- Powdery mildew – description of the disease
- Causes and symptoms of the appearance on roses
- What is dangerous for rose gardens and garden plantings?
- Treatment measures
- Chemical control methods
- Tilt KE
- Fundazol
- Alirin B
- Fitosporin-M
- Folk remedies against the disease
- Fresh manure
- Garlic infusion
- Mustard
- Soap and soda solution
- Milk whey
- Preventing re-infestation and protecting roses
- We comply with growing conditions
- Removal of weeds and fallen leaves
- Tool processing
- We regulate fertilizers correctly
- Autumn soil preparation and digging
- Selecting Resilient Rose Varieties
Beautiful and well-maintained flower beds are the pride of homeowners. Gardeners often try to select the most striking plants to decorate their gardens, and roses are one of them. For roses to become the highlight of the landscape, they need proper care, including disease prevention. Powdery mildew on roses requires immediate treatment.
Powdery mildew – description of the disease
Powdery mildew is a fungal disease that often affects rose bushes. It is caused by a fungus called Sphaerotheca pannosa. Other names for this disease include powdery mildew and powdery mildew.
The parasite's spores are airborne, carried by precipitation, and can be transmitted from an infected plant to a healthy one via poorly disinfected tools or gardener's work clothes. The powdery mildew pathogen spends the winter in leaf litter, bark crevices, and under bud scales. With the arrival of spring, the fungus begins to actively reproduce and infect rose bushes.
If treatment isn't started promptly, the plant's leaves curl, dry out, and fall off the bush. Furthermore, the fungal infection spreads to the stems and flower stalks.
In addition to downy mildew, rose bushes are also susceptible to downy mildew. Despite its similar name, this disease is caused by a different pathogen—the fungus Pseudoperonospora sparsa. The infection results in cracked bark on shoots and the appearance of small purple or brownish spots on young leaves. As a result, the leaf blades become deformed and eventually fall off. The outer petals of flower buds turn black, and the rose bush begins to stunt.
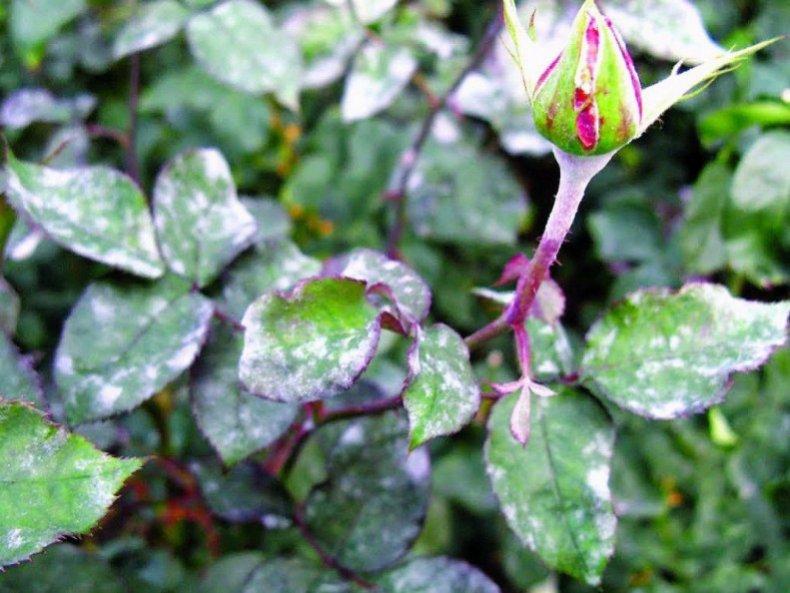

Causes and symptoms of the appearance on roses
The following factors contribute to the appearance of powdery mildew on roses:
- Excessive planting density and, as a result, lack of ventilation.
- Lack of adequate lighting.
- Purchasing already infected planting material and planting it in a rose garden without quarantine.
- Failure to follow the watering regimen or fertilizing schedule. Fungus is caused by excessive nitrogen in fertilizers and a deficiency of phosphorus and potassium.
- Heavy soil that does not allow air and moisture to pass through well.
- Weeds growing around the rose bushes.
- High air humidity, sharp changes in night and day temperatures.
The consequences of bush damage by powdery mildew are:
- slowing down and complete cessation of growth of shoots and stems;
- loss of decorativeness by buds;
- blackening of leaves;
- weakening of the immunity of roses.

