- History of selection
- Description and Features
- Characteristics of the variety
- Frost resistance
- Drought resistance
- Productivity and fruiting
- Applications of berries
- Disease resistance
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site selection and preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Protection from birds and insects
- Preparing for winter
- Preventive spraying
- Methods of reproduction
- Cuttings
- Graft
- Layers
- Diseases and pests
- Leaf roller
- Phylloxera
- Felt mite
- Harvesting and storage
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The new hybrid grape variety, "Memory of the Teacher," appeared only three years ago, but has already been highly praised by gardeners and farmers.
Hybrid grape varieties developed by amateur breeders almost always boast unique environmental resistance characteristics and excellent taste.
History of selection
This new fruit crop was created by crossing the well-known Talisman variety with the Cardinal grape. The variety's creator and developer is Evgeny Georgievich Pavlovsky, a folk breeder from the Rostov region and a student of the renowned winegrower I.A. Kostrikin.
In 2016, the "Memory of the Teacher" grape variety was added to the state register of fruit crops, with a recommendation for cultivation throughout the country.
Description and Features
The variety inherited only the best qualities and characteristics from its renowned relatives. From Talisman, the fruit tree inherited large berries and resistance to low temperatures, and from Cardinal, a unique muscat flavor and early ripening.
- The Memory of the Teacher grape variety grows tall and spreading, with multiple light-brown fruit shoots.
- The leaf blades are large, five-lobed, slightly wrinkled, and dark green in color.
- The clusters are not just large, but enormous, reaching 60 cm in length and weighing from 600 g to 2.5 kg. The clusters are conical or cylindrical in shape, with a moderate berry coverage, which prevents the fruit from becoming deformed.
- The berries are large, weighing up to 15 g, oval in shape, with thick, dark red skin.
- The fruit's flesh is juicy, dense, and crisp, with a sweet flavor and a pleasant muscat aftertaste and aroma. Each berry contains 1-2 seeds.
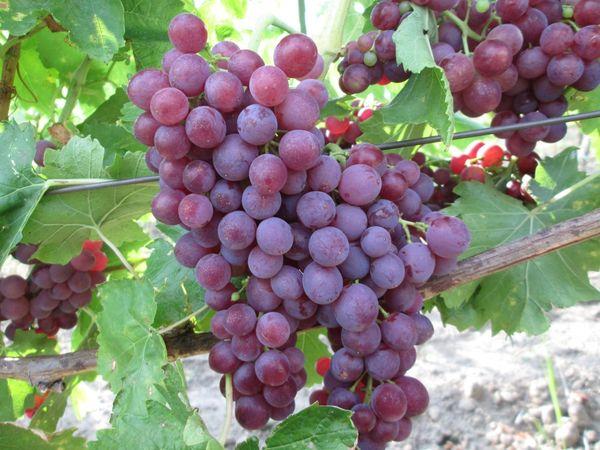

Note! Following state testing, the "Memory of the Teacher" grape was awarded a tasting score of nearly 9 points on a 10-point scale.
Characteristics of the variety
A distinctive feature of this fruit crop is the rapid and complete maturation of the fruit-bearing vines and the early ripening of the berries. However, due to early flowering, there is a risk of spring frosts, which grapes are very sensitive to.
Frost resistance
Following state testing, the subzero temperature limits for comfortable overwintering of the fruit crop have been established. The berry bush survives winters with frosts down to -23 degrees Celsius. However, since there are still few observations of the hybrid grape variety, the results may improve.
Drought resistance
Even short-term droughts cause significant damage to berry bushes and negatively impact the quality and quantity of the harvest.
Productivity and fruiting
A positive aspect is the rapid ripening of the berries. From the beginning of the growing season to full ripening, the berries take 100 to 105 days.

