- History of origin
- Description and Features
- Main characteristics of the variety
- Purpose
- Ripening time
- Productivity
- Taste qualities
- Frost resistance
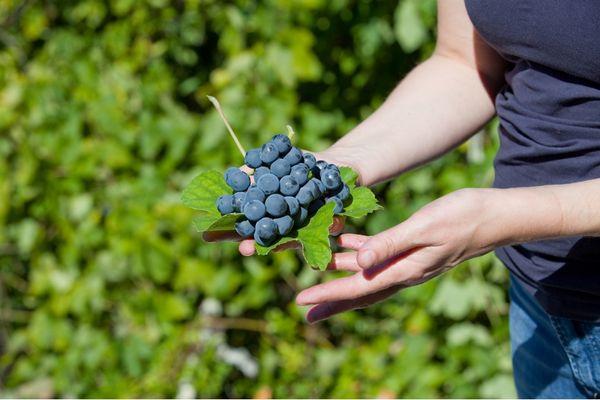
- Bunch
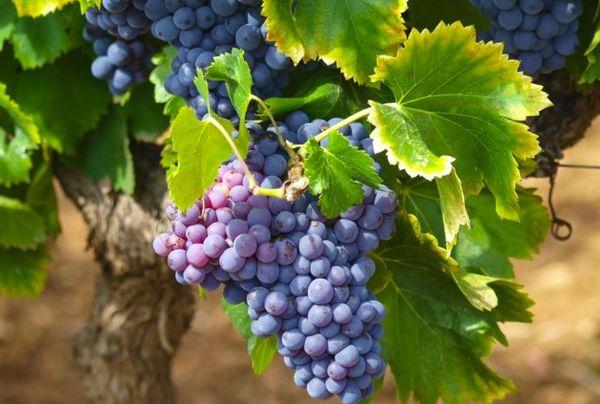
- Berries
- Disease resistance
- Methods of reproduction
- Cuttings
- By vaccination
- Layering
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Mulching
- Garter
- Preparing for winter
- Protection from birds and wasps
- Preventive measures against pests and diseases
- Pros and cons of the variety
- Harvesting and storage
- Applications of berries
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The Zilga grape variety is popular. This plant is characterized by high yields and frost resistance. It is a commercial grape variety, so it is primarily used for winemaking. To achieve good results, it requires proper care. This includes timely fertilization, watering, and pruning.
History of origin
The variety was developed in the early 1960s by Latvian breeder P. Sukatnieks. It is the result of crossing several varieties, including Dvietes Zilas, Yubileyny Novgorod, and Smuglyanka. The result was a frost-hardy variety that is resistant to diseases and produces large fruits.
Description and Features
This grape variety is distinguished by long vines exceeding 2 meters. Eighty-five percent of the vines mature within the first year after planting. They are covered with large, dark green leaves. They are trilobed and finely dissected. The undersides of the leaves have a smoky-blue bloom.
The flowers of this plant are bisexual, making it easily pollinated. The harvest can be collected within 100-110 days after bud break. The plant produces aromatic fruits, which are often used for wine production.
Main characteristics of the variety
Zilga grapes are considered a fairly popular crop that produces a good harvest and easily tolerates severe frosts.

Purpose
The berries are versatile. Grapes can be used as table grapes, but are more often used for wine production. This crop can also be used to decorate gazebos.
Ripening time
From the time the buds open until the first fruits ripen, no more than 100-110 days pass.
Productivity
This variety is characterized by high yields. With large-scale training, each plant can yield up to 23 kilograms of fruit.
Taste qualities
The berries are characterized by a subtle muscat flavor. Acidity levels range from 4.5 to 5 grams per liter. The grapes received a tasting score of 7.1.

