- History of selection
- Characteristics of the Hungarian plum
- What does a plum tree look like?
- Fruits and harvest ripening times
- Collection, storage and processing of fruits
- Benefits and harms
- Features of crop cultivation
- Timing and technology of planting
- Choosing a location
- Soil requirements
- Preparing the seedling
- Tree planting plan and layout
- How to care for plum trees in open ground
- Watering and fertilizing
- Trimming
- Means and rules of processing
- Preparing for winter
- Reproduction
- Popular varieties of the cultivar
- Dubovskaya
- Bogatyrskaya
- Italian
- Moscow or Tsaritsynskaya
- Belarusian
- Pulkovskaya (Pokrovka, Zimovka or Zimnitsa)
- Donetsk
- Michurinskaya
- Vanheim
- Hungarian Domestic (Ugrian, Common)
- Azhana
- Hungarian Korneevskaya
- Ural
- Voronezh
Growing the Hungarian plum is a relatively simple process, as this plant is considered quite undemanding. Today, many varieties of this crop are known. They share common characteristics: a dark blue fruit with a bluish bloom and an elongated shape. To ensure a bountiful harvest, it is necessary to select the right variety based on the region's climate and adhere to basic agricultural practices.
History of selection
There is no precise data regarding the origin of the Hungarian plum. Some say it is a hybrid, created by cross-pollination of cherry plum and blackthorn in the Caucasus. Other sources suggest the plant's origin was Asia. In any case, the plant received its name because it arrived in Russia from Hungary in 1900.
The crop was originally planted on the shores of the Black Sea. This Italian variety is considered heat-loving and not frost-resistant. However, it produces the sweetest fruit.
Over time, many varieties were developed that proved adaptable to frost and drought. These plants retained their qualities. Today, they are grown in various regions.
Characteristics of the Hungarian plum
This variety of plum has certain characteristics that distinguish it from other trees.
What does a plum tree look like?
Trees of this variety are considered medium-sized, reaching 3-5 meters in height. The crown is oval in shape and has a pointed tip. This cultivar is characterized by dense shoots with a reddish-brown hue.
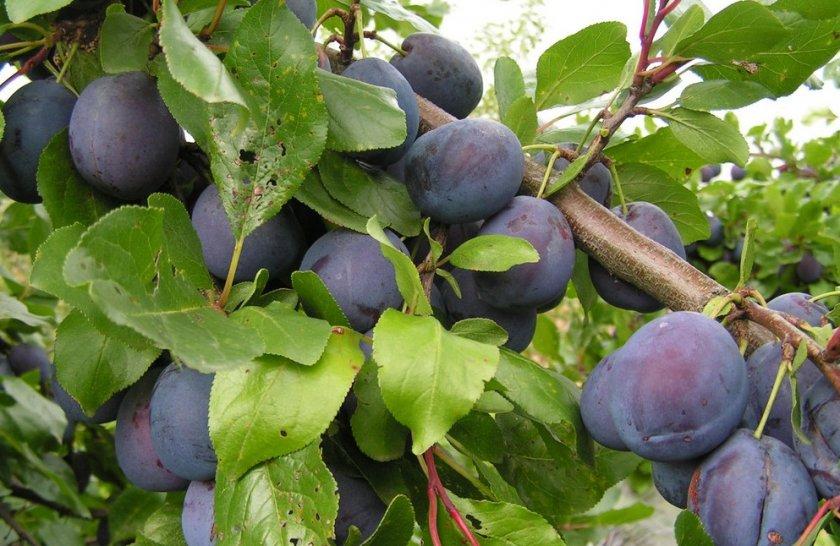

Fruits and harvest ripening times
The fruits are typically oval and slightly elongated. They are large—4 centimeters wide and 5.5 centimeters long. The skin is dark blue or reddish. The surface of the fruit has a waxy coating. They are slightly asymmetrical. On one side, the plums are slightly flattened, while on the other, they are convex. A distinct seam is also present.
Plums are characterized by dense and firm flesh. It can be yellow-green or amber in color. The pit is small and easily separated.
Hungarian cheese is considered quite sweet in taste. It contains 16% sugar and no more than 0.75% acid.
Ripening time varies depending on the growing region, ranging from mid-season to late. The crop is characterized by stable yields. Five-year-old plants can produce 50 kilograms of fruit. Mature plants yield up to 220 kilograms.

