- History of the Pogremok apricot breeding
- Advantages of the variety
- Description and characteristics of the culture
- Dimensions and height of the tree
- Fruiting
- Flowering and pollination
- Ripening time and harvesting of fruits
- Tasting evaluation and scope of application of apricot
- Drought resistance, winter hardiness
- Resistance to diseases and pests
- Rules for planting operations
- Optimal timing
- Site selection and preparation
- Preparing the planting hole and seedlings
- Tree planting technology
- What to plant next to it?
- Further care of the crop
- Watering and fertilizing
- Crown formation
- Caring for the tree trunk circle
- Preventive treatments
- Covering a tree for the winter
- Methods of reproduction
- Gardeners' reviews
The Pogremok apricot variety was developed in the 20th century. Many gardeners appreciate it for its frost resistance, transportability, and pleasant flavor. Furthermore, it's very easy to care for, making it suitable for growing in a variety of climates, including northern regions, as long as proper care and disease prevention are followed.
History of the Pogremok apricot breeding
The Pogremok variety was developed in the Voronezh region at a station where breeding efforts have been ongoing for many years. This fruit tree is distinguished by its above-average frost resistance. It adapts to a variety of climates and soil conditions, and is easy to care for.
Advantages of the variety
Thanks to its many qualities, the Pogremok variety grows almost everywhere. These include:
- Self-fertility, meaning the apricot does not require other sources of pollination.
- Large fruits about 60 g.
- The fruits are bright yellow in color, the apricots have a pleasant taste, with a hint of sourness.
- When the fruit is ripe, the stone comes off easily.
- The fruits can withstand transportation and remain fresh for a long time.
- High level of frost resistance.
Description and characteristics of the culture
Due to its characteristics, the crop has a number of advantages over other apricot varieties.
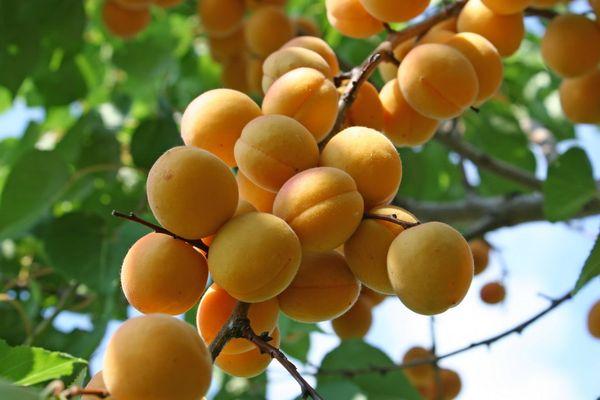

Dimensions and height of the tree
The tree grows up to 4 meters in height. The crown is spherical and sparse.
Fruiting
The rattle tree begins bearing fruit 4-5 years after planting. Before this period, the buds are plucked to allow the tree to gain strength. Apricots are highly productive, but all fruits are harvested after ripening to prevent them from falling off.
Flowering and pollination
Apricot blossoms in May. Although the fruit tree is self-pollinating, pollinator trees are planted nearby to increase the yield.
Ripening time and harvesting of fruits
Apricots begin to ripen in midsummer, but the fruits ripen at different times. The fruit is harvested during this period, although in northern regions, it's harvested in late August or early September.
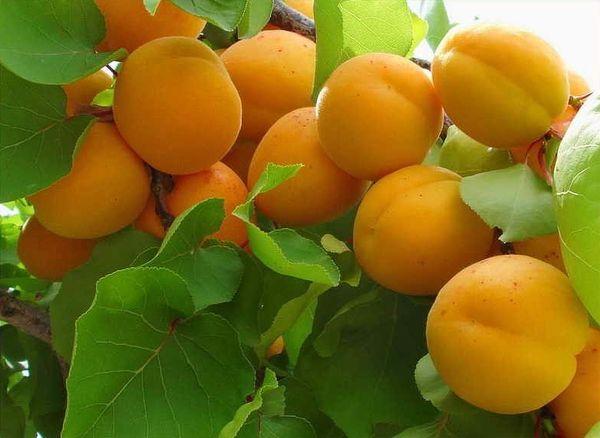

Tasting evaluation and scope of application of apricot
The pleasant flavor of the Pogremok apricot makes it versatile, and the fruit also travels well. Therefore, it can be eaten fresh or used as a base for compotes and jams. This variety is noted to be particularly suitable for making dried apricots.
Drought resistance, winter hardiness
The variety is frost-resistant and resistant to sudden temperature changes. This applies to both the tree trunk and flower buds.
The fruit is drought-resistant because its roots are nourished by groundwater.
Resistance to diseases and pests
Apricot trees aren't particularly resistant to pests, but with proper care, the tree thrives and grows vigorously. High humidity can cause symptoms of disease to appear on the fruit and leaves.

