Gardeners often ask how to treat tomatoes against powdery mildew. Indeed, this pest has become increasingly common in our gardens, sometimes destroying the entire harvest. This problem is especially troubling for gardeners and farmers in the southern regions with their high humidity.
How powdery mildew manifests itself on tomatoes, signs of the disease
Powdery mildew on tomatoes is caused by a fungal infection. This condition is commonly known as "white spot" or "ash-powdery mildew." When tomato plants are infected with this disease, a white coating appears on the leaves. Initially, these white spots appear on the leaf surface, but they quickly merge to form a single white area.
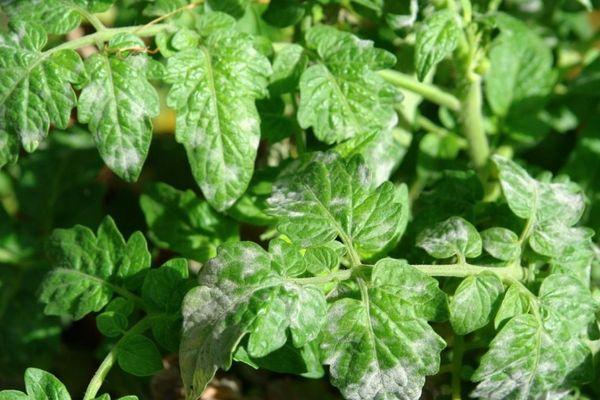

Sometimes this bloom spreads to the petioles and stems of the bush. In advanced cases, the bloom completely covers the plant. Spores are carried by air currents and infect neighboring plants. Hence the name of the disease—powdery mildew.
In addition to the leaves, other parts of the tomato bush are also affected:
- young shoots;
- fruit;
- peduncles;
- petioles.
Symptoms of the disease first appear on the lower part of the tomatoes, gradually moving upward.
If powdery mildew has affected the fruit, you'll notice cracks on the tomatoes, covered with a white coating and rot. The blossoms will turn black, and brown spots will appear on the fruit, gradually increasing in size. The fruit will also become soft.
Causes of powdery mildew
The disease is caused by the ascorbic fungus Sphaerotheca pannosa. The best conditions for tomato disease development are shade and temperatures above 20°C. Powdery mildew can also be caused by temperature fluctuations during the day and night, as well as by soil that is saturated with nitrogen.
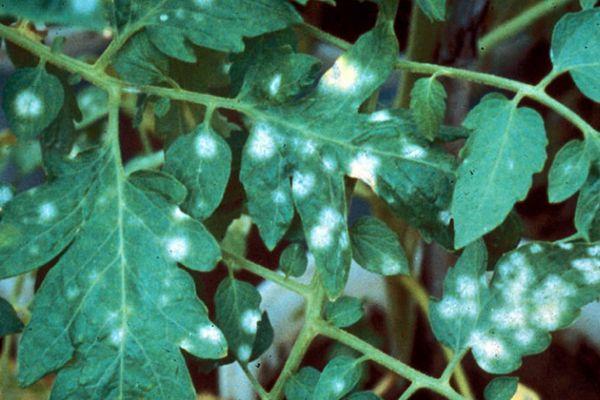