Frost resistance
The plant tolerates frost well. It can withstand temperatures down to -25 degrees Celsius and even lower.
Bunch
The clusters are cylindrical in shape, dense in texture, and large in size. On average, a bunch weighs 320-400 grams.
Berries
The fruits are large, weighing 4.1-4.3 grams. The berries are oval in shape and blue in color. The flesh is slightly slimy.
Disease resistance
This grape variety is virtually immune to mildew and oidium, with a resistance rating of 4 points.
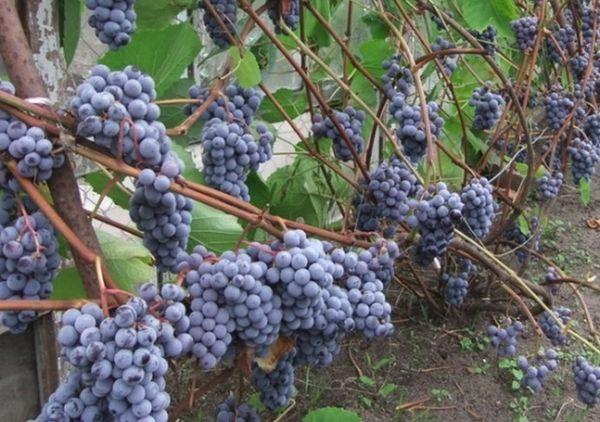

Methods of reproduction
There are several methods of propagating crops, each of which has its own characteristics.
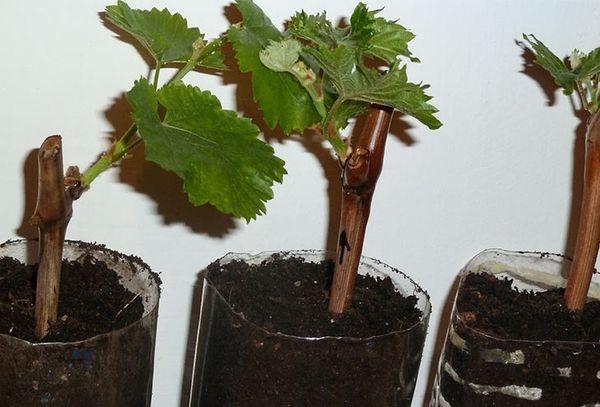
Cuttings
It's best to prepare planting material in the fall, during pruning season. When selecting cuttings, take branches with a diameter of 7 millimeters. They should be brown in color and 40 centimeters long. Each cutting should have three buds.
Place the resulting material in water for 8 hours, air it out, and tie it into bundles. Sprinkle with sawdust and place it in a bag. Store the planting material in the ground, cellar, or refrigerator.
Before planting, soak the cuttings for 2 days, changing the water periodically. Plant the plants in pots and water every 2 days. Grapes are transplanted into the open ground in September.

By vaccination
Grafting can be done in spring, summer, or fall. Many methods are known today. Beginning gardeners are advised to choose a simple copulation, cleft graft, or semi-cleft graft.
Layering
For this method, select a healthy bush and dig a 50-centimeter trench around it. Remove the leaves from the bottom and place them in the trench. Cover with soil and compact. Pour two buckets of water under the bush. Once the water has soaked in, cover with soil.
This method ensures rapid plant development. It takes root easily and is disease-free. The advantage of this method is the dual nutrition the plant receives from the emerging roots and the mother plant.
How to plant correctly
To achieve success in growing crops, it is very important to carry out planting work correctly.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
Planting should be done in spring or fall. In the former case, the procedure is carried out after the end of spring frosts. The soil should warm up to 10 degrees Celsius.
In autumn, weather conditions influence planting timing. After planting, the plant needs one month to adapt. During this period, there should be no risk of frost.

