- Features of the structure and names of parts of the grapevine
- Standard
- Head
- Sleeves
- Fruiting arrow
- Replacement knot
- Fruiting link
- Why do you need to trim unnecessary shoots?
- Seasonal differences in pruning
- Rules and timing of circumcision
- Pruning methods
- Short
- Average
- Long
- Mixed (according to Guyau)
- Bush formation schemes
- Sleeve pattern
- Fan shape
- Cordon form
- Formation according to Moser
- By bowl type
- VNIFS-1
- Small fan without a standard
- Standard version
- According to Kurdyumov
- How to shape grape bushes
- In the first year
- In the second year
- In the third year
- Mature bush
- Accelerated forming methods
- N. I. Sklyar's method
- Scheme of stepsons (author F. Bashirov)
- Magarach Research Institute Method (vine bending)
- Green
- Types of special spring pruning for damaged grape bushes
- Frostbite
- Vine defect
- How to prune properly in summer
- Pinching out stepsons
- Thinning
- Embossing and brightening
- Care after pruning
- Basic pruning mistakes
- Pro tips for beginners
- Conclusion
Those who decide to grow vineyards will need to periodically prune their grapes. Many gardeners find this quite difficult, so it's recommended to learn how to prune grape vines properly beforehand.
Features of the structure and names of parts of the grapevine
Grape seedlings consist of several parts, which have specific names and characteristics.
Standard
A grapevine's trunk is the trunk that grows vertically. It begins at the soil surface and ends at the first branch on the stem. The trunk is considered an extension of the trunk below ground level.
The main difference between a grape rootstock and a tree rootstock is that it is created artificially.
This part of the plant provides stability to the entire vine. The appearance of the vine also depends on the characteristics of the trunk. The trunk's height can vary, ranging from forty centimeters to two and a half meters. Everything depends on the age of the vineyard and its growing conditions.
Head
Another important part of grape vines is the head. Many gardeners don't know where it is or what it looks like. The head of the vine is located at the top of the plant's trunk, near the first lateral branches of the main stem. Its main characteristic is its size, as the head is slightly wider than the trunk. Therefore, it can be seen with the naked eye.

The grape head does not form on the bushes immediately, but in the second year after planting the seedling.
Sleeves
It's no secret that several large shoots extend from the head of a grapevine. Gardeners call these shoots "branch arms."
Each bush may have a different number of such branches. However, most often, their number does not exceed six. The number of shoots directly depends on the age of the seedling and its shape.
At first, the stems are small and thin, but over time they grow to 30-40 centimeters in length. The stems become covered with a dense bark that protects them from mechanical damage. If the sleeves grow to 50-60 centimeters, they are called horns.

Fruiting arrow
A fruiting stem is a vine with a diameter greater than five millimeters. The main function of this shoot is to form clusters of berries for harvesting.
The diameter of the fruit vine is very important, as it must withstand the weight of ripe berries. A minimum diameter of 4-5 millimeters is considered appropriate.
However, it's recommended to leave shoots 6-8 millimeters thick on the bushes. Excessively thick vines are also unsuitable, as they will produce few flowers. Such shoots should be 20-35 centimeters long.
Replacement knot
A replacement shoot is a young, one-year-old vine that has been pruned back to two buds during cultivation. Two to four young buds are left on the pruned shoot. The remaining shoot is used to form a higher-quality, fruit-bearing vine in the future. It also prevents the bush from becoming overgrown.

Some people don't leave replacement branches on seedlings and cut them out completely. In this case, to form fruiting shoots, you'll need to use the stems furthest from the base. These are best suited for growing fruit clusters.
Fruiting link
A fruiting link is one of the parts of a bush, which consists of an annual vine, a sleeve, and perennial branches.
Experts recommend developing fruiting links, as the yield of the grown seedlings depends on this.
The formation of such shoots depends on the age and variety of the vine. When pruning fruiting branches, their location, as well as the rate of growth and formation of young inflorescences, are also taken into account.

