- History of the variety
- Characteristics and description of the Forest Beauty pear
- Habitat
- Dimensions of a mature tree
- All about fruiting
- Flowering and pollinating varieties
- Harvest ripening time
- Collection and use of fruits
- Frost and drought resistance
- Typical crop diseases: treatment and prevention
- Tree pests
- Specifics of planting crops
- Site layout plans
- Distance between trees
- Timing and technology of planting
- Pear tree care activities
- Seasonality of irrigation
- Regularity of fertilizing
- Features of crown formation
- Caring for the tree trunk circle
- Preparing for winter
- Reproduction
- Gardeners' reviews of the crop
The Lesnaya Krasavitsa pear variety is one of the oldest, serving as the biological basis for 30 new hybrids developed by Russian geneticists. As a distinct species, this pear is prized by gardeners for its winter hardiness, attractive appearance, and sweet fruit flavor. A distinctive feature of this variety is its long-lasting fruiting. Some trees produce fruit for up to two hundred years.
History of the variety
The cultivar was not included in the State Register of Breeding Achievements of the Russian Federation, as the Forest Beauty is not the result of scientific experiments. However, this has not diminished the fruit tree's popularity in Europe and the former Soviet Union. The Forest Beauty has been known to the world for at least two centuries. The pear tree, with its juicy, sweet fruits, was discovered by chance in a Belgian forest near the town of Alost.
Characteristics and description of the Forest Beauty pear
The pear's attractive appearance, sweetness, and juiciness are marred by its short shelf life. Gardeners consider the following to be other disadvantages of the Forest Beauty:
- low immunity of the crop to fungal diseases;
- fruits become smaller with age;
- weak connection of the fruit with the stalk.
In addition to the positive characteristics of the fruit, the advantages of pears include:
- winter hardiness;
- drought resistance;
- abundant fruiting;
- undemanding to soil composition.
During flowering, the pear tree enhances the decorative value of the area.
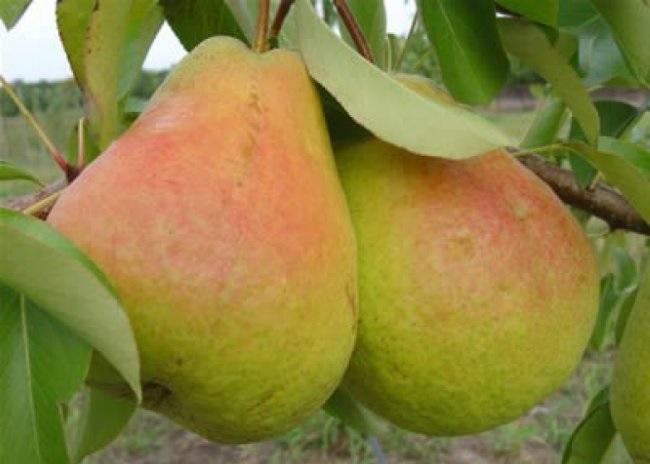

Habitat
The forest beauty is widespread in Europe, the Baltic states, Central Asia, Moldova, Ukraine, and Belarus. In Russia, it grows in the Kuban region, the Astrakhan and Volgograd regions, Kalmykia, and the North Caucasus. With proper cultivation practices, it produces a good harvest in southern Siberia.
Dimensions of a mature tree
A mature Lesnaya Krasavitsa pear tree reaches a height of 5 m. Its broadly pyramidal (columnar) crown becomes more spreading with age. This is due to the skeletal branches shifting away from the trunk due to the weight of the fruit.
The pear tree's bark is gray, and its brown shoots are straight, thick, and arched. The dark green, glossy, egg-shaped leaves are arranged spirally on the branch.

All about fruiting
The Forest Beauty is not an early-fruiting pear variety. Fruiting does not begin until the tree reaches its 7th or 8th year. By this time, the tree's growth has also ceased.
When fully ripe, the 120–150 g fruits are golden in color, with a bright blush appearing on one side. The fruit is ovoid in shape. The stalk is thick and shortened, widening toward the top. The skin is thin and rough. The white or light yellow flesh is juicy, tender, and sweet, with a subtle tartness.
100 g of product contains 0.5 g of organic acids per 10 g of sugars.
Flowering and pollinating varieties
The umbrella-shaped inflorescences of the Forest Beauty pear bloom with pale pink, 5-petal, cup-shaped flowers in April–May.
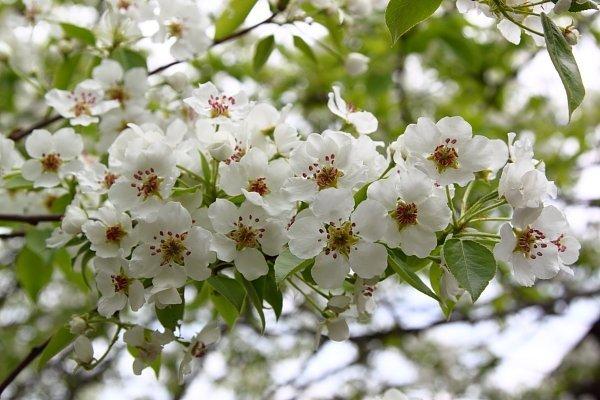

