- Description and Features
- Advantages and disadvantages
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Soil requirements
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Preparing the site and planting hole
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering
- Top dressing
- Caring for the tree trunk circle
- Protection from diseases and pests
- Preparing for winter
- Trimming
- Methods of reproduction
- Seeds
- Cuttings
- Layering
- Dividing the bush
- Use in landscape design
- Tips from experienced gardeners
Viburnum gordovina is found in the dense forests of Central and Southern Europe. It can be seen rarely in Morocco and Algeria. It grows in soils with a high calcareous content. The word "viburnum" in Russian comes from the word "raskalenny" (red-hot). In ancient Rus', the berries were believed to have been heated by the sun's rays. Our ancestors used the juice of ripe berries to make ink.
Description and Features
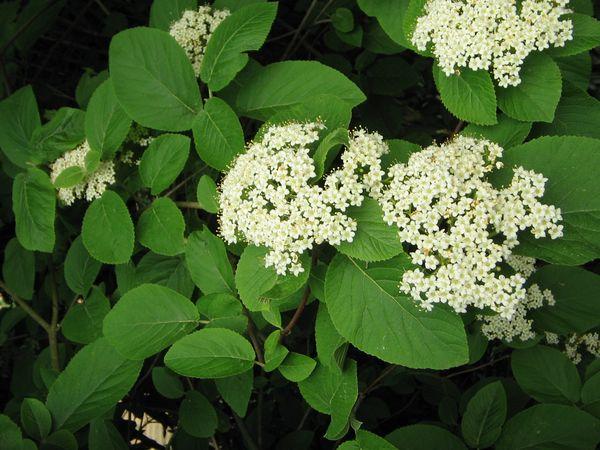
Viburnum Gordovina has dark emerald leaves, slightly wrinkled, oblong ovals up to 18 cm in diameter. All branches and leaves are heavily pubescent. The bark is gray. When the shrub reaches three years of age, the bark begins to crack.
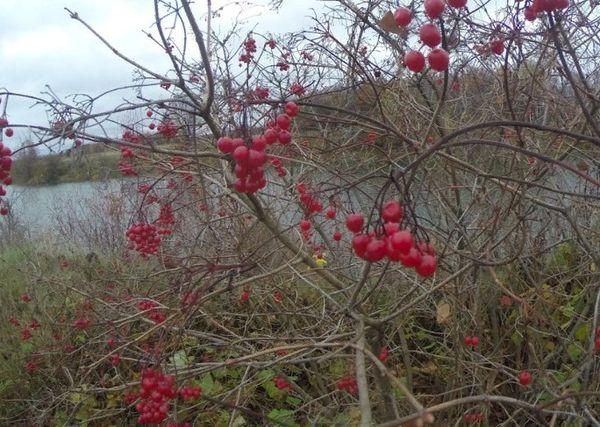
The bushes reach a height of up to 6 meters. They have a dense crown, up to 3-4 meters in diameter, with foliage and stems closely pressed together. The berries are small, gathered in oval-shaped clusters. After flowering, the berries initially appear greenish, then turn scarlet, and finally black.
Fully ripe berries are slightly wrinkled, but very juicy and sweet. The scarlet berries, however, are still unripe and cannot be eaten.
Viburnum Gordovina grows very slowly, with stems growing 30 cm per year. However, viburnum grows for approximately 60 years.
In early summer, it blooms with numerous clusters of whitish-cream flowers. It blooms for two to four weeks. Because the berries take a long time to ripen, they don't ripen at the same time.
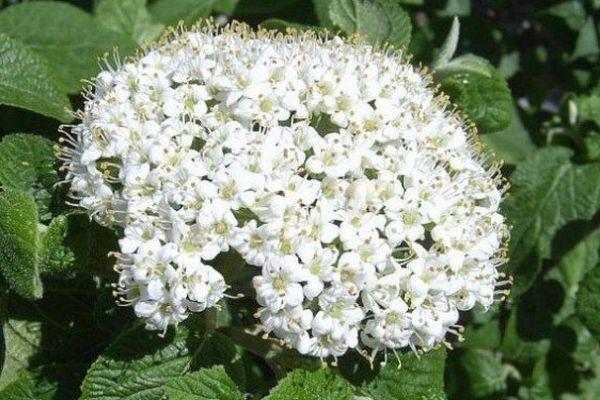

Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- Viburnum Gordovina is excellent for strengthening soil prone to erosion.
- The plant easily withstands both severe frosts and heat and drought.
- It grows easily within the city limits in heavily polluted air.
- She is not afraid of shading.
- She has excellent immunity to diseases.
- It is very decorative.
According to reviews from professional gardeners, it has no drawbacks.
How to plant correctly
Viburnum tolerates sudden weather changes well. It thrives in both full sun and shade. If planted in a shaded location, it's best planted in fertile soil. Varieties with variegated, decorative leaves are best planted in well-lit areas.