Under favorable weather conditions and proper care, a single bush can yield up to 10 kg of berries. Industrial production yields up to 20 tons of ripe bunches per hectare.
Important! The "Memory of the Teacher" grape variety is self-pollinating; the berry bushes do not require neighboring pollinators.
Applications of berries
This variety is considered a table variety, and the berries are recommended for fresh consumption. Fresh fruits contain the beneficial substances and vitamins necessary for vital functions and health.
The berries are also used to make juices, nectars, compotes, and sauces for various dishes. The fruits are large and beautiful, often used as a decoration for desserts and baked goods.
Grapes are excellent for making marmalade, preserves, and jams. Thrifty and experienced home cooks freeze, can, dry, and make homemade wine and liqueurs.
Disease resistance
This hybrid fruit variety has only recently appeared in gardens and vegetable patches, so it has not yet been possible to provide an objective assessment of the berry bushes' resistance to diseases and pests.
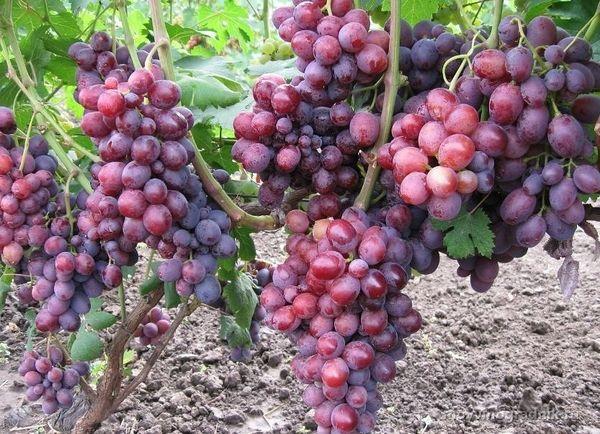

After state testing and official registration of the variety, its description indicated high resistance to fungal diseases and pests. However, as a rule, the pros and cons of a varietal crop only become apparent in practice.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Before planting a hybrid crop, it is necessary to thoroughly familiarize yourself with all the advantages and disadvantages of the variety.
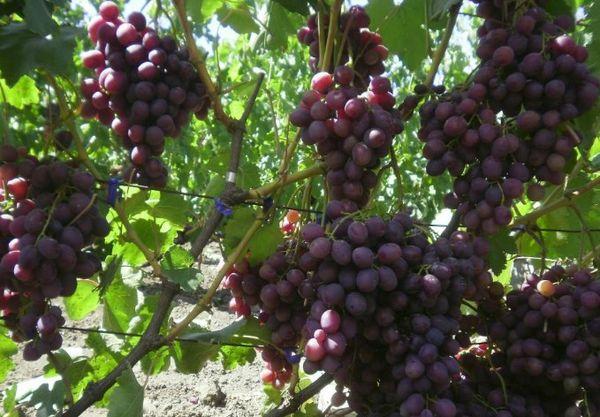
Pros:
- Early harvest dates.
- Large berries with excellent taste.
- Fast and complete ripening of the vine.
- Excellent commercial quality of fruits and the possibility of long-distance transportation.
- Annual fruiting.
- Simultaneous ripening of bunches.
Note! After ripening, the bunches can remain on the vine for a long time. The berries do not fall off or crack, and they acquire a sweeter, more muscat-like aroma.

Cons:
- Frequent overload of fruit-bearing shoots.
- The variety is demanding regarding soil composition.
- A clear watering schedule is necessary.
- The berry crop does not tolerate prolonged drought and heat.
Other disadvantages include poor resistance to low temperatures and to diseases and pests. However, the variety is still being monitored, so its characteristics may improve over time.
How to plant correctly
When planting grapes on a plot of land, it is important to remember that the berry crop will grow and bear fruit in one place for up to 20 years, and the large size of the Memory of the Teacher grape bushes requires a large area for cultivation.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
The timing of planting seedlings in open ground is calculated depending on the climatic and weather conditions of the growing region.

