- Do hostas need to be prepared for winter?
- Timing depends on the growing region
- Leningrad Oblast
- Urals and Siberia
- Middle zone
- South of Russia
- Rules for autumn plant care
- Removing faded buds
- Trimming
- Enhanced watering
- Top dressing
- Mulching
- Protection from pests and diseases
- Methods for covering hostas
- What mistakes do novice gardeners make?
- Nitrogen fertilizers are used
- Lack of mulch
- Use of special materials for covering
- Soil drying out
- When does hosta emerge after winter?
- Useful tips for gardeners
Hosta is a perennial ornamental plant used by gardeners to beautify their gardens. Unlike many shade-tolerant plants, it produces beautiful blooms even in the absence of full sunlight. One of the most important steps in hosta care in the fall is preparing it for winter. If properly insulated, the plant will delight with decorative foliage and attractive flowers when warmer days arrive.
Do hostas need to be prepared for winter?
Some gardeners believe that hostas don't require special winter protection, as they are highly cold-resistant. However, if left uncovered in temperate climates, and especially in northern regions, they will freeze over the winter and won't display their full decorative qualities come summer. If the perennial is planted outdoors in southern regions, there's no need to use special covering materials, as winters there are mild, and a layer of mulch will suffice.
Timing depends on the growing region
The specific timing for preparing hosta for winter frosts depends on the growing region and its climatic features.
Leningrad Oblast
The first frosts in this region occur in early November, so winter preparations for plants begin in mid- to late October. The absence of extremely low temperatures in the Leningrad Region means that bulky shelters are unnecessary; a layer of organic mulch around the plants is sufficient.
Urals and Siberia
If an ornamental shrub is grown in the Urals, all preparatory work should be completed as early as September. In winters with little snow, additional protection should be installed before the first frost, using agrofibre or spruce branches.
Middle zone
To prepare hostas for winter in the Moscow region and central Russia, work begins in late September and ends in mid-October.
If the forecast does not predict severe frosts, you can limit yourself to a layer of mulch made of wood chips or dry peat.
South of Russia
In southern regions, hostas require virtually no cover. During the coldest winters, gardeners apply a thin layer of mulch in late October or early November.
Rules for autumn plant care
Before winter, hostas need more than just covering. Autumn care consists of several sequential stages. Careful maintenance is essential to ensure the plant survives the cold season without problems.

Removing faded buds
The first thing to do in the fall is to cut off the faded flower buds along with the stems. This way, the plant won't waste energy feeding them. It's important to do this before the flowers begin to form seed pods.
As a rule, the hosta flowering period begins in mid-August and ends by the end of September.
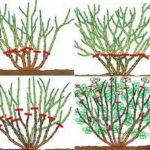
Trimming
Gardeners disagree about pruning hostas. Some believe this procedure is unnecessary, and the plant will overwinter perfectly well with its leaves and stems intact. Furthermore, the nutrients contained in the above-ground portions naturally transfer to the root system, helping it survive the cold season.
Other gardeners believe that fallen leaves before winter are a perfect breeding ground for insect pests, so they shouldn't be left under bushes. As soon as the spring sun warms, pests begin to damage the plants.
The optimal method is partial pruning, which involves removing diseased, damaged, and dried stems. It's also essential to trim the leaves if the ornamental shrub is planted in a low-lying area where water accumulates during thaws. Leaves and stems are trimmed so that at least 10 cm remains above the root collar.
As for the timing of this procedure, the signal is the complete yellowing of the leaves. This means they have already transferred all their valuable nutrients to the root system. The first frost should be at least two weeks away. Afterward, all cuts are sprinkled with charcoal to prevent infection.
Enhanced watering
This ornamental shrub is a moisture-loving plant, so it needs to be watered generously when preparing for cold weather. Insufficient soil moisture will cause the plant to wilt. Preparation begins three weeks before the cold weather sets in, pouring two buckets of water under each plant. The water should be settled and heated to 15-17 degrees Celsius.
Top dressing
In the fall, it's recommended to feed hostas with organic compounds. This will allow large leaf blades, the plant's main attraction, to form in spring. To ensure the root system receives nutrients in an easily accessible form, plant debris must rot and be digested by soil bacteria. This creates what's known as organic fertilizer—humus.

