- History of selection
- Description and Features
- Characteristics of the variety
- Frost resistance
- Drought resistance
- Productivity and fruiting
- Applications of berries
- Disease resistance
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site selection and preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Protection from birds and insects
- Preparing for winter
- Preventive spraying
- Standardization
- Preventive measures against diseases and pests
- Methods of reproduction
- Cuttings
- Graft
- Layers
- Harvesting and storage
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
A relatively new domestically bred hybrid grape called Galahad is gaining increasing popularity. What are its advantages? Does it have any disadvantages? What are the characteristics of this variety? What are its characteristics? How do you properly care for it? What are the planting rules and propagation methods? How is the harvest carried out? We'll explore all of this in detail in this article. We'll also get important tips and advice from experienced gardeners.
History of selection
This grape variety was developed in Russia in 2007. Russian breeders from the Ya. I. Potapenko All-Russian Research Institute of Viticulture and Winemaking crossed three varieties to create Galahad. The breeding process took place in two stages. First, Talisman (or Kesha) was pollinated with pollen from Muscat Vostorg, then the resulting intermediate variety was crossed with Vostorg.
The breeders faced a challenging task with several components. They were required to create a grape variety that would be tolerant of climate conditions and care. The grapes were planned for cultivation in the northern regions of the country. At the same time, the hybrid was expected to produce high yields, early maturity, large fruits, and excellent flavor.
As a result, breeders successfully combined all these qualities to create a versatile grape variety. And now Galahad is becoming increasingly popular among professionals and amateurs alike.
Description and Features
Galahad grapes grow and ripen quickly. Ripening time varies by region: the further north the region, the longer the ripening period.
It is ready for berry picking 95-105 days after the buds open (at the end of July).

Pollination of grapes occurs independently.
Main characteristics of the variety:
| Variety of sort | hybrid | |
| Purpose of the variety | table (or dessert) | |
| Taste and chemical characteristics of juice | Sugar content (%) | 18-21 |
| Acidity (g/l) | 5-6 | |
| Characteristics of the bunch | Form | cylindroconical |
| Size (cm) | 27 x 22 and above (extra large) | |
| Density | moderate | |
| Weight (g) | 600-1200 | |
| Characteristics of berries | Form | elongated-oval, ovoid |
| Color | light, amber-yellow | |
| Size | medium or large | |
| Length (cm) | 2.5-3.5 | |
| Weight (g) | 10-15 | |
| Consistency | relatively firm, juicy, fleshy pulp, skin of moderate density with a whitish waxy coating, sometimes with brown spots (this is normal) | |
| Leaves | Color | light and medium green |
| Form | dissected, five-lobed | |
| Veins | yellow-green, pronounced | |
| Taste | moderately sweet, harmonious | |
| Tasting score (score) | 8.9 (high) | |
Characteristics of the variety
Grapes grow into large, vigorous bushes with massive trunks and strong, developed shoots. If left unchecked, the vines can reach heights of 30 and even 40 meters. To ensure easy maintenance, they are kept to a height of 2.5-3 meters.
With good care, grapes are capable of productive life for up to 130-150 years.

