- Selection of the Cathedral pear variety and regions of cultivation
- Main advantages and disadvantages
- Description and characteristics of the variety
- Tree size and annual growth
- Branching of the root system
- Life expectancy
- Fruiting
- Flowering and pollinators
- Ripening time
- Productivity and taste
- Application of pears
- Drought and cold resistance
- Immunity to diseases and pests
- Peculiarities of planting pears
- Deadlines
- Site selection and soil preparation
- Distance between trees
- Tree planting diagram and rules
- How to care for fruit crops
- Watering
- Fertilizer application schedule
- Weeding the trunk circle
- Pruning and crown shaping
- Whitewash
- Diseases and pests: preventive treatments
- Preparing for the winter period
- Methods of reproduction
- Gardeners' reviews
Pear trees are essential in every garden. They are easy to grow, and modern varieties can withstand temperatures below -30°C.O and survive for long periods without water. The Cathedral pear variety is one such variety. Its fruits are delicious and contain vitamins A and C, B vitamins, potassium, calcium, iron, magnesium, copper, and zinc, as well as fruit acids and sugars. They are also rich in dietary fiber and pectin. Let's look at the characteristics of the Cathedral variety, how to plant it correctly, train it, and maintain its productivity.
Selection of the Cathedral pear variety and regions of cultivation
At the end of 1989, scientists and breeders from the Moscow State Agrarian University "Moscow State Agricultural Academy named after K. A. Timiryazev" S. P. Potapov and S. T. Chizhov submitted pear samples obtained from crossing seedlings 32-67 (Forest Beauty x Tema) and 72-43 (Forest Beauty x Duchess Bedro) for state testing.
The seedlings successfully passed tests for winter hardiness and drought resistance, demonstrated consistently high yields, and in 2001 the variety was entered into the state register under the name Cathedral.
Initially, it was recommended for cultivation in the Central region (Moscow, Vladimir, Bryansk, Kaluga, Ryazan, Smolensk and Tula regions), but is now actively moving into Western Siberia and the Volga region.
The variety is new and in less than 20 years of existence it is difficult to fully evaluate it in different regions of the country.

Main advantages and disadvantages
The advantages of the Cathedral pear variety include:
- restrained growth force - pruning requires less time and effort, and less consumption of preparations when spraying;
- early entry into fruiting – the first fruits can be obtained in the third or fourth year of the tree’s age, or in the second or third year after planting;
- the variety does not have high requirements for soil fertility or moisture, and easily tolerates harsh winters;
- high yield – according to the variety’s creators, each tree can produce an average of 60-100 kg of pears annually;
- the most convenient ripening period is the second half of summer;
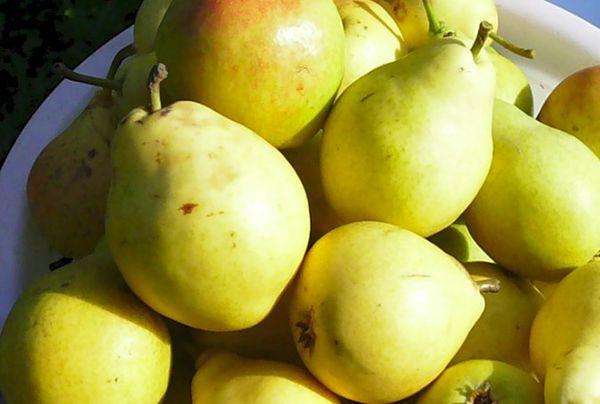
- Very tasty fruits with a balanced acidity and sweetness, the stone cells in the pulp are very small, unnoticeable, the pulp as a whole is tender and juicy - this pear is suitable for dietary and baby food;
- A wide range of processing options for Cathedral pears – suitable for pickling and making compotes from whole pears, jams, juices, desserts, and drying in an electric dehydrator.
The disadvantages of the Cathedral form include:
- not too large fruit size – 100-110 g;
- short shelf life of fruits – no more than 15 days;
This variety has many more advantages than disadvantages.
The pattern in the fruiting of the Cathedral pear is that the higher the pear yield, the lower the average weight of each individual fruit.
Description and characteristics of the variety
When selecting a variety for your dacha or garden plot, it's recommended to carefully study the description of each fruit and berry variety to ensure you make the right choice to meet the needs of all family members.