The optimal humidity for powdery mildew development on tomatoes is 95-99%, and the temperature is +20…+25°C. Powdery mildew progresses under the following conditions:
- lack of moisture in the soil;
- lack of potassium;
- little light;
- excess nitrogen nutrition;
- dense plantings;
- sharp temperature fluctuations.
How to overcome the disease
How to combat powdery mildew on tomatoes: There are measures to combat this fungal disease, which affects many plants, and they can be very effective. The key is to recognize the disease as early as possible.
If action isn't taken promptly, the disease will destroy the entire crop. Therefore, it's important to know how to combat powdery mildew. Chemical treatments, particularly fungicides, can be used. Folk remedies for eliminating the mildew can also be effective.
First, you need to cut off all branches and leaves with plaque to prevent the infection from spreading, and treat the pruning shears or scissors with an antiseptic. If you see that the plant is beyond saving, it's best to remove it completely to prevent it from becoming a source of infection for other crops.
Let's look at some ways to deal with laundry:
- Using a soda-soap solution. If you use 5 liters of water, you'll need 25 grams of washing soda and 5 grams of soap. Combine these ingredients to form a soapy solution, then apply it to the plants and surrounding soil. This is done while the solution is cooled. For best results, perform several applications, three days apart.
- Treat the plant with a potassium permanganate solution. This solution kills the infection. Dissolve 2.5 g of potassium permanganate powder in 10 liters of water and mix well. Apply the solution three times, every 5 days.
- Bordeaux mixture. Mix 100 ml with 10 liters of water. The first treatment is carried out 15-20 days after planting. The second treatment is carried out after the appearance of signs of disease. Copper sulfate can be used in the same way. The calculations are slightly different here: 200 g of copper sulfate is used per 10 liters of water.
- Here's a recipe for making a serum solution. By spraying the plant with this solution, you not only treat it but also provide it with additional nutrition. The serum is diluted with water at a ratio of 1:10. After applying the solution, a film forms on the plant's leaves and stems, preventing the fungus from breathing and continuing its growth. Spraying is carried out in dry weather. For best results, apply three applications at 3-5 day intervals.

These folk remedies will be effective if the area affected by the fungus is not very extensive. For widespread tomato infestations, it's better to use chemical treatments. This will protect not only the tomatoes but also other plants in the greenhouse.
Treatments are carried out 1 to 4 times, depending on the severity of the plant's damage. Each treatment should be carried out 8 to 10 days after the previous one.
The most commonly used chemicals for powdery mildew include:
- Fungicides Tiowol.
- Topsin. In addition to eliminating white plaque on tomatoes, this product effectively combats gray mold.
- Nimrod.
- Timorex Gold. Also eliminates late blight.
The dangers of white bloom on tomato crops
The danger of plant disease is as follows:
- The leaves wither, curl, turn yellow and fall off.
- Even if new leaves appear in place of the diseased leaves, the latter are twisted and underdeveloped.
- The process of photosynthesis slows down, which has a detrimental effect on the plant.
- If left untreated, the plant dies.
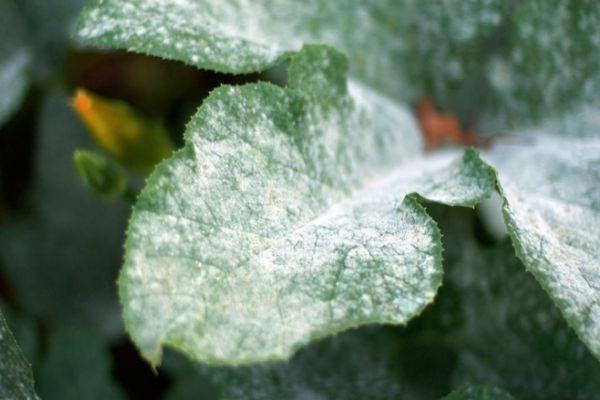

Powdery mildew - preventive measures
If proper agricultural practices and preventative measures are followed, powdery mildew will not appear on tomatoes. These measures include the following:
- Practice crop rotation. Tomatoes should be planted in a particular area in rotation. This means that after harvesting tomatoes, plant them again in the same spot only after 3-5 years. Also, avoid planting tomatoes after potatoes. Instead, plant them in a bed where root vegetables or peas were previously grown.
- Follow proper agricultural practices. Regularly loosening the soil will help it dry out faster and become more oxygenated.
- Maintain optimal climate conditions in the greenhouse. This is because greenhouse tomatoes are more susceptible to white mold than ground-grown ones, due to higher humidity and poorer ventilation in enclosed spaces. Therefore, ventilate the greenhouse daily, remove side shoots from the tomatoes promptly, and eliminate weeds. Tomatoes grown in a greenhouse should have bare stems.
Powdery mildew on tomatoes is a dangerous disease that can lead to the destruction of the entire crop. Inspect your plants frequently for white mold. If you spot it during the developmental stage, you can save your tomato plants. Powdery mildew affects more than just tomatoes; it can spread to other crops via air currents. This disease is common on roses, cucumbers, potatoes, zucchini, watermelons, and other plants.