- General information about the plant
- Popular varieties and types
- The specifics of growing asparagus
- Preparation of planting material
- Planting dates
- Spring planting
- Autumn
- Site preparation
- The process of planting in open ground
- The nuances of growing in a greenhouse
- How to plant asparagus on a windowsill
- Tips for caring for the crop
- Moistening the leaves
- Trimming
- Hilling
- Weeding and loosening
- Top dressing
- Watering asparagus
- Diseases, pests and methods of control
- Diseases
- Rust
- Rhizoctonia
- Fusarium (root rot)
- Pests
- Asparagus leaf beetle
- Asparagus fly
- Processing asparagus
- Methods of plant propagation
- Dividing the bush
- Cuttings
- Seeds
- Harvesting and storage of crops
Asparagus belongs to the Asparagus family, which includes approximately 200 species. The plant can be either a herb or a subshrub. It is characterized by developed roots and stems. The upper parts of the sprouts are considered a unique product, very popular among many people. This is why many gardeners are interested in the pressing question: how does asparagus grow?
General information about the plant
The plant is distinguished by its developed roots and branched stems. The branches bear numerous cladodes, or branches that are needle-shaped and gathered in clusters. The plant's leaves are small and underdeveloped, with a spiny or scaly texture. The plant produces small flowers, which can be solitary or clustered in inflorescences.
In autumn, the bushes bear numerous berry-like fruits, filled with seeds. The plant is found in the European part of Russia. It is grown in sunny areas sheltered from the wind.
Asparagus sprouts are incredibly healthy. They contain a large number of vitamins, micro- and macronutrients. The plant also contains a large amount of plant proteins. The crop also contains a unique element, asparagine, which has beneficial effects on organs and systems.
Popular varieties and types
The plant has about 200 varieties. The most popular ones are types of asparagus include the following:
- Purple is a rare variety of the plant. It is grown in complete darkness, with short bursts of light. This helps stimulate pigment production.
- White – characterized by a delicate flavor and soft sprouts. To achieve this color, the plant is carefully covered with soil. The lack of photosynthesis helps give the plant its white hue.
- Green – this variety has a rich flavor. It contains many vitamins A and C, which have antioxidant properties. The pulp also contains many B vitamins.
- A legume—also known as asparagus beans—it contains a high amount of protein, similar in amino acid composition to the proteins found in meat and fish.

The most popular varieties of this crop among gardeners are:
- Argenteuil asparagus is considered a high-yielding variety. It has fleshy stems and light purple heads. The plant is characterized by tender flesh with a slightly sweet flavor. The harvest occurs in May.
- Snowhead is characterized by a sweeter flavor. Asparagus has bright green shoots. Harvesting begins in early May.
- Dutch Green – designed for growing green fruit. This variety does not require bleaching.
- Slava Braunschweig – distinguished by its long stems and white heads. The sprouts have a soft consistency.
The specifics of growing asparagus
Growing asparagus for food requires many considerations. This requires choosing the right temperature and site. Cultivating the plant in the Moscow region can be quite challenging. However, some gardeners succeed.
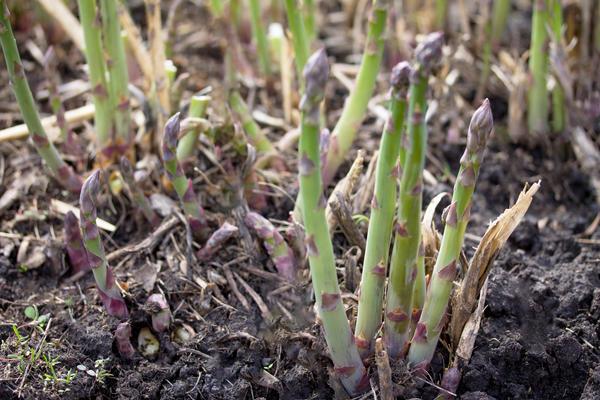

