- Reasons
- Hot summer
- Lack or excess of moisture
- Insufficient feeding
- Excess fertilizer
- Climate zone
- Frosts
- Improper care
- Diseases
- Pests
- Description and treatment of diseases
- White spot
- Fomoz
- Bacteriosis
- Alternaria
- Powdery mildew
- Pests and control methods
- Carrot psyllids
- Root-knot nematodes
- Carrot fly
- Prevention
- Crop rotation
- Timely removal of affected leaves
- Soil cultivation
- Using reliable varieties
- Moderate watering
- Proper fertilization and feeding
- Weeding and loosening
Many people wonder why carrots turn yellow in their garden beds. There are many possible causes of this problem, including weather conditions, diseases, pests, and improper care. To solve the problem, you need to identify the underlying cause.
Reasons
There are many factors that can cause carrot tops to turn yellow. To resolve the problem, it's important to clearly identify the root cause.
Hot summer
Hot, dry weather often causes carrot leaves to turn yellow. Overwatering during hot weather can also cause problems. Since predicting weather conditions is difficult, carrots are planted in several stages.
Lack or excess of moisture
Carrots often dry out when they're under- or over-watered. To avoid these problems, it's important to ensure proper watering. Before the first shoots appear, the plant should be watered frequently, in small amounts. As the roots develop, water less frequently, but with larger amounts.
Insufficient feeding
If the soil is deficient in nutrients, carrot leaves may turn yellow. Fertilize the crop 3-4 times per season. The first fertilizer application is made 20 days after sprouting. Urea, potassium magnesium sulfate, and superphosphate are used for this purpose.
After 2-3 weeks, the plants are fed a second time. For this, complex fertilizers are used. The third time, the soil is fertilized during the active root growth stage, using organic fertilizers. A couple of weeks before harvest, ash or potassium sulfate is added.

Excess fertilizer
Excessive amounts of nitrogen fertilizer and manure can cause white spot, or septoria, to develop. This causes the foliage to turn yellow and fall off. This problem most often occurs in the fall and spring.
Climate zone
Yellowing of the crop leaves may be due to the incorrect choice of variety for a particular climate zone.
Frosts
Unstable weather conditions are often accompanied by night frosts. This can cause carrot leaves to turn yellow. Since predicting weather conditions can be quite difficult, the plant is planted in several stages.

Improper care
Carrot seedlings often turn yellow due to improper care. This can be caused by insufficient watering, insufficient or excessive fertilizer application, or untimely loosening and weeding of the beds.
Diseases
Carrots turn yellow and dry out due to various diseases. These include white spot, leaf spot, powdery mildew, bacterial wilt, and early blight.
Pests
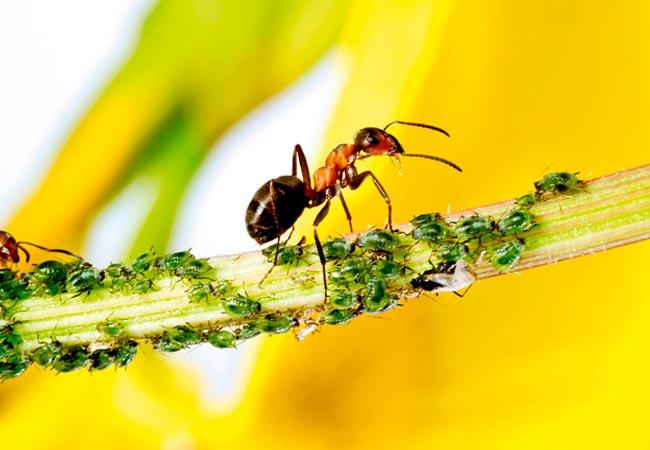
The plant's foliage may turn yellow due to various pests. Psyllids, cutworms, and carrot flies are particularly dangerous. These dangerous insects gnaw on the fruit and feed on its sap, causing the leaves to turn yellow.

Description and treatment of diseases
A variety of diseases can cause yellowing leaves. To address the problem, it's important to identify the underlying causes promptly.
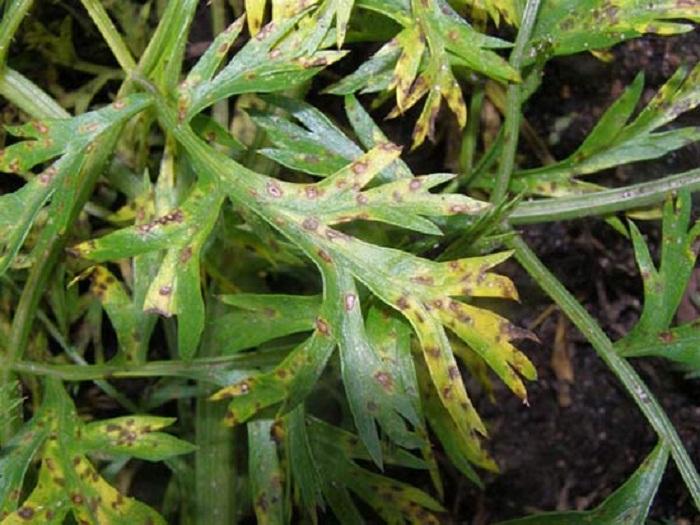
White spot
Affected leaves curl and dry out. White spot attacks the plant in cold and cloudy weather. It most often occurs in spring and fall. The disease is caused by excessive amounts of manure and nitrogen. To prevent its development, it is necessary to apply fertilizer regularly.

