- Types and characteristics of plum prunings
- Sanitary
- Rejuvenating
- Thinning
- Formative
- When is pruning recommended?
- In the spring
- In summer
- In the fall
- Basic rules for performing the operation
- For seedlings and young plums
- For a fruit-bearing tree
- For the old plum
- How to design a crown
- In the form of a bowl
- Tiered
- Bushy
- Pyramidal
- Formation of columnar varieties
- How to prune a tall plum tree?
- Do I need to trim the lower branches of my plum tree?
- How to trim water sprouts?
- Caring for plums after pruning
Many gardeners are interested in how to prune plum trees properly. The procedure varies depending on the variety, growing style, and the gardener's preferences. The most popular method is to create a tiered crown. This is used for almost all fruit-bearing trees, including plums. There are also other options for shaping the plant's branches.
Types and characteristics of plum prunings
There are several types of tree pruning, each with its own unique characteristics. These include:
- sanitary;
- rejuvenating;
- thinning;
- formative.
Sanitary
A mandatory annual procedure, especially for older fruit-bearing trees. At the end of the season, after the harvest and leaf fall, remove all dry, damaged, and diseased shoots. Failure to do this will result in more frequent diseases, a dense crown, and reduced yields.
Rejuvenating
This pruning is performed only on mature, fruit-bearing plum trees, those at least 8 years old. This type of pruning extends the plant's lifespan. At the end of the season, ¼ of the tree's branches are pruned. Pruning is performed on one side. Within 4 years, a plum tree can be completely rejuvenated.
Important! Cutting too many branches will kill the plant, as it won't have time to recover in time for the next season.
Thinning
Once a permanent crown has formed, thinning of the branches is necessary. Abundant shoot growth prevents air from reaching the leaves, traps moisture, and blocks sunlight. Such an environment fosters the growth of fungi and putrefactive bacteria, which cause plum diseases. This procedure is performed after harvesting, with every fourth or fifth shoot pruned.

Formative
Before the tree reaches 2.5 meters, both novice and experienced gardeners shape the crown. Branches are pruned to achieve a specific branching pattern. This process begins when the tree is one year old, in the spring, before the sap begins to flow. Branch growth is monitored for the first five years. Branches growing in the wrong direction are pruned immediately.
When is pruning recommended?
Each type of pruning has its own timing, after which the plum tree recovers more quickly. The procedure is performed in spring, summer, or fall. The condition of the branches is monitored throughout the garden.
In the spring
At the beginning of the season, some shoots are removed to shape the crown. Damaged branches are trimmed from older plum trees. The optimal time for this spring procedure is early April, before buds begin to form.

In summer
Summer pruning has its advantages. Pruning is typically done on mature, fruit-bearing plants in July. In summer, the plant has leaves, which make it easier to identify damaged and diseased branches. These branches are often marked by curled and yellowing foliage, and fruit and buds that fall and dry out. Branches showing signs of disease, such as gray coatings, black spots, and growths, are also removed.
In the fall
Sanitary and rejuvenating pruning is performed at the end of the last month of summer, after fruiting. Plum trees expend less energy on fruit formation and new shoots, so they can focus all their energy on recovery after the pruning.
Important! You can prune no more than ¼ of the branching at a time.
Basic rules for performing the operation
Different types of pruning are used for young, fruiting, and mature plum trees. During the first four years of growth, seedlings are shaped, and in subsequent years, the tree's condition is monitored and rejuvenated.
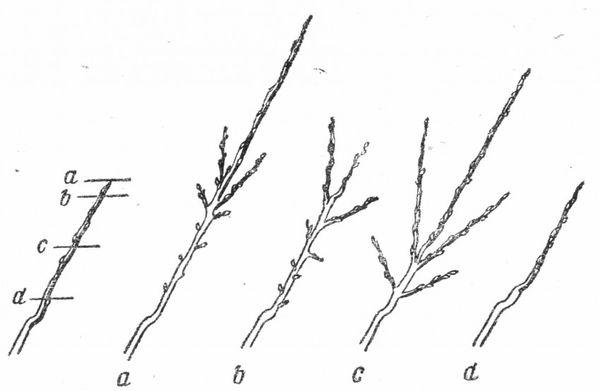
For seedlings and young plums
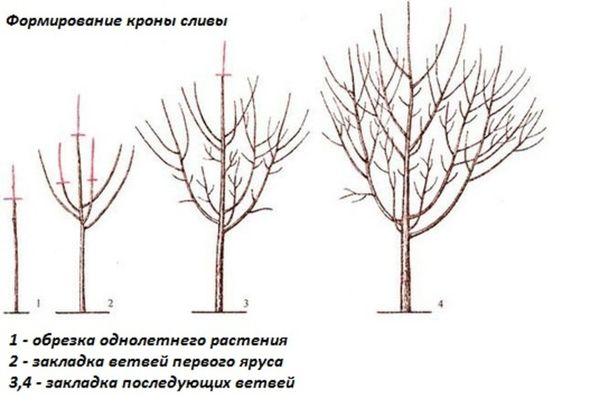
After replanting a young plum tree, the crown is formed starting in the first year of growth. First, the crown is cut off. The remaining branches are shortened by 1/3. The main branch should remain longer than the scaffold branches. This forms the lower tier. To do this, perform the following steps:
- Select 3-4 branches that remain skeletal. The remaining shoots are removed completely down to the base of the trunk. Avoid leaving stumps that are too large or making cuts at a steep angle.
- The branches of the first tier are left 30 cm long.
- The central shoot of the seedling remains 20 cm higher than the others.
- All stumps are covered with garden pitch to prevent infection.
In the second year after planting, the procedure is repeated. To do this, step back 50 cm from the bottom tier. Select 3-4 skeletal shoots and shorten them to 30 cm. Cut the apical branch back by 10 cm. This forms the second tier. In the third year, the third tier is established.
Important! During each operation, remove suckers and competing branches.
For a fruit-bearing tree
After four years of vegetation, crown formation ceases. This procedure is performed for sanitation and to improve the tree's condition. All dry, broken, and rubbing branches are removed. Branches growing above the central shoot, deepening into the crown, are called suckers.

