- When does hazelnut fruiting begin?
- The main causes of violations
- Low self-fertility
- Wrong choice of seedling
- The location was poorly chosen
- Violations and errors in care
- Frosts and adverse weather conditions
- Methods to fix the problem
- Pinching
- Kidney blindness
- Controlling the orientation of branches in space
- Rejuvenating pruning
- Preventive measures
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Why aren't mature hazelnut trees bearing fruit? This problem worries gardeners and homesteaders who planted hazelnut trees to harvest tasty, nutritious fruit. If a seemingly healthy hazel tree serves only as a decorative ornament, it means the plant isn't receiving favorable conditions for reproduction and is only struggling to survive. Other reasons for a hazelnut tree's lack of fruit include poor agricultural practices and unfavorable weather conditions.
When does hazelnut fruiting begin?
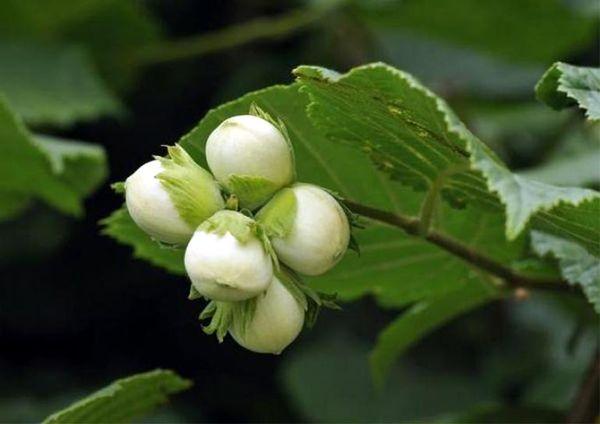
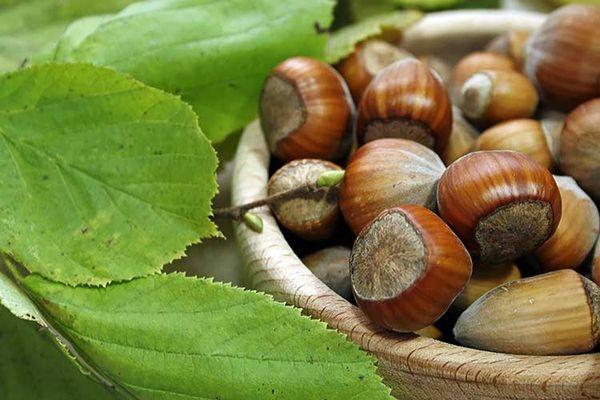
While hazelnuts planted as seedlings produce their first fruits in the fourth year, bushes grown from nuts don't begin bearing fruit until the sixth year. A full harvest is harvested after 7-8 years of the tree's life, and the maximum yield (a bucket per bush) is reached after 15-20 years.
Depending on the growing climate, the nuts ripen in August or September. Once ripe for consumption, they fall from the bush.
The main causes of violations
Incorrectly selected hazelnut seedlings, mistakes made during hazelnut care, and recurrent frosts can all lead to fruiting problems. This unfortunate situation can be corrected by following proper care guidelines.
Low self-fertility
When purchasing a hazelnut seedling from a specialized nursery, inquire about the self-fertility of the variety you're interested in. A lack of harvest may be due to low self-fertility.