Preparation of planting material
Asparagus seeds take a long time to germinate. Sprouts can only be seen after about a month. To accelerate the process, soak the seeds in warm water for 4 days. Then place them on a damp cloth. As sprouts emerge, place them in the soil. If the cloth dries out, moisten it with water.
Planting dates
The crop can be planted at any time of year. Experienced gardeners do this in spring or fall.
Spring planting
In early spring, asparagus should be planted before the buds begin to grow. At this point, the soil should be fertilized with compost. 10 kilograms of compost per square meter is required. Immediately after planting, the crop requires ample watering.
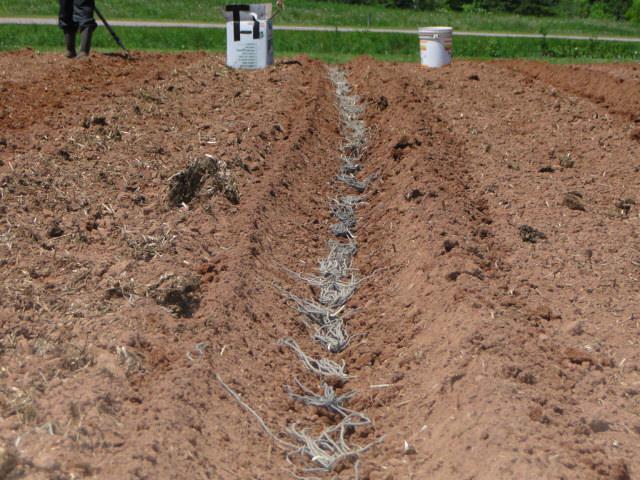

Autumn
First, the area needs to be dug up and fertilized. It is recommended to use 30 grams of potassium sulfate, 60 grams of superphosphate, and 20 grams of ammonium sulfate per square meter.
When planting asparagus in winter, don't plant it too deep. Instead, form a small mound at the top. This will protect the roots from the cold and help the plant grow productively.
Site preparation
To improve the soil quality, prepare the site in the fall. This requires adding manure. Fertilizers containing phosphorus and potassium are also used. If the soil is too acidic, add chalk or lime. After this, the beds can be dug.
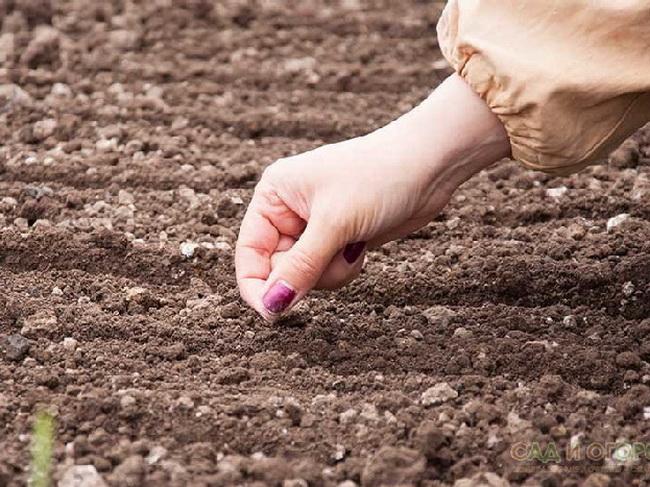

