- What is late blight?
- Causes of the disease
- Symptoms and signs of the disease
- Methods of struggle
- Chemicals
- "Hom"
- Furacilin
- Fitosporin
- Trichopolum
- Metronidazole
- Ordan
- Folk remedies and recipes
- Milk solution
- Brine
- Copper sulfate
- Straw tincture
- Yeast against late blight
- Copper wire
- Iodine for late blight
- Ash solution
- Addition of ash
- Tobacco
- Sour milk whey
- Processing technology
- Varieties resistant to infection
- Possible mistakes in fighting the disease
- Dealing with damaged tomatoes
- Can you eat tomatoes with late blight?
- How to protect harvested tomatoes from late blight?
- Prevention of late blight on tomatoes
- In open ground
- In greenhouses
Late blight is often found on tomatoes, and gardeners wonder how to combat the disease. Late blight develops in the second half of summer. Experienced gardeners recommend using both folk remedies and chemicals.
What is late blight?
Tomato late blight is a fungal disease. During the winter, the parasite's spores burrow into the soil, surviving low temperatures. With the arrival of spring, they awaken and begin active growth.
A detailed description of late blight helps gardeners understand that this is the disease that infects tomatoes. The spores affect absolutely everything related to gardening:
- seeds of culture;
- tops;
- live on the walls of the greenhouse;
- live on garden tools.
Late blight is more aggressive in cold and damp weather. It primarily develops in tomato plants where fresh air is poorly supplied. Late blight spreads rapidly in response to temperature fluctuations, inadequate plant care, and in plants with a weakened immune system.

Causes of the disease
Before treating late blight, it's recommended to identify its cause. The disease affects tomatoes for the following reasons:
- Planting tomatoes near potatoes.
- Cold and rainy summer.
- Irrigation of tomatoes and frequent watering.
- Lack of nitrogen in the soil.
- Lime in the ground.
- Tomatoes lack copper, potassium, manganese and iodine.
It has been proven that late blight develops in potato tubers and only then spreads to tomatoes. Knowing the cause allows you to choose the right method of controlling the disease. By regularly monitoring the condition of tomato plants, you can prevent the disease from spreading.
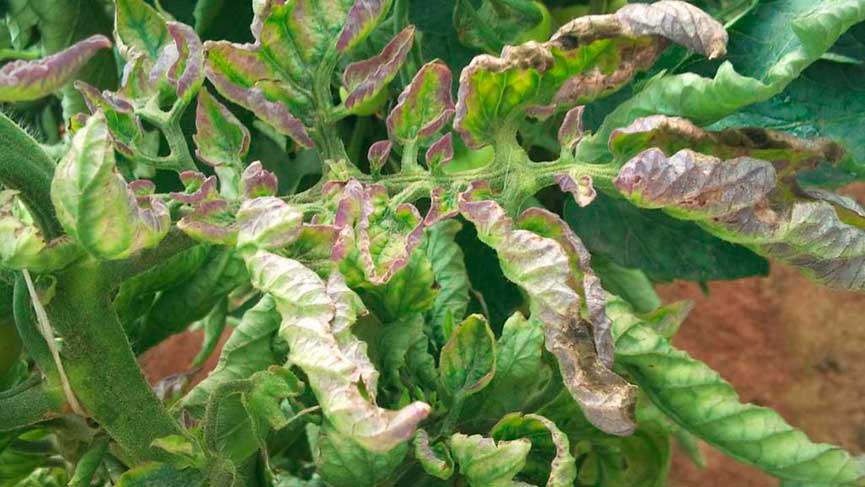

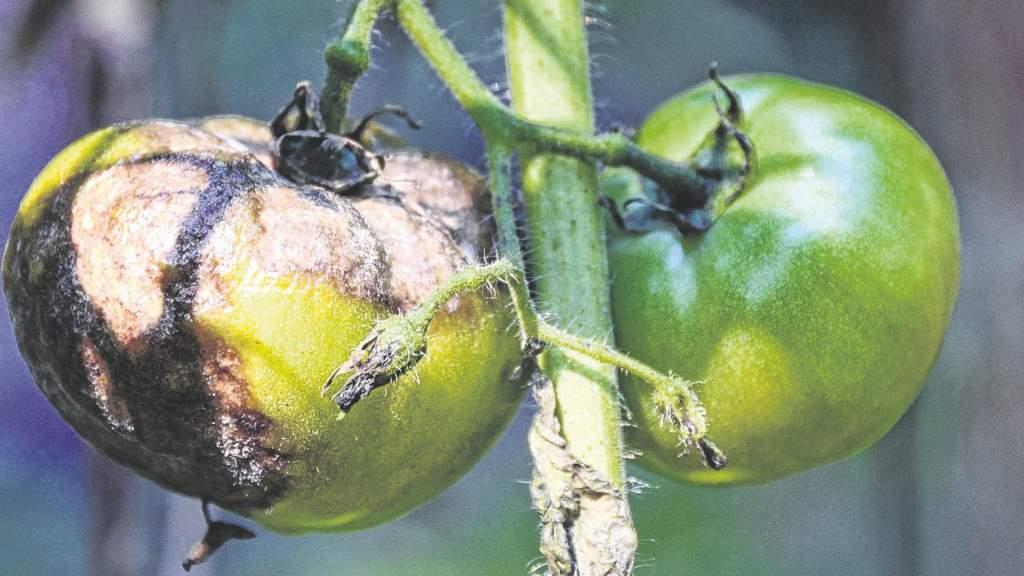
Symptoms and signs of the disease
Phytophthora is identified by brown spots that initially appear on the leaves. Gradually, similar spots appear on the stems and fruits. The infection begins on the underside of the leaf.
The spots vary in shape and size. At the initial stage of late blight, a whitish coating appears. Over time, the tomatoes are affected through the stem.
If clean fruit is picked from diseased bushes, it will become spotted during storage. The spots are a deep brown color. Late blight can deprive a gardener of a harvest in 5-6 days.
Methods of struggle
Today, there are two known methods for treating late blight:
- folk;
- chemical.

