- What is characteristic of the Arosa variety?
- History of the culture's development
- Description of the bush and root crop
- Taste properties and applications of potatoes
- Pros and cons
- Necessary conditions for growth and fruiting
- In which areas is it recommended to grow?
- Optimal location and lighting of the site
- Humidity and temperature conditions
- Favorable and unfavorable neighbors and predecessors
- Planting Arosa in open ground
- Deadlines
- Preparing the soil and planting site
- Preparing seedlings
- Planting pattern and depth
- Proper care of potato plantings
- Regularity of irrigation
- What and how to feed
- Mulching and loosening the soil
- Hilling up the beds
- Therapeutic and preventive treatment
- Rhizoctonia or black scab
- Late blight
- Silver scab
- Harvesting and storage
- Reviews of Arosa from experienced vegetable growers
The main goal of potato farmers, gardeners, and vegetable growers is to obtain a large, high-quality vegetable harvest. Therefore, breeders in developed countries are creating unique potato varieties that boast not only high yields and excellent taste, but also rapid root ripening.
The Arosa potato is exactly such a variety, which has already gained recognition among professionals.
What is characteristic of the Arosa variety?
Like any plant bred through the work of breeders, the Arosa potato is endowed with the best qualities of this vegetable crop and is capable of growing and ripening in difficult climatic conditions.
History of the culture's development
German plant breeders often delight the global community with their unique developments. At the end of the last century, a new, improved potato variety, Arosa, was developed, which, according to experts, exceeded all expectations in testing.
In 2000, the Arosa potato variety was included in the state register of vegetable crops and was permitted for import and propagation in many regions.
Description of the bush and root crop
Mature plants grow to medium-sized bushes with spreading, upright branches. Bright green foliage densely covers the entire bush, with medium-sized leaves with pointed tips. Each bush has 5 to 7 strong stems, which produce large inflorescences. During flowering, large purple or red flowers open. The roots are large, weighing 80 to 130 grams each, oval in shape, with thick pink skin. The flesh is a rich yellow when cut.
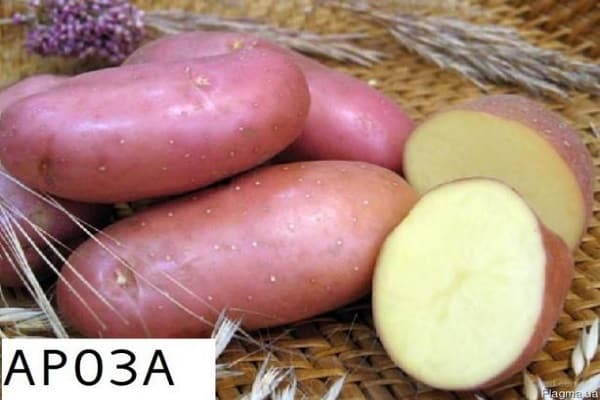

The tubers are rich in fiber and vitamins, with starchy substances ranging from 11 to 15%. The roots ripen 2-2.5 months after planting. The first young tubers can be dug up at 40-45 days of growth. The yield of these tubers on an industrial scale can reach up to 70 tons per hectare. Private growers rate the Arosa variety as productive. A single plant produces 11 to 17 ripe, large tubers.
Taste properties and applications of potatoes
The Arosa potato boasts excellent flavor across all parameters. This table vegetable variety is used in the food industry for the production of chips, semi-finished products, and French fries.
In cooking, this variety is used as a versatile one. The tubers do not overcook when cooked, making them suitable for any dish.
Pros and cons
To decide whether to plant Arosa potatoes in your garden or on a farm, you need to study all the characteristics, advantages, and disadvantages of this variety.

Advantages of the variety:
- With proper care, the yield rate is high.
- Immunity to viral and fungal infections.
- Ability to ripen in drought conditions.
- The taste qualities of the variety were rated with the highest scores.
- Possibility of long-term storage and long-distance transportation.
- The variety is resistant to mechanical damage.
Important! The Arosa potato is resistant to climate change, so it is grown in both southern and northern regions.
Disadvantages of the variety:
- Weak resistance to scab, late blight and rhizoctonia.
- The Arosa variety is demanding of fertilizers and top dressing, but does not tolerate an excess of minerals in the soil.

