- Optimal timing for raspberry propagation
- Spring
- Summer
- Autumn
- Necessary tools for carrying out work
- Specifics of bush propagation
- Root suckers
- Root cuttings
- Green cuttings
- By dividing the bush
- Woody shoots
- Scottish method of raspberry propagation
- Lateral shoots or suckers
- Propagation of raspberries by seeds
- Rooting the top
- How to care for seedlings after planting
- Potential problems and difficulties
Many people are interested in the pressing question of how to propagate raspberries. Today, there are a variety of methods that achieve excellent results. Cuttings, layering, and seeds are used to propagate the bushes. Side shoots or rooting the tops are also possible. This allows every gardener to choose the best option based on their abilities.
Optimal timing for raspberry propagation
To achieve excellent results in raspberry propagation, first of all, you need to choose the right method for carrying out the procedure.
Spring
This season is considered the least stressful. Under the sun's influence, raspberries root well and adapt easily to external factors. Lateral layers or suckers are used for this procedure.
Summer
For summer propagation of raspberries, young cuttings that have not yet had time to harden are used. These cuttings are highly prone to root formation. This procedure is best performed in August.
Autumn
At this time of year, raspberries are propagated by cuttings. For this purpose, 3-4 year-old plants with strong shoots are used. It is recommended to harvest planting material in September.

Necessary tools for carrying out work
To successfully propagate the crop, you'll need to properly prepare the necessary tools. You'll need the following:
- shovel;
- sand;
- planting material;
- bags;
- pruning shears or knife.
Specifics of bush propagation
To propagate bush raspberries while preserving the plant's varietal characteristics, it is necessary to choose the right method for carrying out the procedure.
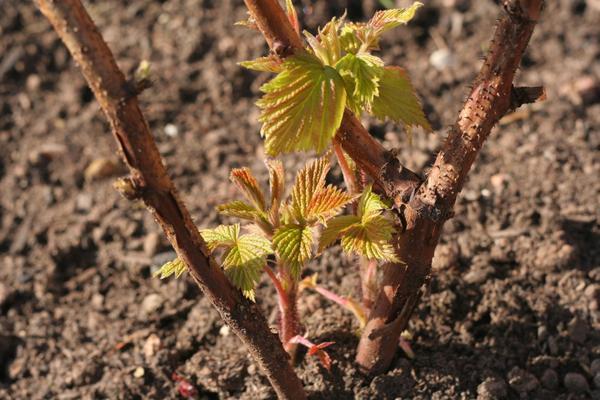

Root suckers
The plant is characterized by root growth, from which new stems emerge. This method helps maintain order in the garden.
To do this, the rhizomes that have grown beyond the bush should be carefully dug up and divided into sections containing young shoots. These can then be immediately transplanted to a new location. This method is recommended for propagating raspberries in the fall.
Root cuttings
Cuttings are taken in spring or fall. To do this, carefully dig up the soil 40 centimeters from the center of the bush. Then carefully dig out the adventitious root, preserving as many branches as possible.
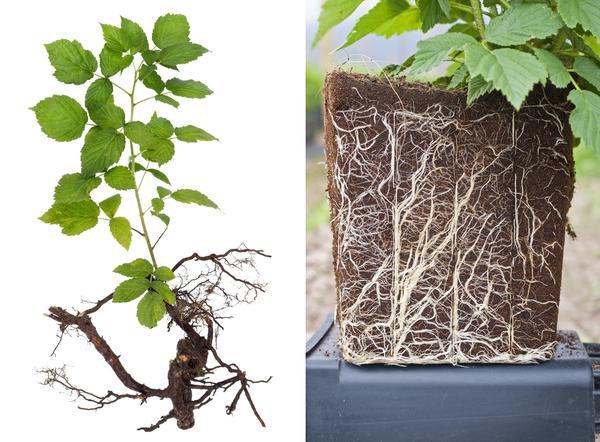

