- Preparing cuttings for grafting
- Recommended timeframes
- How to choose a bush
- What should a mouthpiece be like?
- Size and appearance
- Frost resistance
- Vigorous growth
- Disease resistance
- Developed underground trunk
- Preparing cuttings
- How to store properly
- The main methods of grafting
- In the standard
- Into the cleft
- Half-split
- Drilling
- Copulation
- Budding in the butt
- Right on target
- On the old bush
- To the root
- Re-grafting
- Improved method
- Green to green
- How to graft
- In the spring
- In summer
- In the fall
- In winter
- Conditions of survival
- Aftercare
- Watering
- Hilling
- Loosening and weeding
- Spraying
- Trimming
- Support or trellis
- Pros and cons of the propagation method
- Using grafting shears
- Common mistakes beginners make
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
- Conclusion
Many gardeners plant grapes in their plots to harvest ripe berries in late summer. This garden crop is considered quite capricious and therefore requires proper cultivation to ensure good fruit production. It is recommended to familiarize yourself with the rules and tips for grafting grapes in advance.
Preparing cuttings for grafting
Before grafting, it is necessary to prepare the cuttings that will be grafted onto the plant.
Recommended timeframes
In order for the vaccination to be effective, it is necessary to determine in advance the optimal timing for the procedure. Those who have been growing grapevines for a long time recommend grafting when the outside temperature reaches 15 degrees Celsius. Therefore, the procedure is most often performed in mid-spring.
Some people are rescheduling work until summer and fall. If the vaccination is done in the fall, it will have to be completed by early November.
How to choose a bush
Before grafting the scion, select the rootstock to which the cutting will be grafted. Experts recommend choosing the strongest rootstock in the area, with a well-developed root system that fully utilizes the soil's potential. Avoid choosing plants weakened by pest attacks or disease. Therefore, when choosing a rootstock, pay attention to its appearance to ensure it is disease-free.

What should a mouthpiece be like?
Having selected a suitable bush, they begin to select the cutting that will be grafted onto the plant.
Size and appearance
When choosing a suitable scion, pay attention to its appearance and size. Avoid grafting seedlings with foliage covered in yellow spots or other discoloration. These signs indicate the development of dangerous diseases that will negatively impact yield. The scion should be medium-sized; overly large plants should not be used, as they may fail to thrive.
Frost resistance
It's no secret that grapes need to be frost-resistant to prevent the plant from being damaged by sudden temperature drops. Therefore, it's important to select scion varieties that are frost-resistant and can withstand temperature fluctuations.
Vigorous growth
Grape cuttings can vary in growth rate. Experienced gardeners recommend using vigorous, fast-growing scions. The only drawback of such cuttings is that they will need to be pruned frequently due to the large number of additional shoots that form. If vigorous cuttings are not pruned, the yield of the seedlings will decline.

Disease resistance
Grapes, like other garden crops, can be susceptible to dangerous diseases that can kill the seedlings. To reduce the risk of disease, it is recommended to graft cuttings resistant to common diseases. Grafting diseased scions onto healthy vines is contraindicated, as they will infect the plant. Therefore, seedlings showing signs of developing diseases are never used for grafting.
Developed underground trunk
The underground trunk is the part of the plant that grows in the soil. It develops from a cutting planted in the ground. It is recommended to use seedlings with a well-developed underground trunk, strong shoots, and well-developed adventitious roots. Such plants are considered the most robust, as they are resistant to low temperatures and fungal diseases.
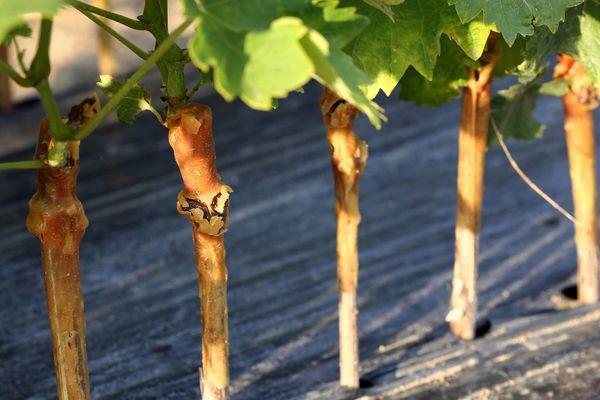
Preparing cuttings
Preparing cuttings for high-quality grafting begins in the second half of autumn. Preparatory work should be completed before the first frost to prevent the plants from deteriorating due to low temperatures. Cuttings are taken from healthy, productive seedlings.

During preparation, the following steps will be performed:
- The cut cuttings are soaked for two minutes in a three percent solution of copper sulfate;
- Spread the soaked stems on a flat surface and dry.
How to store properly
Prepared cuttings should be stored in suitable conditions to prevent them from weakening or spoiling. Some gardeners who have never grafted grapes store them at room temperature. However, cuttings cannot be stored in such conditions for long, as they will begin to wilt. Therefore, experts recommend storing prepared grape stems in a cellar or refrigerator where the temperature will not exceed 5°C (41°F).
The main methods of grafting
There are several grafting methods that you should be familiar with before you begin.
In the standard
Many gardeners use this method of grafting grapevine seedlings. The main distinguishing feature of this technique is that the cutting is grafted onto the upper part of the vine's rootstock. This procedure is most often performed in the spring, before the summer heat sets in.

