- How to choose the right young seedling
- Lignified
- Vegetative
- Selecting a location on the site
- Preparing for planting in open ground
- cuttings
- Hardening
- Growth activator
- Trimming
- Plot
- Planting dates
- Spring
- Summer
- Autumn
- Fertilizer
- Treatment of seedlings from diseases and pests
- Inventory
- Step-by-step diagram and methods for planting vines
- Depth of the planting hole
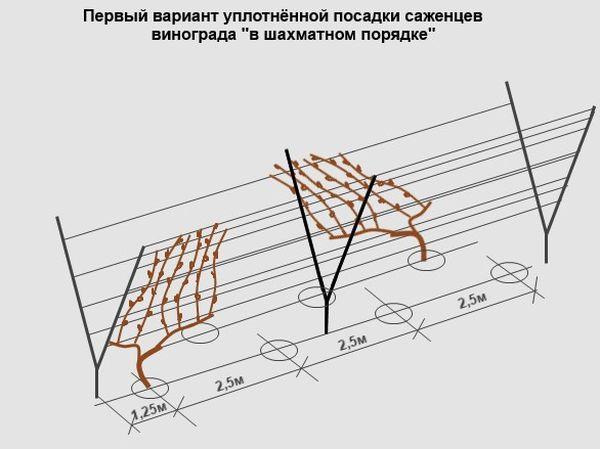
- Distance between bushes
- Drainage
- Rules for care after planting
- Regional features
- Middle zone
- Volga region
- Siberia and the Urals
- Common mistakes
- Tips and recommendations
- Result
Proper grape planting determines not only the plant's growth but also its subsequent yield. Seedlings are selected according to specific criteria, and subsequent care is also crucial.
How to choose the right young seedling
When planting grapes, choosing the right planting material is crucial. The type of cutting determines the growth rate and subsequent development of the plant.
Lignified
This type of seedling is harvested in the fall. Externally, the planting material resembles a bush with several shoots. A cutting with a full root is dug from a mature bush. These seedlings have hidden buds that awaken in the spring and produce new shoots.
Planting material requires proper storage in a cool place throughout the winter. Otherwise, root rot may develop. To preserve the plant, bury it in soil or use special boxes. Fill the boxes with nutritious soil. The seedlings are regularly moistened and checked for pests.
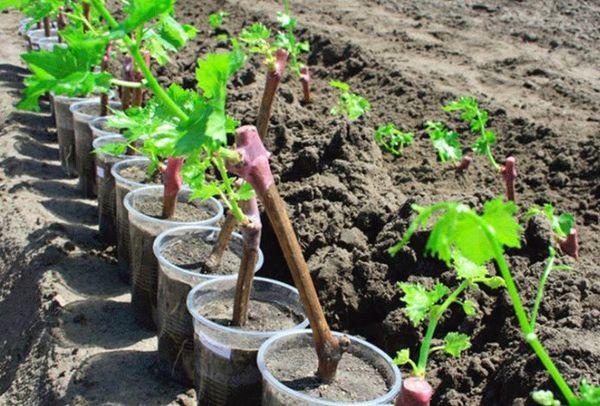

Vegetative
This type of planting material has the following features:
- in spring the cutting is planted in the ground;
- the cutting has a closed root system;
- There are green leaves on the stalk.
These types of cuttings are frequently used. They are suitable for further propagation a year after planting. A large number of cuttings can be harvested from a single mature bush, which is a great advantage for gardeners growing planting material for future sale.
Selecting a location on the site
Choosing the right planting location is important, especially if you're planting cuttings in a small area. When choosing a planting location, consider the following criteria:
- the planting site must be located at least 5 meters from the trees;
- should be well lit by sunlight;
- It is not recommended to plant grapes near buildings that could shade the crop;
- do not plant cuttings in lowlands or areas with close groundwater levels;
- there should be no drafts that could damage the bushes.
Great importance is also given to the soil, which must contain all the useful substances, since the bush is planted in a permanent place.
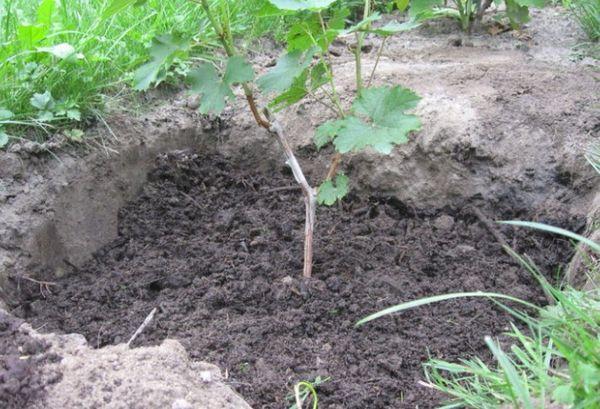