You can determine that plants have been affected by powdery mildew by the following signs:
- the appearance of a greyish-dirty coating, reminiscent of scattered flour;
- the formation of small droplets of moisture after the maturation of spores;
- By autumn, the plaque thickens and small, dense dark spots form.
If timely measures are not taken to save the bushes from disease, they will not survive the winter and will die.
What is dangerous for rose gardens and garden plantings?
The main danger of powdery mildew is that it spreads quickly across a property, affecting not only outdoor flowers but also other cultivated plants. The fungus attacks apple and pear trees, grapes and gooseberries, squash, and cucumbers. Therefore, treatment should be initiated immediately when the first symptoms appear.
In addition to the loss of decorative appearance, there is a sharp decrease in the winter hardiness of shoots and buds, which leads to the death of the plant during the winter.
Treatment measures
If preventative measures aren't taken promptly and the fungus begins to affect rose bushes, the plants are treated with chemicals and folk remedies. Which method is most effective depends on the extent of the disease. It's recommended to treat rose bushes in the summer at the first sign of the disease; this gives you a chance to overcome the disease before fall.

Chemical control methods
Chemical treatments are more effective than folk remedies for combating powdery mildew, but if used incorrectly, they can cause damage to plants. Therefore, before applying any treatment, it's important to carefully read the instructions and calculate the correct dosage.
When spraying plants, wear protective clothing to avoid chemical contact with skin. Wear gloves, a work gown or coveralls, and a headscarf. Dispose of any remaining spray solution, and thoroughly wash the container.
Tilt KE
You can eliminate powdery mildew symptoms with Tilt KE. Its main active ingredient is propiconazole. This systemic fungicide penetrates plants through the leaves and stems. The advantage of this product is that it not only provides a curative effect but also inhibits further sporulation.
To prepare a working solution, use 0.5 ml of Tilt EC per liter of water. It should be used immediately after preparation; do not store it, as it will lose its potency. Apply this systemic fungicide once per season. Its action begins within 2-3 hours.

Fundazol
A fungicide developed by Hungarian specialists, Fundazol, is also used to treat roses. When signs of disease appear, prepare a working solution by dissolving 10 grams of the product in 10 liters of water. It is recommended to apply the solution four times per season. When using Fundazol, keep in mind that it belongs to toxicity group 2 and can cause dermatitis with prolonged skin contact.
Alirin B
Alirin B is a biological product. Its advantage is that it not only inhibits the growth of fungal spores but also promotes the restoration of beneficial soil bacteria. The product is completely safe for humans and animals, as its active ingredient is of biological origin. Alirin B is available as liquid, powder, and tablets.
When using the product, keep in mind that its effectiveness is only evident when daytime temperatures are above 10 degrees Celsius. To treat rose bushes, prepare a working solution of 2 tablets per 1 liter of water. The product's active period is 2 weeks. Spray 4-5 times per season.

