- Features of structure and flowering
- Benefits of using in landscape design
- The most beautiful and popular varieties
- Green Jade
- Coral Altar
- The Kiao Sisters
- The Giant of Hemosa
- The Smell of Lily
- Peach under the snow
- Tender spring
- Agricultural technology and care for tree peonies
- Preparatory work
- Planting dates and patterns
- Seeds
- seedlings
- Watering and fertilizing
- Trimming
- Transfer
- Preparing for winter
- Pests and diseases of tree peony
- Gray rot
- Ring mosaic
- Rust
- Fighting parasites
- Reproduction methods
- By dividing the bush
- By cuttings
- Layering
- By vaccination
- Breeding from seeds
- Difficulties encountered when growing a peony tree
The tree peony is a relative of the herbaceous peony. Its native land is China. Its woody stems with flowers adorned imperial palaces. This perennial has undergone significant changes since ancient times thanks to English breeders. Varieties with gigantic flowers and unusual fragrances have been developed. Despite their short flowering period and susceptibility to fungal diseases, landscape designers and gardeners have come to love these shrubby varieties for their fantastically colored buds.
Features of structure and flowering
External differences of the tree peony:
- height from 80 centimeters to 2 meters;
- rigid trunk with straight shoots;
- dense light brown bark;
- spherical shape of the bush;
- leaves are pinnate, with a fibrous pattern;
- flower diameter - from 12 to 20 centimeters;
- petals are smooth, double, semi-double;
- the color of the buds is single-color or two-color.
Tree peonies bloom earlier than usual. The flowers of hybrid varieties are yellow, a color not found in herbaceous species. The bloom period lasts 2-3 weeks. Buds form at the ends of the flowering shoots.
Varietal differences become apparent with subsequent blooms. Therefore, the first flower on a young seedling is pruned immediately after it opens.
Benefits of using in landscape design
The tree peony has three advantages:
- suitable for planting in groups and single bushes;
- universal for creating prefabricated compositions and placing individual color accents;
- conveys the concept of the garden not only with exotic flowers, but also with an original aroma.
Tall, spreading varieties should be planted as individual bushes, next to a gazebo, a bench, or at a bend in a path. Their irregular shape will create a mysterious atmosphere. Low-growing varieties are planted as hedges along the edges of alleys, paths, and along the perimeter of a property.
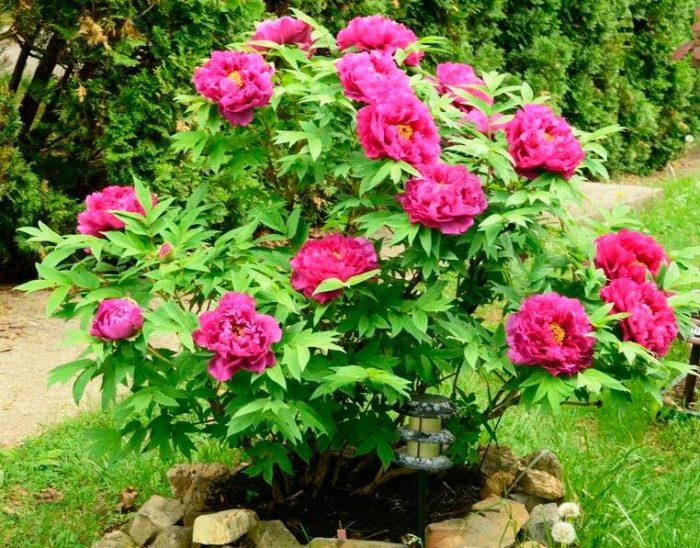

