- Should I trim?
- At what age do trees begin to form a crown?
- How does pruning affect growth and crown formation?
- Sanitary and formative - what's the difference?
- Seasonal schedule for the formation of columnar apple trees
- Winter
- Spring
- Summer
- Autumn
- Tree formation schemes
- In one barrel
- In several trunks
- Pyramidal
- With a broken main trunk
- Pruning lateral shoots
- Pruning the apical shoot
- Necessary tools
- Technique for performing work
- Tree care after pruning
- Common mistakes of beginning gardeners
Pruning columnar apple trees plays a major role in crown formation and plant development. The procedure is carried out according to a schedule and a specific pattern. Pruning improves the tree's condition, increases yield, and creates a beautiful appearance.
Should I trim?
Pruning annual shoots plays an important role in tree development. They are removed in spring and fall. Thinning the crown improves apple tree development and stimulates fruit production. Annual shoots draw nutrients from the trunk. These nutrients are insufficient for fruit development, resulting in reduced yields.
Important! Pruning is contraindicated when buds begin to form. In this case, it's best to postpone it until the fall.
At what age do trees begin to form a crown?
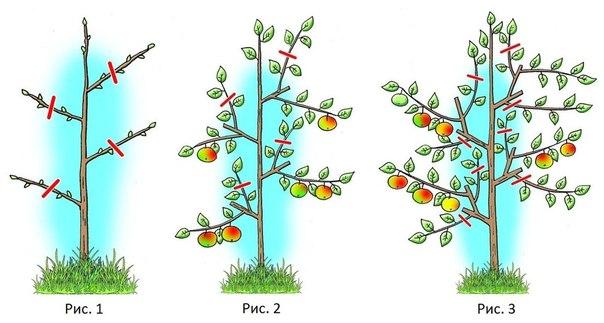
Crown formation begins in the first year of life. If left unpruned, a columnar apple tree will develop a spreading crown. After planting, prune the central shoot by 1/3. In the second year, prune half of each new shoot. This process is repeated every year. At the end of the season, dead and damaged branches are removed. If left unattended, the tree will naturally branch out in different directions.
How does pruning affect growth and crown formation?
Pruning and thinning branches allows new fruit-bearing shoots to emerge, thereby increasing yield. It also prevents branches from becoming tangled, increasing sunlight exposure to the foliage.

Crown shaping improves the apple tree's appearance, giving it a neater look. Branches begin to grow upward rather than sideways, preventing them from tangling with neighboring trees.
Sanitary and formative - what's the difference?
Sanitary pruning is performed after the harvest. This involves removing one-year-old shoots that provide no benefit to the plant.
All damaged shoots, broken ones, those with uneven or uncharacteristic colored bark, and those affected by diseases are trimmed.
Formative pruning is performed during the first six years of the growing season. After planting, the central shoot is cut off. In subsequent years, the remaining branches are shortened, except for the central shoot. This procedure is performed to give the young tree the desired appearance.
 Important! When cutting down a large section of a tree, seal the area with garden pitch.
Important! When cutting down a large section of a tree, seal the area with garden pitch.
Seasonal schedule for the formation of columnar apple trees
Each season has its own type of thinning and crown shaping for columnar apple trees.
Winter
During winter, the tree is dormant. Avoid cutting or breaking branches, as this can cause disease and frost damage. Any treatments should be carried out in early spring, when the apple tree awakens and begins to form buds.
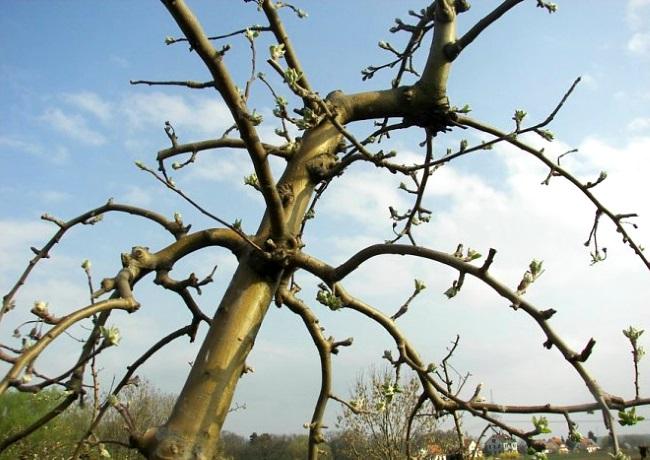