Preparing for planting in open ground
To ensure rapid plant growth, it's essential to prepare the planting material. Failure to do so may result in the cutting's poor adaptation to its new location.
cuttings
To obtain a good bush, select only healthy cuttings. When cut, the root should be light in color; brown or dark roots may indicate a defective cutting. The buds should be firm and not fall off when pressed, but remain intact. If the cutting has exposed roots, remove the lower nodes. Treat the cutting with a potassium permanganate solution to reduce the risk of fungal infection.
Hardening
Cuttings grown from green shoots require preliminary preparation for exposure to sunlight. To do this, follow these steps:
- for 4 days the seedlings are placed under a canopy, the sun's rays should fall in a diffused manner;
- the planting material should be exposed to the sun for 5 days;
- The cuttings are sprayed with water twice a day.
When unhardened cuttings are planted, the plant slows down and may go dormant. If grapes are grown in a greenhouse, regular ventilation and gradual sun exposure are necessary.
 Important: Planting material grown in greenhouse conditions requires several times more hardening than regular cuttings.
Important: Planting material grown in greenhouse conditions requires several times more hardening than regular cuttings.
Growth activator
Before planting, cuttings are soaked for 2 hours in a growth activator. This process speeds up the rehabilitation process in the new growth site and accelerates the formation of new roots.
Trimming
One strong shoot should be left on the cutting; the others are pruned. The shoot should have at least 2-3 buds. All damaged root areas should also be removed to reduce further infection. The cut on the cutting should be at an angle and free of visible damage or rot.
Plot
The area where the grapes will be planted must be prepared in advance. Remove all plants and roots. The soil must be leveled, and all holes and mounds must be removed. Spread humus or manure over the area in an even layer. Thoroughly till the soil. The soil should be light and well-drained.

Before planting, you need to dig holes and prepare a nutrient mixture, which consists of the following components:
- 2 parts soil;
- 1 part peat or humus;
- 0.5 parts of mineral fertilizers.
If the soil is clayey, it is necessary to additionally add 1 part of river sand.
Important: If the soil contains a lot of sand, dig a deeper hole. This will reduce the risk of root washout.
Planting dates
Grapes can be planted in either spring or autumn, but depending on the planting time, certain features must be observed.
Spring
Grapes should be planted in the spring as soon as the soil warms up. This is most often in April. However, in warmer conditions, planting can be done as early as mid-March. When planting in the spring, follow these guidelines:
- provide the seedling with plenty of moisture;
- use a layer of mulch;
- remove weeds.
Grapes planted in spring tolerate a change in growing location better, and there is no risk of cuttings dying from low temperatures.

Summer
Grapevines are rarely planted in the summer. July is considered the best time. The seedlings are planted and watered daily. Also, during the first week, the planting material should be given some shade to prevent leaf burn.
Autumn
Planting seedlings in the fall is rarely done. Small 2-3-year-old bushes are used for fall transplanting. Fall transplanting has some disadvantages, including:
- the plant may not tolerate frost well;
- It is necessary to carefully cover the grapes from exposure to low temperatures;
- shoots may be damaged by rodents.
However, in autumn, planting material adapts to a new growth location much faster, since the roots are formed.
Fertilizer
To ensure the seedlings gain strength quickly, prepare a fertilizer before planting. During planting, add 1 liter of chicken manure diluted with water to the hole. Superphosphate is also added to provide the roots with all the necessary minerals.
 Important: Use organic fertilizers only after the fermentation process. Pure products can damage roots and lead to burns and rot.
Important: Use organic fertilizers only after the fermentation process. Pure products can damage roots and lead to burns and rot.
Treatment of seedlings from diseases and pests
Before planting cuttings in open ground, it's important to pre-treat them against pests. To reduce the risk of problems, treat the seedlings with the following products:
- The first treatment is carried out using Nitrofen. This treatment will eliminate all pests.
- The second treatment is carried out to treat diseases; copper sulfate or Bordeaux mixture can be used for this.
- The third treatment is used to accelerate shoot growth. Special preparations containing a growth activator are used. This procedure is carried out after planting the seedlings in the soil.
The seedlings that are purchased already undergo a processing procedure before being sold.
Inventory
Before planting seedlings, it's necessary to prepare all the necessary equipment. The gardener will need:
- shovel;
- plastic pipe;
- garden shears;
- material for making trellises.