The scent of peonies and other plants combine to create a special garden aura. The resinous scent of conifers, combined with the scent of flowering shrubs, will fill the garden with a calming fragrance. Peonies also pair favorably with elderberries and clematis.
The most beautiful and popular varieties
Tree peonies are classified by region of origin:
- European-Chinese - flowers with a bright pink spot at the base of the bud, the main colors are white, purple, crimson;
- Japanese - flowers are double, semi-double and smooth, rising above the leaves;
- Peony Delaway hybrids - bush shape similar to herbaceous relatives, atypical yellow bud color, low-growing.
There are also white and classic Chinese varieties.
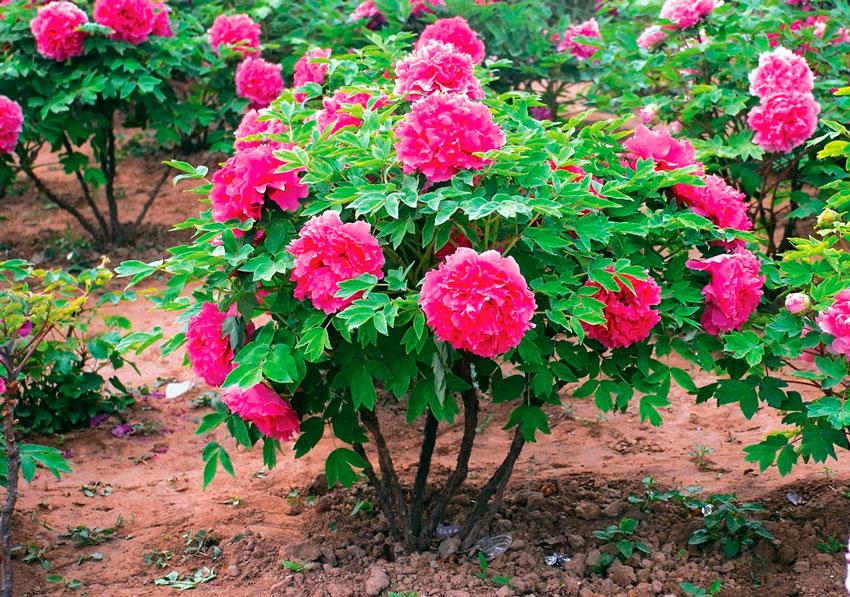

Green Jade
The double, rounded flowers consist of white petals with a green edge. This late-blooming variety grows up to 2 meters in height.
Coral Altar
A profusely blooming red variety. The petals are pink at the edges and darken to a burgundy hue toward the center. Large buds with double petals exude a sweet fragrance.
The Kiao Sisters
A large-flowered, bicolor Japanese variety. Part of the petals of each bud are creamy white, while the rest are red. The flowers are 16 centimeters across and have a rose-like shape.
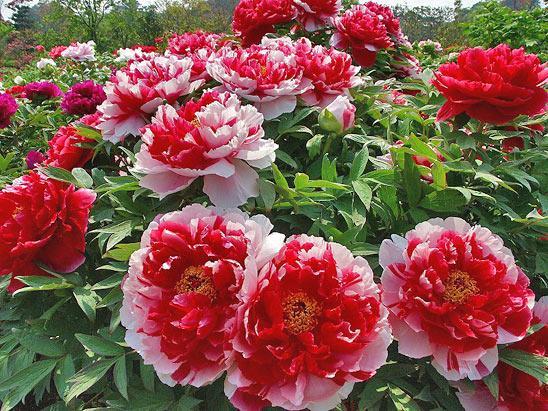

The Giant of Hemosa
A double, large-flowered variety. Pink-red buds with a bright yellow center reach 16 centimeters in diameter.
The Smell of Lily
A tall, white variety with lush, semi-double petals and a golden center. The open buds resemble chrysanthemums.
Peach under the snow
Lush, double buds remain on the bushes for two weeks in late May. The pale pink at the edges of the petals fades to a rich scarlet toward the center.
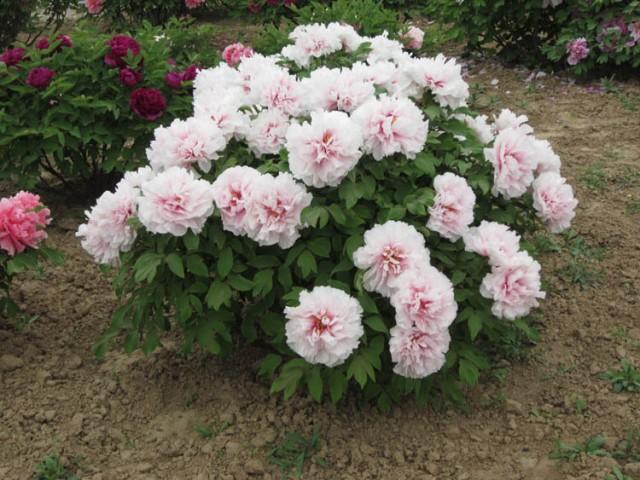