The first method is based on food products. Everyone is familiar with them, as they are constantly encountered. The second method involves the use of substances of chemical origin.Treatment begins with folk remedies. If positive results are not achieved, chemical treatments are used.
Chemicals
Gardeners choose products that provide maximum effectiveness after processing tomatoes.
"Hom"
This is a contact-action product. Its active ingredient is copper oxychloride. It acts on the surface without penetrating into the fruit or leaves. "Hom" is used not only for treatment but also for prevention. Spraying with the product is repeated up to six times per season. It is not washed off by rain and remains effective for 14 days after treatment. It is recommended to refrain from using the product one month before harvest.

"Hom" is available as a powder that is diluted with water according to the instructions. Spraying is done in sunny weather, morning or evening. When working with the product, wear protective clothing. Do not store the prepared solution.
Furacilin
This antibacterial product is intended for human use, but gardeners successfully use it to treat late blight on tomatoes. Furacilin is convenient because it can be easily stored as a ready-to-use solution throughout the summer. Its bactericidal properties prevent it from spoiling.
The recipe is simple. Crush 10 tablets and add 10-12 liters of water. Spray before flowering, when fruit sets, and during tomato ripening. The product is safe for humans.
Fitosporin
This medication belongs to a group of biological pesticides containing bacteria. It can be combined with other medications. It eliminates late blight and prevents its recurrence. After spraying with Fitosporin, beneficial microorganisms penetrate the plant tissue and destroy the fungus. The medication is not harmful to humans. Tomatoes are eaten after treatment, after being washed in warm water.
When preparing the solution, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- The liquid should not come into contact with metal. Plastic is preferable.
- Water for preparing the solution should be within 35 °C.
- To activate beneficial bacteria, the liquid is kept in the sun.

You can get rid of late blight by repeating the spraying every two weeks. The entire plant, not just individual parts, should be treated. The treatment is repeated after precipitation.
Trichopolum
A product with antifungal and antimicrobial properties. It is used for human treatment. It has recently come into use among gardeners. Two tablets are required per 1 liter of water. Tomatoes should be sprayed every two weeks. Since the solution does not linger on the surface of the plant's leaves, treatment is repeated after rain.
Metronidazole
It is an analogue of Trichopolum. The instructions for preparation and use are the same. It differs from Trichopolum in price.
Ordan
The product contains two active ingredients: cymoxanil and copper oxychloride. It penetrates the plant and remains on the surface. The preparation method depends on the intended use—treatment or prevention.
Potatoes are treated simultaneously with tomato spraying. This procedure is especially important if the two crops are planted close together. After treatment with "Ordan," the fruits should not be eaten immediately. It is recommended to wait a week.
"Ordan" is hazardous to humans. To prevent the risk of allergic reactions, it is recommended to wear protective clothing. The substance should be diluted and used according to the instructions.

Folk remedies and recipes
Unlike chemical treatments, they don't act as quickly. They're considered a gentler method not only for plants but also for the human body.
Milk solution
The product has an important property in the fight against such diseases: it suppresses pathogenic flora. A solution made by mixing with water and other components helps combat late blight. It is also used as a preventative measure.
Brine
A must-have in every kitchen, it's used solely as a preventative measure. Add 250 g of salt to 10 liters of water. Spray the plants with the resulting solution, and repeat the process after precipitation.
 When salt comes into contact with the crop, it covers its parts with a white coating, which prevents fungus from penetrating into the plants.
When salt comes into contact with the crop, it covers its parts with a white coating, which prevents fungus from penetrating into the plants.
Copper sulfate
Another way to protect green plants from late blight is with copper sulfate. Dissolve 50 ml of liquid soap and 1 tablespoon of copper sulfate in 10 liters of water. The copper combats the fungus, and the soap helps the solution stay on the plant longer.
Straw tincture
To prepare the solution, take rotted hay that has begun to rot. Add 1 kg of the hay to water. Leave the container to steep in a warm place with 100 g of urea added. After three days, strain the liquid. Spray the bushes with the mixture. Bacillus subtilis, introduced into the solution along with the hay, prevents the development of late blight on tomatoes.