Why do you need to trim unnecessary shoots?
Fall and spring are the seasons for pruning grapevines. Some gardeners don't know why they need to prune their vines, so it's recommended to understand the main goals of this procedure in advance:
- Increasing yield. Experienced gardeners recommend removing excess shoots to increase yield. This involves pruning shoots that are not producing fruit clusters.
- Monitoring seedling growth. Without regular pruning, bushes can become excessively wide and tall.
- Increasing berry size. Removing all unnecessary shoots will improve the flow of nutrients to the berries, resulting in larger berries.
Seasonal differences in pruning
Vineyard pruning occurs at various times of the year. Therefore, it's recommended to understand the main seasonal differences in stem pruning:
- Spring. Many experienced gardeners do not recommend pruning vines in the spring, as this is when the sap begins to flow. If you have to prune the stems in the spring, it's best to remove only young branches that have not yet begun to bear fruit.
- Summer. Stem pruning is not recommended in summer to avoid damaging the bushes. During this time, pruning and partial side shoot removal are acceptable. This is done to prevent the development of fungal diseases.
- Autumn. This is the most suitable time for pruning. In autumn, all shoots should be shortened by 10-20%.

Rules and timing of circumcision
Before pruning your vineyard, it's recommended to understand the optimal timing. Gardeners recommend doing this in early fall, after the berries have ripened and the harvest is about to begin.
If the harvest has not yet been carried out and there are clusters of berries on the stems, there is no need to prune.
Sometimes people don't have the opportunity to prune in the fall and have to do it in the spring. It's recommended to do this in mid-March, before the sap begins to actively flow through the branches. Pruning or shortening branches in late April or May is not recommended.
Pruning methods
There are four common pruning methods used by many gardeners.

Short
Most often, grape growers use short pruning. The key feature of this method is that all shoots are shortened to 3-4 buds. As a result, replacement branches are formed from the pruned stems.
There are several recommendations for proper pruning. If the first bud from the base of the stem points inward, it should be shortened to three buds.
When a lateral shoot begins to emerge from the first bud, it is immediately broken off. This is done to ensure that the replacement shoot will grow outward from the bush in the future.
Average
Some gardeners don't want to prune shoots too short, so they opt for medium pruning instead. Experts recommend this method when growing frost-resistant grape varieties.

During the procedure, each branch on the grapevine is shortened. It is trimmed so that seven buds remain. The total number of buds on the bush should not exceed fifty. If there are too many, the procedure will have to be repeated and the longest branches shortened.
Long
This method of shortening branches is used much less frequently than the previous two. Experienced gardeners recommend long pruning of seedlings in the following cases:
- when shortening vines that will be used for growing cuttings;
- when using a bend in the vine in the form of an arc or ring;
- when growing tall grape varieties.
Using this method, 10-15 buds are left on each shoot. When growing Asian grape varieties, ten more buds can be left. This is done to improve fruiting and increase the number of fruit clusters.

