- Botanical description and characteristics
- The most beautiful varieties of groundcover roses
- Akhtiyar
- Swany
- Knirps
- Hollywood
- Four seasons
- Growing conditions requirements
- Features of use in landscape design
- Planting and caring for the flower
- Site selection and preparation
- Preparing the seedling
- Dates and seating arrangements
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Mulching, loosening and weeding
- Pruning and shaping the bush
- Preventive treatments
- Preparing for the winter period
- Methods of breeding ground cover
- Layering
- Cuttings
- Gardeners' reviews of the crop
The first varieties of groundcover roses bloomed only once per season. Their petal colors were limited. Today, breeders have developed numerous varieties with varying flower shapes and colors. Inflorescences form almost continuously throughout the season. They are used in a wide variety of landscape settings. Below is information on planting and caring for groundcover roses, as well as how to use them in your garden.
Botanical description and characteristics
Groundcover roses are a group of roses ranging in height from 50 centimeters to 1.5 meters. Their distinctive feature is the spreading nature of their shoots. They can be bushy or climbing. During flowering, the bushes are covered with inflorescences of a variety of colors. The buds can be single or double. They open early. Many varieties bloom intermittently throughout the season. The bushes exude a delicate fragrance. Groundcover roses are hardy, winter-hardy, and have good immunity.
Important! When purchasing bushes of a particular variety, you need to know how far the crown spreads. This determines the spacing between planting holes.
The most beautiful varieties of groundcover roses
Breeders have created numerous varieties of this crop. The best of them are as follows.
Akhtiyar
Rose bushes are strong and arching, reaching a height of 120 centimeters. The inflorescences consist of 6-7 buds up to 10 centimeters in diameter. They bloom once per season. During this period, the bushes emit a strong floral fragrance.
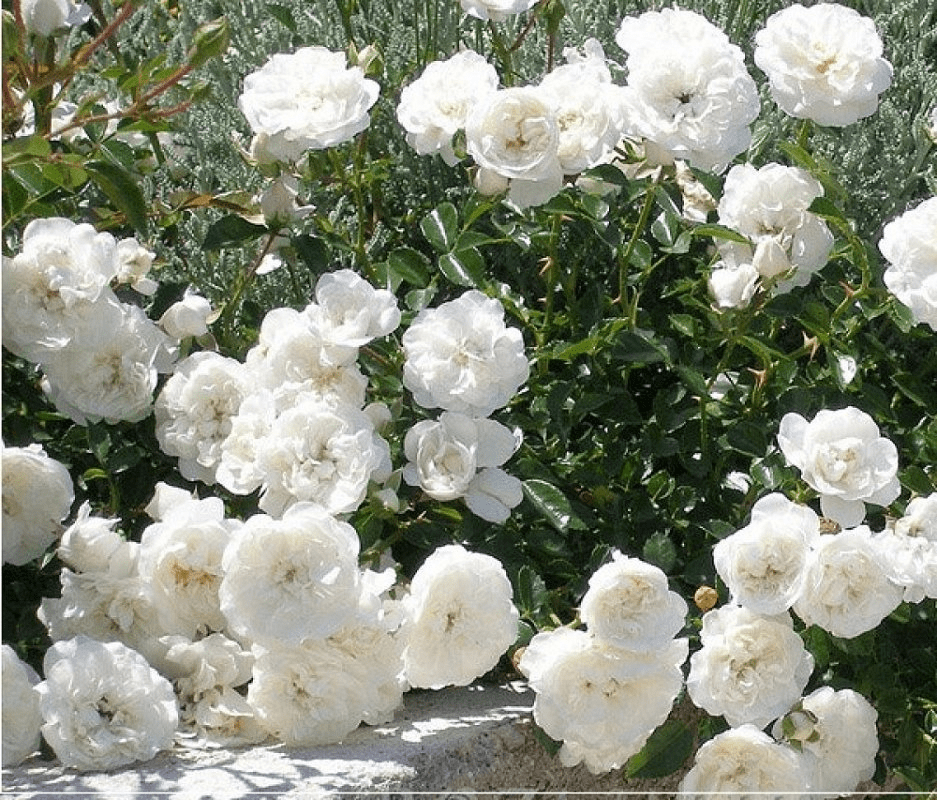
Swany
This variety was bred by the Meilland company. Spreading bushes reach a height of 80 centimeters. The leaves are dark green and glossy. Blooms profusely. 5-20 densely double buds form on the stem. Their primary color is white. The center is a soft pink. The Swanni rose is used in gardens to create a romantic corner.