In the south, autumn planting is allowed, 4-6 weeks before the first frost.
In temperate climates, berry bushes are best planted in the spring, when the soil warms up to +15 degrees.
Site selection and preparation
A site for planting seedlings should be chosen with good sunlight, sheltered from strong drafts and winds, and a low water table. Grape vines grow and bear fruit best in slightly elevated areas with loose, fertile soil. Highly acidic soils, lowlands, and marshy areas are not suitable for grape cultivation.
- The area is carefully dug to a depth of at least 60-80 cm, weeds are removed and the soil is loosened.
- Humus, organic fertilizers and a mineral complex are added to the soil.
- 4-6 weeks before planting, dig holes.
- The width and depth of the holes are 70-80 cm, the distance between plants is from 1.5 to 2 m, between rows 3 m.
- If there are no buildings near the site, a supporting structure is erected to form and support the grape bushes.
- Drainage is placed in the hole, fertile soil is added and the plant is watered.
Tip! To support the young plant, drive a support stake into the hole.

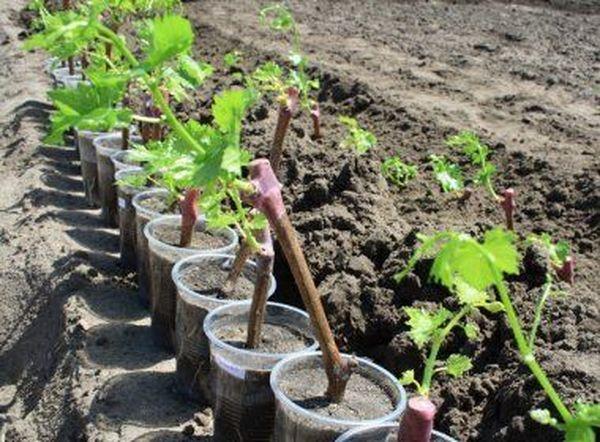
How to select and prepare planting material
High-quality planting material is purchased in nurseries and specialized stores.
- The seedling is carefully examined for damage and infection by diseases and pests.
- Plants that are 1-2 years old and have fruit buds or green leaves take root best.
- The rhizomes are well developed, moist, without broken parts or unknown formations.
A day before transferring to open ground, the plant is placed in a mixture of clay and water, after which the roots are treated with a weak solution of potassium permanganate.
Planting diagram
Before starting planting, the rhizomes of the seedling are trimmed, leaving only long branches.
- The plant is placed in the prepared planting hole.
- The roots are carefully distributed in the hole and covered with soil.
- The soil is compacted and watered, and the seedling is tied to a support peg.
After finishing the work, the tree trunk circle is mulched with humus.
Care instructions
The Memory of the Teacher grape variety is easy to care for, but requires careful watering and timely pruning of the bushes.
Watering mode
To grow a healthy and fruitful grape bush, it is necessary to carefully care for the seedlings.
Young plants are watered once every 7-10 days. Once the bush has established roots, switch to a standard watering regimen for fruit crops.
Grape vines are watered 3-4 times per season, approximately once a month. Each plant receives 30 to 50 liters of water. The amount of water depends on the age and size of the vine.
Important! The plant especially needs watering before flowering and during fruit set.

Top dressing
Grape vines expend a great deal of energy to ripen the vines and berries. Fruit-bearing crops require additional nutrition.
- In early spring, plants are fertilized with a solution of cow or bird manure.
- Before flowering and during fruit formation, the bushes are fed with minerals.
- After harvesting, humus, organic matter and a mineral complex are added to the soil.
Advice! Nitrogen fertilizers are recommended to be used only at the beginning of the growing season.
Trimming
Sanitary pruning of bushes is carried out in spring and autumn, removing old, broken, damaged and diseased shoots and branches.
Formative pruning of bushes is carried out in the fall, cutting fruit-bearing shoots to 6-8 buds.
Grape bushes produce many side shoots, which must be removed in a timely manner.
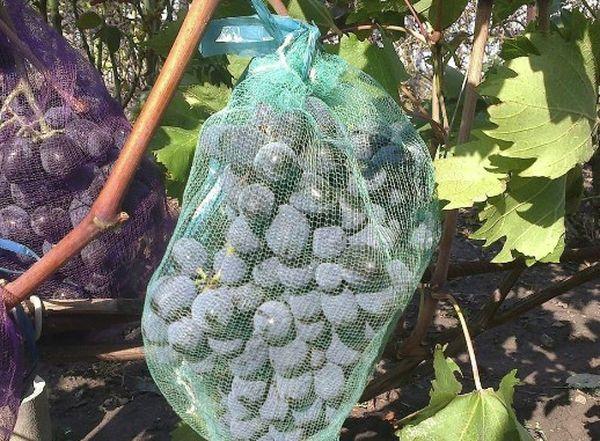
Protection from birds and insects
To protect against birds and large insects, grape clusters are protected with fine-mesh nets that block access to the berries.
Also, shiny objects are hung to scare away birds.

