- How is peat formed?
- Peat extraction technology
- Milling
- Lump
- Transitional peat
- Peat as a fertilizer: pros and cons
- Comparison
- With humus and manure
- With black soil
- With chicken droppings
- What is peat used for?
- Properties of peat
- Composition of peat
- Peat acidity
- Degree of decomposition
- Types of peat
- Lowland peat
- High-moor peat
- Transitional peat
- Neutralized peat
- Use of peat
- For the garden
- For the greenhouse
- For the garden
- For plants
- For flowers
- Winter use
- Fertilization of individual crops
- Potato
- Strawberry
- Tomatoes
- Cucumbers
- Cabbage
- Fertilizing soil with peat
- Preparation of peat
- When to apply?
- Dosage
- Mulching with peat
- Soil fertilization
- Organization of peat compost
- Methods
- Spot composting
- Layered
- Peat-based fertilizers
- Peat oxidate
- Peat extract
- An alternative to peat fertilizers
- Manure
- Humus
- Humus
- Bird droppings
- Silt
- Feces
- Sawdust, tree bark
- Green manure
- Compost pits
Many people know about peat from their school years, but not everyone has considered its origins. It's the decayed particles of plants or animals that form in marshy areas under high humidity conditions. How effective is peat as a fertilizer for potatoes and other crops? This article will discuss this and many other aspects of its use.
How is peat formed?
After the death of vegetation and animals living in bodies of stagnant water or swamps, they settle to the bottom, forming biomass through accumulation over many years.
Under the weight of subsequent layers, the formations are compressed; high humidity and limited access of oxygen contribute to the decomposition of the composition with the formation of the specified mineral.
Peat extraction technology
The extraction technology involves several methods. More details are below.
Milling
The deposit is developed using open-pit mining, with the gradual removal of thin layers of deposits in short cycles. It is characterized by the following operations:
- milling the surface layer: a strip no wider than twenty-five meters is cut and dried;
- to increase the intensity of liquid evaporation, the layers are stirred;
- swathing – formation of triangular cross-section rolls from the dried composition;
- removal of compressed fertilizer from the rolls;
- stacking – storing raw materials in stacks;
- insulation – protection from the effects of natural factors.

After harvesting and processing the layer, the sequence is repeated up to fifty times per season. This method is used in the extraction of all types of this mineral and offers numerous advantages, including low labor intensity, low resource consumption, and high product quality.
Lump
Extraction is carried out in two ways:
- excavator - deepening with bucket equipment to the required depth with subsequent extraction of raw materials;
- slot milling – depth no more than 0.4 meters.
The technology involves the following operations:
- extraction of raw materials and their formation into briquettes;
- laying out briquettes for drying in an open area;
- storing dried products in stacks.
It is used for raw materials characterized by a low degree of decomposition and ash content.

Transitional peat
Transitional minerals are associated with groundwater, making extraction difficult. Developing such deposits requires additional costs for dewatering, which is associated with greater labor intensity.
Peat as a fertilizer: pros and cons
The use of peat as a fertilizer has the following advantages:
- increasing the looseness of clay or sandy soil;
- improving air exchange;
- enrichment of the soil with useful substances;
- soil disinfection – kills fungi and microbes, being a natural antioxidant;
- protects against the harmful effects of pesticides;
- normalizes soil acidity;
- promotes rapid warming of the soil;
- refers to complex fertilizers;
- good insulation for winter;
- prevents the spread of pests and weeds.

However, along with the advantages, there are disadvantages to using only this type of fertilizer:
- If low-quality fertilizers are used simultaneously with peat, the development of crops slows down, even to the point of death;
- use in pure form leads to an increase in soil acidity;
- worsens the properties of loose fertile black soil;
- attracts mole crickets.
Using this mineral alone does not increase crop yields. It is recommended for use in conjunction with other fertilizers to improve the structure of clay soils.
Comparison
Below is a more detailed description of the qualities of peat fertilizer compared to other compounds, and which is better to use in various cases.
With humus and manure
The main difference between peat and the fertilizers mentioned above is its increased acidity, which facilitates its effective use in conditions of poor, non-acidic soils with sandy and clayey composition.