Knirps
The bushes range in height from 70 to 120 centimeters. The leaves are dark green and small. Double pink buds are gathered in flower clusters. The flowers are 3-4 centimeters in diameter. The buds open from June until the first frost. The fragrance is faint.
Hollywood
Goblet-shaped white flowers form on sturdy stems. Each bud contains up to 23 double petals. The leaves are glossy, dark green. A delicate fragrance emanates from the bushes during bloom. Disease resistance is average.

Four seasons
The plant grows 60-80 centimeters tall. Densely double pink flowers form on drooping shoots. The flower cluster consists of 10-15 buds, up to 9 centimeters in diameter, each containing approximately 100 petals. The variety has good immunity.
Growing conditions requirements
Groundcover roses prefer a well-lit location. The flowers of some varieties are prone to fading when grown outdoors. Therefore, they should be kept in partial shade during hot midday hours. Groundwater in the rose planting area should not be too close to the soil surface. Excessive moisture can lead to root rot.

Features of use in landscape design
Tall groundcover roses look spectacular as solitaires. They also decorate arches, pergolas, and arbors. Low-growing varieties are planted in rock gardens, near ponds, and in raised beds. They can be used to create a border along a garden path. Roses are also used to delineate areas in the garden.
Note! A bush looks beautiful when half of its shoots are secured vertically to a support, while the other half spread freely along the ground.
Planting and caring for the flower
Roses grow in the same place for many years. They have their own specific growing conditions. Therefore, the location for the plants is carefully selected. The decorative appearance of the bushes depends on proper care.
Site selection and preparation
Choose a location that receives morning and evening sunlight and provides shade at midday. The scorching sun can cause the petals to fade. They should be planted away from high walls and fences. If the soil is wet, install drainage pipes.
Groundcover roses prefer loam. Peat, sand, and compost are added to heavy soil. If the soil is too light or sandy, it is weighed down with clay or turf. Otherwise, moisture will quickly drain away from the root system. Limestone is added to acidic soil.
Preparing the seedling
Thin, weak branches and broken roots are trimmed from the bush. The cut is made at an angle above a bud located on the outside of the shoot. To ensure the root system is hydrated, it is placed in a container of water. Potassium permanganate powder is added for disinfection.
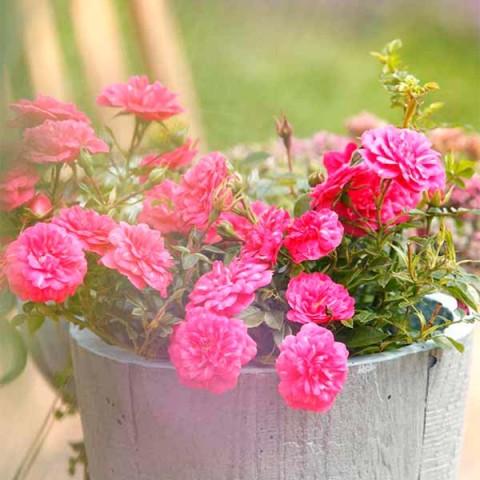