Tender spring
The ruffled flowers combine vibrant and pale shades of red and pink. The buds measure 20 centimeters across. This variety is suitable for cutting.
Agricultural technology and care for tree peonies
For annual blooming, planting time and a well-chosen location are crucial. Tree peonies thrive outdoors throughout the year. During this period, they should not be replanted, otherwise they will not bloom.
Preparatory work
Site preparation begins a month before planting:
- choose a level place, without trees;
- soil - dry, neutral acidity;
- planting holes are dug at intervals of 1-1.5 meters, with a depth and width of 60 centimeters;
- the excavated soil is mixed with peat and compost;
- A layer of sand is poured onto the bottom for drainage.
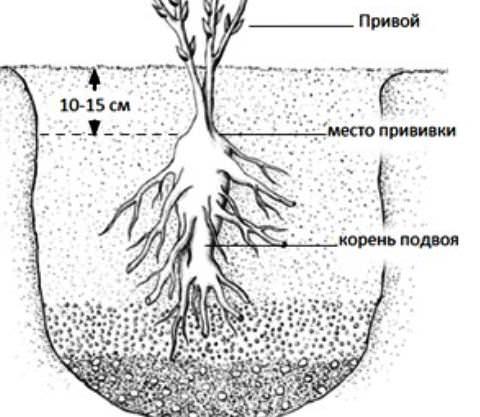
Before planting, add 500 grams of bone meal, 20 grams of ferrous sulfate, and 200 grams of superphosphate to the hole. Mix the fertilizer with the soil that's then used to cover the seedling.
Planting dates and patterns
Tree peonies are planted in spring or autumn, depending on the type of seedlings.
Seeds
Tree peonies produce seed pods in September. The seeds are planted in seedling trays at a depth of 3 centimeters. The trays are then dug into the garden soil and covered for the winter. Seedlings will emerge in the spring.
Seedlings are transplanted to a permanent location in the second year of growth. When planting, maintain a 1-meter interval.
seedlings
Tree peony seedlings are divided into two groups: those with their own roots and those grafted. The former are grown from seeds or by dividing the bush and are more viable. Grafted plants develop more quickly. However, their base is a herbaceous peony, whose roots grow and rot. These seedlings are sensitive to replanting. They should be kept in the same location for their entire life.

The planting time is selected in accordance with the type of root system of the seedling:
- closed - planted from spring to autumn;
- open - August, September.
Potted seedlings are left with a ball of soil. They take root faster and even bloom the same year if planted in the spring. Young plants with bare roots, when planted in the spring, actively form a crown, but the roots don't have time to develop. As a result, the peonies don't receive enough nutrition to maintain dense foliage and bloom. Over the fall and winter, the plants will develop a strong root mass.
Watering and fertilizing
Tree peonies need to be watered generously. Seven liters of water are poured under the bush each month. To ensure the soil absorbs the moisture completely, it is moistened at dusk. During periods of heavy rainfall, the soil around the tree trunk is loosened.
Peonies are fertilized 3 times a year:
- in spring, before the leaves appear;
- during the period of bud formation;
- in the fall, before wintering.
In early spring, nitrogen fertilizer is applied to the tree trunks, and closer to flowering, potassium and phosphorus fertilizers are added. Foliar mineral fertilizer dissolved in water is also used. Spray the plants with it in the morning or evening.

For better adhesion to the leaves, add 20 grams of grated laundry soap to the fertilizer solution. Before the expected cold snap, feed peonies with bone meal, 200 grams per bush, and wood ash, 300 grams.
Trimming
Flowers appear on older shoots. Therefore, pruning tree peony varieties is limited to spring sanitation and rejuvenation procedures. Branches are shortened to the bud, and damaged shoots are removed. To increase the number of buds, a third of them are cut off before they open.
Every 10 years, the bushes are completely pruned to renew themselves. Undergrowth grows at the base of the herbaceous scions and must also be removed.
Transfer
Only mature, fully grown plants with their own roots are replanted. The best time of year is autumn or winter. For winter replanting, prepare the site in the autumn months. The bushes are pruned beforehand, leaving a third of the shoot length.