Rules for planting operations
A planting site is selected and a hole is dug. The tree is planted in spring or early fall.
Optimal timing
In the southern region, it's typical to plant seedlings in mid-autumn, after the leaves have fallen. This will allow the root system to strengthen before early December. In the northern region, it's recommended to plant fruit trees in the spring, after the snow has melted and the soil has warmed. In the temperate zone, it's common to plant apricots in both spring and fall.
Site selection and preparation
To plant a seedling, you need to choose a location that meets the following criteria:
- a site on flat or elevated terrain;
- absence of strong gusts of wind;
- availability of natural daylight.
Another important factor is that the soil should not accumulate water.
Preparing the planting hole and seedlings
The Pogremok variety is purchased from a nursery or an agricultural institute. The seedlings should have an open root system. Furthermore, the apricot should be free of any damage or mold.

Before planting, the seedling is placed in a mixture of water and clay.
Tree planting technology
- After choosing a location, dig a hole up to 70 cm deep.
- They make a mixture of compost, wood ash, and superphosphate.
- The mixture is poured in a thin layer into the hole and left for several weeks.
- The seedling is placed in a hole.
- The root system is covered with soil and then thoroughly watered.
What to plant next to it?
A separate plot is allocated for growing this apricot variety. Perennials and various spring flowers are planted nearby.
It's not recommended to plant rattlesnails near other fruit crops, as they don't interact well. Apple trees, plum trees, and raspberry bushes should be spaced 4 meters apart.
Further care of the crop
Growing involves regular care, which includes watering, fertilizing, and so on.

Watering and fertilizing
To ensure proper tree development, regularly feed the tree with complex, organic, and mineral fertilizers. The choice of fertilizer depends on the season. There are two types of fertilizer:
- Root fertilization. This involves applying fertilizer close to the tree's trunk. This method is the most popular because the nutrients are absorbed into the soil over a long period of time.
- Foliar application. The entire crown is fertilized, allowing all the necessary nutrients to be absorbed through the leaves for several days.
The rules for watering the Pogremok apricot are very simple: once every 2 weeks in spring and autumn, and once every 7 days in dry summers.
Crown formation
Crown formation involves pruning actively growing branches in the spring and removing dead ones in the fall. After pruning, everything is treated with a special solution.
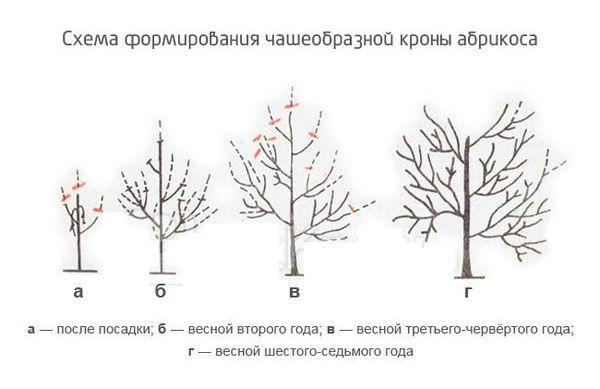
Caring for the tree trunk circle
The soil around the trunk is regularly loosened to remove weeds. This is necessary to prevent the tree from losing nutrients.
Preventive treatments
To avoid the occurrence of diseases and various pests, do the following:
- careful pruning of branches;
- spraying the crown in spring;
- soil moisture control;
- covering the tree for the winter to prevent damage due to temperature changes;
- removal of damaged leaves and fruits.
Covering a tree for the winter
Before winter, the fruit tree is watered and fertilized. The trunk is covered with a special net to protect it from various rodents.
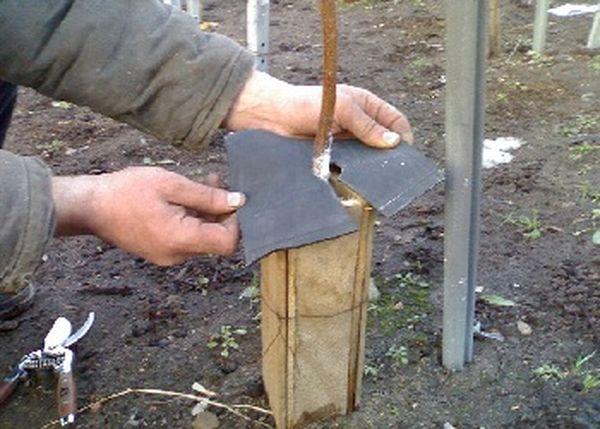

Methods of reproduction
The best propagation method for the Pogremok variety is by cuttings. Cuttings are taken in early summer. Only healthy, fresh shoots are selected for propagation, as they root better.
After this, the shoots are planted in a container with substrate and cared for until autumn.
Gardeners' reviews
This plant is popular and has received many positive reviews from gardeners. Here are two:
Maria Muromtseva, Kursk: "Four years ago, I planted the Pogremok apricot tree, and since then, it has grown to about 4 meters. The fruit is large and delicious. The tree serves as a pollinator for another variety."
Anastasia Ivanova, Saratov: "I purchased a two-year-old seedling from a nursery. The first fruits were picked a year ago. These apricots are versatile and excellent for drying."