The process of planting in open ground
Before planting asparagus in the garden, dig holes 30 centimeters deep and 40 centimeters wide. Leave a meter between each hole. The bottom should be loosened further. It's recommended to do this to a depth of 15-20 centimeters. After this, add a mound of loose soil. It should reach the edge of the hole. To plant the asparagus, place the seedling on the mound. First, shorten it by 3-4 centimeters. Then fill the hole with soil, firm it down, and water it. Once the water has been absorbed, cover the bed with dry soil.
The nuances of growing in a greenhouse
This vegetable is distinguished by its versatility. Therefore, it can be easily grown in a greenhouse. A winter harvest can be obtained by forcing sprouts from mature rhizomes of 5-6-year-old plants.
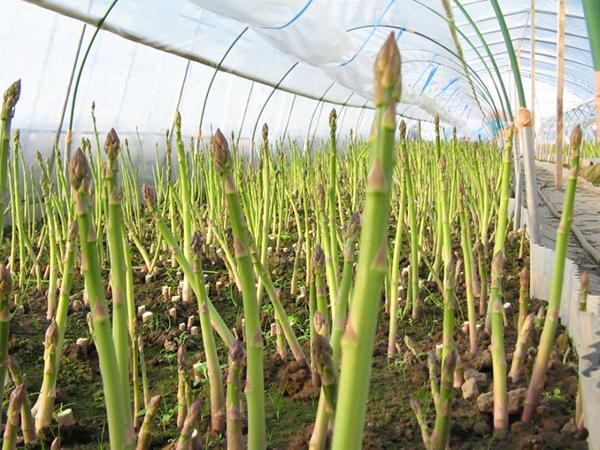

To do this, perform the following steps:
- In October, the plant roots should be dug up and placed in a cellar. The temperature should be between 0 and 2 degrees Celsius.
- In the first half of December, the roots are planted in a greenhouse. Small containers are used for this, which are placed quite closely together. There should be at least 18-20 roots per square meter. A layer of 20 centimeters of compost is added on top. Then, the containers should be covered with black film.
- During the first week, the temperature should be around 10 degrees Celsius. As the roots grow, it can be raised to 18 degrees Celsius. Temperature parameters should be monitored for two months, during which time the harvest continues.
How to plant asparagus on a windowsill
Even if you follow proper gardening practices, it's impossible to grow full-grown, edible asparagus indoors. The plant has fairly long roots that require a lot of space. Therefore, asparagus is grown for indoor decoration. For edible use, it must be transplanted into the ground.

Tips for caring for the crop
Growing asparagus in your garden requires proper care. It's a delicate plant that requires strict adherence to basic guidelines.
Moistening the leaves
The plant doesn't like excessive moisture. However, it does require periodic foliar moistening. Therefore, it needs to be watered regularly, while avoiding stagnant water.
Trimming
Asparagus requires proper pruning. It's important to remember moderation. During the first year, remove no more than 2-3 shoots. As the plant grows, you can get up to 20 standard shoots from each seedling.

Hilling
This procedure is performed to improve the taste and whiten the sprouts. It should be performed when the plant reaches 20 centimeters in height.
Hilling helps delay the opening of the terminal bud, which would make the stem unfit for consumption. This procedure isn't necessary in summer, but it's essential for winter. This protects the plant from root freezing.
Weeding and loosening
Light loosening is recommended after watering. This procedure is performed at least eight times per season. The seedlings under the mound require sufficient oxygen to thrive. To improve aeration, you can use a special roller with nails.
Timely weeding of the beds is also important. Removing weeds helps protect the crop from harmful insects and diseases.

Top dressing
To stimulate shoot growth after the first weeding, fertilize the soil with a manure solution. Mix the slurry with water at a ratio of 1:6. After three weeks, add bird droppings. To prepare the solution, mix it with water at a ratio of 1:10. The final application is made just before frost sets in.
At this stage, a complex mineral preparation is required. If the area was fertilized before planting, additional fertilizer should be applied only in the second year.
Watering asparagus
For the first 1.5 to 2 weeks, the plant requires frequent watering. Subsequently, reduce the amount of water. During drought, it may be necessary to water the area every day. The rest of the time, the soil should be kept slightly moist. Otherwise, the shoots will develop a fibrous structure and bitterness.