Preparing for winter
Selected tree peonies survive temperatures below -20°C (-7°F). Young seedlings and plants in regions with unstable, damp weather will need protection.
How to prepare plants for winter:
- do not water from August;
- organize protection from precipitation, install canopies over bushes;
- loosen the soil around the tree trunks deeply;
- lay peat mulch, 1 bucket per bush;
- at the beginning of October, carry out pruning - leave a third of the length of the shoots;
- Wrap with agrotextile in several layers, but do not tie at the bottom so that the plants receive oxygen.
Instead of agrofibre, young peonies are covered with spruce branches, installed above the seedlings in the shape of a house.

Pests and diseases of tree peony
Fungal diseases are one of the reasons peonies fail to bloom. At the first sign of disease, remove damaged shoots, leaves, and buds and treat the bush with a fungicide or copper sulfate.
In April and August, once every 10 days, carry out preventative treatment of the tree trunk circle with fungicides Skor or Fundazol.
Gray rot
The disease affects young shoots and leaves of tree peonies. Brown spots are a hallmark of gray mold. As the disease progresses, the marks become covered with a gray coating containing visible black dots. These are small myceliums containing spores. If the disease appears during flowering, buds fail to open and also become moldy. Gray mold spreads quickly and spreads to other plants.

Ring mosaic
Signs:
- light and dark spots with a border on the leaves;
- white coating;
- tissue death.
The disease is caused by a virus for which there is no cure. At the first sign of mosaic, the plant should be dug up and burned.
Rust
The disease also begins with brown spots on the leaves. The undersides of the leaves become covered with spore-laden bumps. The plant stops growing and dries up. This dangerous disease can spread throughout the garden during windy weather. The light spores are carried by the wind. On peonies, they can originate from coniferous trees. Rust often affects bush peonies in years with rainy springs or summers.
Fighting parasites
Insects rarely bother bush peonies. Plants are more likely to become infested by nearby trees and flowers. Avoid planting this oriental shrub near anthills and cabbage beds. Otherwise, their leaves will become aphid dens.

Other insects that crawl on peonies:
- bronze beetles - cause the withering of opened buds;
- Nematodes kill the roots of the plant and are recognized by swellings on the trunk and drying leaves.
How to control pests:
- against ants, spray plants with insecticides Absolut, Great Warrior;
- collect beetles by hand and disinfect against larvae;
- To combat aphids, use Aktara 3 times every 10 days.
For prevention, you can use a folk remedy: prepare a tobacco decoction. A kilogram of the herb is steeped in 5 liters of water, infused for 24 hours, boiled for an hour, strained, and diluted with 2.5 liters of water. To make the decoction last longer on the leaves, add 100 grams of grated laundry soap.
Reproduction methods
Tree peonies propagate quickly vegetatively. Seeds are germinated to produce seedlings with their own roots. This process takes 2-3 years. For rapid growth and flowering, division or cuttings are recommended.

By dividing the bush
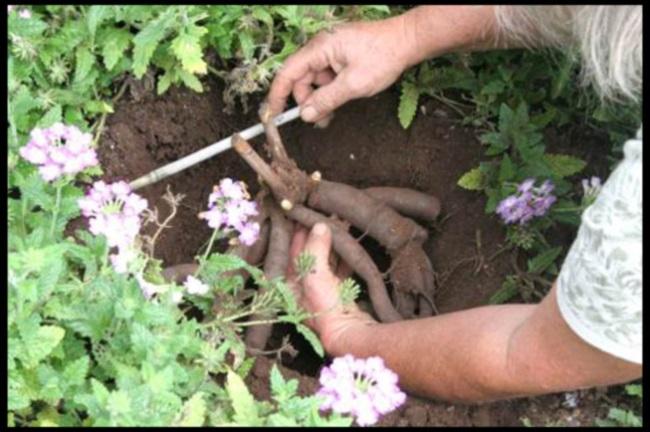
A bush peony is ready for division at 5 years of age. This process begins in August or September:
- dig up the plant;
- separate the parts with roots 10-20 centimeters long and 3 large shiny buds;
- The cut areas are treated with a fungicide and sprinkled with charcoal.
Peony divisions are planted in a pre-prepared place according to the usual rules.
By cuttings
Tree peony cuttings are taken from June to July, in the morning twilight:
- young shoots are cut into pieces with 2 buds and 2 leaves;
- the lower leaf is torn off, leaving the petiole, the upper one is cut in half;
- the end with the leaf petiole is dipped into a root stimulator solution for 24 hours;
- plant in a mini-greenhouse with a peat-soil mixture, deepening the bud by 4 centimeters;
- In containers with cuttings, high humidity is maintained by watering and spraying.