Dates and seating arrangements
Groundcover roses are planted in the ground in spring or fall. The timing depends on climate conditions. In colder regions, spring is best to allow the bushes to establish themselves before frost sets in. In southern regions, fall planting is acceptable.
The landing is carried out as follows:
- dig a hole 50-70 centimeters deep and in diameter;
- a layer of drainage material is placed on the bottom;
- fertile soil is poured into a mound;
- a seedling is placed vertically in the middle;
- cover with soil and water generously.
The distance between bushes is determined depending on the variety of roses, as well as their purpose in the design of the site.
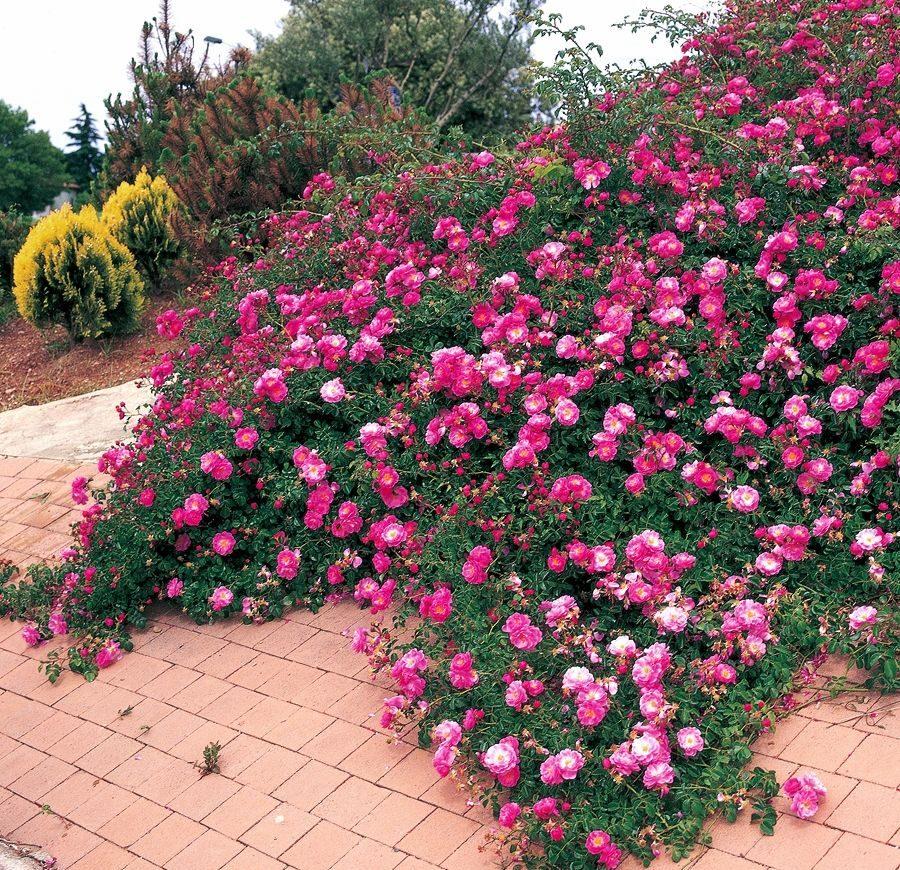

Watering mode
Water frequently immediately after planting. Subsequently, water the soil after the top layer of soil has dried. Water groundcover roses in the morning or evening. Apply at least 10 liters of water under the bush. Overhead irrigation is not recommended, as it promotes disease.
Top dressing
When leaves begin to appear on the shoots in spring, the first feeding is done. Use a mixture of nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus. A complex mineral fertilizer is applied before flowering. If the rose blooms several times during the season, each time it is fed during the budding period. Fertilize the soil during the blooming period. Potassium is added in the fall.

Mulching, loosening and weeding
Groundcover roses have spreading stems, making them somewhat challenging to care for. They require soil loosening and weeding, which is difficult to accomplish. Therefore, the soil around the trunk is mulched immediately after planting. The covering material helps retain moisture and prevents weed growth.
Pruning and shaping the bush
A bush planted in the fall should be lightly pruned in the spring. This encourages the formation of numerous lateral branches. Subsequently, only shoots that thicken the crown are pruned. In addition, sanitary pruning is performed, removing dry, broken, and diseased stems. Every five years, the bushes are rejuvenated, leaving cut shoots 25 centimeters tall above ground. Experienced gardeners do not recommend winter pruning.
Preventive treatments
To prevent diseases and pests from appearing around the roots, remove dried leaves and plant debris. It's a good idea to dig up the soil around the roses in the fall. Fungicides are used to prevent and treat diseases. Insecticides will keep harmful insects away.