Tree size and annual growth
In adulthood, Kafedralnaya trees remain of medium height, not exceeding 3-4 m. The variety's annual shoot growth is moderate, not exceeding 30-40 cm. Kafedralnaya pear trees reach their maximum size at 7-10 years of age.
The crown grows in a regular cone shape with the apex at the top, with a clearly defined central core. This makes pruning and shaping the trees very convenient during the first years of life.
An important feature of the Kafedranaya pear variety is its uncluttered crown, with no inward-growing shoots. This can be explained by the balanced distribution of growth factors within the plant. Fruiting shoots, or rings, gradually develop on third- and subsequent-year branches. Occasionally, in favorable years, fruit may form on the previous year's shoots.
The Cathedral pear cultivar is ideal for grafting other varieties onto it. Its branching pattern allows for 3-4 branches in different directions, each grafted with a different variety.
Branching of the root system
The Cathedral pear trees have two types of roots:
- deep;
- superficial.
In general, the growth and branching patterns of roots depend on the rootstock used. This can be quince or wild pear grown from seed. Deep roots are large, grow quickly, and their main function is to anchor the tree, or provide stability, anchoring it in the soil. Over the years, these anchor roots become overgrown with sucker roots.

Surface roots are designed to absorb water and nutrients. They are located at a depth of 5 to 12 cm, branch extensively, and extend in a radius of 2 to 4 meters in all directions from the trunk. When digging the soil in the garden in the fall, be careful. If the shovel encounters roots, avoid them to avoid damaging them with the sharp blade and weakening the tree's growth.
Pear tree surface roots can produce suckers. This should be controlled regularly by cutting them back 1-2 cm below the ground.
Life expectancy
Pear trees, and this variety in particular, are extremely long-lived. The Cathedral variety can produce for 40-50 years, and overall, the trees can live up to 200 years. This is due to the tree's extremely dense wood and the presence of stone cells in its structure.
Fruiting
The first fruits are borne on three- to four-year-old Cathedral pear trees. Pears can be grown in groups or as single trees. During the first years of fruiting, it is recommended not to overload the trees.
The rule of thumb is to leave no more than 1-2 fruits per shoot, and remove the remaining ovaries by hand. This procedure can be omitted in subsequent years.
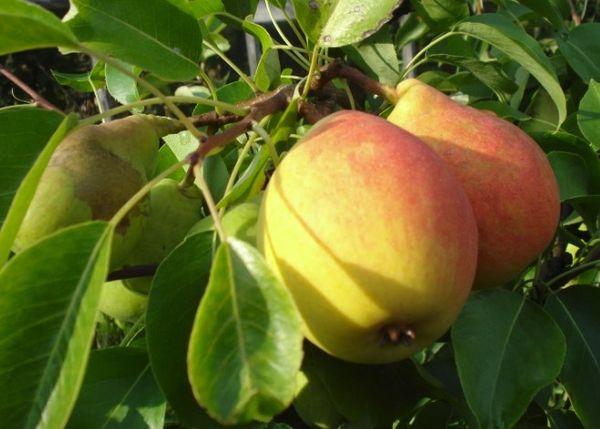