Fitosporin-M
This is a next-generation microbiological product whose main active ingredient is the bacterium Bacillus subtilis 26 D. Fitosporin-M is active from the moment of application and is low-risk for animals, insects, and humans. Its main advantage is its ability to be used at any stage of plant development. A working solution for treating rose bushes is prepared by mixing 1.5 g of powder per liter of water. Fitosporin-M can be used an unlimited number of times until the flowers are completely healthy.
Folk remedies against the disease
Folk remedies for treating rose powdery mildew are used only in the early stages of infestation and as a preventative measure. In advanced cases, they are ineffective.
Fresh manure
To prepare the medicinal solution, dissolve 1/3 of a bucket of fresh manure in a bucket of water. Let the solution steep for three days, stirring occasionally. Then strain through cheesecloth and dilute in 10 liters of water.
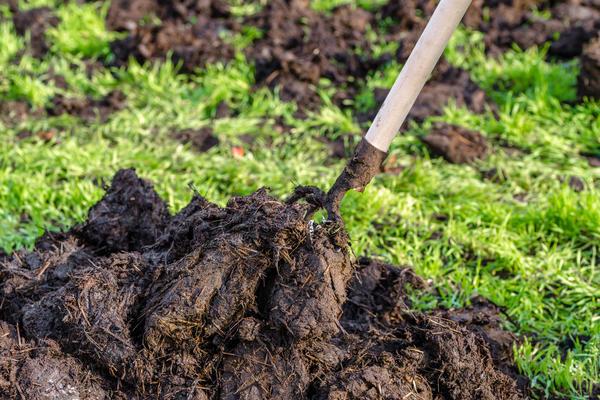

Important! Prepare the solution immediately before spraying the bushes.
Garlic infusion
An effective remedy against powdery mildew can be made using garlic. Take 5 cloves of garlic, crush them, and pour boiling water (1 liter) over them. Let them sit for 24 hours and then dilute with 3 liters of cold water. Spray the bushes at the first signs of the disease and as a preventative measure.
Mustard
A mustard solution is used not only for treating indoor flowers but also for spraying garden plants. Take 2 tablespoons of the powder and dissolve them in a bucket of water. It's used not only for spraying roses but also for watering the soil around the trunks.
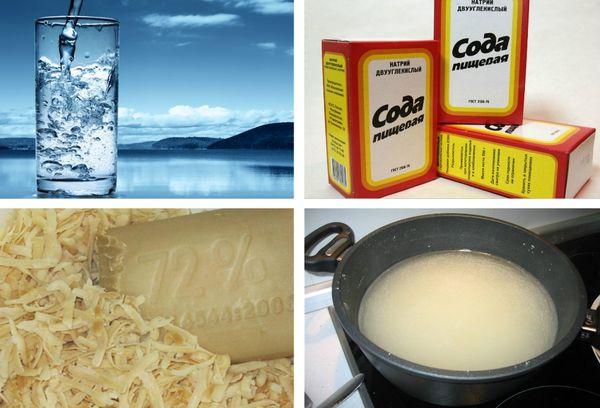
Soap and soda solution
A solution made from baking soda and soap helps combat mildew. Prepare the solution by mixing 1 tablespoon of baking soda, 1 tablespoon of finely ground laundry soap, and 1 tablespoon of sunflower oil. Dissolve all ingredients in a liter of water and apply to plants once a week.

Milk whey
The serum is used after preliminary irrigation. One liter of serum is diluted in 5 liters of water and 10 drops of iodine are added. Apply 2 or 3 times a month.
Preventing re-infestation and protecting roses
To protect garden roses from re-infestation, follow agricultural practices and carry out regular preventative maintenance.
We comply with growing conditions
Rose bushes are planted in sunny places where moisture does not accumulate and there are no drafts.
Removal of weeds and fallen leaves
Regularly loosen the soil around the bushes, removing weeds along the way. With the arrival of autumn, be sure to rake up all fallen leaves and burn them outside the property.

Tool processing
All gardening work should be carried out only with disinfected tools. For this purpose, use a solution of potassium permanganate, alcohol, or hydrogen peroxide.
We regulate fertilizers correctly
Avoid using fertilizers with high nitrogen content, as it is considered a factor in fungal growth. Ensure that fertilizers contain phosphorus and potassium.
Autumn soil preparation and digging
In the fall, the final preventative treatment of the bushes is carried out and the soil around the roses is dug up.
Selecting Resilient Rose Varieties
For garden planting, select varieties resistant to powdery mildew. For example, Augusta Louise, Cadillac, Galaxy, Aspirin, Westerland, and Aphrodite.