- Signs of barren flowers on cucumbers
- The bushes are not blooming
- Flowers are falling
- Few ovaries
- The ovaries do not ripen and do not fill out
- The ovaries are drying up
- Reasons for the absence of ovary
- In the greenhouse
- Crop density
- Violation of temperature regime
- Mistakes when watering
- Insufficient lighting
- Weak roots
- Cold soil
- Problems with cucumber pollination
- In open ground
- Poor quality seeds
- Unbalanced fertilizers
- Incorrect soil preparation
- Watering with cold water
- When should you sound the alarm?
- What to spray cucumbers with to help them set fruit
- Folk remedies for stimulating ovary formation
- Fertilizers
- Store-bought biostimulants
- Preventive measures
Parthenocarpic hybrids don't require bees, and self-pollinating varieties aren't particularly affected by weather. They thrive in greenhouses, producing high yields. However, even these cucumbers sometimes fail to set fruit, despite blooming profusely. A decision must be made immediately regarding the plants. If you water this heat-loving crop with cold water, or if the soil is overwatered or too dry, the bushes will produce buds, but no green fruit will develop.
Signs of barren flowers on cucumbers
If care rules are ignored and the nutrient balance is disrupted, plants become sick and fail to bear fruit. Excess nitrogen in the soil promotes vigorous leaf and stem growth but inhibits bud formation.
The bushes are not blooming
Cucumber seeds collected two or three years ago usually germinate well, but the resulting plants often produce numerous shoots and don't always flower. Seeds from fresh cucumbers rarely provide reliable seedlings for cucumber development; such seeds germinate poorly. Weak seedlings, even if they do take root, produce few juicy fruits.
Flowers are falling
If agricultural practices aren't followed and plants are planted too densely, the roots begin to experience nutrient deficiencies, and the leaves interfere with pollination. Flowers fall off:
- at temperatures above 33 °C;
- due to watering with cold water;
- due to high humidity.

Buds fall off plants affected by powdery mildew. If seeds are selected incorrectly, and male flowers predominate, female flowers also fall off.
Few ovaries
The development of cucumber fruit, which is pollinated by bees, is greatly influenced by weather. Bees hide on cloudy and rainy days, and fly over the plants when the sun shines, and only then does pollination occur and the fruit develops.
Parthenocarpic hybrids have female flowers. Their formation requires a significant amount of nutrients, and the bushes lack the energy to produce fruit without additional feeding.

The ovaries do not ripen and do not fill out
The cucumbers formed after pollination stop developing when the temperature drops to 13–15°C. In cold weather, cucumbers lose their ability to absorb nutrients. The ovaries do not fill out:
- in case of nutritional deficiency;
- when fruit harvesting is rare;
- in dense plantings.
Extreme heat has a negative impact on the growth of cucumbers; they cannot ripen when the plant lacks moisture.
The ovaries are drying up
The small cucumbers that appear in place of the flowers dry up and fall off when the soil does not warm up above 13°C, with sudden temperature fluctuations, or when the bushes are not receiving enough nutrition.