Preparing for the winter period
In the south, groundcover roses can successfully overwinter without cover, especially if winter-hardy varieties are planted. In northern regions, a frame is erected over the bushes and covered with lutrasil. If the shoots are long, they are bent to the ground. To prevent the stems from rotting, spruce branches are placed underneath them.
Please note! In mid-autumn, perform a moisture-replenishing watering to promote a successful wintering of groundcover roses.
Methods of breeding ground cover
The easiest way to propagate the plant is by layering and cuttings. Experienced specialists use budding. Seed propagation is not used by gardeners due to the labor-intensive process. Furthermore, this method may not preserve the parental characteristics.
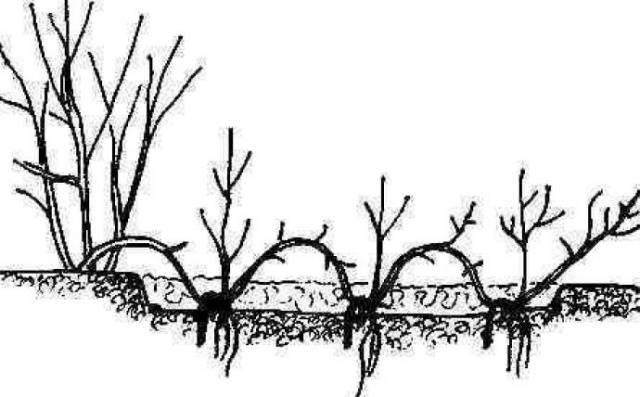
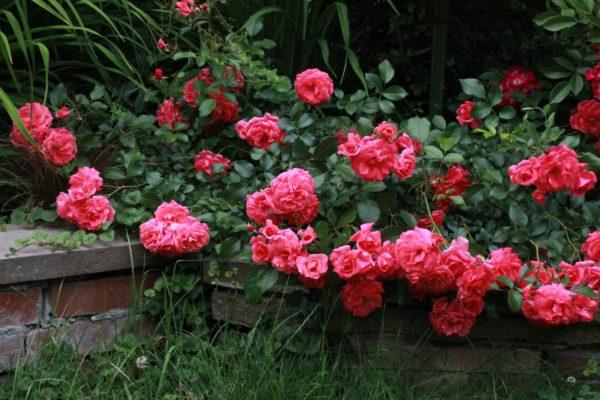
Layering
This method can be used to propagate tall roses with trailing or spreading stems. To do this, dig furrows and place leaf-stripped stems in them. Water regularly throughout the growing season. The following fall, transplant the young plants to their permanent location.

Cuttings
For propagation, cuttings are taken in the fall and stored in a cool place. Planting begins in the spring. To do this, follow these steps:
- the cuttings are cut so that they have 3 internodes;
- placed in a growth stimulator for 2 hours;
- prepare 15-centimeter-deep grooves in the garden;
- cuttings are planted at a distance of 15-20 centimeters;
- The groove is filled with substrate, watered generously, and mulched.
Young bushes are planted in a permanent location the following autumn.
Gardeners' reviews of the crop
Groundcover roses enhance a garden, hiding unsightly outbuildings. Gardeners describe them as an easy-to-grow plant that accentuates the elegance of a landscape. Roses are planted individually or in groups, with long vines trailing along supports.
Natalia, Podolsk: "Groundcover roses are the most easy-to-grow in my garden, especially those with small flowers. To protect against weeds, I mulch the soil with geotextile and crushed stone. In winter, I cover the bushes with spruce branches. If any shoots freeze, I prune them in the spring. After that, new branches with beautiful flowers quickly grow."
Oksana, Moscow region: "I plant low bushes in the garden in a mass. I use roses with long stems as single plants; they look better that way. They bloom beautifully! The only downside is that it's hard to remove plant debris from under the drooping shoots. But on the plus side, moisture is better retained under them, and weeds are fewer."