Humus and manure are more versatile and rich in nutrients. However, many are put off by the high pest and weed seed content and the need for additional soil preparation.
With black soil
Chernozem is characterized by high fertility and a granular, lumpy structure. Its application is similar to peat; both are mixed with sand and loam to improve the soil structure. However, chernozem is more suitable for normal plant growth. It retains moisture better, contains more plant-available nutrients, and has a more balanced pH. When choosing from these fertilizers, the appropriateness is determined by the intended use.
Black soil is used for sowing over large areas, peat – in greenhouses and hotbeds.
With chicken droppings
Chicken manure has the highest concentration of nutrients of any organic fertilizer, so it's not applied pure, but diluted as a top dressing. Compared to peat, its application requires more labor, and excessive concentrations can damage plants.

What is peat used for?
The unique qualities of this mineral allow it to be used for various purposes:
- In the energy sector – as a fuel in power plants and boiler houses. Its lower energy intensity is offset by its greater environmental friendliness and high production costs;
- in agricultural activities – as an additive to other fertilizers, increasing their effectiveness and improving soil structure;
- In animal husbandry – as bedding for cattle and poultry. It retains heat and absorbs moisture. It is used as a water filter for animals and aquariums, purifying and normalizing the acid balance of the liquid;
- in construction – as a moisture- and heat-insulating material;
- in the alcohol industry - in pure form for the production of whiskey and drying malt;
- in medicine – for mud baths and the production of certain medicinal products;
- for environmental purposes – in wastewater treatment plants, as filtering and sorbing elements, and to eliminate the consequences of environmental disasters.
The unique chemical composition of the substance ensures its versatility and indispensability in some areas of life.

Properties of peat
The beneficial qualities, composition, and properties of this fossil have been studied in detail over the course of its long history of use. This substance is an important component of the natural ecological balance, accumulating organic decay products and combining them with atmospheric carbon.
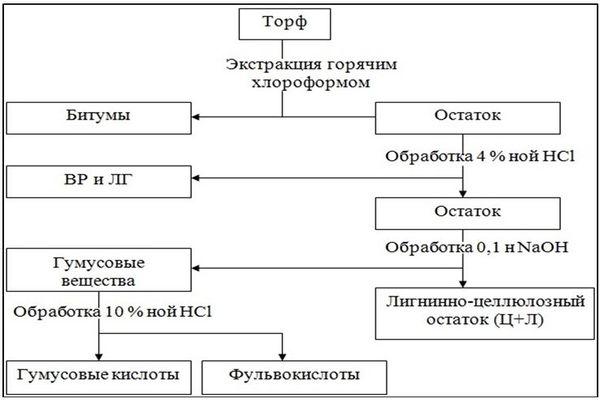
Composition of peat
The substance is characterized by the content of:
- biological residues;
- mineral components;
- humus.
The degree of ash content is determined by mineral components, and the color shade is determined by humus.
There are three types of state of the said fossil: liquid, gaseous and solid.
Peat acidity
The acidity values of the mineral vary within the range:
- for lowlands: 5.5-7.0 pH – slightly acidic or neutral environment;
- for transitional: 3.2-4.6 pH – slightly and moderately acidic environment;
- for top-dwelling: 2.6-3.2 pH – highly acidic environment.
Please note: If the acidity is less than 5.5%, using the substance in its pure form is not recommended.
Degree of decomposition
There are three degrees of decomposition of this natural fertilizer (in percent):
- low - up to twenty; used as bedding for animals, thermal insulation material for greenhouses, as raw material for hydrolysis;
- average - twenty-one to forty; purpose - fuel, production of complex fertilizer compositions;
- high - over forty-one; the widest scope of application in various industries.
The degree of decomposition determines the scope of application of the composition.