Reasons for the absence of ovary
Fruits sometimes fail to set not only when cucumbers are grown in a garden bed and it was cold and damp during flowering, but also in closed ground.
In the greenhouse
Parthenocarpic varieties, which do not require wind or insects for pollination, produce fruit well in protected soil because they produce only female flowers.
Crop density
Polycarbonate greenhouses don't offer much space, but beginning gardeners are tempted to plant more cucumbers in hopes of a good harvest. If densely planted crops don't break through, the growing plants suffer from nutrient deficiencies and insufficient sunlight. The extra shoots drain energy, and fruit fails to set.
Violation of temperature regime
Cucumbers don't tolerate cold well, but at 33–35°C, which occurs during hot weather outside and poor ventilation in the greenhouse, the leaves begin to yellow, and pollination fails. The optimal temperature for the development and fruiting of this vegetable crop is 23–27°C.
Mistakes when watering
Cucumbers thrive in moist soil and don't tolerate dry air. The roots of the plants are weak, and their large, broad leaves promote rapid evaporation. During flowering, water the plants frequently to prevent the soil from drying out. Avoid using cold water:
- Cucumbers are starting to get sick.
- Growth is slowing down.
- The ovary is not formed.
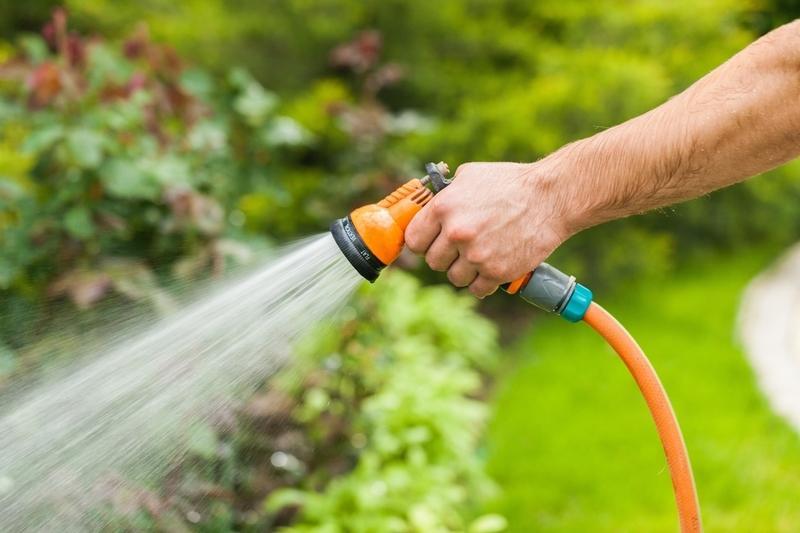

The newly emerged fruits are deformed and bitter. It's best to sprinkle them with water before buds form.
Insufficient lighting
If cucumbers are planted denselyThey begin to shade each other, and photosynthesis is impaired. Vegetable growers recommend planting no more than three plants per square meter. If the number of plants increases, the ovaries will turn yellow and dry out. Shoots should be pinched before they reach 25 cm in length.
Weak roots
Cucumbers, like other vegetable crops, obtain the mineral and organic nutrients they need for growth from fertile soil. However, if the plants have weak roots, growth slows and fruit set is poor because the supply of nutrients to the shoots is reduced.

Cold soil
Cucumber seeds germinate when the soil temperature is 15–16°C, but for the seedlings to grow and develop, the soil must warm up to at least 20 degrees and not cool down to 15 degrees at night, otherwise you should not expect cucumbers to set.
Problems with cucumber pollination
Parthenocarpic hybrids grown indoors don't require insects. To ensure fruit set on regular varieties, the greenhouse needs to be ventilated to attract bees for pollination.
In open ground
If cucumbers are not setting fruit in the garden, the cause of this phenomenon is not necessarily damp and cloudy weather.

Poor quality seeds
The seed material must be prepared for planting, stratified, disinfected and treated with a growth stimulator.
If this is not done, the seedlings may not emerge, and when the seeds sprout, the bushes will be weak and will develop and bear fruit poorly.
Unbalanced fertilizers
Cucumbers grow quickly, producing abundant small cucumbers after pollination, unless the plants suffer from a micronutrient deficiency. A potassium deficiency weakens the roots and impairs nutrient absorption.
A sulfur deficiency causes stems to become thinner. Cucumbers become watery and develop a bitter taste when nitrogen metabolism is disrupted. Fruit growth slows when phosphorus is deficient. Excess micronutrients also negatively impact plant development.
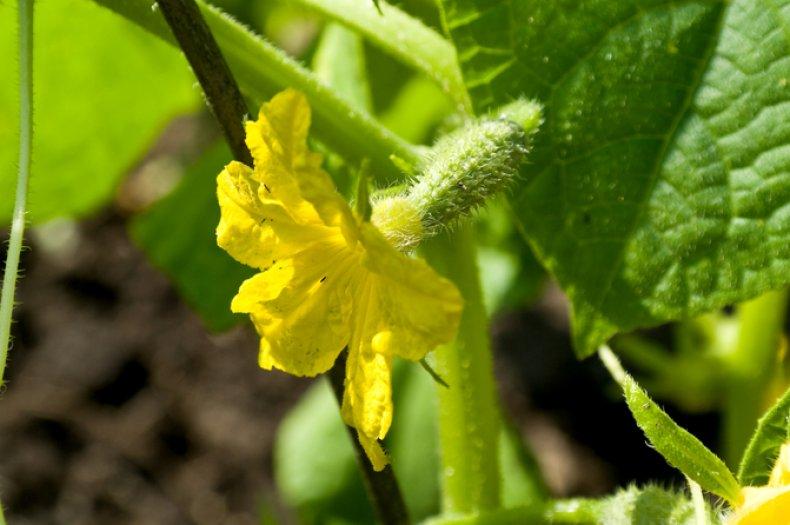