This increases the quality and quantity of fruiting. This procedure is performed twice per season: in the spring, before bud formation, and in the fall, after harvest. For yellow plums, crown formation is extended by one year.
For the old plum
Trees older than 8 years undergo rejuvenation treatments. This involves pruning ¼ of the branches for 4 consecutive years. They are shortened by 10-15 cm, and suckers, broken, damaged, dry, and diseased branches are removed. A plum tree in need of rejuvenation exhibits certain signs:
- crop yields are decreasing;
- the number of fruiting shoots decreases;
- the fruits are localized mainly in the upper part of the plum;
- the number of annual branches decreases.
How to design a crown
Depending on the variety and the gardener's preference, plum trees are shaped into different types of crowns:
- cup-shaped;
- tiered;
- bush;
- pyramidal.
The procedure is different for columnar varieties. It is aimed at maintaining the plum's dwarf stature for easier harvesting.
 Important! Proper crown formation increases yield and makes plum cultivation easier.
Important! Proper crown formation increases yield and makes plum cultivation easier.
In the form of a bowl
This type of crown can be achieved by limiting the growth of the central shoot. It is shortened by 30 cm annually. The plum devotes all its energy to the formation of lateral branches. Gradually, the tree's branches take on a bowl-shaped appearance. This allows the tree to remain low in height, making harvesting and handling easy without the need for unnecessary equipment. Furthermore, the foliage receives maximum light, increasing fruit production.
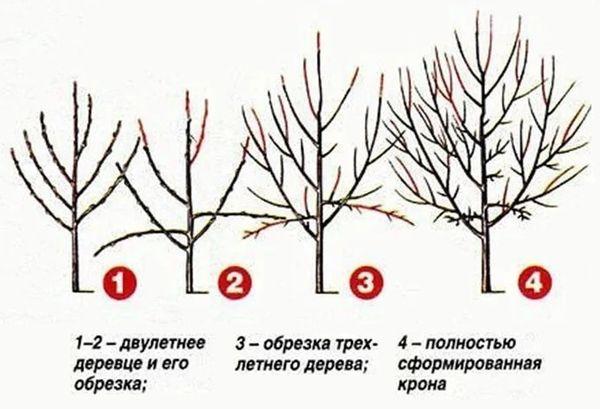
Tiered
This option involves creating four separate tiers on the plum tree. The tiered system is the most popular for fruit-bearing trees. To properly perform this procedure, follow a specific algorithm:
- They retain the central shoot until the 4th year of vegetation.
- On each tier, 3-4 skeletal shoots are preserved.
- All other branches are removed.
- In the 5th year, the main shoot is shortened to increase the growth of annual branches.
Bushy
It's rarely used for plums. It has its advantages in cold regions:
- retains heat inside the crown throughout the season;
- the low growth of the tree does not require special equipment for working and harvesting;
- additional air circulation inside the branches, preventing the formation of rot and fungi;
- takes up little space.
This pruning scheme involves shortening the main shoot as much as possible. A compact tree takes up little space in the garden. The plant's energy is focused on producing lateral branches.
Pyramidal
Trees with this type of crown don't grow very tall. During the first three years, the main scaffold shoot is pruned. The longest branches should be formed on the first tier, shorter on the second tier than on the first, and shorter on the third tier than on the second. From the fourth year onward, irregular branches and suckers are monitored, and the crown shape is maintained.
Formation of columnar varieties
These plum varieties are gaining popularity due to their compact size and narrow crown. The tree's branching pattern is genetically determined. There's no need to train the branches. Sanitary, thinning, and rejuvenating pruning are performed annually.