The fruits of the Kafedralnaya pear are perfectly shaped, without a funnel at the wide end, weighing 100-110 grams each. They are green when ripening, gradually turning yellow. When exposed to the sun, the fruits acquire a delicate orange-red blush. The spots on the skin are almost invisible. The pear surface is smooth, sometimes slightly bumpy. The stalk is thick and curved.
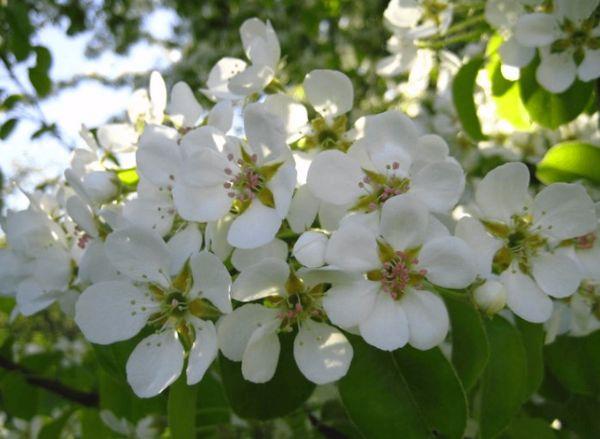
Flowering and pollinators
The Cathedral pear tree blooms in the first and second ten days of May. This cultivar is partially self-fertile. However, for a consistently high yield, it's best to have several other pollinating varieties on the plot or within 400 meters of neighboring trees:
- Lada;
- Chizhovskaya;
- Samaritan woman;
- Ruddy golden eagle;
- Oryol summer;
- Marble;
- Prominent;
- August dew.
The presence of apiaries near summer cottages is very favorable for pollination.

Ripening time
The Cathedral pear is a summer variety. In the Central region, ripening occurs in mid- to late August. In the Volga and Black Earth regions, ripening has been observed in the first ten days of August. In Western Siberia, the fruits are ready in late August to early September.
Productivity and taste
One hundred square meters of pear orchard yields 180-240 kg of fruit. The trees are productive.
The fruit has excellent flavor and tender flesh. It received a tasting score of 4.6 out of 5.
Application of pears
This variety is suitable for all types of processing. Compotes and desserts made with Kafedralnaya pears are especially delicious. Slices are added to puddings and fruit salads with creamy fillings. By using the correct settings in an electric dehydrator, dried fruit with high commercial quality is achieved.
Drought and cold resistance
Plants can withstand frosts of -30 OIn snowless winters, young trees may experience root freezing and frost cracks in their trunks. They tolerate the summer period well in any growing region due to their well-developed root system.

Watering allows you to achieve larger fruits and ensures the formation of full-fledged fruit buds for the next season.
Immunity to diseases and pests
The Cathedral cultivar has high immunity to apple and pear scab, rust, and all types of powdery mildew. Young plants can be attacked by black aphids, and silkworms rarely eat the leaves.
The variety is generally unpretentious.
Peculiarities of planting pears
To ensure maximum long-term productivity from trees, it's important to follow a number of planting and care guidelines. Let's take a look at them.
Deadlines
In regions with a warm, long autumn, planting is permitted from the second ten days of September until the end of the first ten days of October.
When planted in autumn, the trees must take root before the onset of persistent frosts.
Plants that have survived retain shiny bark, while those that have died have dull, wrinkled, and dry bark.
In regions where it is difficult to meet this condition, it is preferable to plant in the spring - from the second half of April until approximately the end of May.