Site preparation
This grape variety is considered to be tolerant of soil conditions. Grapes grown in poor, rocky soil are suitable for winemaking.
A sunny area sheltered from north winds is ideal for planting. To decorate a gazebo, plant the plant on the south side.
It's best to prepare the plot in advance. If you plan to plant a single bush, it's recommended to dig a hole 60 centimeters deep and 70 centimeters wide. When planting multiple bushes, arrange them in a row. The distance between plants should be 1.5-2.5 meters. The distance between rows should be 2 meters.
How to select and prepare planting material
To ensure a high-quality and abundant harvest, it's crucial to choose the right planting material. It's recommended to purchase bare-root seedlings immediately before planting. A young plant should have at least three fully formed roots. The cut should be light and moist.

Before planting, it's recommended to bury the plant in the soil. This will help prevent the roots from drying out.
When purchasing a container plant, it's recommended to keep it on a windowsill for a few days. After that, it should be gradually hardened off. It's recommended to first move the plant into a greenhouse, then outdoors.
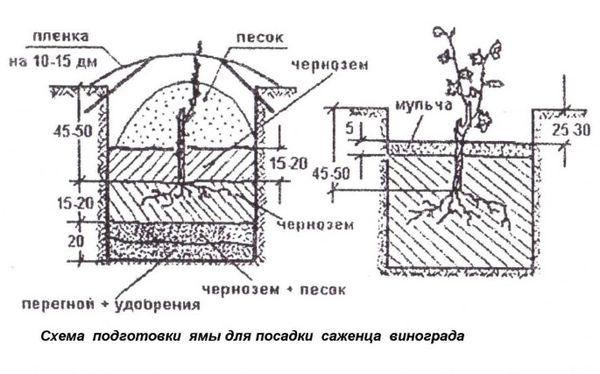
Planting diagram
To carry out planting work, you need to perform the following steps:
- Mix the top layer of soil with well-rotted manure. It is recommended to add 200 grams of superphosphate and potassium chloride under each bush.
- Place the plant on a mound of substrate and spread out its roots.
- Place a plastic or ceramic tube with a diameter of 4 centimeters nearby.
- Pour a bucket of warm water into the depression.
- Cover the root system with nutrient substrate.
- Make a ridge of soil around the bush.
- Pour out another bucket of water.
- Cut the plant into 2 buds and coat the cut with paraffin.
- Cover the soil around the grapes with humus.
Care instructions
For a crop to thrive, it requires high-quality care. This care must be comprehensive.
Watering mode
This grape variety tolerates waterlogged soils with difficulty, but requires moderate soil moisture. Only young plants require ample watering. The greatest water requirements occur during the active growing season, before the buds open.
Once the buds have formed, watering should be stopped. Resume watering only during prolonged droughts. A small ditch should be made around the perimeter of the bed to catch excess water.
Top dressing
Every three years, the plant requires organic fertilizer. To do this, dig a trench 1 meter in diameter around the bush. Place fully rotted manure at the bottom and cover with soil. One bucket of fertilizer is required per plant.