Fomoz
The disease develops in the fall. It is caused by a fungus that overwinters in the tops, roots, and seeds. The top of the fruit is affected first, followed by the entire vegetable, which becomes covered with brown spots and black spots.
It is very difficult to cure the disease, so it is necessary to follow the rules of prevention.
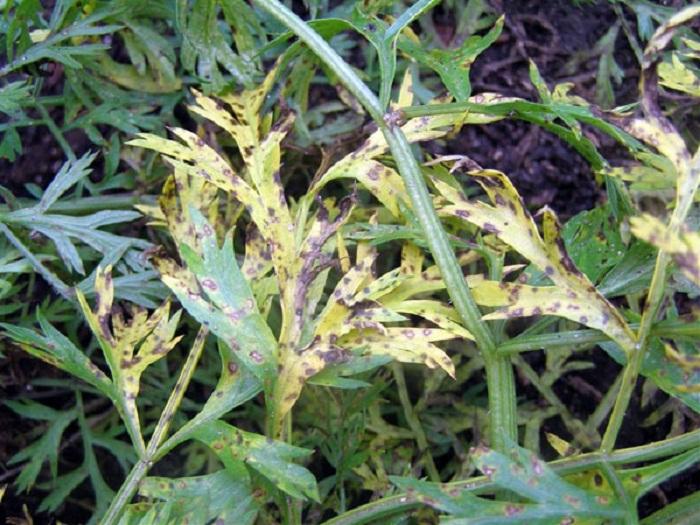
Bacteriosis
With this disease, the tops of the carrots become spotted and have a yellow border. The spots then darken, but the yellow borders remain. The disease then attacks the petioles, which become covered with brown stripes. Ulcers and spots also appear on the roots. To prevent the disease, carrot seeds are soaked in hot water before planting. Once sprouts appear, they should be treated with a fungicide. This should be done after 20 days.

Alternaria
The disease is transmitted from contaminated soil and seeds. Leaves become darker and curl. Gradually, Alternaria affects cuttings and root vegetables, developing a bitter taste. The vegetables also become covered with black spots. Before the leaves dry out, it's important to spray the affected plants with fungicides.
Powdery mildew
Leaves affected by powdery mildew become covered with a white coating. The carrot tops also become more brittle. The disease is caused by a lack of fertilizer and moisture. Fungicides are used to control the disease.

Pests and control methods
Various pests can cause carrot leaves to turn yellow. To address the problem, you need to determine its cause.
Carrot psyllids
These small insects resemble flies. They often lay eggs on carrot leaves, which feed on the sap of the tops. As a result, the tops turn yellow and dry out. Spraying with a soap solution or tobacco infusion helps combat the problem.
Root-knot nematodes
They are white, round worms. The insects thrive in moist soil and lay eggs in the roots. If carrots are infested with parasites, they should be watered with a Decaris solution. Use one tablet per liter of water.
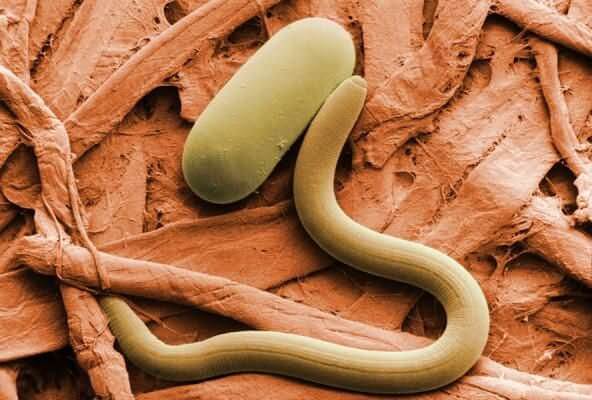
Carrot fly
The first symptom of plant damage is a bronze tint to the leaves. After some time, the plant dries up. If the seedlings are not thinned out in a timely manner, the flies lay their eggs in the soil. As a result, the larvae damage the root vegetables. Treating carrots with chemicals such as Actellic, Sharpei, and Arrivo can help prevent problems.
Prevention
To prevent yellowing of carrot leaves, you need to provide them with proper care.
Crop rotation
Strict adherence to crop rotation rules helps prevent the accumulation of specific pathogens in the soil. The plant is replanted in its original location only after 3-4 years. Furthermore, the crop should not be planted after onions and cabbage, as these plants share the same pests and diseases.

Timely removal of affected leaves
To prevent the spread of diseases, remove infected or diseased leaves during the crop's maturation. Infected tops should be burned, followed by soil treatment.
Soil cultivation
Farmayod can be used to disinfect garden beds. To do this, use 100 milliliters of solution per 10 liters of water. Use 10 liters of the product per 5 square meters. After 10 days, add compost and products containing beneficial bacteria to the soil.

Using reliable varieties
Choosing the wrong carrot variety can cause yellowing leaves. Early-ripening varieties with a short growing season are easiest to grow. These include Parisian Carrotel, Bangor, and Amsterdam.
Varieties such as Perfection and Vitaminnaya are resistant to carrot fly. To avoid phoma, you can grow varieties such as Moskovskaya Zimnyaya and Nantskaya 4.
Moderate watering
Overwatering in hot weather can lead to various diseases. Warming the water can help prevent this. To increase disease resistance, add mullein and micronutrients.

Proper fertilization and feeding
To prevent foliage yellowing, natural and synthetic fertilizers are used. They protect against diseases and increase yields. Natural fertilizers improve the mechanical properties of the soil. Organic fertilizers increase crop yields.
Weeding and loosening
These procedures help prevent crusting and ensure air access to the roots. This helps prevent dangerous diseases. To prevent crusting, the soil is additionally treated with peat.
Yellowing carrot leaves can lead to crop loss and even death. To address the problem, it's important to identify the underlying causes and take prompt action.