Recommendations for choosing deadlines
The seedling is placed in the ground in the fall when the leaves fall, before the first frosts have set in, or in the spring before the leaves have blossomed.
If the seeds are sown in the fall before winter, the first shoots will appear in August.
Soil requirements
Viburnum prefers chernozem and silt-loam soils. The soil should be neutral or slightly acidic and well-moistened.
How to select and prepare planting material
When purchasing, inspect the seedlings; they should appear healthy. If the viburnum seedling has an exposed root system, carefully examine the roots; they should not be diseased. Before planting, soak them in water for 3-4 hours.
Preparing the site and planting hole
Select a suitable site. Thirty days before planting, scatter potassium sulfate, superphosphate, and peat over the soil, then till the soil. Dig planting holes 0.4 m deep and 0.5 m in diameter, leaving 1.2-2 m between holes.

Add humus and peat, 3 tablespoons of urea, and a glass of ash to the excavated soil. Add some of the prepared substrate to the bottom of each hole.
Planting diagram
Place the seedling in the hole and cover it with soil, being careful not to cover the root collar. Gently compact the soil. Pour 3 buckets of water under each plant. Make a circular funnel around the seedling so you can water the shrub. Then, apply a 10 cm layer of peat or rotted sawdust around the trunk.
Care instructions
To ensure good growth and a beautiful ornamental appearance, Gordovina viburnum requires watering, loosening the soil after irrigation, and removing weeds. After three years of growth, remove the initial mulch layer, loosen the soil, and add a new layer of peat.
Watering
This shrub prefers well-drained soil, so it should be watered generously. After planting, it's essential to water the plant until it becomes established. It's best to water in the evening with settled water, moistening the soil to a depth of 40 cm.

Once the bush has matured, you can water it once a week. It needs moisture when the berries are ripening. Watering should be done in the area around the trunk.
Top dressing
You can feed the crop with nitroammophoska in the spring, and only with phosphorus and potassium in the fall.
If the gardener wants to feed the plant with organic matter, it can be added in the fall when tilling the soil. Phosphorus and potassium can be added to the manure. In the spring, before the buds swell, urea (2 tablespoons) can be applied, and before the buds open, potassium sulfide (2 tablespoons) can be applied.
Caring for the tree trunk circle
Weeds should not be allowed to grow, they should be pulled out regularly, and the soil should be loosened after watering.
Protection from diseases and pests
Viburnum gordovina can be affected by aphids, fruit moths, and scale insects. Viburnum is also susceptible to leaf spot and powdery mildew.
In case of pest attacks and as a preventative measure, spray the shrub with insecticides. To eliminate scale insects, spray with Karbofos, and to get rid of aphids, it's best to plant Trichogramma. If the plants are damaged by the viburnum leaf beetle, spray with chlorophos (0.2%).
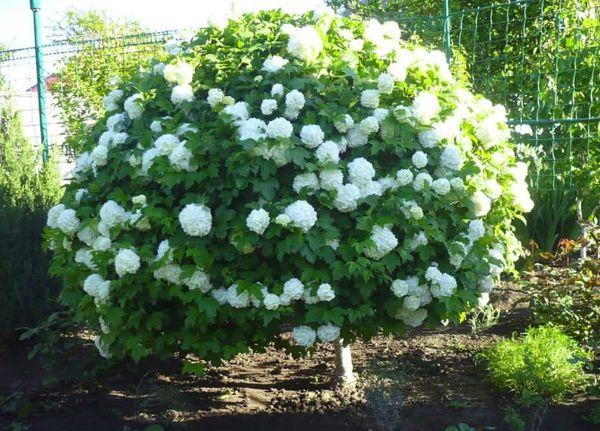

If the crop is susceptible to spotting and powdery mildew, it should be treated with fungicides. To reduce the risk of disease, you can spray the crop with garlic and onion infusions, or dust it with tobacco.
Preparing for winter
Viburnum Gordovina is very frost-hardy and doesn't require any winter preparation. Just make sure the peat mulch layer is at least 5-7 cm thick.
Trimming
Pruning is done in early spring. Old, dried, and diseased branches are removed. To ensure a healthy crown, manually pinch off the tops of shoots longer than 0.3-0.4 m. If you want to grow the viburnum as a tree, then in the second year after planting, prune all side shoots, but leave the central trunk. New branches will grow from this trunk each year. These should be pruned. It's also a good idea to pinch off the growing point.
After 6-10 years of growth, the plant needs to be rejuvenated, leaving the 10 best branches and cutting off the rest completely.
If the viburnum is weak, cut it back, leaving a stump 30 cm above the ground. This will allow a new bush to grow.