After flowering, grapes need to be fed with phosphorus fertilizers. To do this, add 1 cup of wood ash under the bush. In the fall, the plant needs potassium, which increases frost resistance. Ash or complex mineral fertilizers with a high potassium content are used as fertilizer.
Bushes periodically experience chlorosis, which causes yellowing of the leaves. This problem is caused by iron deficiency.
A composition based on 1 liter of water, 4 grams of ascorbic acid and 2.5 grams of ferrous sulfate will help replenish the deficiency.
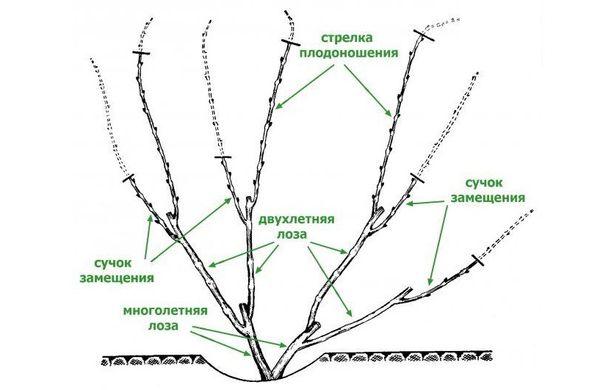
Trimming
The plant grows rapidly and therefore requires regular pruning. This procedure increases yield. Pruning is also necessary to prevent fungal infections.
This procedure should be performed in spring or fall. Bushes 1-2 years old do not require pruning. Plants are shaped using fan-shaped pruning. Three to four of the strongest shoots are left and pruned above the eighth bud.
Zilga produces numerous shoots, which need to be systematically removed. This will help prevent overloading the bush and improve the vine's ripening.
Mulching
It's recommended to weed the soil under the bushes. Alternatively, mulch the soil. Organic matter such as hay, compost, or grass can be used for this purpose. The mulch layer should be at least 5 centimeters thick.
Garter
Experienced gardeners recommend tying the bush to a trellis. For this purpose, a multi-arm fan-shaped training system is recommended.
Preparing for winter
This variety is highly frost-resistant, so covering it is not recommended. In the Baltic countries and southern regions of Belarus, it can be left on trellises.
In the Moscow and Leningrad regions, the plant's roots need to be protected with spruce branches. The shoots should be trimmed as much as possible. When grown in Siberia, the bush requires more substantial insulation.
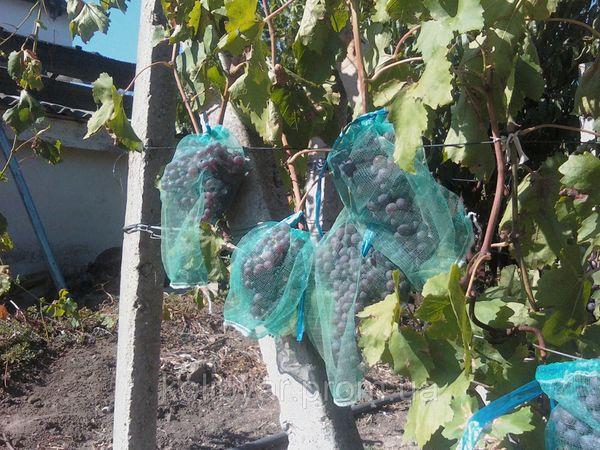
Protection from birds and wasps
Grapes are not susceptible to wasp attacks. Therefore, they can be kept on the vines for a long time, which increases the sugar content of the fruit. To prevent damage to the berries by birds, it's recommended to use netting.

Preventive measures against pests and diseases
Zilga is highly resistant to fungi. It is virtually immune to gray mold, mildew, and powdery mildew. However, gardeners recommend preventative treatments. This is especially important during prolonged droughts or high humidity.
To prevent dangerous diseases, remove dead branches and weeds. Treat the bushes with fungicides or 1% Bordeaux mixture twice a season.
Pros and cons of the variety
Culture has many advantages:
- not affected by wasps;
- does not require any special care;
- is resistant to fungal infections;
- in southern regions it does not require shelter;
- easy to root;
- has high frost resistance.
The downsides include the mediocre taste of the fruit. However, since this variety is considered a commercial variety, this drawback is rather minor. Many gardeners also consider the need for systematic pruning to be a drawback. This is due to the rapid growth of the shoots.
Harvesting and storage
When harvesting, the clusters should be carefully trimmed using specialized garden shears. It is recommended to store the fruit in wooden crates that allow air circulation. This helps prevent rotting. To preserve freshness longer, store the fruit in a cool, dark place.

Applications of berries
Zilga grapes can be eaten fresh. However, they are most often used to make wine and raisins. The berries retain their shape and nutritional properties for a long time and are easy to transport.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
To achieve good results in growing this crop, you need to follow these recommendations:
- apply fertilizers on time;
- systematically weed the beds;
- control soil moisture;
- mulch the soil;
- carry out pruning.
The Zilga grape variety is considered quite popular. It is widely used for wine and dried fruit production. To achieve good results, proper care is essential.