Mixed (according to Guyau)
Sometimes none of the above pruning methods are suitable, so people use a mixed method. Experienced gardeners recommend using a mixed pruning method when growing low-growing grape varieties.
The use of this technique helps to improve yields and increase the size of berries.
When performing mixed pruning, a replacement branch is formed, which should be located on the outer part of the bush. Each branch should have 3-5 buds. However, to increase fruit clusters, more buds can be left.
Bush formation schemes
There are various bush formation schemes that every gardener should be familiar with.
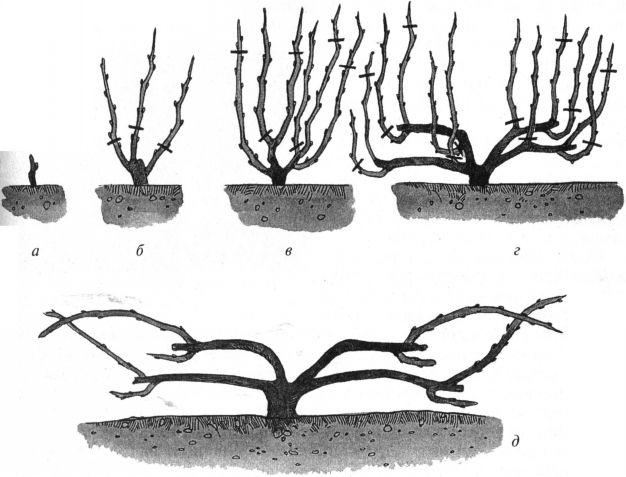
Sleeve pattern
This is the most popular method used by many winegrowers. It is recommended to use it only when the seedlings are planted correctly, with the top bud located at a depth of 5-6 centimeters.
In this case, when growing a seedling, you will not have to worry about forming a trunk.
When using this method, trellises are installed on either side of the bush, to which the branches are tied. Each plant should have 3-4 branches. In the fall, they are shortened by 10-15 centimeters. In the second year of cultivation, all buds except the top two are removed from the shoots.
Fan shape
Another popular method is fan-shaped vineyard planting. This method's distinctive feature is that not just one fruiting unit is left on the vines, but several. These are arranged in a fan-shaped pattern on vertical trellises.
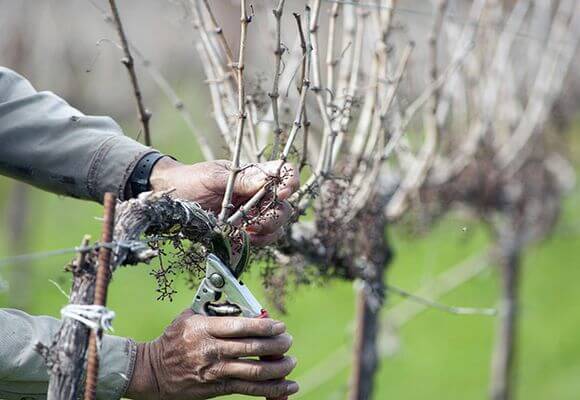

Fan-shaped pruning is performed the following year after planting the seedlings in the garden. By the third year of cultivation, an increase in yield will be noticeable thanks to the fan-shaped technique. The main advantages of this method include simplified grapevine care, easy rejuvenation, and the ability to form new branches.
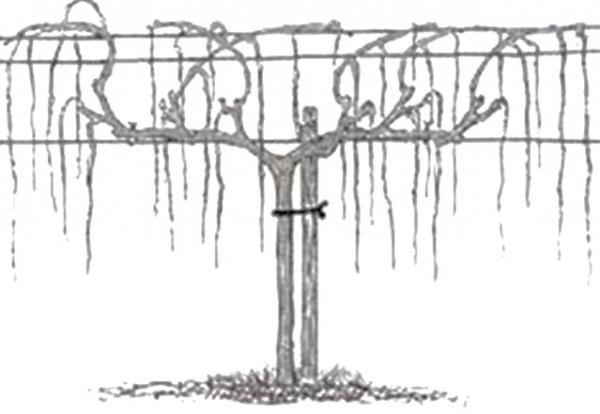
Cordon form
When using this method of training, the vines are pruned in the second year after planting them in the garden. Three buds should remain. A restoration shoot is formed from another vine. The plant is then left undisturbed and allowed to grow until the onset of winter. Before frost sets in, the vines are covered to prevent freezing.
In the spring, the vines are pruned, leaving five buds. The pruned shoots can weaken, so they are tied to the trellis beforehand. This prevents them from breaking in the wind or from the strain of the newly formed fruit clusters.
Formation according to Moser
This is a specific method of shaping vines, invented by Lenz Moser. Using this method simplifies the process of growing and maintaining a vineyard. Those who have used this method for many years recommend tying fruiting branches to trellises. This prevents the vines from bending under the heavy load of grapes forming on the clusters.
It is not necessary to tie branches that do not have fruit to supports.
By bowl type
This is a popular method of shaping bushes, often used by gardeners. The main advantages of this method include increased yields, improved growth of fruiting shoots, and ease of care for the planted seedlings.
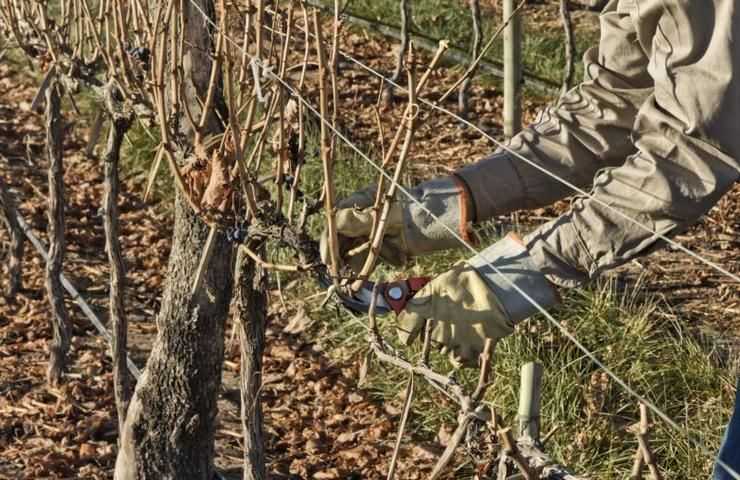

