- Why is it so important to plant an apple tree correctly?
- Timing and optimal temperature for planting trees
- In the spring
- In summer
- In the fall
- When is it better to plant: in spring or in autumn?
- Preparatory work
- Criteria for selecting a seedling
- The best place
- Distances between plantings
- Favorable and unfavorable neighbors
- Suitable soil composition
- Preparing the planting hole
- On clay
- On peat
- On the sand
- On loam
- Step-by-step guide to planting a seedling
- Features of planting columnar apple trees
- Dwarf varieties
- Planting the Melba apple tree
- For tall apple trees
- Planting apple trees with a closed root system in spring and summer
- When to plant in different regions of Russia
- Further care of the tree
- Possible problems and solutions
The apple tree is a classic fruit grown in almost every garden. Thanks to its unique qualities, adaptability to any weather conditions, and ease of care, it has become popular in every region. It's worth understanding how to properly plant an apple tree and subsequently care for it to ensure fruitful results.
Why is it so important to plant an apple tree correctly?
Selecting a healthy seedling, planting it in suitable soil at the right time, and then caring for it according to proper agricultural requirements will allow you to grow a luxurious tree with an excellent apple yield.
Timing and optimal temperature for planting trees
Timely planting of young apple trees in open ground is one of the most important stages of their cultivation. Choosing the optimal timing, taking into account regional and weather conditions, ensures that flimsy seedlings transform into fragrant trees with a luxurious crown and increased yield.
In the spring
Most varieties adapt well to any growing conditions, but spring planting has several advantages over other times of the year:
- Moisture-rich, nutritious soil accelerates the survival of seedlings;
- During the warm period, the root has time to grow and gain strength before the winter bad weather;
- by the time the first cold weather sets in, the tree takes root and adapts to the surrounding conditions;
- fruiting of an adult tree when planted in spring begins a year earlier;
- Unexpected problems associated with adaptation are easy to control during the summer-autumn period.
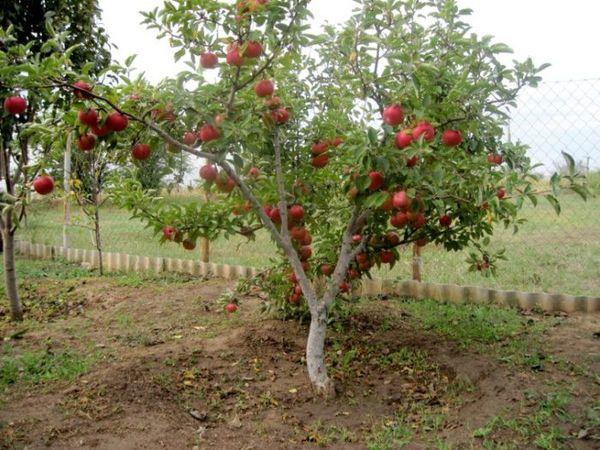

Frozen soil can destroy fragile roots, so it's important to take your time. Experienced gardeners believe that once the soil has warmed to the depth of a bayonet spade, you can begin planting apple trees.
In most regions, planting begins in mid-April. However, once the seedlings' leaves begin to unfurl, their survival rate drops significantly.
In summer
Planting young apple trees in summer is a last resort. The delicate root system of seedlings quickly depletes and dies in hot weather due to lack of moisture. Upon purchase, seedlings should be immediately placed in a moist environment and dug into the ground as quickly as possible. Cool, rainy weather is preferred for transportation. Trees with closed root systems, planted with a root ball, have a much better chance of rooting.
In many regions, the main heat and dry period are already coming to an end by August, so on a cloudy day with low temperatures, it is quite possible to start planting.
In the fall
Gardeners begin autumn planting in October-November during the rainy season.
It has a number of advantages:
- the seedling does not waste energy on vegetation, intensive growth and root development occurs;
- surviving trees are resistant to temperature fluctuations and are more hardened compared to their spring counterparts;
- Autumn rains fully saturate the seedling with the necessary moisture, and drying out of the root system is excluded.
However, autumn weather is unstable; frost can strike unexpectedly and destroy a fragile apple tree.
When is it better to plant: in spring or in autumn?
There's no definitive answer to the question of when is the best time to plant apple trees. It all depends on personal preference and the climate zone you live in. They're often planted in early spring, as it's too early to tend to the garden beds and the gardener has plenty of free time.
In regions with mild climates, fall planting offers certain advantages. Severe cold weather arrives only in midwinter, giving seedlings time to establish roots. In northern regions, the short autumn often gives way to sudden frosts, and fragile apple trees can perish.
Preparatory work
Growing a healthy apple tree and getting a bountiful harvest requires some effort. You need to select a healthy seedling, find a suitable location, cultivate the soil, apply fertilizer, and carefully care for the growing tree.
Criteria for selecting a seedling
Selecting a healthy seedling and preparing it for planting is very simple; even a novice gardener can handle it:
- Seedlings are purchased from specialized nurseries with a good reputation and zoned varieties are selected.
- Pay attention to the grafting site: it should be well tightened and show no signs of rot.
- You shouldn't buy container-grown seedlings for spring planting, because the roots are the only indicator of a tree's condition.
- A plant with well-developed roots, without obvious damage or signs of rot, will definitely take root and grow into a healthy tree.
- One-year-olds are selected based on their massive roots, ignoring any underdeveloped crowns—such a seedling will quickly take root and catch up with even its three-year-old counterparts.
- The stem should be free of obvious damage or growths. If you lightly pick at the bark, you'll see a healthy, bright green stem.
These simple rules will help you choose a good seedling and grow an excellent tree.
The best place
Choosing a suitable location on the plot guarantees the safety of the seedling during the winter and during the spring flood.
A gentle slope makes an excellent planting location. Open sites in regions with unstable climates often result in apple trees freezing in early spring. In arid areas with mild climates, north-facing slopes are preferred, while in colder regions, south-facing slopes are preferred.
You shouldn't plant a young seedling in place of an old apple tree. Dying trees release phloridzin into the soil, which weakens young plants. It's best to plant apple trees in the same area as cherry or plum trees.
Low groundwater levels negatively impact the growth and development of apple trees. Reaching for the groundwater with their roots, the tree develops poorly, withers, and loses winter hardiness and productivity.
Distances between plantings
Proper placement on the site is essential for growing full-grown trees and obtaining good harvests. Mature trees should not block the sun from one another or become entangled with their roots. If a gardener decides to plant several apple trees at once, it's important to adhere to the recommended spacing between seedlings. Deviating too far from the standard spacing can cause a number of problems:
- crop yields are significantly reduced;
- shading and nutrient deficiency occur;
- the likelihood of developing fungal diseases increases.
The distance between individual seedlings in a row depends on the characteristics of the variety.