Collection, storage and processing of fruits
When picking Hungarian plums, it's important to accurately assess the ripeness of the fruit. If the fruit is still firmly attached to the branches, it's too early to pick it. The full flavor will be revealed when the fruit remains in your hand after you touch it. However, it's best to wait until the plums begin to fall.
The fruits store well and are characterized by excellent transportability. They are considered versatile. They are eaten raw, dried, frozen, or pickled. Prunes, which are rich in vitamins, are made from Hungarian plums.
Benefits and harms
The darker the plum's skin, the more beneficial nutrients it contains. The Hungarian plum is considered a very healthy fruit, containing a large amount of vitamins, minerals, and pectin. Plums can be part of a diet. 100 grams of plums contain no more than 42 kilocalories.
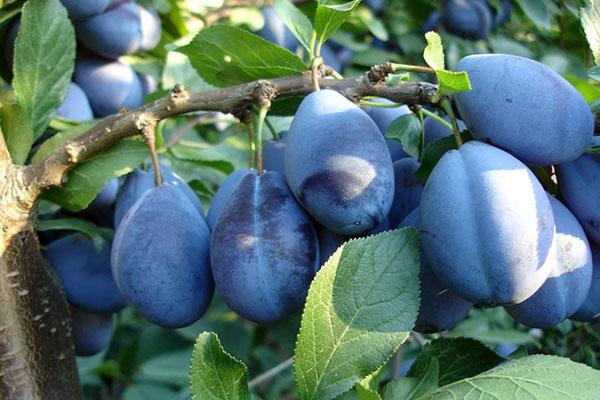

Using the product allows you to achieve the following results:
- strengthen the immune system;
- eliminate the effects of free radicals;
- prevent the occurrence of malignant tumors, bronchial asthma, arthritis, heart attack;
- reduce blood cholesterol levels;
- improve the functions of the visual organ;
- strengthen the heart and blood vessels;
- restore bowel function.
However, there are certain contraindications to fruit consumption. Excessive salad consumption can lead to kidney stones. Therefore, people prone to this problem should avoid plums.
Features of crop cultivation
To grow a crop, you need to properly plant it and provide it with proper care.
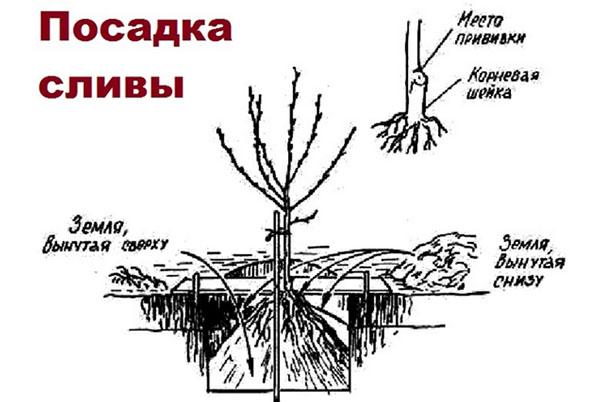
Timing and technology of planting
When planting a crop in the spring, there's a risk it won't take root. Therefore, it's recommended to plant it in late summer. Late August or early September is ideal.
Choosing a location
Hungarian sage should be grown in a sunny location. It's recommended to plant it at elevated sites. Lowlands accumulate large amounts of water. It's important that the site is well-heated and protected from drafts.
Soil requirements
Hungarian rhododendron requires sandy or loamy soil. Acidic soil is unsuitable for this plant. To reduce soil acidity, add 600 grams of wood ash. Dolomite flour can also be used.

