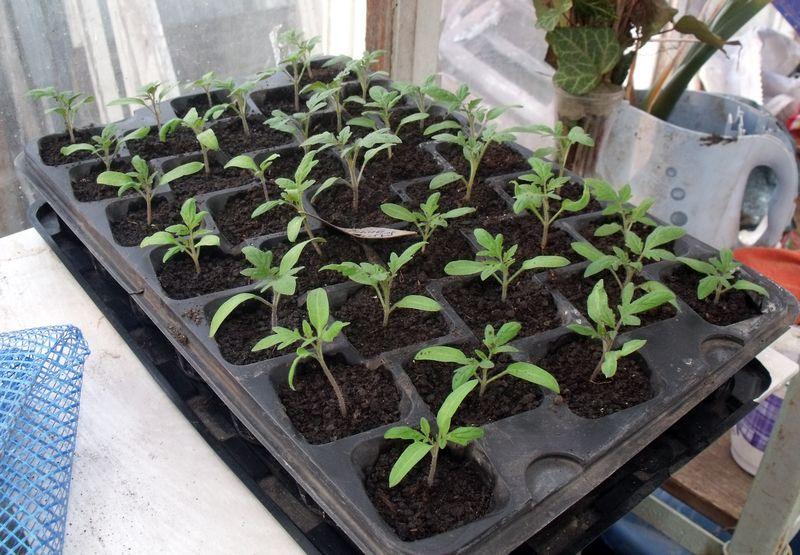
Caring for tomatoes after
Root pinching and replanting can be very stressful for a plant. Experienced gardeners know the rules for caring for a transplanted plant. To help it overcome this stress, it's important to monitor the temperature: the optimal temperature for transplanted plants is 18 degrees Celsius.
For 12-14 days, it is necessary to monitor the watering level: use a spray bottle or water using a tray, that is, place the pots with seedlings on a tray filled with water.
Picking out elongated tomato seedlings
Seedlings, due to less than optimal growth and development conditions, can become elongated. This is dangerous because the stem will become unable to support its own weight and will bend in various directions. To help these shoots grow, use one of two methods:
- The stem is cut and rooted in water with the addition of rooting stimulants, while providing adequate lighting and lowering the air temperature. After the cuttings have rooted, they are replanted separately.
- The seedlings are transplanted separately without pricking out. Watering is stopped one day beforehand, and the dehydrated plants are placed in a tall pot. The long stem is bent into a spiral and covered with loose soil. The result of this transplant: the plant is indistinguishable from a normal pricked out shoot. After this procedure, water generously and provide optimal lighting conditions.

What problems may arise and how to deal with them
It often happens that, despite following basic transplanting guidelines, seedlings still stop growing. They may appear sickly and stunted.
The seedlings are not growing
Growth cessation may be a sign of one of several care errors:
- Insufficient watering. Pinching the central root encourages the development of lateral roots, which stimulates the development of the shallow root system, which requires more frequent watering.
- Slow formation of adventitious root system.
- Mistakes made during transplantation (roots not placed deep enough in the hole, soil not compacted enough around the sprout).
- Lighting conditions (direct sunlight can cause burns, which affect the development of the entire plant and slow it down.)
- Diseases (diseases such as black leg cannot be identified immediately; they develop due to watering seedlings with cold water).
- Spread of pests (spider mites often appear on seedlings).
- Insufficiently drained container (lack of drainage system leads to rotting of the root system, damage to the entire central root).
- Lack of mineral substances in the soil.
- Increased indoor air temperature.

Plants are dying
The seedling's death is attributed to a disease the plant has contracted. After transplanting, the shoot is quite weak, so the risk of infection increases. Rot can be one of the causes. It is often caused by overwatering with cold water, low room temperatures, and mineral deficiencies in the soil.
The seedlings are falling
Another problem that occurs after transplanting tomatoes is seedling drop. This occurs due to unfavorable growing and development conditions. To avoid this, follow these guidelines:
- plants are not planted close to each other;
- For transplantation, strong shoots are selected, weak and non-viable ones are removed;
- the soil for transplanting is disinfected with a weak solution of manganese;
- for seedlings, seeds are treated with a solution of manganese or a saline solution;
- Proper watering is done early in the morning.

Seedlings may fail due to disease. A common fungal disease of tomatoes is fusarium wilt. It can occur if the seeds aren't treated before planting. In this case, the fungus attacks the plant's roots, then climbs up the stem to the very top, whereupon the seedlings collapse and appear unviable.
The measures to combat this phenomenon include replanting into fresh soil in compliance with all requirements.
Is it possible to grow seedlings without picking?
Experienced gardeners choose the most suitable methods for themselves. They adjust them based on individual conditions. Many believe that tomatoes don't need to be pricked out.
- reduces the time spent on growing seedlings;
- allows you to plant tomatoes earlier than those that have been transplanted;
- allows you to sow seeds for seedlings later.
For further growth without transplanting, seeds are planted in individual cups. These cups should be large enough to accommodate the seedling's continued growth.