If grapevines are planted near existing supports, they should be supported slightly at first to prevent damage. Once the vines have established themselves, they can be tied to the fence. Before using garden shears and spades, disinfect the equipment to reduce the risk of disease.
Step-by-step diagram and methods for planting vines
To plant grapes, you need to follow the following algorithm of actions:
- Prepare the planting hole. Place a layer of crushed stone at the bottom. Fill a quarter of the hole with the nutrient mixture prepared earlier. Leave the hole for 1-2 days to allow the soil to settle.
- Insert a plastic pipe into the side of the hole. This is done to make watering the plant easier. When watering, the pipe allows water to flow into the soil rather than spreading across the surface.
- Place the grape seedling in the soil and spread out the roots. Cover with soil and compact lightly.
- Place a small structure on top for shade. You can use a container without a bottom, such as an old bucket.
- After 5-6 days, the shading stops and the seedling is exposed to regular sunlight.
When planting grapes using cuttings, it is necessary to follow the following algorithm of actions:
- cuttings of at least 40 cm in length are used;
- the material is prepared 2 weeks before flowering begins;
- Before planting, the cutting is placed in water or growth activator for two days;
- the prepared soil is watered generously and the cuttings are inserted, the lower eye should be immersed in the soil by 5-7 cm;
- A peg must be inserted near the cuttings, which will later act as a support;
- water the cutting and add a little soil on top, thus making a mound;
- When the first shoots appear, they are tied up.
Cuttings need to be watered regularly and the soil loosened to prevent rot and mold. When the first leaves appear, provide shade for the cuttings to prevent sunburn. If replanting the cuttings the following season, use insulation.
Important: Place 2-3 cuttings in each hole. The strongest one is left, and the others are removed.
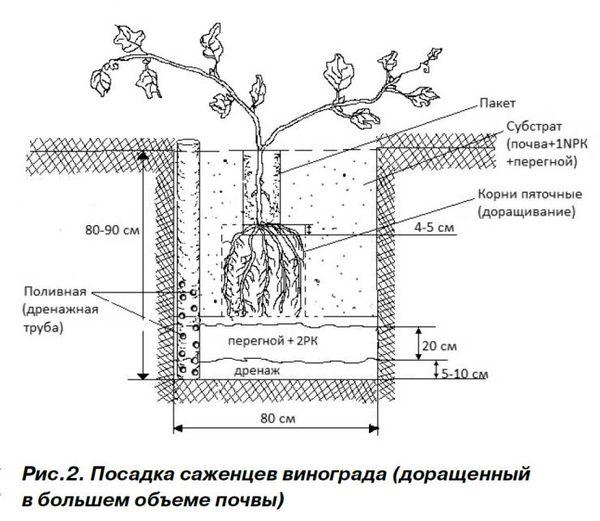
Depth of the planting hole
Gardeners recommend preparing a pit for planting grapes in the fall. In the spring, the pit is fertilized and used for its intended purpose. The pit should be 80 cubic centimeters in size. This size will allow the grape roots to develop actively. The pit is filled with a nutrient mixture, and a small hole up to 45 cm deep is dug in the center. This hole will be used for planting the seedling.
Distance between bushes
The distance between bushes should be at least 2.5 meters. If the bush is planted near a fence, a 50-60 cm gap should be maintained between the fence and the seedling. This will allow the vine to climb the fence without interference.
If using cuttings, plant them in rows, space them at least 20 cm apart. Leave a 1-meter gap between rows. Once the cuttings have rooted, they can be transplanted to the desired locations.
Drainage
Drainage is essential to prevent water from stagnating and damaging the roots. Crushed stone, broken brick, or large rocks can be used for drainage, and a watering tube is also necessary. If gardeners don't use a drainage layer, they must carefully ensure the soil in the planting area is loose and that water is evenly distributed during watering.