Plums don't do well in dry sandy soil. In such soil, fruit buds fall off and yields decrease. Adding lime to the planting hole is not recommended, as it can burn the roots. If liming is necessary, apply it early, during soil cultivation.
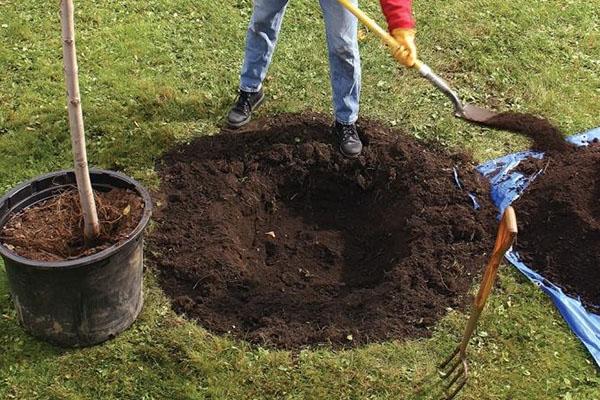
Preparing the seedling
It's best to purchase a sapling from a specialized nursery. When choosing a tree, consider the following criteria:
- even trunk;
- age – 1-2 years;
- fresh root system;
- dwarf or semi-dwarf rootstock;
- no damage to the bark;
- absence of dry branches or rotten roots.
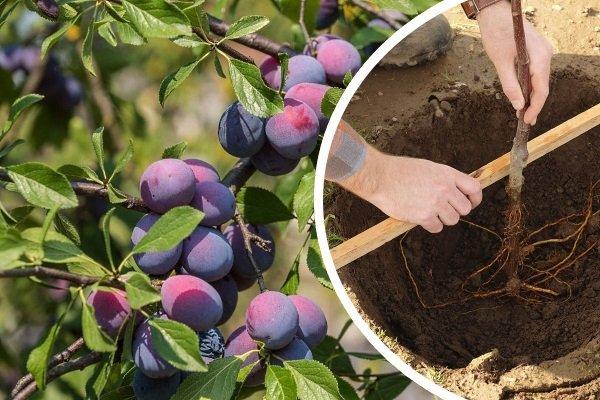

It's best to buy seedlings in plastic containers filled with fertile soil. This allows you to plant the tree without stress or damaging the roots. Simply remove the seedling from the container and transfer it to the hole. This should be done with the root ball still attached.
If the seedling was purchased without a container, it is recommended to moisten its roots. Afterwards, they are evenly distributed over the mound of soil in the hole.
Tree planting plan and layout
To plant a plum tree, it is recommended to follow these steps:
- Dig a planting hole two weeks in advance. It should be 60-70 centimeters wide and 50-60 centimeters deep.
- It is recommended to place a peg in the center of the hole, 20 centimeters deep.
- Fill the hole with fertile soil, mixing it with humus. It is also recommended to add 100 grams of ammonium nitrate, 200 grams of potassium chloride, and 500 grams of superphosphate. Gravel and river sand are also recommended.
- Place the seedling on a mound of soil and spread the roots evenly.
- Fill the hole with fertile soil, water it, and mulch it. Peat or sawdust are good choices.