Preparing for winter
In regions with cold winters, grape bushes require additional insulation in the form of film or special fiber.
The plant is removed from its supports, bent to the ground, the branches secured, and the bush wrapped in the prepared material. Dry leaves and a layer of soil are sprinkled on top of the wrapped plant. After the snow falls, a large snowdrift is raked away from the plant.
Before wintering, grape bushes are watered generously, and the trunk circle is mulched with a thick layer of humus or compost.
Preventive spraying
To prevent the vineyard from being damaged by diseases and pests, preventative treatment of the fruit crop is carried out twice a year.
The first time the bushes are sprayed is in early spring, before flowering, using chemical or biological preparations.
Also, treatment is carried out in late autumn, before covering the plant for the winter.
Methods of reproduction
The grape variety "In Memory of the Teacher" is propagated by vegetative methods.
Cuttings
Cuttings are taken in late spring from strong shoots of mature plants. Each shoot is cut into an equal number of 25-30 cm long cuttings. Each cutting must have 3-4 buds or green leaves. The plants are planted in containers with fertile soil. In early fall, the young seedlings are transferred to a prepared planting hole.

Graft
Cuttings are also used for grafting, but they are grafted onto the rootstock of an old grape bush.
Layers
Layers are young shoots of fruit trees. In early summer, the layer is bent down to the ground and covered with soil. The upper part of the shoot remains above ground. In the fall, the rooted seedling is separated from the mother plant and transferred to a separate hole.
Diseases and pests
Poor care of fruit crops and unfavorable weather conditions increase the risk of disease and pest infestation.

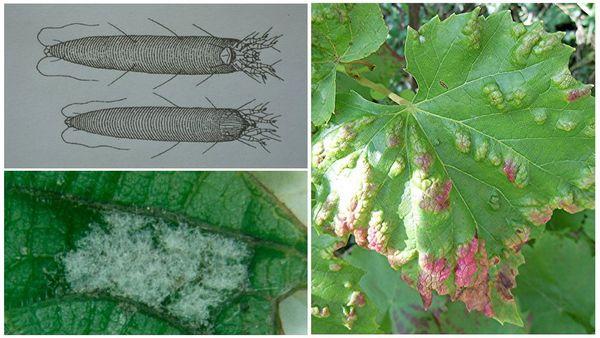
Leaf roller
The small butterfly feeds on plant sap. However, the pest is most dangerous during its caterpillar stage. The insects destroy leaves, shoots, ovaries, flowers, and fruits. Chemical and biological pesticides are used for control and prevention.
Phylloxera
Grape aphids, imported from America, can destroy a grapevine in a short period of time. The pest attacks both the upper part of the plant and the rhizomes.
To combat the pest, insecticide-based preparations are used, treating bushes and soil.
Felt mite
The pest attacks the leaves, buds, shoots, and fruits of grapevines. Symptoms include small, brown and white, felt-like growths.
To combat felt mites, high concentration chemicals are used.
Harvesting and storage
Harvest time varies depending on the grape growing region. The "Memory of the Teacher" variety is an early-ripening variety, with berries beginning to ripen in August in southern regions. In temperate climates, harvesting begins in mid-September.
The bunches ripen simultaneously, the fruits do not fall off or crack, and the berries are harvested slowly. Slightly overripe fruits become sweeter and more aromatic.
In the refrigerator, grapes can be stored for a long time without losing their appearance or taste.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The basic recommendations for growing the "Memory of the Teacher" grape variety revolve around timely watering and regulating the load on the fruit bushes. The optimal number is 30-40 fruit buds per mature plant.