Spring
Shoots are pinched back, each by 25-30 cm. This encourages the formation of new branches with new buds, increasing yield. The main goal is increased green growth.
Summer
Unnecessary green shoots from the current year are pruned. These usually grow from the central conductor. This summer procedure is carried out with extreme care to avoid damaging the apple tree's bark. Root suckers are removed.
Autumn
This is done after harvesting. All dry, broken, diseased, damaged, and crossing branches are removed.
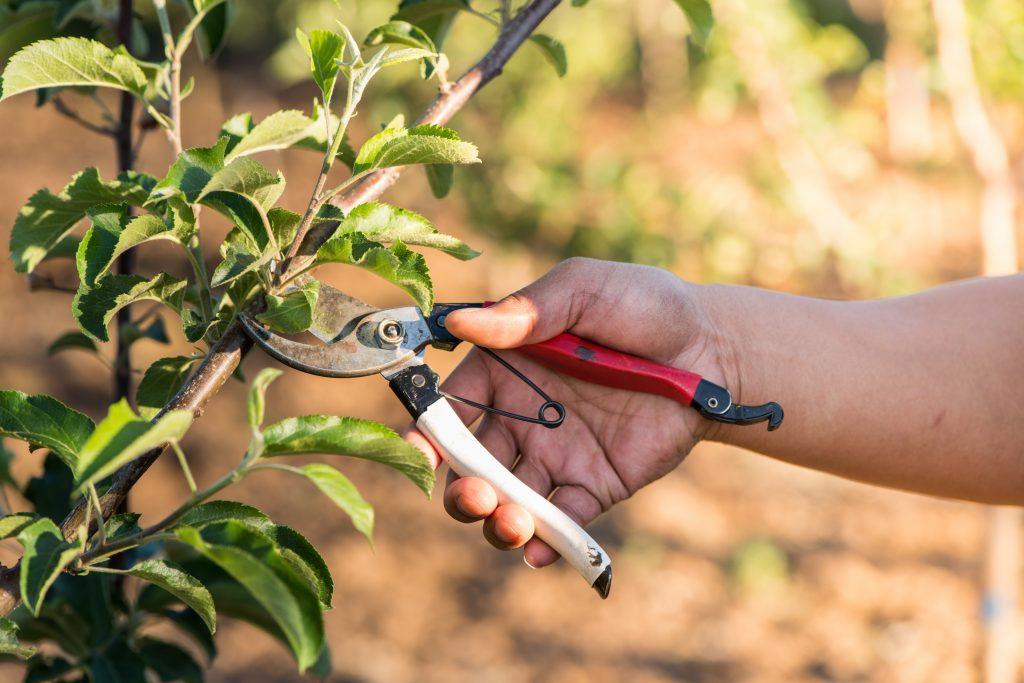

Tree formation schemes
When pruning a columnar apple tree, use one of the following methods. To achieve the desired result, strictly adhere to the diagram.
In one barrel
To form a single-trunk apple tree, after planting, prune the central trunk, but not by two-thirds, but by one-third. Then, each year, trim the side shoots so they are level.
In several trunks
Multi-trunk formation involves creating two separate trunks after the first pruning, each branching off from the lower main trunk. To achieve this, branches are removed annually from each main shoot, aiming for the same level.

Pyramidal
In the first year, part of the trunk is removed. In subsequent years, lateral shoots are removed, making sure they are longer at the bottom than at the top. This allows the crown to form into a pyramidal shape.
With a broken main trunk
If the trunk is broken, the apple tree is supported and tied. The damaged area is coated with garden pitch. The desired crown shape is shaped. If shoots emerge from the fracture after treatment, they are removed and re-sealed.
Pruning lateral shoots
Shoots are removed using pruning shears, a knife, or scissors. This should be done carefully to avoid damaging the apple tree's bark. The cut should be angled upward. The crown's shape depends entirely on this manipulation.

Pruning the apical shoot
Until the sixth year of the growing season, the top of the tree is preserved and not removed. Its pruning indicates the completion of trunk formation.
Necessary tools
The following instruments are used to perform the manipulation:
- a thin knife for removing thin branches and burrs;
- pruning shears;
- long-handled pruning shears for upper shoots;
- ladder;
- sharp scissors.
After cutting, garden pitch or other disinfectant mixtures are applied to its place.
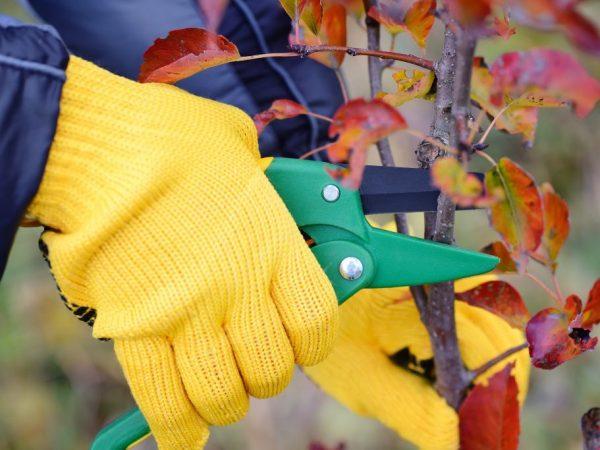

Technique for performing work
It takes at least five years for an apple tree to develop a columnar crown. Each season, different shoots are removed to shape the tree. With this pruning method, the central stem is left intact, removing only the side branches. There are two pruning options: partial or complete. This technique has several rules that must be followed to perform it correctly. The sequence of actions involves:
- After transplanting the seedling to the ground, the apical shoot is removed. This is done in the spring, before the sap begins to flow through the trunk.
- In the second year, the lateral branches are cut off, but the central one is left alone so that it will serve as the basis for the formation of the column.
- In the third year, weak branches are cut off completely, and the side branches are made shorter to a length of 30 cm.
- In the fourth year, all weakened shoots are removed, and the lateral shoots are shortened to 40 cm.
- In the fifth year, the top of the trunk is cut off to limit upward growth.
Important! Every year, at the beginning of the season and after harvesting, apple trees are sanitized.

Tree care after pruning
After pruning, the area is treated with garden pitch. New shoots will form in the area within 2-3 weeks. After this spring treatment, the apple tree is fed with organic fertilizer, and throughout the season, regular watering and monitoring for pests and infections are carried out.
After winter treatment, the apple tree is covered for the winter and the trunk is coated with whitewash to protect it from harmful rodents.
Common mistakes of beginning gardeners
Some novice gardeners make mistakes when pruning columnar trees:
- Too many shoots have been pruned. If the tree is left too bare, it will have to expend a lot of energy to recover.
- Damage to the bark by the instrument facilitates the penetration of infection and a decrease in immunity.
- If you cut too much from the top in the first year, the plant may die.
- The length of the lateral shoots is maintained at the same length so that the “column” is more pronounced.