Site selection and soil preparation
The Cathedral pear tree should be planted in a sunny, wind-protected location. Loamy soil is preferred, though clay soil is acceptable.
Planting holes are prepared in the fall. They are dug to a depth of at least 0.8 m and left uncovered over the winter to prevent harmful microorganisms from freezing.
In the spring, the edges of the hole are leveled, fertile soil or humus is added to the bottom in a 30 cm layer, rotted manure and 50-60 g of Azofoska fertilizer are added, and all ingredients are thoroughly mixed.
Distance between trees
Trees should not shade each other in the garden. Pears, apples, and cherries should be planted at a distance of 4-5 meters. Cathedral pears can be planted near a fence at a distance of 2-2.5 meters from the fence.
Tree planting diagram and rules
When purchasing a bare-root seedling, the roots should be kept moist at all times. Immediately before planting, root cuts and shoot tips should be renewed. Planting should be done using a 4x4 or 5x5 m pattern.
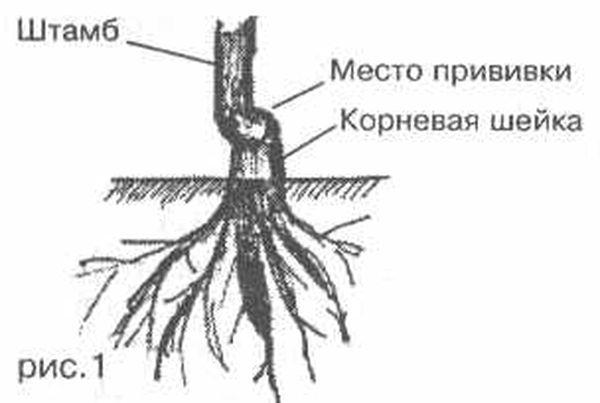
Place the seedling in the center of the hole and gradually cover it with fertile soil. Once the roots are completely covered, gently tamp the soil down, then water with 10-15 liters of water. Once the moisture has been absorbed, fill the hole with fertile soil or mulch with peat or spruce branches.
How to care for fruit crops
Caring for a pear tree is not difficult.
Watering
In a dry summer, the pear is given:
- in May after flowering – 1 watering;
- in June – 2 waterings;
- in July – 3 or 4 waterings;
- in the first ten days of August – 1 watering;
- moisture recharge at the end of September.
Watering should be abundant and reliably moisten a layer of at least 50 cm. 80-120 liters of water are poured under a mature tree.
Fertilizer application schedule
Every year you need to add organic matter to the pear tree - this could be well-rotted manure or humus.
In early spring, apply a Reasil zinc fertilizer during the first watering. In the first half of June, apply urea or ammonium nitrate at 40 g per 10 liters of water. At the end of July, add 30-40 g of potassium chloride and superphosphate to the holes before watering.
Weeding the trunk circle
After each watering, weed and lightly loosen the soil around the tree trunks. If you keep the holes mulched, this step is unnecessary.

Pruning and crown shaping
During the first year, the Cathedral tree is not pruned. Beginning in the second year, the first tier of the crown is formed. Three branches are left at a 120-degree angle.O to each other.
The following year, the second tier is formed similarly to the first, but the branches of the second tier are positioned in the gaps between the branches of the first. During the productive period, pruning and thinning techniques are used.
Whitewash
Tree trunks are vulnerable to cracking in February and March. During this time, it's advisable to whitewash them with a special whitewash based on slaked lime.
It's best to purchase the solution from a specialist store. Manufacturers may add substances that combat pests that overwinter under the bark.

Diseases and pests: preventive treatments
During the summer, two preventative treatments are carried out: at bud break, use Fufanon for pest control, and after flowering, use Skor for rust and scab control.
Preparing for the winter period
For the winter, the trunks of young trees are mulched with spruce branches. The crowns are covered with one or two layers of non-woven covering material. Mature trees do not require covering.
Methods of reproduction
In garden plots, the easiest method is to graft behind the bark or into a cleft. If desired, you can graft a young quince seedling with a bud from the Cathedral pear tree.
Gardeners' reviews
Angelina Viktorovna, Tula region.
"I've had a Kafedralnaya pear tree growing in my garden for nine years now. The tree is slender, with clean, unblemished leaves. It started bearing fruit in its third year—we harvested two dozen pears. Now I harvest five to six buckets each year. I'm very happy with the variety."
Stepan Petrovich, Samara.
"We brought the Cathedral pear from a Moscow nursery. It's taken well. We're currently harvesting 50 kg of juicy pears per tree. We mostly eat them and give them to neighbors and friends, and everyone loves them!"