Favorable and unfavorable neighbors
Planning your orchard with suitable trees and shrubs in mind will ensure excellent apple tree growth and a bountiful harvest. Unfavorable neighbors for apple trees include:
- rowan
- acacia;
- horse chestnut;
- pear;
- peaches;
- nuts;
- currant.
The apple tree coexists well with the following crops:
- cherries;
- plum;
- cherries;
- gooseberries;
- cherry plum.
Compatible cultures have a positive influence on each other, so it is important to pay close attention to this issue.
Suitable soil composition
The soil must provide adequate oxygen access to the roots. Growing apple trees in heavy soils often results in slow growth and low fruit production. They also do not tolerate highly acidic soils.

For normal growth and development of apple trees, different types of soil require optimization in the following ways:
- wood ash, bone meal and horse manure are added to loams;
- the composition of clay soil is improved by adding peat, organic fertilizers and wood ash;
- sandstones are supplemented with peat, plant compost, manure and complex fertilizers;
- Swampy areas require the use of large amounts of sawdust and compost.
The application of biological preparations significantly improves soil fertility and protects seedlings from fungal and bacterial infections after transplanting into open ground.
Preparing the planting hole
The planting hole should be prepared at least two weeks before planting the seedlings. Its size should accommodate the root system and allow for free development of lateral roots during the first few years of growth. The planting hole should be at least a meter in diameter and up to 80 cm deep. A drainage layer placed at the bottom will prevent waterlogging and root rot.

On clay
Apple trees grow poorly and are prone to disease in clayey, unprepared soil. To grow a strong, high-yielding tree, it's important to properly prepare the soil for planting.
A drainage layer is installed at the bottom of the pit. The following materials are used for drainage:
- crushed stone;
- river pebbles;
- broken brick;
- gravel.
It's best to fill the hole with a nutrient-rich substrate consisting of river sand, humus, peat, and ash. To drain water during heavy rains, dig a drainage trench around the tree's trunk and fill it with fine stone or sand.
On peat
Before planting an apple tree in peatland, the soil should be revitalized. This is done by deep digging, simultaneously adding lime or chalk and complex fertilizers. The hole is filled with a drainage layer of dry branches or grass. Once the dry vegetation has rotted, it becomes an excellent growing medium.
On the sand
Sandy soil is poor in nutrients and retains moisture for a long time. For healthy apple tree development, it's necessary to prepare a nutritious soil mixture consisting of black soil, humus, and peat in a 3:1:1 ratio. Seedlings in sandy soil require more frequent fertilizing.