To prevent plants from being affected by diseases, the tubers are treated before planting in open ground.
Necessary conditions for growth and fruiting
The Arosa potato is undemanding about soil and care, making it easy for even beginners to grow. However, there are some specific growing guidelines for Arosa, and they must be followed to ensure a high-quality harvest.
In which areas is it recommended to grow?
Following testing and inclusion in the state register of vegetable crops, the Arosa potato variety is recommended for cultivation and production in the following regions:
- North Caucasus.
- Middle and Upper Volga.
- Ural.
- Eastern and Western Siberia.

Farmers and gardeners successfully grow and propagate the Arosa potato variety in the central and southern regions.
Optimal location and lighting of the site
A site for planting potatoes should be level, well-lit, and well-ventilated. Close proximity to groundwater and soil water can have a negative impact on potatoes. If planting vegetables in such soil is unavoidable, the beds should be raised 10-20 cm above ground level.
Humidity and temperature conditions
The variety is undemanding regarding soil moisture and tolerates prolonged heat and drought well. Although Arosa is not considered frost-hardy, the plants easily tolerate minor fluctuations in spring temperatures.

Favorable and unfavorable neighbors and predecessors
Potatoes grow and thrive if preceded by the following vegetable crops: garlic, peppers, beets, cucumbers, or any greens. Legumes also leave behind fertile soil.
After these crops, the soil is saturated with nutrients useful for the growth and development of potatoes.
Important! It is strictly forbidden to plant potatoes after any varieties of tomatoes, sunflowers, or plants from the nightshade family.
Planting Arosa in open ground
To obtain a high-quality and abundant vegetable harvest, the main rule is to strictly adhere to the rules for planting tubers in open ground.
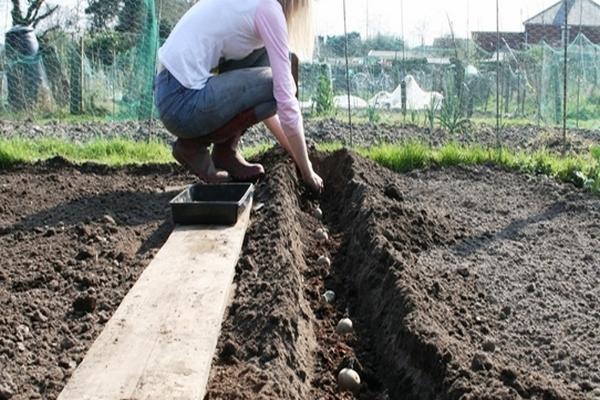

Deadlines
Planting dates are calculated based on the region where the vegetable crop is grown. In warm and mild climates, potato planting in open ground begins in mid-April. In central regions with a temperate climate, planting begins in early May. In northern regions, they wait for consistently warm weather and soil temperatures reaching 10-12 degrees Celsius.
Preparing the soil and planting site
Preparing the plot for planting potatoes begins in the fall. The soil is thoroughly tilled and mixed with organic fertilizers. If the soil is poor, phosphate and potassium fertilizers are added.
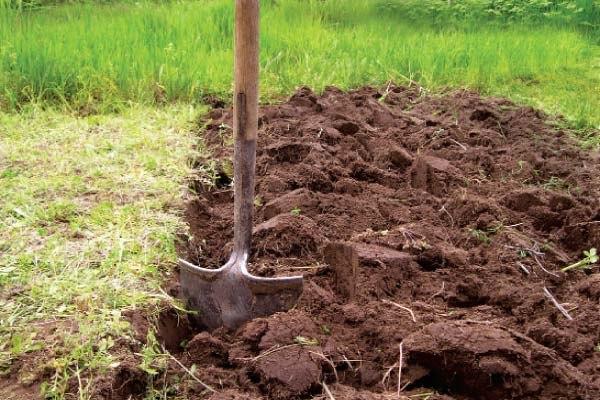

In the spring, the beds are dug up and loosened again.
Preparing seedlings
Planting material is prepared in advance, 2-3 weeks before planting. Tubers from previous harvests are selected for germination. Planting material is also purchased from specialized nurseries and garden centers. The roots are cleaned of excess soil and dirt and inspected.
Tubers for planting are selected to be smooth, medium and small in size, without obvious damage or diseases.
Any spots on seedling tubers may indicate that the plant has been exposed to a virus, fungus, or pest. Therefore, before planting outdoors, the tubers are disinfected with professional pesticides.
Planting pattern and depth
The distance between the holes is 25-35 cm, between the beds 50-60 cm. The hole is dug to a depth of 10-12 cm, the tubers are deepened by 6-8 cm.