To graft a plant, you'll need to remove ten centimeters of the topsoil and dig a hole 60-70 centimeters deep. Then, locate the node on the rootstock where the scion will be attached.
Into the cleft
This method is used by almost every gardener, making it the most popular. To cleft graft grapes, follow these steps:
- removing the top layer of soil and digging around the bush;
- cutting off the rootstock to form a low stump;
- two cuttings are cut off from the bottom with a knife;
- a half-centimeter deep cut is made in the stump;
- The first and second scions are placed into the cleft, after which the grafting site is wrapped with adhesive tape and damp paper.
Half-split
This is also a common method, popular among gardeners and horticulturists. Half-cleft grafting is virtually identical to the previously discussed method. The only significant difference is the number of cuttings, as in this case only a single scion is used.

Drilling
Those looking to quickly graft a seedling can use the drilling method. This method involves the following steps:
- the scion is removed from the cellar and stored for 1-2 days at a temperature of 15-20 degrees;
- the drill is disinfected in potassium permanganate, after which a hole with a diameter of five millimeters is made in the barrel;
- a cutting is placed into the drilled hole.
Copulation
When using copulation, a cut is made on the scion at a 45-degree angle. Then, a similar cut is made on the rootstock so that the scion can be grafted onto it. The cuts should then be joined and secured with adhesive tape, duct tape, or electrical tape. The bandage is removed from the stem only the following year, when the graft has strengthened.
Budding in the butt
Budding is considered one of the most reliable methods of grafting grape seedlings, as many scions take root when using this method. Budding involves the following steps:
- the top section of the scion, about two centimeters long, is cut out;
- making an incision on the rootstock;
- joining the rootstock to the scion using adhesive tape.

Right on target
Those who prefer not to use butt grafting use butt grafting. A distinctive feature of this technique is that all cuttings are grafted onto a two-year-old sprouted rootstock. To perform this procedure, you need:
- shorten the rootstock by several internodes;
- cut a shallow hole in the rootstock and attach the cutting to it;
- Strengthen the connection with adhesive tape.
On the old bush
Some gardeners prefer to graft onto an existing vine. The key advantage of this method is that it allows two different grape varieties to be attached to a single trunk. Three or more buds are left on the cuttings. The grafting site must be carefully sealed. This is done using adhesive tape and plasticine, which is applied to the joint.
To the root
Sometimes gardeners graft grapevine cuttings into the rootstock. This method is considered reliable, as the risk of the grafted shoot dying is extremely low. During this procedure, the soil is dug to a depth of thirty centimeters to expose the root system. The trunk is then sawn and a five-centimeter-deep split is made in it. One or two scions are inserted into this split, after which the joint is secured with electrical tape.

Re-grafting
Sometimes, after the first grafting, the cutting fails to take root and begins to wilt. This most often occurs if serious errors were made during the procedure. To save the cutting, a re-grafting will be necessary. When re-grafting, extreme care must be taken to avoid damaging the plant.
Improved method
Sometimes people use Tittel grafting. This technique is considered improved, as it allows for the formation of thicker and stronger branches. First, an incision is made in the woody bark of the trunk, into which the scion is inserted. Before attaching, the scion is carefully cleaned of bark and sharpened. To ensure a secure attachment, the trunk and scion are wrapped in bast.
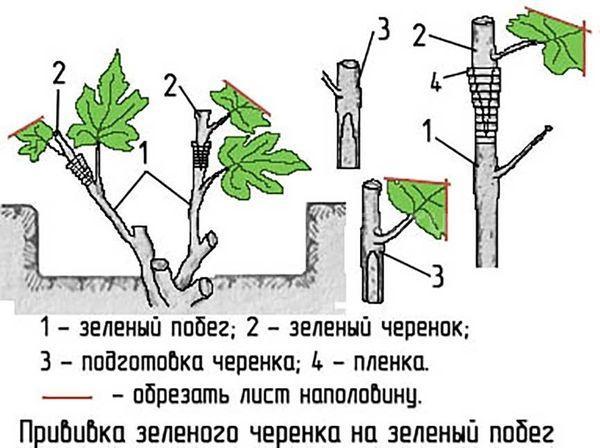
Green to green
Using the green to green method, perform the following sequence of actions:
- The vine is pruned to leave two strong shoots. This procedure is performed with a sharpened knife.
- The scion is trimmed so that it has one bud. Then a cut is made from the bottom.
- The cut scion is connected to the rootstock and sealed with adhesive tape.
How to graft
To understand the specifics of grape grafting, you need to understand how the procedure is carried out at different times of the year.
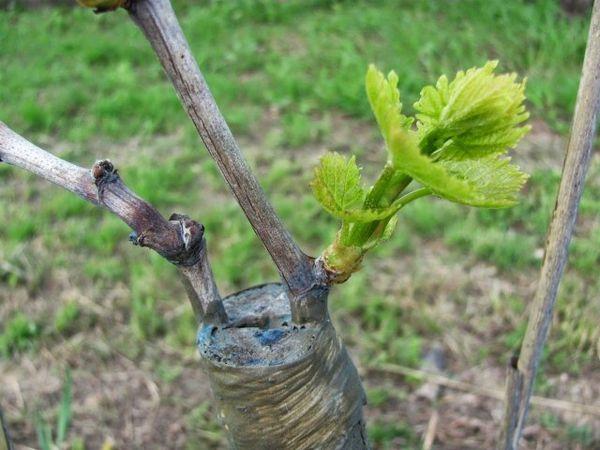