Columnar plums are grown as ornamental plants. They delight with their abundant blooms in spring and produce sufficient fruit for fresh consumption. They are not suitable for commercial cultivation, as they do not produce high yields.
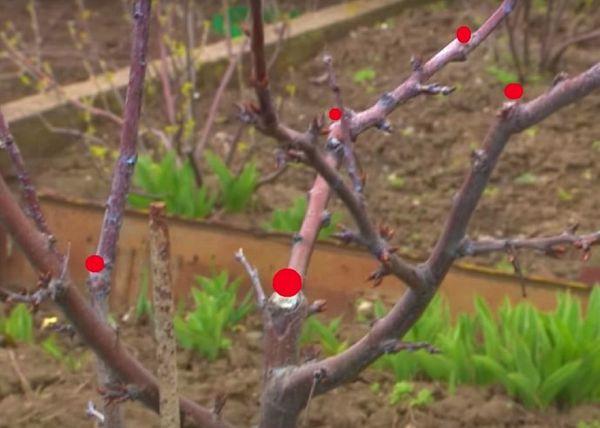
How to prune a tall plum tree?
If you don't work on shaping the crown of a young tree from the start, it can reach 8 meters in height by its fifth year. This complicates harvesting and tree maintenance. To improve the tree's quality, you need to shorten the central shoot. If the plum tree is less than 10 years old, this procedure is performed within one season. To do this:
- The central branch is cut to a length of 2.5 m.
- Lateral shoots are shortened to the same length.
- Remove shoots, damaged, dry and broken branches.
- All cuts are sealed with garden pitch.
By the next season, the plum tree will begin to grow lateral branches and produce more fruit. For plants older than 10 years, this process is carried out gradually. Within 3-5 seasons, the plum tree will reach an acceptable size. To achieve this, the central and skeletal branches are shortened by 30 cm each year. At the same time, a sanitary treatment is carried out.
 Important! Tall plums produce a smaller harvest.
Important! Tall plums produce a smaller harvest.
Do I need to trim the lower branches of my plum tree?
Gardeners have a rule. All branches below the main shoots are removed. This also applies to basal shoots. All branches are removed completely. The cut areas are sealed with garden pitch. This procedure is performed every year at the beginning and end of the season. All excess shoots take up some of the energy the plum tree would otherwise use to form fruit.
How to trim water sprouts?
Water suckers are vertical branches that do not bear fruit. They are pruned throughout the season, reducing yield. Many gardeners prefer to train these branches to grow horizontally. This encourages fruiting. This is achieved by using guy ropes and weights secured to the water suckers.
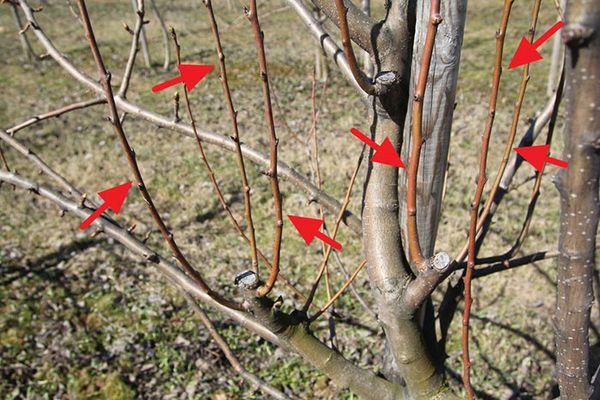
Active growth of vertical branches begins after pruning. Increasing their number significantly thickens the crown, draws sap from the plum tree, and reduces the yield.
Caring for plums after pruning
To help plum trees strengthen after pruning, certain procedures are necessary. For new growth, they require additional nutrients. Care includes the following:
- All cut areas are coated with garden pitch, brilliant green solution, and copper sulfate to prevent infection from getting under the bark.
- Mineral fertilizers containing nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are applied. Nitrogen fertilizers are used only after spring pruning.
- Water the plum tree around the trunk. Use 4-6 buckets of water per young plant, and 8-10 buckets per mature, fruiting plant.
- The tree trunk circle is mulched with straw, moss, wood shavings, and chopped grass.












Is this really that critical? I've always only removed dead branches, and I certainly haven't shaped the crown, as it grows normally without it and looks just like the pictures in the article.
How could air access be reduced or could yield be affected? The canopy isn't that dense there, actually.
Well, this is my opinion and it may be wrong, I won’t argue.