Methods of reproduction
Viburnum Gordovina is propagated by shoots, division of the bush, seeds and cuttings.
Seeds
Viburnum seeds have an excellent germination rate—80%. However, when sowing seeds, the root grows in the first year. The sprout will only emerge a year later. The plant will grow slowly for the first two years, then more rapidly. Before sowing, the seeds are stratified, meaning they are placed in the refrigerator for 6-7 months.
Important! To ensure proper germination, seeds can be stored for 3 months at a temperature of 18-20 degrees Celsius, followed by 3-4 months in a refrigerator at -3 to 5 degrees Celsius.
Then, place the seeds in the soil to a depth of 3 cm. It's best to mark the spot where you planted the seeds. The soil should be kept constantly moist and covered with a layer of peat for the winter. Seeds can be sown in early spring or towards the end of October.
Cuttings
Cut 100 mm long shoots with two buds between June 20th and 30th. Then trim the upper leaves in half, and trim the lower leaves completely. Make the upper cut straight and the lower cut at an angle. Then add Kornevin to a container of water and place the cuttings. Once small roots have grown on the branches, transplant them into a greenhouse.
To create a substrate, you can mix 1 part peat and 1 part sand. The plant should grow at an air temperature of 22-25 degrees Celsius.
Please note: The lower the temperature in the greenhouse, the less effective the root growth of the cuttings will be.
The greenhouse also needs to be constantly ventilated, but drafts should be avoided. Water regularly to keep the soil moist.
Layering
In the spring, the shoots are bent down to the ground. Dig 10-15 cm long trenches in this area and bury the shoots in them. By autumn, the shoots will have developed roots and need to be separated from the parent plant and transplanted to a new location.
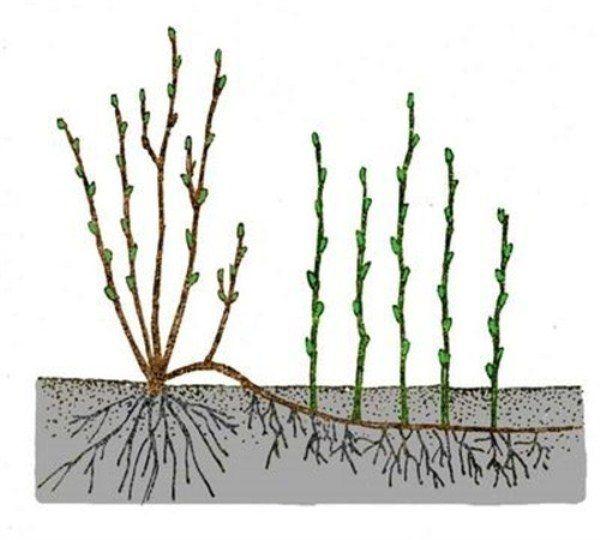
Dividing the bush
Only young bushes are divided. If the shoots are close to the ground, they can be bent down and pinned to the ground. Then, sprinkle them with soil, provide some shade, and water regularly. Each new viburnum shoot should have three renewal buds. Then, in the fall, they are separated and replanted.

Use in landscape design
Viburnum berries are not grown for sale because the ripening time of the berries is long and they do not ripen at the same time.
Viburnum has strong roots, so it's planted on slopes and ravines to prevent soil collapse. It's also planted as a hedge. It's used for urban landscaping because it tolerates high levels of air pollution very well.
Tips from experienced gardeners
Viburnum gordovina shouldn't be planted in peat, sand, or podzolic soils. Otherwise, it will produce few berries, and any that do appear will be unfit for consumption. If the soil is acidic, add dolomite flour or lime.
After uprooting apple, plum, pear, or cherry trees, you should not immediately plant Gordovina viburnum in the same place, as these plants may have the same diseases, and the soil may contain pests that will then attack the plant.