How to care for plum trees in open ground
To ensure a bountiful harvest, plum trees require comprehensive care.
Watering and fertilizing
Plum is a moisture-loving plant. One of its key advantages is its tolerance to drought. There are varieties that can even tolerate extreme heat. However, such conditions are considered extreme and negatively impact the plant's health.
Therefore, experts advise watering the plant regularly. For normal development, a mature plant requires 5-6 waterings per season. It's important to maintain a standard of 8-10 buckets of water. Watering is essential during the following periods:
- during flowering;
- during the formation of ovaries;
- during fruit growth.
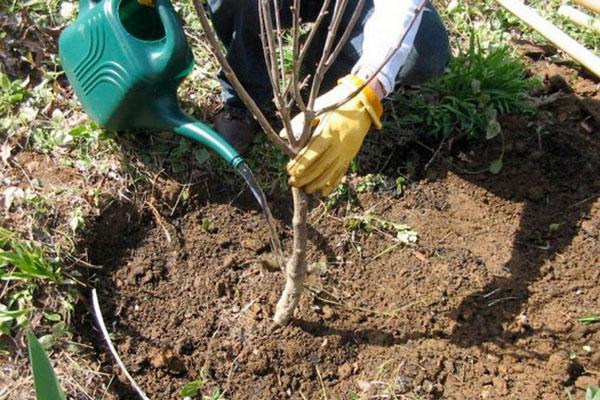 When the fruit begins to ripen, the tree should be watered. This will positively impact the yield. It is recommended to water seedlings more frequently. A young tree requires 3-4 buckets of water.
When the fruit begins to ripen, the tree should be watered. This will positively impact the yield. It is recommended to water seedlings more frequently. A young tree requires 3-4 buckets of water.
Timely application of fertilizers is also crucial. After planting, the soil is fertilized with mineral fertilizers. If the soil is fertile, the amount of fertilizer should be reduced.
The first application of nutrients is in mid-May, and the second a month later. This allows for good growth in the fall.
As seedlings develop rapidly, the amount of fertilizer should be reduced. To ensure a harvest in the third or fourth year, nitrogen fertilizer use should be gradually phased out.
Trimming
To form a proper crown and prevent disease, annual pruning is recommended. The Hungarian tree produces a bountiful harvest. Therefore, it's best to leave only the most stable branches that form a right angle with the trunk. It's recommended to give the Hungarian tree a sparse, tiered crown.

During the pruning process, it's important to remove any undergrowth. Also, remove any frozen shoots and branches growing deep into the tree's crown. It's recommended to prune the tree in early spring. During this time, the temperature should be stable and not drop below -10°C (14°F). Pruning should not be performed before the onset of cold weather.
Means and rules of processing
Hungarian rhododendron is resistant to diseases and pests. Under poor conditions, there is a risk of developing rust, clasterosporium, moniliosis, and coccomycosis. Copper-containing preparations are used to treat fungal diseases. Bordeaux mixture is a good choice, with a concentration of 1%.
In addition to spraying, it's important to remove plant debris from the tree's trunk circle and remove any affected leaves and shoots. It's recommended to remove these from the area and burn them.
As a preventative measure, treat the tree in the spring with a Bordeaux mixture solution. Its concentration should be 3%. This procedure is performed before bud break. Plum trees are often attacked by pests such as codling moths, sawflies, and shoot moths. Insecticides can help control these insects. Harvesting is permitted only one month after the procedure.

Preparing for winter
Most plum varieties tolerate frost well. Mature trees do not require additional insulation. However, gardeners recommend mulching the area around the trunk. Peat or humus are good choices for this.
Young plants will require more effective insulation. For this, the trunks should be wrapped in burlap or covered with spruce branches. Artificial materials are not recommended, as they will cause the trees to rot, leading to trunk rot.
Reproduction
Hungarian can be propagated in different ways:
- By seeds. Before planting in the ground, the seeds undergo stratification in the refrigerator. This lasts from September to March. Then they are planted in the ground, and in the fall, in a nursery. After one year, the seedling can be transplanted to its permanent location.
- Vegetative propagation. This can be done using shoots and cuttings. The most effective method is rooting shoots with small roots. These can be immediately transplanted to their permanent location.
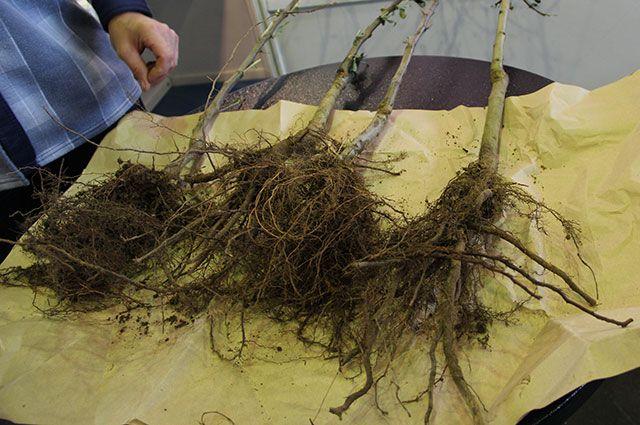