If there are no pollinators in the neighboring area within 30 m of the planned planting, then a pear of a different variety with the same flowering period is planted in the area.
Suitable pollinators for the Forest Beauty variety:
- Lemon;
- Marianne;
- Clapp's Favorite;
- Williams.
Pollinators are necessary for the crop, since the variety is partially self-fertile and will not bear fruit abundantly without planting other varieties nearby.
Harvest ripening time
Depending on the growing region, the fruit fully ripens in the last ten days of August or early September. Farmers harvest up to 150 centners per hectare, while amateur gardeners harvest 50–80 kg of fruit from a young tree and up to 200 kg from a pear tree older than 40 years. A record harvest of 400 kg was recorded in Crimea.
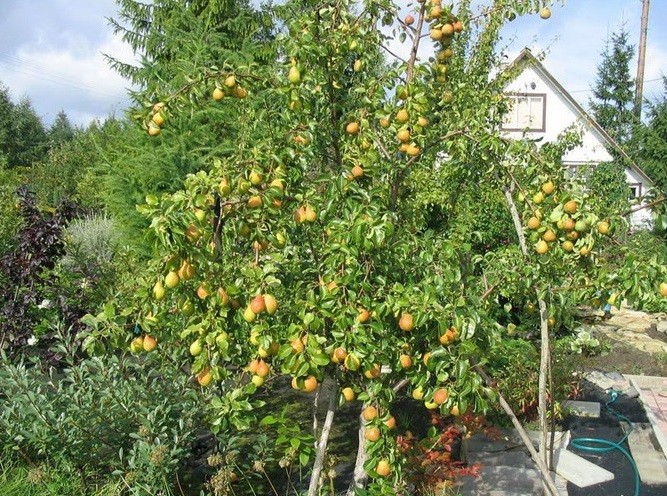

Collection and use of fruits
Due to the fragile connection between the fruit and the stalk, it is recommended to harvest 1–2 weeks before full ripening.
The fruits are picked carefully, stems included, avoiding mechanical damage. At room temperature, the fruits remain fresh for 3 weeks. They can be stored unchanged for up to 3 months. To do this, the crates containing the fruits are moved to a ventilated room with 85% humidity and a temperature between 4–8°C.
Forest Beauty pears are suitable for canning, drying, making candied fruit, and adding to fermented milk products. However, fresh pears are healthier.
When trying to get rid of obesity, nutritionists recommend including pears in your diet, as the energy value of the fruit is only 47 kcal.
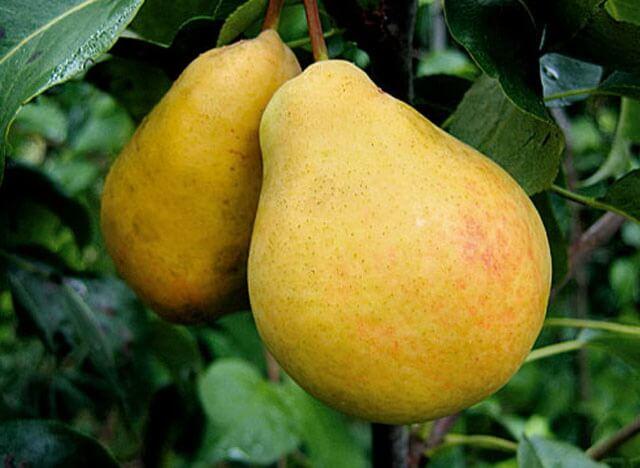