If planting is planned in a harrow, then the same distance is left between the root crops.
Proper care of potato plantings
Timely and proper care is a guarantee of healthy and fruitful plants at the end of the season.
Regularity of irrigation
The variety's drought tolerance eliminates the need for a tight, strict irrigation schedule. During the entire growing and maturing period, potatoes require no more than three waterings.
Irrigation work stops completely 2-3 weeks before harvesting.
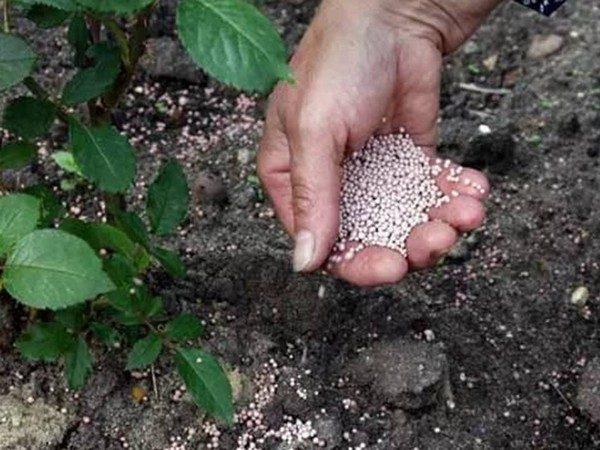
What and how to feed
If you applied fertilizer and other nutrients to your potatoes when planting, this is sufficient for their development and growth. In some cases, additional feeding is required during bud formation and flowering.

Mulching and loosening the soil
Soil loosening and mulching are carried out in conjunction with irrigation. Loosening the soil removes weeds and retains moisture. After loosening, the soil is mulched. Straw or sawdust are suitable for mulching.
Hilling up the beds
Initially, hilling is done on beds with young shoots. Further work is carried out when inflorescences form and when the potatoes finish flowering.
Therapeutic and preventive treatment
Although the variety is resistant to most diseases, some of them can affect plants and cause significant damage to the crop.

Rhizoctonia or black scab
The appearance of black spots on root vegetables indicates a scab infestation. In this case, the potatoes are sprayed with special chemicals.
Late blight
Dark spots, root rot, and drying out of the plant are the first signs of late blight. Potatoes require immediate treatment with professional products.
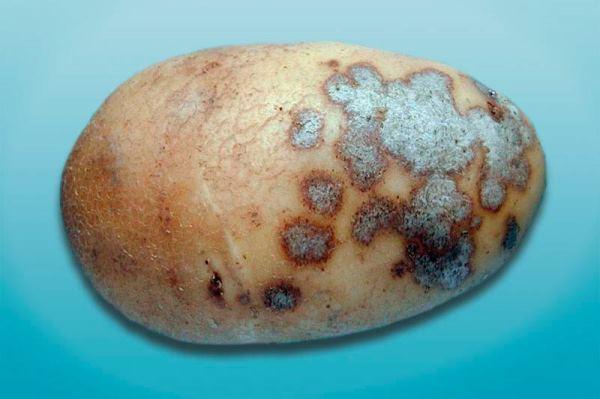
Silver scab
If brown lesions appear on root crops, they will soon shrivel and die. After harvesting, the crop is treated with a special preparation to stop the spread of the disease.
Harvesting and storage
Harvesting occurs 60-65 days after planting. The tubers are carefully removed from the soil and dried.
Dried potatoes are placed in prepared containers or bags and stored for a long period in a dark, well-ventilated and cool place.
Reviews of Arosa from experienced vegetable growers
Ekaterina, Izhevsk
I grow many potato varieties, but Arosa is my favorite, both in terms of flavor and yield. It requires little care and grows with virtually no watering. It keeps for a long time without losing its flavor.
Nikolay Timofeevich, Sevastopol
The Arosa potato has only recently appeared in my garden, but it has already displaced other varieties I've been planting for years. It's delicious and doesn't fall apart at all when boiled. It requires virtually no care—just plant and harvest.
Sergey Vladimirovich, Ryazan
A neighbor recommended Arosa, and I've been planting this variety in my garden for five years now. The yield is simply astounding; I've never seen such a variety before. The tubers ripen smooth, beautiful, and delicious. They keep all winter and spring in the cellar, occasionally sorting through and setting aside wilted tubers.