Experienced gardeners recommend propagation by grafting. However, this method is considered quite labor-intensive.
Popular varieties of the cultivar
The culture has many varieties, each of which is characterized by certain features.
Dubovskaya
The tree is frost-resistant and begins bearing fruit after five years. The fruits are oval and weigh 30 grams. The skin has a purple hue. Inside, there is yellow-green flesh. The variety is considered self-fertile.
Bogatyrskaya
These are medium-sized plants with a spreading crown. The tree bears fruit abundantly. One plant can produce up to 120 kilograms of plums. The harvest takes 4-5 years. Plums weigh 30-60 grams.

Italian
This tree has a wide crown—up to 6 meters. Fruiting occurs every 4 years. Dry weather negatively impacts the yield. The fruit is harvested in late August. One plant produces 50-70 kilograms of plums. The fruits are large, reaching 40 grams.
Moscow or Tsaritsynskaya
The plant grows to a height of no more than 3 meters and has a dense crown. Fruiting begins after 6-8 years. A single tree can yield up to 35 kilograms of plums. The plant is self-fertile and produces a harvest in early September. Its advantage is its frost resistance.
Belarusian
The tree reaches 3.5 meters in height. It is characterized by a rounded, spreading crown. Fruiting begins after three years. Yields reach 30 kilograms. The variety is considered partially self-fertile. The harvest ripens in late August.

Pulkovskaya (Pokrovka, Zimovka or Zimnitsa)
The plant grows to 4 meters in height. Fruiting begins in the third year. One tree produces 25 kilograms of fruit. The plant is considered partially self-fertile. Pollination is required for optimal yield.
Donetsk
This variety bears fruit every five years. The fruit ripens in early August. The tree reaches 4 meters and produces up to 25 kilograms of fruit. Each fruit weighs 30 grams and is distinguished by its rich purple hue.
Michurinskaya
The tree reaches 4 meters. This variety is considered mid-season and is prized for its juicy fruits. The plums do not fall for a month. However, the plant is not very frost-resistant.

Vanheim
This variety is early-bearing and produces a harvest in 3-4 years. Mature plants yield up to 120 kilograms of fruit. Harvesting begins in early August. The plant is resistant to fungi.
Hungarian Domestic (Ugrian, Common)
Yields reach up to 150 kilograms. Harvesting begins in late August or early September. The fruits are covered with a blue-black skin and are often used to make prunes.
Azhana
The tree begins to bear fruit after 4-5 years. Mature plants produce up to 70 kilograms of fruit. The fruits ripen in late August. This variety is best grown in areas with mild climates.

Hungarian Korneevskaya
This plant reaches 4 meters in height and has a pyramidal crown. Fruiting begins in the third or fourth year. Yields reach 30 kilograms. The plant is considered self-fertile and ripens in late August.
Ural
This Hungarian variety was bred in the Urals. The low tree produces large, oval, juicy fruits. The variety is noted for its high yield.
Voronezh
The plum tree reaches 3 meters in height and has a paniculate crown. Fruiting begins at 5 years of age. Yields reach 30 kilograms.
The Hungarian plum boasts excellent yields and delicious flavor. It's easy to care for and comes in a variety of cultivars, allowing gardeners to choose the perfect one.