The bush is formed into a bowl-shaped structure in the same way as when using the fan-shaped method. The main distinguishing feature is that in this case, you have to leave shoots that point toward the row spacing. When forming bushes using the fan-shaped method, these shoots had to be pruned.
VNIFS-1
If bushes are to be trained using this method, they should be planted two meters apart. If they are planted too close together, training using this method will not be possible.
Using this method, special anchors are installed in rows of grapes, between which strong wire is stretched.
A year after planting, all branches longer than eighty centimeters are tied to established shoots. In the spring, they are pruned, leaving four buds on them, which will form the future fruiting unit.

Small fan without a standard
For a compact backyard vineyard, training seedlings without standard stems is suitable. This will allow you to grow compact grape vines, saving space in the garden. Plants should be spaced 55-65 centimeters apart, with a distance of about one and a half meters between each row.
Standard-less plants need to be grown under special covers to protect them from temperature fluctuations. The cover is best made of durable material.
Standard version
To form standard bushes, you need to prune as follows:
- During the first year of cultivation, shoots are pruned by 2-3 buds. This is done in early spring to ensure the branches are strong by the end of summer.
- The following year, the main shoot is cut back to three buds. This is called reverse pruning, whereby the lateral shoots below the trunk are completely cut off.
- In the spring of the third year of cultivation, the main stem is cut to 70-80 centimeters.
- A year later, in the spring, the upper branches are cut off from the bush so that new and stronger shoots can form by summer.