Frost resistance
The most favorable regions of the country for growing this grape are the southern and central regions. It also thrives in neighboring countries. However, the grape also thrives in the northern regions of the country, as it is highly frost-resistant. The plant can withstand temperatures as low as -25 degrees Celsius.
Drought resistance
Galahad tolerates high temperatures well. The grapes need to be watered generously, but infrequently. It tolerates drought well (but ideally for no more than 2-3 weeks or a month at most).
Productivity and fruiting
Galahad's yield is high.
Typically, 65 to 75% of the grapevine's shoots are covered with large, abundant clusters of berries. The variety's yield coefficient is 1.3-1.5.
The plant is bisexual. Its flowers are self-pollinating. The berries ripen with a color change: initially light green, they then turn green-yellow, and when ripe, they acquire a light amber color, which is especially visible when held up to the light.
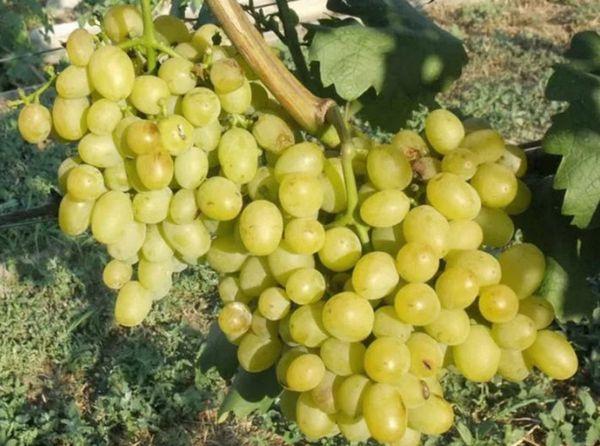

Applications of berries
Galahad grapes are used for table or dessert purposes. This means they are eaten fresh. However, many winegrowers do process them, primarily for juice. They also make preserves, jellies, desserts, compotes, and liqueurs. This variety is not used in wine production.
Disease resistance
Grapes are very resistant to pests and diseases. But not to all of them:
- Diseases such as gray mold (a fungal disease) are not dangerous for it – it resists it well.
- Average resistance is observed in relation to mildew (2.5 points), oidium (3.0 points).
- Wasps ignore grapes.
- Many birds love its fruits.
- Root rot is the most common disease of this variety. It occurs when the soil is too moist (overwatering), stagnant (melt or rainwater), or when the air is constantly cold and damp.
- Does not tolerate substrate with excess salts and high acidity.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Despite the fact that Galahad grapes are such a versatile variety, they still have both advantages and disadvantages.
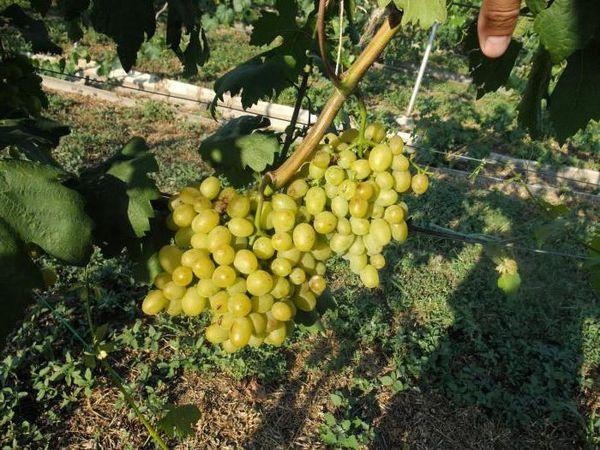

Advantages:
- The plant is unpretentious in care and planting.
- Grapes are undemanding to climatic conditions: they are drought-resistant and tolerate high (+35…+40 degrees) and low temperatures (down to -25 degrees).
- Galahad grows quickly, develops, and produces an abundant harvest.
- Grapes are self-pollinating.
- It has high taste characteristics.
- Grapes are easy to store and transport. When kept at the correct temperature, they last a long time, maintaining their shape.
- Wasps don't like him.
- It has good immunity to many diseases and resistance to parasitism.
Flaws:
- If the harvest is not collected on time, the berries begin to easily separate from the comb and fall off.
- When exposed to direct sunlight, berries tend to darken and may crack.
- Despite the pronounced resistance to pests, some insects and especially birds cause damage to grapes.
How to plant correctly
The planting process for Galahad grapes is generally the same as for other grapes. However, it does have a few unique characteristics.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
This hybrid is best planted in the spring. It can also be planted in the fall, but the main problem is the inability to predict the onset of frost. Since the seedlings need 2.5 months or more to adapt, they simply won't have time to take root in the fall. Therefore, the optimal season for planting grapes is spring.
Site selection and preparation
The Galahad grape thrives in sun and warmth. Therefore, planting it in shady areas is not recommended. The hybrid's productivity will decline sharply under such conditions. A higher elevation is best.
The plant requires a large area, as it grows rapidly. The distance between adjacent grape bushes should be 2 meters, and between rows – 3 meters.
Planting holes for grapes are prepared in advance (in the fall). They should be 70-80 cubic centimeters in volume, with mineral or organic compounds at the bottom. These are alternated with layers of soil. Sifted wood ash can be used. The entire hole is compacted, watered with 50-60 liters, and left until planting in the spring.