In September, the cuttings begin to root. In mid-October, the mini-greenhouse lid is removed for 30 minutes a day, and then the time spent outdoors is gradually increased. In the spring, the cuttings are transplanted into covered raised beds called nurseries. In the fall, shoots will emerge from the buds. The seedlings will be ready for transplanting into the open ground in their second year.
Layering
The time for propagating tree peonies by cuttings is May, the period preceding flowering.
Stages:
- select an external flexible shoot;
- cut the surface lengthwise, the length of the cut is 10 centimeters;
- treated with a root growth stimulator solution;
- lower the shoot with the cut part to the ground;
- secure with a bracket and sprinkle with soil.
The rooted shoot is watered generously. Roots appear in September. However, the new bush can only be separated the following fall.

By vaccination
Tree peonies are characterized by a long growth period. Own-rooted seedlings begin to bloom 3-7 years after planting. To accelerate development, cuttings of bush peonies are grafted onto herbaceous rootstocks.
Preparations for grafting are made in May:
- dig up the stem with roots and store in a cool place for 2-3 weeks;
- young shoots are cut from the bush;
- each cutting should have 2 buds, 3 centimeters of the shoot are left under the lower bud, 2 centimeters under the upper one;
- the blanks are cleared of leaves.
Peony grafting into a cleft:
- the rootstock stem is cut crosswise and the core is cut out in the shape of a triangle;
- one end of the scion is cut into a wedge shape;
- insert the scion into the rootstock;
- treat the joint with garden pitch;
- secured with a special tape.

Grafting into the butt:
- the rootstock stem is cut at an angle;
- the end of the scion is also cut off;
- combine the blanks and secure with tape.
In the southern regions, peony grafting is done in June, leaving one bud and leaf on the cuttings.
Grafted plants are planted in sand-filled hotbeds, deepening the soil to the bud. The seedlings are placed in the shade and watered generously. In September, the buds of established grafts will begin to enlarge. The seedlings can be planted in the garden and covered for the winter, or left in hotbeds until spring. When planting, the graft site is deepened by 2-3 centimeters.
Breeding from seeds
The collected seeds are dried for three days. To speed up germination, the hard seed coat is filed down. Stratification is also used: seedling trays are buried in the ground for the winter and then transferred to a greenhouse in the spring.

Tree peony seeds germinate only 10 percent of the time. Therefore, for propagating bush varieties in the garden, it's easier to use one of the vegetative methods.
Difficulties encountered when growing a peony tree
The main problem gardeners face is the lack of flowers on bush peonies. The plants are healthy, but they don't bloom.
Mistakes in growing tree varieties:
- Fresh manure is a favorable environment for the development of rot. Of the organic fertilizers, only dry compost can be added;
- dense planting, close proximity - the peony needs a lot of space to grow and bloom in a permanent area;
- premature pruning - a seedling needs a year for the full development of roots and shoots; peonies are pruned in the second year of life in the fall, otherwise they weaken and do not bloom;
- recessed or superficial location of the grafting site - the optimal depth is 10 centimeters.
A common reason for a tree peony's reluctance to form buds is soil conditions. The soil should be kept moderately moist and nutrient-rich according to the plant's growing season. The plant requires phosphorus and potassium for flowering. Nitrogen promotes shoot and leaf growth, but excess nitrogen inhibits peonies' ability to bloom.