According to Kurdyumov
Some gardeners use a technique developed by renowned winegrower Kurdyumov. The basic idea behind his method is to pinch off growing shoots early, before they develop unwanted branches.
If you pinch regularly, the crop you are growing will not need pruning.
This method is very convenient, as it allows gardeners to stimulate shoot growth wherever desired. Pinching should be done carefully to avoid damaging the shoots. It is recommended to use sharp scissors. Removing stems manually is not recommended.
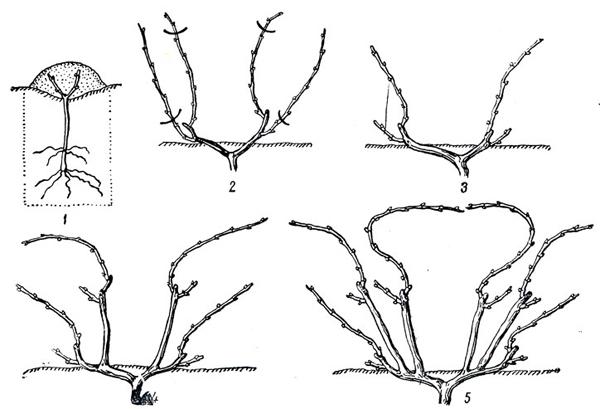
How to shape grape bushes
Training grapevine seedlings takes several years. It's important to familiarize yourself with the key aspects of seedling training for each growing year.
In the first year
After planting, a young one-year-old seedling doesn't need to be pruned. It needs time to strengthen its shoots and main stem. Therefore, during the first year until autumn, the bush is left alone and its growth is not restricted in any way.
The first pruning begins in early or mid-September, after the harvest is complete. This involves cutting the plant almost to the ground, leaving just a few buds on the stem.
The pruned main shoot should not be very long and therefore its length should not exceed 15-20 centimeters.
In the second year
A two-year-old bush will need to be pruned more frequently than a one-year-old. Experts recommend forming new branches in the second year. These should be formed from the longest and largest shoots. However, if there are small, vigorous branches, these can also be formed into branches. To do this, trim all branches so that 20-30 millimeters remain from the base.

As the sleeves grow, they are tied to supports and, if necessary, shortened to prevent them from becoming too long. Their length should be 50-60 millimeters.
In the third year
Three-year-old plants stop developing trunks, and young shoots emerge from the remaining shoots. Fruiting shoots form from the older branches, from which the ripe fruit can be harvested in the second half of summer.
Three-year-old seedlings are pruned before the first frost. All immature shoots with young leaves are removed from the plants. These should be cut off completely to prevent new shoots from appearing the following year. It's best to cover the pruned bush to protect it from winter frosts.

Mature bush
A mature, fruiting bush is formed in the fourth and fifth years of cultivation. Early-ripening grape varieties like July can be pruned in late summer. To do this, remove all unnecessary shoots from the bush that do not produce grapes.
Fruit-bearing branches are pruned in the spring. The tops and tendrils are cut off with pruning shears. Care must be taken when pruning to avoid accidentally cutting off fruit-bearing shoots, which may contain grape clusters.
Accelerated forming methods
There are four effective shaping methods that will help accelerate seedling development. It's important to familiarize yourself with the specifics of each method beforehand.

N. I. Sklyar's method
This method is used by those who want to harvest a large, ripe crop in the third year of vineyard cultivation. The key to Sklyar's method is the use of strengthened two-year-old seedlings for planting.
When growing them, they are provided with enhanced nutrition and regular watering.
During the first pruning, only four buds are left on the bush, which will later become fruiting branches. In the second year, all remaining branches should be shortened, leaving three lateral shoots on each, which will form the lateral branches.
Scheme of stepsons (author F. Bashirov)
The essence of the scheme under consideration is the deliberate stimulation of the development of young grape shoots, which will subsequently be used to form fruit-bearing branches with grape clusters.

Three to four months after planting the grape seedlings, the young shoots are carefully pinched back to a height of no more than seventy centimeters. Small side shoots can then be seen in the leaf axils of the pinched shoots. Some of these are removed, leaving only those located at the top. The following year, these are used to produce fruiting stems.
Magarach Research Institute Method (vine bending)
Using the vine bending technique, several of the strongest branches are left on the seedlings. After a year, they are shortened by three buds to ensure they have time to grow into strong shoots by early autumn.
When the plant reaches three years of age, the shoots are shortened to five buds and tied to installed trellis supports.
Buds on tied branches should not be pruned, as they will eventually grow into fruiting stems. After a few years, some branches will stop bearing fruit and will need to be pruned completely to allow new shoots to grow in their place.