The lower leaves of the bushes turn yellow, become enlarged, and pollination of flowers is poor due to a lack of nitrogen. However, when cucumbers are regularly fed with fertilizers containing this micronutrient, the plants develop abundant foliage, but few ovaries are formed.
Incorrect soil preparation
When growing cucumbers in a garden bed, the planting location should be changed regularly. The crop does not tolerate heavy clay soils or marshy ground, but prefers loose, slightly alkaline soil.
Before preparing the beds, which need to be wide, it is necessary to normalize the acidity and add fertilizer to the depleted soil; otherwise, the cucumbers will grow poorly and will not yield abundant fruit.
Watering with cold water
This vegetable crop thrives on moisture, but if irrigation rules aren't met, leaves turn yellow, flowers fall off, and fruit buds dry out or rot. To avoid being left without cucumbers, water for irrigation is heated in the sun to 20–25°C, rather than taken straight from the tap.

When should you sound the alarm?
Female flowers contain a cylindrical mother fertilization cell, located among the petals and resembling a miniature green cucumber. It is here that the ovary develops. Insects transfer pollen from the male buds.If the bushes are covered with flowers without a mother plant, you need to determine the cause of the problem and take immediate action.
What to spray cucumbers with to help them set fruit
To improve the formation of cucumbers, special substances are used that contain essential microelements and hormones that can enhance growth.

Folk remedies for stimulating ovary formation
If flowering is sparse, experienced gardeners recommend spraying cucumbers with boric acid, dissolving a gram of the powder in a liter of water. Iodine inhibits the growth of fungi that cause powdery mildew and stimulates bud formation. It boosts plant immunity and provides cucumbers with phosphorus and calcium foliar feeding infusion of ash.
To attract bees to open beds, a well-known folk method is used: spraying flowers with sweet water.
Fertilizers
When buds appear, cucumbers grown in the garden are fed with 20 grams each of potassium salt, ammonium nitrate, and 40% superphosphate mixed in a bucket of water. During flowering in the greenhouse, the bushes are fertilized with nitroammophoska or cow manure, which helps improve ovary formation.

Store-bought biostimulants
You can spray cucumbers with modern products that increase plant resistance to stress. "Epin" contains hormones that, when released into pollen, promote fruit formation. The biostimulants "Bud" and "Ovary" are based on gibberellic acids; they promote active cucumber development, and the cucumbers grow, rather than fall off.
The product NV-101, which is produced by a Japanese company:
- Strengthens the immune system.
- Enhances silicon absorption.
- Stimulates ovary formation.
Energen Extra, a product containing potassium salts, is sprayed on plants during flowering. This product helps transport nutrients from the foliage to the young plants.

Preventive measures
To avoid excessive barren flowers and ovary drop, cucumbers need to be protected from low and high temperatures and prevent the development of diseases.
Preventative measures to increase fruit production include:
- using high-quality seeds for sowing;
- regular watering with warm water;
- fertilizing with organic and mineral fertilizers;
- spraying with growth stimulants;
- timely formation of whips.
For greenhouse cultivation, it's best to choose self-pollinating varieties or parthenocarpic hybrids. Avoid overcrowding, either indoors or in a garden bed.