Frost and drought resistance
The Forest Beauty pear is considered the most frost-hardy (down to -45°C) among European varieties. Its flower buds and blossoms are resistant to recurrent spring frosts. The pear does not reduce its fruiting during temporary drought, but prolonged summer heat weakens the tree.
Typical crop diseases: treatment and prevention
Among the most common diseases, the Forest Beauty pear is most often affected by:
- Scab. Whitish spots appear on the undersides of leaves, eventually turning brown. If the spores reach the flowers, the ovary fails to form. Scab that strikes the plant during fruiting manifests itself as spots on the fruit and woodiness of the pulp. To combat the disease, treat the plant with Horus, Tridex, and Merpan.
- Fire blight. The disease begins with blackening of buds and wilting of flowers. It then spreads to the leaves, which dry out and curl, branches, and trunk bark. After the trunk turns black, the tree dies. In the initial stages of fire blight, spraying the plant with antibiotics a week before flowering can help.
- Fruit rot. Spreading brown spots appear on the fruit, making it inedible. To prevent the spread of spores, affected fruit are removed from the branches and disposed of. To prevent foliar damage, treat the Lesnaya Krasavitsa pear tree in spring and fall with a lime solution (1 kg per bucket of water) and Bordeaux mixture. Horus and Azofos are suitable treatments.
Disease prevention includes spring treatment of pears against pests that carry pathogenic microorganisms, sanitary pruning, and adherence to agricultural practices.
Tree pests
Insects that harm the Forest Beauty, treatments, and preventive measures:
- Pear fruit sawfly. Yellowish larvae burrow into fruit ovaries, eating away the cores of the fruit, moving from one to the next. After feeding, they fall into the soil, where they overwinter. To prevent insect attacks, dig up the area around the tree trunk by 10 cm. Before and after pear blossom, treat the tree with Actellic, Kemifos, and Iskra.
- Red fruit mite. This red, microscopic (0.4 mm) insect is dangerous at any stage of development. Yellow spots form along the leaf veins, later turning gray. Photosynthesis is disrupted, crop development is inhibited, and fruit size decreases. Control and prevention measures include whitewashing the trunks and spraying the tree with ascaricidal agents (Fitoverm, Karachar, Karbofos).
- Pear fruit moth. The white, 1.5-centimeter-long caterpillars of the gray fruit moth feed exclusively on fruit, often located at the top of the tree canopy. Sticky belts and pheromone traps are used to control the insect. During mass flight of the moths, insecticides (Klinmix, Agravertin, Karbofos) are used.

Gardeners repel pests not only with chemicals, but also with folk remedies - infusions of tansy, wormwood, and marigolds.
Specifics of planting crops
No matter how undemanding and unpretentious the plant, when planting a pear, the timing, pattern, and technique must be followed. The subsequent development and fruiting of the crop depend on proper planting.
Site layout plans
The choice of planting pattern for the Lesnaya Krasavitsa pear depends on the shape of the plot. If the plot is flat, square patterns are used, with trees planted at the corners of a square in even rows with 5-meter spacing.
When using a rectangular pattern, maintain a distance between pears of 4x3 m.
You can plant the seedlings in a checkerboard pattern, with a fifth tree added in the center of the square. This arrangement is used to prevent soil erosion if the plot is located on a slope. To save space in a small area, pear trees are planted in a triangle.

Distance between trees
Medium-sized pear varieties, including Forest Beauty, are planted 3–4 m apart from each other. They are spaced at least 2 m from the boundary with the neighboring plot.
Timing and technology of planting
In regions with warm and temperate climates, it is recommended to plant Lesnaya Krasavitsa pears in the fall, 1.5 to 2 months before the first frost. In areas with long, cold winters, plant the crop in May.
The hole is dug 60 cm deep and 1–1.2 m wide. To increase soil fertility, the following fertilizers are added to the topsoil:
- humus, manure or compost - 2 buckets;
- 1 kg of wood ash;
- 30 g potassium salt;
- 0.5 kg of superphosphate.

The seedling is shortened to 50 cm, and the branches are trimmed by a quarter. The root is soaked in Kornevin, disinfected in a manganese solution, and dipped in a clay slurry.
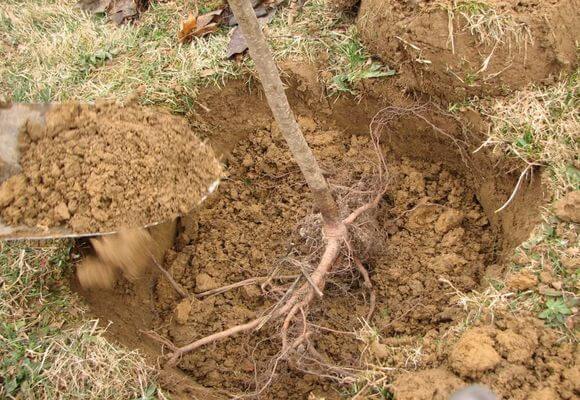
Planting algorithm for the Forest Beauty pear variety:
- stepping back from the center of the hole by 20–30 cm, drive in a support stake;
- make a mound at the bottom;
- lower the seedling onto the top of the elevation, straightening and directing the roots in the desired direction;
- fill it with substrate, shaking the tree so that no voids form;
- the soil is compacted, the pear is tied to the support;
- water generously (10 l) through a groove along the diameter of the tree trunk circle:
- mulch.
When compacting the soil, ensure that the root collar rises 3–5 cm above the surface.