Grapes require adequate soil drainage to prevent waterlogging. Therefore, they prefer loose, fertile soil. Peat or loam are ideal. However, they can also thrive in sandy and limestone soils.
If the groundwater level is too close to the surface (2-3 meters), avoid planting in that area. Alternatively, install high-quality drainage (pebbles or crushed stone) to ensure water drainage.
How to select and prepare planting material
Planting material must be selected very carefully. It should be purchased from professionals in specialized stores or grape nurseries. Buying from unfamiliar, unverified gardeners at farmers' markets and fairs is a significant risk.
- It's important to pay attention to the grape seedling's root system. The roots should be healthy (no signs of rot, mold, cracks, or growths), strong, yet flexible. When cut, the roots should be white.
- The shoots are strong and green.
- The leaves should be firm, green, without spots, not wrinkled or wilted.
- The buds are swollen and elastic.
Before planting (10 days to 2 weeks), the roots of the seedling are trimmed and placed in a warm place.
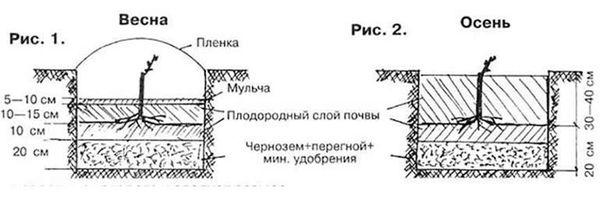
Planting diagram
Planting is carried out as follows:
- In the spring, prepare the seedling. Ten days to two weeks beforehand, trim the roots and place it in a warm place. One day beforehand, place it in room-temperature water.
- Before planting, spread out the root system, place it in the hole, and generously sprinkle with black soil mixed with sand. Shake the plant regularly to avoid air pockets.
- The soil is compacted and thoroughly rammed.
- Each bush is watered generously.
- The seedling is tied to a peg.
- A canopy is erected for the first season to prevent direct exposure to sunlight.
Care instructions
Compared to other grape varieties, Galahad is quite easy to care for.
Watering mode
This hybrid grape requires abundant watering—up to 40 liters per plant. However, watering should be approximately once every 1-2 weeks. This also depends on weather conditions. If there has been heavy rainfall, the next watering can be postponed.