In the spring
Spring grafting is performed when the buds on the rootstocks begin to swell. These buds typically swell in mid- to late April. The procedure should be performed at temperatures of at least 15-17 degrees Celsius.
A few days before work begins, the cuttings are disinfected and trimmed at the bottom. Then, the vineyard trunk is dug around and a split is made in it. The scion is inserted into the hole and secured with twine.
In summer
June is considered a good month for grafting using green cuttings. Sometimes this procedure is performed in July, before the hot weather sets in. To graft, the cuttings must be trimmed, sharpened, and inserted into a cavity cut in the rootstock.
August is not suitable for using green cuttings, and therefore a combined grafting method is used, when plants are joined in a cleft.
In the fall
September is the ideal time to graft grapevines onto split scions of old seedlings. Before beginning, all scions are soaked in a liquid to stimulate seedling growth. They are then trimmed off along with the above-ground portion of the trunk. The cuts are treated with a disinfectant, after which the grafting process takes place. The length of the connecting section of the stem should not exceed three centimeters.

In winter
Long-time grape growers advise against grafting in winter due to low temperatures. In winter, the procedure can only be performed if the vineyard is grown in a greenhouse.
Conditions of survival
There are several conditions that contribute to the survival of grape vines:
- the procedure is carried out at a temperature of fifteen degrees Celsius;
- using garden tools that have been disinfected beforehand;
- correctly selected rootstock and scion;
- proper storage of cuttings.
Aftercare
Grafted plants become very weak and therefore will require careful care.
Watering
If the grapevines lack moisture, they will bear less fruit, so they will need to be watered regularly. Water the soil every other day or daily during hot weather. Each seedling requires 10-15 liters of water. Water should be applied at the roots to prevent drips from falling on the foliage. Avoid using water that is too cold, so warm it in the sun to room temperature.

Hilling
To protect vineyards from winter frosts, seedlings are hilled. This procedure helps protect the plant's root system from the effects of low temperatures. When hilling, the main stem of the seedling is covered with soil and fallen leaves to a height of 20-30 centimeters.
Loosening and weeding
Over time, weeds appear in grape plots, sucking nutrients and moisture from the soil. To prevent them, weed several times a month to remove all excess grass. Weeding also loosens the top layer of soil, which can become crusty over time.
Spraying
Spraying the vineyard with insecticides and fungicides is carried out in the following cases:
- after tying the branches to the support posts;
- during the formation and swelling of buds;
- during the period of ripening of fruit brushes;
- after harvesting ripe fruits.
Trimming
To increase the yield and improve the taste of ripe grapes, vineyards are pruned. All unnecessary side shoots that do not produce fruit are removed from the vines. Yellowed branches that are beginning to wilt are also removed.
Most often, pruning is done after tying the seedlings to the supports.
Support or trellis
Sometimes gusts of wind can cause grape stems to break. To strengthen them, special supports must be installed. For this purpose, two-meter-high metal or wooden posts are driven into the ground near each vine. All the branches that bear the fruit clusters are tied to these supports.
Pros and cons of the propagation method
Propagation by cuttings has advantages and disadvantages that should be considered. The advantages of this method include its ease of use and high efficiency, as most grafted seedlings survive. Disadvantages include the slow growth of grafted vines.
Using grafting shears
When performing this work, use special grafting shears designed for cutting stems. They make it easy to trim scions and make grafting holes for rootstocks. Before using the instrument, its blades should be disinfected in potassium permanganate for about ten minutes.
Common mistakes beginners make
Common mistakes include the following:
- too deep a cleft;
- incompatibility of the cutting with the rootstock;
- using an unsharpened tool;
- storing cuttings in unsuitable conditions.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
There are a number of recommendations that will help you graft grapes;
- use the green-on-green or black-on-black technique only in late spring and early summer;
- do not use diseased or weakened cuttings;
- carefully care for the grafted vine so that it does not weaken;
- Do not use non-disinfected instruments.
Conclusion
Some gardeners decide to graft grapevines. Before doing so, it's important to understand the basic methods and recommendations for the procedure.