Pear tree care activities
The abundance, regularity of fruiting, and dessert taste of the fruit depend on irrigation regulation, timely fertilizing, pruning, and preventative and curative treatments.
Seasonality of irrigation
Until rooting occurs, water the seedling every two weeks; a mature tree monthly. It's recommended to pour the water not under the trunk, but into a trench dug 20 cm from it. While a bucket of water is sufficient for a seedling, a mature tree requires 40 liters at a time.
Regularity of fertilizing
The first time a pear tree is fed is in the second year after planting. In the spring, when the flower buds are opening, the tree is watered with 5 liters of water containing 100 g of dissolved urea. During flowering, nitroammophoska is used. Use 50 g of dry matter per bucket of water. You'll need 30 liters of solution per tree.
In summer, in the second half of June, the pear is sprayed with nitroammophoska according to the instructions for use.
After harvesting at the end of September, add 1 tablespoon of superphosphate granules and 200 g of ash per 1 sq. m of the tree trunk circle to a depth of 10 cm.

Features of crown formation
In the first year, before planting, the main trunk is shortened to 50–80 cm. The following spring, four skeletal branches, directed in different directions and angled 45° from the trunk, are left; the rest are removed. Each year, a new tier is formed, 0.5 m above the previous one, consisting of three branches shorter than the lower ones. The difference between a pyramidal crown and a tiered crown is that secondary branches are not left on the tiers, only the shoots that are growing on the understory.
The conductor of the formed tree should be 20–30 cm higher than the side branches of the upper tier.
In a mature tree, skeletal branches are pruned back by a quarter. Diseased and broken shoots are removed each spring, and in the summer, those that are crowding the crown or growing in the wrong direction are removed.
Caring for the tree trunk circle
Caring for the pear tree's trunk area involves loosening the soil at least once every 2-3 weeks to improve moisture and air permeability, regular weeding, watering, and mulching. To preserve nutrients, remove any root suckers that are not useful for propagation.

Preparing for winter
The Forest Beauty tree does not require shelter. Mulching the area around the tree with sawdust, straw, or peat is sufficient. To protect against rodents, the trunk and lower branches are whitewashed with a solution consisting of 10 liters of water, 1 kg of lime, and 200 g of copper sulfate. The trunk of the pear tree is wrapped in metal mesh, the lower part of which is dug into the ground, or coniferous branches are tied to the trunk.
Reproduction
Pear trees are propagated by seeds without any certainty of the end result. Once the rootstock is grown, it's difficult to predict which characteristics will prevail—the parent tree or the wild plant.
The main method of propagation of the Forest Beauty variety is by root suckers, which are separated from the mother tree in September or in the spring before the sap begins to flow.
Due to the poorly developed root system, young shoots often do not take root, so they are placed in a greenhouse in the spring, after soaking the roots in a root-forming stimulator, and planted in a permanent location in the fall.
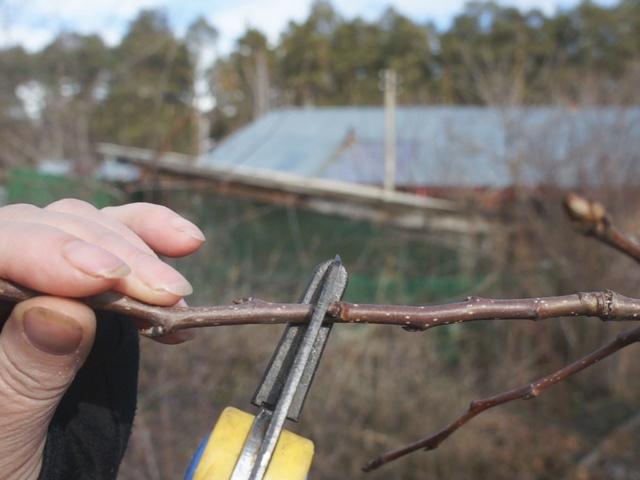

Or, in the spring, before the growing season begins, the root connecting the shoot to the mature tree is severed, and the shoot is irrigated and fertilized with essential micronutrients until fall. In this case, the seedling will develop lateral branches on its roots by fall, and the plant is better prepared for transplanting.
Gardeners' reviews of the crop
In reviews, gardeners note the abundant fruiting and winter hardiness of the crop. Among the disadvantages, they point out susceptibility to scab and a short shelf life of the fruit.
Natalia Alekseevna, 47 years old, Kherson
If you don't sell fruit, I don't recommend planting more than one tree per plot. The crop is extremely productive, but the fruit spoils quickly. I treat my friends and neighbors every year.
Vasily Alexandrovich, 45 years old, Voronezh
Four years ago, I started an orchard. I planted a 'Forest Beauty', which a neighbor recommended as an easy-to-grow tree. The tree died from scab. It turns out this variety, like others, requires preventative treatment.
Matvey Vladimirovich, 59 years old, Minsk
The Forest Beauty has many advantages: beautiful, tasty fruit, frost resistance, and low maintenance. The only drawback was the long wait for the harvest. The pear didn't begin to bear fruit properly until the seventh year after planting.