Types of peat
Depending on the conditions of formation of the biological mass that serves as the basis for the formation of the fossil, several of its varieties are distinguished.
Lowland peat
It is formed from a mixture of tree and shrub species native to lowlands, river mouths, ravines, and hillside valleys. Compared to other varieties, it has the highest nutrient content and a wide range of uses.
High-moor peat
Contains the remains of coniferous trees growing on elevated sites or along watersheds. The composition is characterized by a low degree of decomposition of its components.
Transitional peat
An intermediate stage between the above-mentioned varieties. Contains from ten to ninety percent weakly decomposed upland vegetation, the remainder being lowland vegetation.

Neutralized peat
It is obtained by mixing high- and low-lying varieties of the mineral with lime, clay, or dolomite to neutralize the acidic environment. Another method of neutralization is by mixing high-lying varieties with low-lying varieties.
Please note! Using both upland and lowland varieties in their pure form is not practiced.
Use of peat
In agricultural engineering, this mineral has found a wide range of applications. It improves soil fertility and structure, making it particularly effective for loamy and sandy soils. Further details on its use are provided below.
For the garden
A thin layer of the substance, evenly distributed over the area, is dug to a depth of ten centimeters. This low-lying variety of the fossilized material is used for mulching in the spring, along with nitrogen fertilizers. After harvesting, the component is applied to the upper soil layers.
In addition to improving the soil structure and enriching it with nutrients, this helps prevent unpleasant odors from compost and manure and disinfects the area from pests.
Application rates are from twenty to thirty kilograms per square meter for the lowland variety of fossil.
For the greenhouse
In this case, the high-moor variety is used as a substrate with mineral fertilizers. A single application can last for over three years. Liming maintains the required acidity level.

For the garden
For gardening, rotted compost is used. It is stored for several years, periodically loosened and turned to speed up the maturation process. Mixed with humus, it matures faster. For application, it is diluted with ash or lime.
For plants
In addition to applying the fertilizer to specific areas, the composition is also applied to the trunk area of trees and shrubs. The porous fibrous structure ensures the absorption of nutrients and moisture retention.
For flowers
Peat compost fertilizes the soil and prevents rotting. It's an excellent winterizer for perennials.

Winter use
It's used as an insulating material to protect crops during the winter. Mulch, containing sawdust, manure, tree bark, and leaves, is applied to plants to prevent damage during the most severe frosts.
Fertilization of individual crops
A little more detail about the use of this product for growing various crops.
Potato
It is used in combination with mineral fertilizers in loose, slightly acidic soils. It is applied into planting holes during planting and spread over the soil surface with manure in the fall.

Strawberry
Improves crop fruiting. It's used as a mulch, mixed with sawdust or tree bark at a ratio of 10 to 1. It's added to the hole at planting time and to the garden bed before winter.
Please note: It is not recommended to use the fossil in its pure form due to its high acidity.
Tomatoes
Apply no more than once every two weeks during the season, and place in holes before planting.

Cucumbers
The raw material undergoes preliminary neutralization and is used as part of compost to fertilize the soil.
Cabbage
Use only with acid-reducing measures. Apply directly to the hole before planting.
Fertilizing soil with peat
Some information about the procedure for preparing and applying peat fertilizer.
Preparation of peat
Highly acidic peat can adversely affect soil quality, so it undergoes additional treatment before application. High-moor peat is neutralized, while low-moor peat is aerated and crushed.

When to apply?
The composition is applied in the spring, when planting crops directly into the holes, during the season - in the aisles, in the autumn - the high-moor variety, mixed with the main fertilizer.
Dosage
Application rates are from twenty to thirty kilograms of neutralized or low-lying substance per square meter of area, and up to sixty kilograms when developing virgin land.
Mulching with peat
Only low-lying and transitional varieties of fossil soil with low acidity are suitable for mulching. The mixture is applied in a layer of one to seven centimeters, depending on the intended use. During sowing, the thickness is minimal. Pre-winter mulching is most common and is used without regard to standards for thermal insulation. It is also mixed with humus, sawdust, and black soil.
Soil fertilization
Before using the substance as a fertilizer, it is necessary to carry out measures to neutralize the harmful effects of the substance:
- keeping in a well-ventilated cool place to reduce the concentration of toxins;
- Ensuring the required level of humidity. An overdried composition will not absorb and retain moisture sufficiently.
Please note! Using peat fertilizer is ineffective on fertile black soil. Such compounds should be applied to improve the structure of clay and sandy soils.
Organization of peat compost
The most preferred raw material for preparing peat compost is one with a moisture content of approximately 70 percent. The ratio of the components is determined by the time of application: in equal parts in winter, and in a one-to-four ratio in summer.
The composition additionally includes tops, weeds, sawdust, shavings, food waste, and manure.
Methods
There are several ways to prepare compost.