Green
This method is very similar to the stepchildren method, as it also requires stimulating the development of young shoots on the seedling. Bush formation using this method begins in the first year of cultivation. First, the tops of the vines are pinched to prevent stems longer than 60 centimeters.
On each stem, three of the strongest shoots are left, which will later grow and become fruit shoots.
Formed fruit branches must be properly cared for and lateral shoots removed, as these slow down the development and ripening of fruit clusters.
Types of special spring pruning for damaged grape bushes
There are several special considerations for caring for damaged grape bushes that are best learned in advance.

Frostbite
Sometimes, due to harsh winters, grape seedlings freeze, causing part of the plant to die.
Recommendations for pruning frostbitten grape bushes:
- If less than sixty percent of the buds have frozen, more healthy buds are left on each fruit shoot to compensate for the pruned branches.
- If more than sixty percent of the buds have been frostbitten, you will have to remove all the frozen shoots and get rid of excess growth.
Radical pruning is also possible, where the seedling is dug up and the main shoot is cut to a length of five centimeters. The remaining part is then buried in the ground.
Vine defect
Plants with vine defects require careful care to ensure their normal development. Experts recommend periodic pruning of such seedlings. During this process, shoots with visible defects are removed, as they bear less fruit. Common defects include irregular shoot shapes and new growths appearing on the shoot's surface.

How to prune properly in summer
There are several ways to prune a vineyard in summer.
Pinching out stepsons
Gardeners who have been growing grapes for many years choose June for pinching out side shoots. Sometimes, leaves are removed from shoots by pinching. However, this is very dangerous, as it can damage the stem being pinched. It's best to use specialized gardening tools or scissors for this. Before starting the procedure, be sure to disinfect all tools to ensure their surfaces are free of germs.

During the process of pinching out the shoots, the crown of the stem is removed so that no more than two leaves remain on it. The procedure is performed regularly, once a month.
Thinning
July is the best month for thinning vineyards. This procedure allows better sunlight penetration into the vines and illuminates the grape clusters. Improved light speeds up the ripening of the grapes.
When thinning, first remove all dried leaves and branches that have stopped growing.
When thinning, remove all green leaves near the grape clusters. This procedure, like pinching, is performed at least once a month.

Embossing and brightening
This procedure is similar to regular pinching, but it's performed in August. Pinching should be avoided earlier, as it promotes the formation of unfruitful shoots. During this procedure, the upper portion of the vine is cut off, leaving 10-12 leaves at the bottom. This amount is sufficient for the normal development of the vineyard. Pinching, like thinning, removes excess foliage, which impairs light penetration to the berries. This procedure not only improves light but also increases air circulation.
Care after pruning
The pruned bush must be properly cared for after the procedure, as it weakens after the procedure.
Gardeners recommend adding more mineral and organic fertilizers to the soil, once a week. It's also important to water grape seedlings more frequently to ensure they always have enough moisture.
This can be done every other day or every two days. Use room-temperature water for irrigation. It's best to avoid cold water, as it will negatively impact the vine's development.

Basic pruning mistakes
There are several common pruning mistakes that many beginners encounter:
- Topping. Some believe that topping is the best and most effective pruning. However, this is untrue, as topping negatively impacts plant growth and reduces yield.
- Pruning fruit-bearing branches. Beginning gardeners often prune shoots where berries form. This should be avoided, as it will reduce the yield.
- Failure to adhere to the deadlines. Pruning seedlings should be done at the appropriate time.
Pro tips for beginners
Before pruning your bushes, you should familiarize yourself with some helpful tips to help you do everything correctly:
- Uncovered grapes are pruned in early spring, and covered grapes are pruned in autumn;
- the procedure is carried out with disinfected instruments;
- The pruned grapes are intensively watered and fed.
Conclusion
When growing grapes, you'll need to prune them periodically. Before doing so, familiarize yourself with tips on pruning grape seedlings.