Newly planted seedlings are watered moderately: up to 5 liters per bush. The plant should also be watered a week before flowering. Once the berries begin to ripen, watering is temporarily stopped.
A wide pipe is installed in each planting hole, protruding a few centimeters from the soil surface. This ensures direct watering to the shrub's root system.
Top dressing
Fertilizer placed in a pre-prepared hole will last the hybrid for two years. In the third year, additional feeding can be applied. This is done in three stages:
- In early spring. As soon as the soil has warmed, it is loosened and dry complex fertilizers (Nitrophoska, Kemira-Lux) are applied.
- Before flowering (one week): Prepare a mixture of fresh bird droppings + cow manure + dandelion leaves + nettle leaves. Dilute with water (1:10), add fertilizer containing potassium and phosphorus. The recommended application rate per plant is 12 to 15 liters.
- After flowering (a week later), superphosphate and potassium sulfate are applied either dry when loosening the soil, or in liquid form (diluted with water).
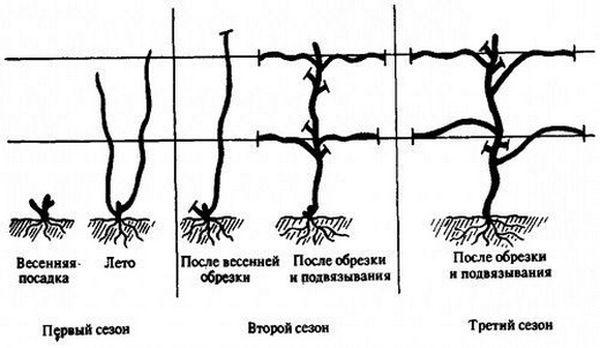
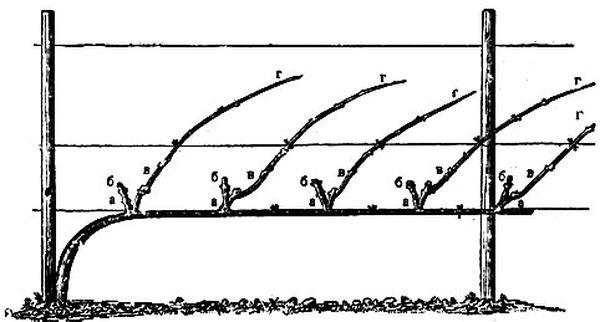
Trimming
Pruning is a mandatory part of caring for the Galahad grape. Two pruning methods are available:
- Pinching. This is done in summer. Weak shoots are removed and excess leaves that create too much shade are trimmed.
- Primary pruning. This is done in the fall. Dry, deformed branches are removed, and unnecessary buds are removed. Six to eight buds should be left on each vine, and up to 40 buds in total on the bush.
This is necessary to balance the strength of the vineyard and obtain a good harvest.
Protection from birds and insects
Here gardeners use two methods:
- Chemical traps. These traps are placed throughout the vineyard.
- Nets. A fine-mesh net is used. A cap is made from the net for each bunch of grapes.
Scarecrows and sound repellents are also used to protect against birds, but they are often not very effective.
Preparing for winter
In southern regions, Galahad grapes don't require any winter preparation, as temperatures at this time aren't critical for the plant. In northern regions, where temperatures drop to -25°C or below, the vineyard is covered with a special material (spunbond).
Preventive spraying
Preventative spraying is carried out three times a year. Bordeaux mixture and copper sulfate are commonly used. The first treatment (with a 3% solution) is carried out in the spring after the grapes are released from winter cover, and the remaining two treatments are carried out during ripening (with a 1% solution).
Standardization
Thinning, or thinning, is the removal of excess inflorescences to produce a harvest of berries with a higher sugar content. This procedure is carried out before flowering in the vineyard to create an optimal load for the plant.
Preventive measures against diseases and pests
As mentioned earlier, Galahad grapes have good immunity to many diseases and a high level of pest resistance. Preventive measures include the following:
- protection from birds and insects;
- preventive treatment (spraying).
Methods of reproduction
This grape variety can be propagated by cuttings, grafting, and layering. Seedlings were discussed in detail above.
Cuttings
Cuttings root and grow into seedlings with virtually no problem. They only require warm weather and well-moistened soil (or submersion in water).
Graft
Grafting is used extremely rarely. Grafting with phylloxera-resistant rootstocks is most often chosen.

Layers
Propagation by layering is the simplest and most reliable method.
A section of grapevine (1 to 2 years old) is planted in soil until roots form. After rooting (after about a year), it is separated from the parent plant.
Harvesting and storage
To harvest grapes efficiently, it's important to do so in sunny, warm, and dry weather. This ensures the grapes have a long shelf life and are easy to transport. Harvesting grapes in cloudy or rainy weather can quickly spoil them and make them unsuitable for transport.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Experienced winegrowers recommend the hybrid variety Galahad. It's fairly easy to grow and care for. However, they warn that the grapes don't tolerate direct sunlight or excessive moisture. Heavy rains can cause the fruit to crack, and the grapes quickly rot. Therefore, it's important to create a drainage system in the area.