Spot composting
This is most often done in winter. A half-meter-thick layer of fossil material is covered with a continuous or discontinuous layer of manure up to 0.8 meters thick and sealed with peat on each side. The work is carried out during a thaw.
Layered
This is done year-round, as needed. A half-meter-thick layer of fossil fuel is applied in a five-meter strip and alternated with manure to form a two-meter-thick stack, topped with a peat coating.
Peat-based fertilizers
In agricultural production, fertilizers prepared on the basis of this fossil are used to enrich the soil with nutrients.
Peat oxidate
An environmentally friendly product that accelerates crop growth. Effective for tomato seedlings and other plants during the development period.

Peat extract
The production method involves electrohydraulic processing, enriching the nitrogen content. It is used not only to improve soil but also to enrich it with nutrients.
An alternative to peat fertilizers
Along with this mineral, many other nutrient compounds are used in plant growing. Below is a more detailed discussion of alternatives to peat-based fertilizers.
Manure
The basic and most popular organic fertilizer. Used for all crops, it enriches the soil with nutrients, but it attracts pests and promotes weed growth.
Humus
The main organic component of soil, added to improve its structure and properties during crop cultivation. It consists of 90 percent organic matter and significantly impacts soil fertility.
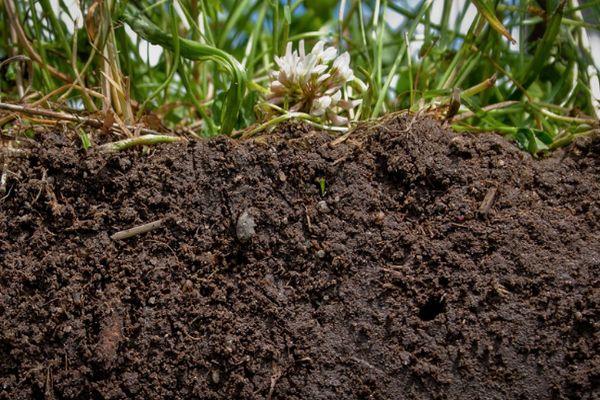

Humus
This is rotted manure, ready to use as fertilizer. It can be applied in winter, in spring, before planting, or throughout the season.
Bird droppings
One of the most concentrated types of organic fertilizer. It should not be used in its pure form. It is diluted in water and most often used as a plant food during the growing season.
Silt
Lake silt is a highly effective agricultural tool, increasing soil fertility, stimulating crop growth, and acting as a natural antiseptic. It has been used in agriculture since ancient times.

Feces
Application methods include industrial scale applications, including calcination, disinfection, and fermentation. They are not used for growing food crops due to their high heavy metal content. They are also available as formulations for lawn grass and ornamental plants.
Sawdust, tree bark
Improves soil structure and can be used for mulching or composting.

Green manure
Specially grown herbs that, when crushed, serve as fertilizer. This environmentally friendly form of soil enrichment with nutrients has found wide application in agricultural production.
Compost pits
During periods of abundant weed growth, weeds are used to prepare compost in specially constructed pits. This allows the waste to be converted into a balanced, nourishing soil, the loose structure of which promotes high moisture retention and increased fertility. Grass seeds should be excluded from the compost to prevent germination; plants containing chemicals are susceptible to fungal and infectious diseases.
As can be seen from the presented material, the use of peat as a fertilizer is quite effective in agriculture; however, this mineral must be used taking into account the soil type, in combination with other components.