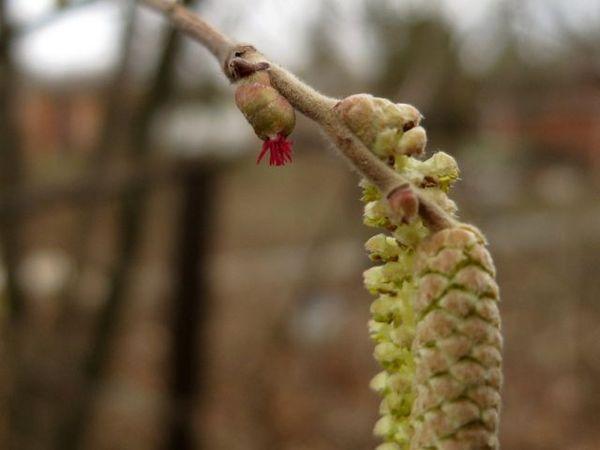
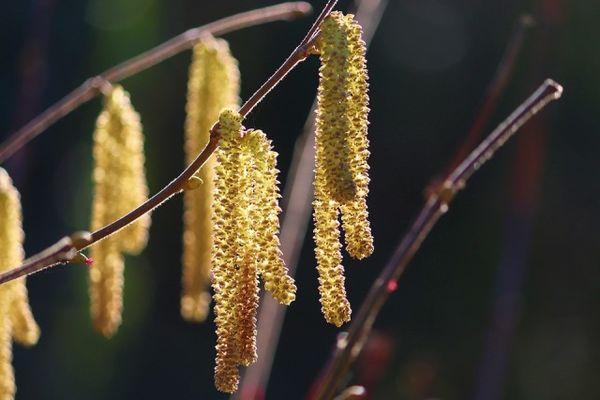
Most varieties have male and female flowers that bloom at different times, necessitating cross-pollination. To resolve this, select several bushes of different varieties, planting pollinators downwind in a suitable location. Preference is given to varieties with high frost-hardiness of male flowers.
Wrong choice of seedling
To avoid buds freezing or hazelnuts dying from winter cold, choose those hazelnut varieties, which are zoned, grow and bear fruit normally in their growing region. For planting in temperate climates, it is recommended to purchase winter-hardy hazelnut seedlings with late, long flowering.
The location was poorly chosen
A hazelnut planting site that is unsuitable for fruiting is characterized by the following characteristics:
- shading;
- exposure to cold winds, drafts;
- groundwater level above 1 meter from the soil surface;
- dry, marshy soil;
- heavy clay soil.
To maintain sufficient space for the hazelnut to feed, neighboring trees should be located at least 4 m away. Suitable soil is fertile, well-drained, with a pH of at least 6.

Violations and errors in care
Failure to regulate the application of nitrogen-rich organic and mineral fertilizers leads to the accumulation of green mass in hazelnuts at the expense of fruiting. This problem can be corrected by regulating the application of fertilizers.
The decline or absence of hazelnut yield is caused by overgrown root suckers, which rob the mother plant of nutrients. Shoots not used for propagation are pruned annually.
If hazelnuts are suffering from drought, don't expect a harvest. Hazelnut trees should be irrigated when soil moisture is below 70%.
Hazelnuts especially need watering during flowering, ovary formation, and also in June-July, when the fruit buds for next year are laid.
The lack of preventative and curative treatments against spotting, rot, and insect pests inhibits the vegetation of hazelnuts and negatively affects fruiting.
Despite its high immunity, hazelnuts require periodic inspections to detect signs of infection by fungal spores and pests, especially during wet, prolonged springs.

Failure to follow proper agricultural practices contributes to the spread of pathogenic microorganisms. The tree trunk area requires regular weeding, loosening, and clearing of fallen leaves and branches.
Hazelnuts become overfed with excessive watering and fertilizing. If a spruce shrub or tree produces large growth but does not bloom, stop watering and fertilizing for a while and reduce the root system. To do this, dig around the hazel on all sides and cut out some of the larger roots. The remaining roots are covered with soil and compacted.
Frosts and adverse weather conditions
Hazelnuts are susceptible to spring frosts during flowering and fruit formation. If temperatures drop below -3°C, there will be no harvest. The appearance of the male inflorescences indicates the approach of a return frost. If the catkins have shrunk by half, a sharp cold snap is imminent. If frost damage occurs, it is recommended to spray the hazel bush with cold water. This will help the frozen hazelnuts thaw gradually, preventing damage.
Prolonged rains, which wash away pollen, interfere with cross-pollination.