Yeast against late blight
This baking ingredient is applied at the first signs of late blight. The solution is prepared during the fruit set period. 100 g of yeast is dissolved in a bucket of warm water, after which the plants are sprayed.
Copper wire
Late blight does not tolerate copper, as it is lethal to it. The method of application is very simple. A small piece of wire is wrapped around the stem above the soil surface. A more effective method involves piercing the plant in the same spot with the wire, and bending the ends toward the ground. This method is suitable only for plants that are sufficiently developed; otherwise, the bush will die. Copper strengthens the plant's immune system and prevents the spread of disease.

Iodine for late blight
The product is used in two versions:
- solution;
- undiluted.
In the first case, iodine, like other components, is mixed with water. The resulting liquid is sprayed on the crop. The second option is more suitable for greenhouse conditions. Open jars of iodine are placed throughout the room.
Ash solution
Ingredients for preparing the product:
- 10 liters of water;
- 5 kg of ash.

To prepare the solution, dissolve the ash in water. Leave the container for three days, stirring occasionally. Add another 20 liters of water and liquid soap to the prepared solution. The amount of prepared solution is sufficient for the entire season. Spray the plants three times: after planting, before flowering, and after fruit set. The solution stores well in a cool, dark place.
Addition of ash
This method doesn't require preparing a spray solution, making it easy to use. To do this, sprinkle ash on the soil between green tomato plants a week after planting. Watering begins after this. Tomatoes require a second application when fruit set.
Tobacco
Tobacco dust is added to the ash-based solution or replaces it entirely. One cup of the mixture is sufficient for one spraying. For the application, use a sprayer, wearing a respirator and protective goggles.

Sour milk whey
Dairy products have virtually no effect. Whey is the most effective. The ratio of milk to water should be 1:1. The mixture should be left to steep before use. Whey is a natural product and completely safe for living organisms. Therefore, whey spraying can be performed daily.
Processing technology
Processing rules:
- The time for spraying is morning or evening.
- It is preferable to choose clear weather without wind.
- When working with toxic drugs, it is essential to use protective equipment.
- For the preparation of chemical solutions, choose containers made of wood, glass or plastic.

Preparing the solution is the initial step in fighting late blight. The spraying will be effective if all steps are followed correctly. Otherwise, late blight will ruin the tomato crop.
Varieties resistant to infection
There are no crops with complete resistance to the disease. To minimize the risk of late blight, it is recommended to choose hybrids such as Zhavoronok F1, Yagodka, De Barao, Pink Dwarf, and others. You can avoid widespread late blight infestations on tomatoes by planting early varieties.
Possible mistakes in fighting the disease
During the peak of the disease's development, watering tomatoes is prohibited, as this makes the disease even more aggressive. Combining several treatments, especially chemical ones, is not recommended for late blight treatment. The most common and widespread mistake of a gardener is the lack of preventive measures.

Dealing with damaged tomatoes
When late blight rages across a plot of land, gardeners wonder: what to do with damaged tomatoes?
Can you eat tomatoes with late blight?
If the fungus has only affected the green part of the fruit and hasn't spread to the fruit, they can be eaten after cooking. Tomatoes with black spots should not be eaten, even if they are removed. The fungal spores have already spread throughout the flesh, even if they aren't noticeable.
How to protect harvested tomatoes from late blight?
You can save tomatoes, both unripe and ripe, by pre-treating them. While green tomatoes can be preserved, red ones should be eaten immediately. They are also used as a base for canning.

Prevention of late blight on tomatoes
Gardeners who have encountered this disease at least once say it's better to avoid it than to fight it. To achieve this, preventative measures are recommended.
In open ground
Preventative measures are taken not only when planting tomatoes but also after harvesting. Any remaining tops are pulled out and burned. Under no circumstances should they be left on the plot. The soil is also carefully managed after harvest. Sand is added to balance the soil composition if excess lime is detected. At the beginning of the new season, the soil is treated with a solution of potassium permanganate.
In greenhouses
Preventive measures taken:
- It is unacceptable for seedlings to be located next to weeds;
- every new year tomatoes are planted in a new place;
- watering should not be abundant;
- It is forbidden to add nitrogen fertilizers to the soil too often.
If you can't avoid late blight on your tomatoes, you need to prepare for a long battle. Late blight is difficult to eradicate. You could save part of your crop or lose it entirely.