Diseases, pests and methods of control
When growing asparagus in the garden, it may be attacked by harmful insects or suffer from various diseases.
Diseases
Asparagus is susceptible to various diseases, each of which has its own characteristics.
Rust
When affected, sprouts darken and enlarge. Rust attacks asparagus gradually. Therefore, it's important to carefully inspect your plants. Fungicides should be used at the first signs of the disease.
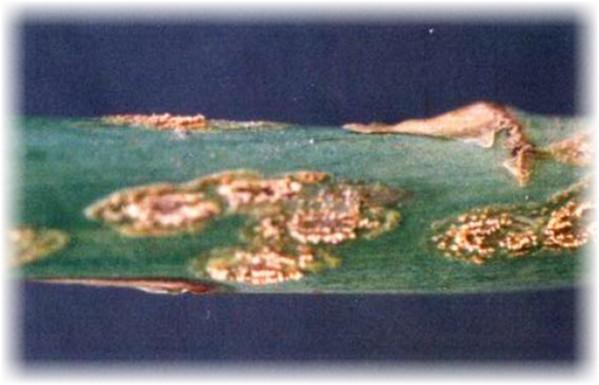
Rhizoctonia
This disease typically affects root crops. Carrots are particularly susceptible. Asparagus rarely experiences rhizoctonia.
Fusarium (root rot)
This is a very dangerous disease that damages plants. It occurs in conditions of high soil moisture.
Pests
Quite often, plants encounter pests. If action is not taken promptly, the parasites will destroy the entire planting.
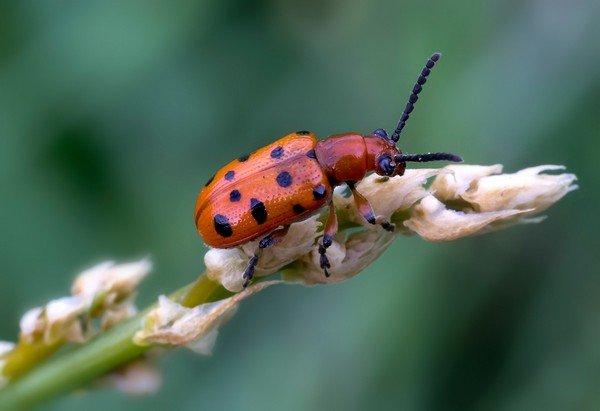

Asparagus leaf beetle
This dark blue beetle has a red border on its back. It feeds on fruits, flowers, and plant leaves. The insect appears in the spring but is most active in midsummer.
Asparagus fly
This insect lays eggs in asparagus shoots. This occurs in May and June. After one week, larvae emerge and feed on the shoots. As a result, the stems become deformed, break, and dry out. Insecticides, such as Actellic, can help combat this problem.
Processing asparagus
Spraying with Bordeaux mixture will help protect asparagus. Other fungicides, such as Topaz, Topsin, and Fitosporin, are also used. Treatments are recommended in spring and fall.

To control insects, it is recommended to treat asparagus with Malathion. This low-toxicity product should be applied at the first sign of pests. If egg nests are detected, they should be removed and burned.
Methods of plant propagation
The plant can be propagated using various methods, including division, seeds, or cuttings.
Dividing the bush
This is the most accessible method of propagating asparagus. It can be done not only in spring, but also in fall or summer. The bush can be divided when replanting. For young plants, this procedure is performed annually, and for mature plants, at 10-year intervals.

Cuttings
From March to June, cuttings should be taken. To encourage rooting, they should be placed in moist sand. Place a cap on top. The cuttings should be misted regularly. It is recommended to remove the bottle daily for a few hours. Rooting will take 1-1.5 months. Then, transplant the plants into pots of the appropriate size.
Seeds
This method isn't popular with gardeners because the seeds germinate rather poorly. However, with the right approach, growing asparagus is quite simple. To do this, soak the seeds in the first half of April. Then, plant them in a soil mixture and spray them periodically.
It's important to keep the soil from drying out. Maintaining an optimal temperature of 25 to 27 degrees Celsius is crucial.
Harvesting and storage of crops
The plant will not produce shoots until the fourth year. Harvesting should begin in May. To do this, carefully rake the soil and remove the shoots. It's important to avoid damaging the roots.
It's recommended to store asparagus on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. This will help preserve its flavor for up to 3 months.
Growing asparagus is a rather complex and labor-intensive process. To achieve good results, it's essential to strictly follow all expert recommendations.