Methods to fix the problem
Proper pruning and shaping of hazelnut trees play a crucial role in fruiting. These measures are aimed at creating a balance between shoot growth and fruit set. If the bush is not pruned, yield will decrease. Excessive pruning weakens the hazelnut tree, directing its energy toward survival rather than reproduction.
Pinching
A hazelnut tree will begin to bear fruit earlier if pinched. This will redirect the tree's energy from producing new shoots to fruit formation. Shoots up to 15 cm long should be pinched. The best time to pinch is mid-July. Trim the tops, leaving 3-4 leaves on each shoot.
Shoots growing from the conductor and main branches should not be pinched, as pinching weakens the hazelnut and increases the risk of frostbite on shortened branches.
Kidney blindness
If a hazel branch has a developed bud, but shoot growth in that area is undesirable, the bud is blinded. Removing unnecessary buds redistributes the feeding direction toward the foliage and other desired branches. This method is used when shaping young hazel trees.

Controlling the orientation of branches in space
To improve light and prevent the crown from becoming too dense, it's recommended to remove the upper shoots of older branches from young hazelnut trees with strong growth. Numerous suckers grow on these shoots, forming a brush at the top. If the hazel tree is older, shoots with the correct growth direction should not be broken off, as they replace aging branches.
To increase hazelnut yields without pruning, vertically growing branches are reoriented to horizontal growth. To do this, in early spring, before the shoots become woody, they are bent to the ground and tied with rope to stakes driven into the ground or to tree trunks.
The main danger when carrying out work is tying the tree with twine, which can result in a broken branch or a wound on the trunk. Old, woody hazel shoots can also be bent. In this case, make cuts at the bend on the underside, one-third the depth of the branch's diameter.
Rejuvenating pruning
After a quarter of a century, hazelnut yield declines due to aging branches. To restore normal fruiting, rejuvenation pruning is performed. Gradually, over the course of 5-8 years, 2-3 old branches are replaced with new ones grown from young shoots. Completely removing branches that have ceased to bear fruit will result in no harvest for several years.
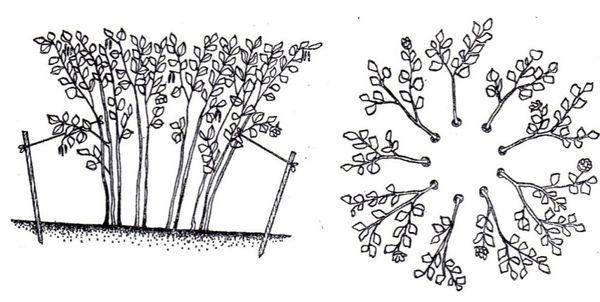
Preventive measures
Prevention of reduced or absent fruiting of hazelnuts consists of the following measures:
- organization of smoking, which increases the temperature by 2 degrees, sprinkling, which increases frost resistance to -5°C in order to reduce the risk of bud damage during recurrent frosts;
- spraying hazelnuts before winter cold snaps with a solution of potassium sulfate, superphosphate;
- autumn and spring whitewashing of tree trunks and branches;
- mulching the tree trunk circle to retain moisture and increase soil fertility.
Replanting hazelnuts to a new location is not recommended. This procedure is painful for the shrub, delaying the onset of fruiting.
It is necessary to immediately choose a suitable place where the culture will develop comfortably.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
To avoid the lack of fruiting when growing hazelnuts, use the advice of experienced gardeners:
- To ensure normal photosynthesis, hazelnuts need sunny locations. If sunlight is insufficient, hazelnut leaves grow horizontally.
- The optimal time for planting is autumn. Hazelnuts require mushrooms that grow alongside the shrub's root system, so when planting, place a 15-centimeter layer of forest litter at the bottom of the hole.
- For better fruiting, use espalier or pyramidal pruning. Branches with male and female flowers are not pruned.
- To preserve varietal characteristics, vegetative propagation methods are used - shoots, layering.
- Branches with hazelnut catkins, which are male inflorescences, are recommended to be bent down to the ground and covered with snow. This increases yield.
Experienced gardeners remind us that when pruning, it is important to remember that female flowers form at the tops of the current year's shoots.