Rules for care after planting
In order for the plant to quickly adapt to a new growing location, it is necessary to follow the specific care instructions for the crop.
| Procedure | Characteristic |
| Correct identification of the main shoot | To ensure rapid growth, it's important to identify the strongest shoot and remove the rest. Strong shoots grow lower than others and have no visible damage. |
| Watering | Water the seedlings every 3-4 days. Use plenty of water, at least 2 buckets. To retain moisture in the soil for a long time, it's important to use mulch. This can be a special fiber or sawdust. Once the cuttings have established themselves, reduce watering to once every 6-8 days. |
| Fertilizing and pest prevention | To encourage new shoots to form, nitrogen and potassium are used. In early spring and fall, organic fertilizers such as bird droppings or compost can be used. If necessary, special mineral complexes designed for seedlings and transplants can be used. Young seedlings are often attacked by pests, so it is necessary to treat them with Bordeaux mixture or other special preparations. |
| Removing stepsons | After 2-3 years, shoots appear, which take away a large amount of essential nutrients from the bush. Therefore, it is necessary to regularly monitor and prune unwanted shoots. |
| Loosening | To ensure that the soil is aerated, it is necessary to loosen the soil and remove all weeds before watering. |
| Trimming | This is carried out one year after planting. The vines are shortened and the seedling is given a sanitary pruning. |
| Tying up | Staking is done as needed. Long vines are secured to supports to form a bush. |
By following proper care, you can get a healthy crop in a short period of time without any effort.
Regional features
The region in which the grapes will be grown determines not only the specifics of the choice of variety, but also the care rules.

Middle zone
This region has suitable growing conditions. Grapes grow and ripen quickly. However, to avoid problems, it's important to choose varieties that are frost-tolerant and disease-resistant. These varieties include:
- Long awaited;
- Pearl of Saba;
- Sukrib.
Grapes can be planted outdoors in the fall or spring. Caring for the plant doesn't require any special skills.
Volga region
Temperatures in the Volga region are often low, so careful cover is essential when growing grapes. The most commonly used grape variety is frost-tolerant and disease-resistant.

It is recommended to choose the following varieties:
- Ivanhoe;
- Laura.
Planting can be done in early autumn or late spring, no earlier than mid-May.
Siberia and the Urals
These regions are characterized by harsh weather conditions, but despite this, grapes can still be grown here. To ensure a productive harvest, special varieties should be used, such as:
- Mystery;
- Pinocchio;
- Thumbelina.
To preserve the bushes, careful insulation is recommended, including covering the vines. Planting is done in the summer. Gardeners often grow grapes in special greenhouses where the required temperature is maintained.

Common mistakes
If a crop fails, it's important to carefully review not only the care instructions but also the seedling's planting. Gardeners often make mistakes that can lead to crop failure. Among the mistakes to consider are the following:
- Seedlings purchased from unverified sources often harbor fungus or other diseases. Such planting material often fails to thrive or infects other plants in the area. To prevent this problem, carefully inspect the seedling; if there are signs of disease or pests, it's best to discard it.
- Unknown variety - when purchasing an unknown variety, you may encounter problems such as improper care or unsuitable weather conditions for growing.
- The roots are not trimmed - when planting a seedling, it is necessary to trim the roots, this will speed up the growth of the bush.
- The seedlings are planted in the shade—grapes prefer a sunny, draft-free location. A lack of sun will result in weak vines and a lack of fruit.
- Incorrect planting is a common mistake gardeners make. If planting rules aren't followed, the plant will undergo a prolonged recovery period.
It's also important to follow the rules for preparing planting material. If seedlings aren't treated promptly, they may die later.

Tips and recommendations
To grow a healthy bush, you must follow these tips and recommendations:
- The height of the support should be at least 2-3 meters.
- The plant must be watered regularly with plenty of water.
- Planting grapes near a fence will allow the plant to bask in the sun during the day. At night, the vine will draw heat from the structure.
- To water the cuttings, you can place a plastic bottle with the bottom cut off between the bushes.
- In the second year after planting, the grapes must be treated with a light solution of copper sulfate.
- Stop watering a week before flowering begins. This will stimulate bud formation.
- In order to maintain the size of the berries, it is necessary to regularly thin the bushes and prune the vines.
- Seedlings planted in a greenhouse can be transplanted into open ground in midsummer. To prevent the plant from dying, mist regularly twice a day.
- It is necessary to plant seedlings early in the morning or in the evening.
- Planting different grape varieties requires strict sequence. Each variety ripens at different times and may require specific care.
Following these recommendations is essential for proper grape planting. Improperly planted grapes are often susceptible to disease and have a low yield.
Result
Grapes are a staple in every garden. Their fruits have a distinctive flavor, and the vines can be used as decoration. To ensure a beautiful grapevine, it's important not only to choose the right variety but also to follow proper planting guidelines.