Healthy fragments larger than 2 millimeters in diameter should be cut into pieces. Their length should be 8-10 centimeters. The prepared cuttings are transplanted into loose, fertile soil. To propagate raspberries using this method, the planting material should be placed in furrows 5-10 centimeters deep.
Green cuttings
To propagate raspberries using this method, you need to take branches that were cut during thinning. In May or June, select shoots 8-15 centimeters in size. They should have 2-3 leaves. It is recommended to carefully trim them and soak them in water. Then, transplant the shoots into a greenhouse.
By dividing the bush
This method is suitable for propagating valuable raspberry bushes that have few root suckers. When dividing the plant, each section should retain at least 2-3 strong shoots with developed roots.
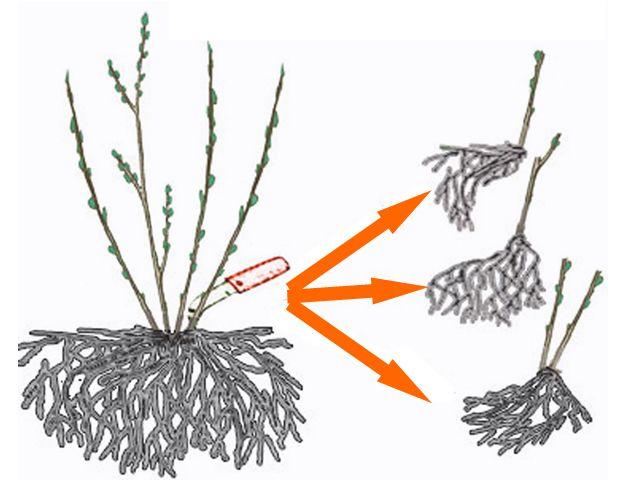
Woody shoots
This method is well suited for propagating berry bushes. Woody shoots emerge from adventitious buds on the plant's roots. Healthy bushes are suitable for propagation.
In early or mid-autumn, dig up any annual shoots that are growing at least 30 centimeters from the main plant. The roots should be at least 12-15 centimeters deep.
Scottish method of raspberry propagation
This method is ideal for propagating everbearing and large-fruited raspberries. First, the bush should be well mulched with humus or peat. This will encourage the emergence of numerous growth buds.
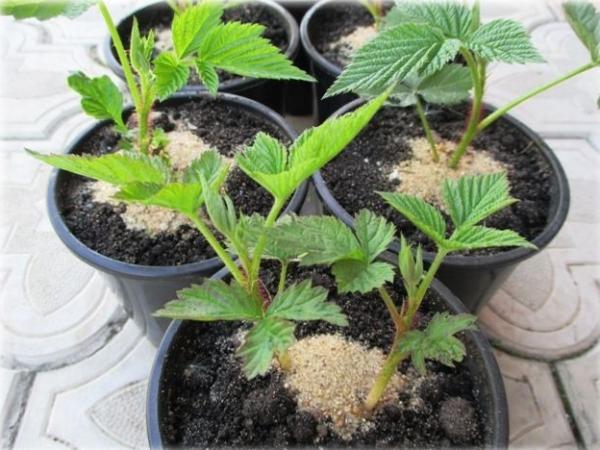

In the fall, cut the cuttings from the roots and store them in a cool room for the winter. Wrap the planting material in damp moss. In the spring, move them to a warmer location and plant them in a mixture of sand and peat. Water the cuttings generously to encourage sprouting. Then, they can be transferred to containers.
Lateral shoots or suckers
Two-year-old raspberries are suitable for this method. In the spring, offshoots form on the bush. These are used for propagation. To do this, select a branch on the north side, bend it to the ground, and bury it. The offshoot will then root. In the fall, it is divided into fragments and transplanted to a permanent location.
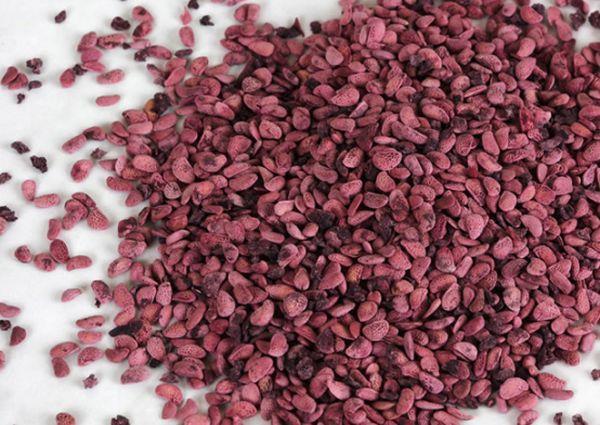
Propagation of raspberries by seeds
Raspberry seeds can be used as planting material. However, growing the crop this way is considered quite labor-intensive. Furthermore, it is impossible to preserve the characteristics of the mother plant at home. This method of propagation is used only for breeding purposes.

Rooting the top
This method involves bending the top of the stem down and burying it. The seedling can be pinned with a stick to prevent it from rising. To accelerate root formation, the shoot should be slightly trimmed before the bud. This labor-intensive method is commonly used to quickly propagate black or purple raspberries.
How to care for seedlings after planting
Planting isn't the only thing that's important. After moving yellow or red raspberries to a new location, they need to be properly cared for. To do this, follow these steps:
- Before the bush begins to bloom, it is treated with copper sulfate.
- Fertilizers are not necessary for the first two years after planting. Subsequently, it's best to use manure infusion, green manure, or bird droppings.
- In autumn, plant green manure between the rows.
- Every year, in autumn or spring, remove shoots that have produced fruit and shorten one-year-old branches.
- Loosen the soil several times during the season and remove weeds.
- Remove root shoots in a timely manner.

Potential problems and difficulties
When propagating raspberries, gardeners sometimes encounter the following difficulties:
- the plant produces an insufficient amount of planting material;
- the bush is not taking root well;
- it is not possible to preserve the varietal characteristics of the mother plant;
- the new bush does not produce large berries;
- the plant is susceptible to diseases and pest attacks.
To avoid complications when growing a plant, it's important to provide it with proper care. To facilitate the plant's adaptation to new conditions, it's recommended to water the soil properly, loosen it, and mulch it.
Raspberry propagation is a complex and labor-intensive process that requires strict adherence to all recommendations. To achieve good results, it's important to choose the optimal method and adhere to the correct procedure.