On loam
The best soil for growing apple trees is loam. When planting in such soil, it's sufficient to add a small amount of peat and coarse river sand to ensure fresh air flow to the root zone.
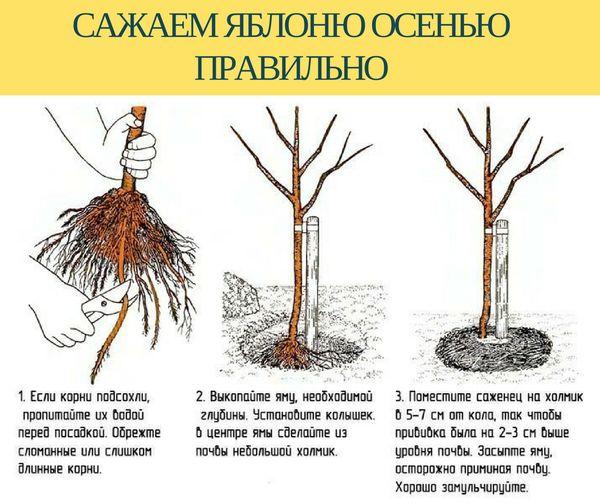
Step-by-step guide to planting a seedling
Plant an apple tree in open ground, adhering to the following rules:
- Before planting, the seedling is placed in water with a small amount of Kornevin added for 6 hours.
- Dried roots and areas with signs of rot are carefully cut off with pruning shears.
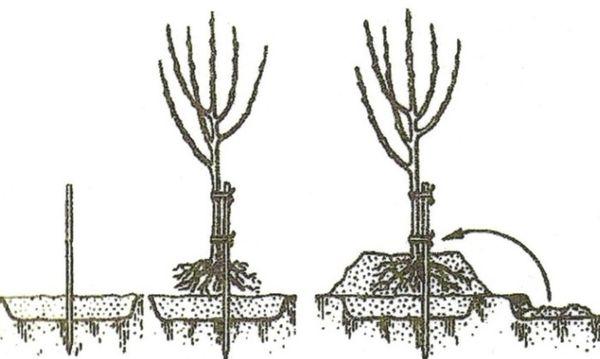
- The planting hole is not completely filled with nutritious soil, but a planting hill is formed.
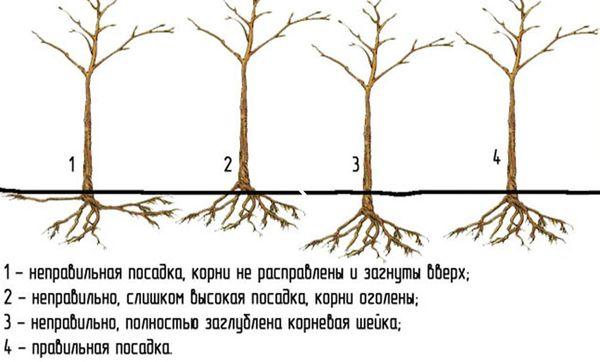
- Place the seedling so that the root collar protrudes 5 cm above ground level, and carefully straighten the root system.
- The hole is filled with the remaining soil and lightly compacted.
- The soil is thoroughly watered.
- If necessary, the seedling is tied up.
When purchasing an apple tree with a closed root system in a container, the seedling is planted in a hole along with a lump of earth.
Features of planting columnar apple trees
Growing columnar varieties is possible even in the smallest garden plots, as the minimum distance between them is just a meter. Their short root system thrives with a groundwater level of 1.5 meters above the ground.

Dwarf varieties
The distance between seedlings for dwarf varieties is 2.5-3 meters. Dwarf varieties require reliable support to prevent the tree from being uprooted in windy weather.
Planting the Melba apple tree
Melba thrives in warm climates alongside other pollinating varieties. It does not tolerate heavy soil or waterlogged areas.
For tall apple trees
The planting pattern for tall apple trees is 5 x 5 meters. Mature trees thrive in water tables no higher than three meters.
Planting apple trees with a closed root system in spring and summer
Apple trees with a closed root system are planted by transshipment. This involves digging a hole in the ground that matches the size of the seedling's root system and carefully placing it inside, complete with a root ball. Cover the top with soil and compact it lightly.
When to plant in different regions of Russia
In cold climates, apple tree planting begins no earlier than the end of April. In temperate climates, spring planting begins in April, and fall planting begins in late September. In the southern regions, fall planting is more common.

Further care of the tree
For normal growth and development, a young apple tree requires moisture. In arid regions, it should be watered generously 1-2 times a week, late in the evening or early in the morning. However, overwatering is still a good idea.
After watering, be sure to loosen the soil at the base. Mulching the soil with any available material will improve oxygen access to the roots and avoid constant loosening.
Possible problems and solutions
The main problems after planting can be diseases and pests, as young seedlings are not yet fully established and cannot cope with them. Rainy seasons often cause scab, so in regions with frequent rainfall, choose a well-lit and wind-blown location for planting.
Early purchase and planting of seedlings in frozen ground often leads to their death, so it is important to strictly adhere to optimal timing and be guided by weather conditions.
No orchard can be imagined without an apple tree. A beautiful and fruitful tree is the result of timely planting in suitable soil and careful, timely care.