What is recommended for fertilizing ornamental shrubs before winter:
- wood ash;
- rotted manure;
- bone meal;
- Fertilizer based on green grass.
You can easily make a simple plant fertilizer yourself using wood ash:
- They collect branches left over from autumn pruning in the garden.
- Dried fallen leaves are added to them and burned.
- Take 300 grams of the resulting ash and dissolve it in a bucket of settled water.
- The resulting solution is used to water the root system of the bushes.
This composition contains an abundance of calcium, which hostas need for successful overwintering. Furthermore, wood ash repels slugs, which often damage plants. In the fall, it's helpful to feed the shrubs with mineral fertilizers that decompose slowly, such as rock phosphate.
In addition, the following fertilizers are used to choose from when preparing for winter:
- 30 grams of potassium sulfate per square meter of plantings (in liquid form).
- 40 grams of superphosphate per 1 square meter.
- Potassium magnesium sulfate, dissolving it according to the instructions for use.
When preparing for winter, never use compounds containing nitrogen, as it will stimulate increased growth of foliage and stems.
Mulching
A layer of mulch placed around plants will help protect them from frost. Mulch protects the topsoil from freezing and shields the root system from icing. Experienced gardeners recommend using organic materials for the insulating layer, such as sawdust, shredded bark, peat, or dry hay.
Protection from pests and diseases
Hostas are considered highly resistant to diseases and pests. Snails and slugs typically attack hostas due to poor gardening practices or high humidity in the area where the shrub is grown. As a preventative measure, adding wood dust to the mulch layer deters pests.

Root collar rot is considered the most dangerous disease. To prevent this, treat the bushes with an aqueous solution of any fungicide.
Methods for covering hostas
The method of covering the plant depends on the growing region. Mulch is the primary insulating layer.
The work is carried out in the following sequence:
- Prepare mulch from tree bark or compost; peat, mown grass, and fallen leaves are also suitable.
- Each bush is covered on all sides with a 10 cm layer of soil. If the leaves are trimmed, a small mound is also made over the hosta stumps.
- In regions with severe frosts, the mulch should be covered with spruce branches or any non-woven material - spunbond or agrofibre.
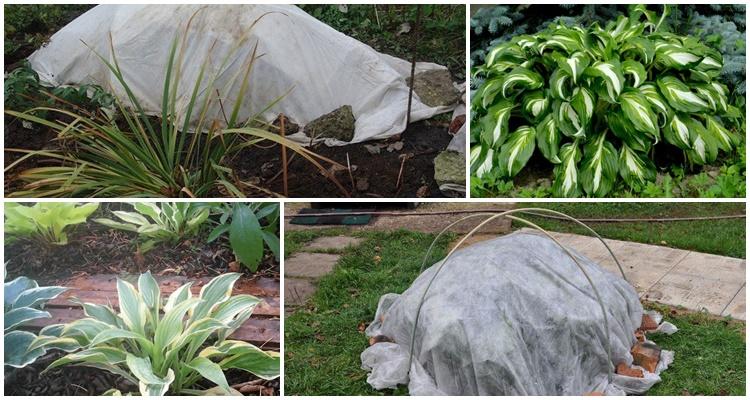

It is important not to forget to rake the mulch away from the roots of plants when spring arrives, otherwise they will rot.
What mistakes do novice gardeners make?
If a gardener is insulating a hosta for the first time, he sometimes makes mistakes during the process.
Nitrogen fertilizers are used
The last time nitrogen-containing fertilizers are applied is no later than the second half of July. Otherwise, the fertilizer will stimulate leaf growth, which will hinder successful overwintering.
Lack of mulch
If you don't apply a layer of mulch over the stumps, the hosta will freeze when the weather gets colder and will refuse to grow or form buds in the spring. Avoiding mulch is only acceptable in regions with mild winters.
Use of special materials for covering
Special non-woven materials are only suitable for insulation in northern regions. In southern areas, such coverings will lead to overheating of plants.
Soil drying out
If you don't carry out moisture-recharging watering in the fall, the soil will dry out and the plants will wither and not bloom in the spring.
When does hosta emerge after winter?
Inexperienced gardeners wait for the first hosta shoots to emerge with the first days of spring, and when they fail to appear, they assume the plant is dead. However, this ornamental shrub emerges from the ground in late May or early June, so there's no need to worry.
Useful tips for gardeners
To properly prepare your hosta for winter, it's important to understand all its requirements. Failure to meet even one requirement can result in the plant's death. Experienced gardeners recommend watering the plants before the onset of cold weather and adding nutrients at least 2-3 weeks before the first frost.