- Description and Features
- History of selection
- Properties
- Caloric content
- Benefits and harms
- Acidity
- Bush characteristics
- Vine
- Bunch
- Productivity
- Taste qualities
- Winter hardiness and drought resistance
- Disease resistance
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site selection and preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering
- Top dressing
- Mulching
- Garter
- Disease prevention
- Chlorosis
- Oidium
- Rot
- Anthracnose
- Bird protection
- Methods of protection against pests
- Grape flea beetle
- Mosquito
- Pillow case
- Wasps
- Preparing for winter
- Pruning and shaping
- Support
- Methods of reproduction
- Layering
- Cuttings
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Harvesting and storage
- Obtaining wine
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The vigorous Alfa grape variety has been cultivated in Russian gardens for nearly 100 years. Developed by American breeders by crossing Labrusca and Riparia, it is used in landscape design as an ornamental plant. It is easy to grow and frost-tolerant. Even a novice gardener can grow this grape variety if they follow the proper cultivation techniques and care for the vines properly.
Description and Features
The Alpha grape produces spreading, vigorous bushes, with vines reaching 9 meters in length. Key characteristics of the variety:
- Late ripening period - 150 days to full maturity.
- The color of ripe fruits is blue-violet with a white waxy coating.
- Yield: 10 kilograms of berries per plant.
- Strong immunity, winter hardiness (up to -45 WITH).
- Used as a pollinator and greening agent.
- The pulp is sour, slimy, with a sugar content of no more than 16%.
- The leaves are large, the clusters are small, cylindrical in shape.
Experts classify the Alpha variety as a technical grape, suitable for processing into wine products. Its taste and color are similar to Isabella grape variety.
History of selection
A North American variety, it's therefore adapted to frost and harsh climates. In our country, it's especially popular with gardeners in the Primorsky Krai. It was created by crossing two varieties: Labrusca and Riparia, and a wild grape. Alpha is grown commercially.
Properties
Different grape varieties vary in flavor balance, sugar and solid content, and calorie content. Eating grapes has a positive tonic effect on the entire body. Ascorbic acid helps strengthen the immune system, and potassium strengthens blood vessels and the heart.

Caloric content
Ripe Alpha fruits contain approximately 16% sugars, with a caloric content of 65 kilocalories per 100 grams of product.
Benefits and harms
Eating dark grapes has a positive effect on the body's hematopoietic function, lowering blood pressure, strengthening blood vessels and the heart, and increasing hemoglobin levels. The berries help restore gastric acid secretion, allow the body to absorb vitamin C in adequate amounts, and are used to prevent colds.
Acidity
Alpha grapes are a wine grape variety. They are distinguished by their distinct acidity and rich grape aroma. These qualities make them popular among winemakers, and the fruit produces delicious homemade wine.
Bush characteristics
Alpha forms a vigorous, spreading vine with large leaves. Its root system is well developed and capable of withstanding frosty winters without shelter.

Vine
It is a vine capable of reaching a length of 9 meters. Alpha is prone to overgrowth and requires pruning and shaping. The trunk is robust and frost-resistant.
Bunch
The clusters are small, cone-cylindrical in shape. The grapes become smaller over time. A single bunch of ripe berries can weigh up to 250 grams, with an average weight of 150 grams.
Productivity
The Alpha grape is a late-ripening variety, with the berries reaching full ripeness in early October. A single mature vine can yield up to 10 kilograms of fruit. The variety is suitable for commercial cultivation.
Taste qualities
The taste of the Alpha grape is an acquired taste. It has a distinct acidity, yet the fruit is very aromatic. The berries have a slimy texture, are juicy, and have seeds and firm skins. Sugar content is 16%.
Winter hardiness and drought resistance
These qualities are the variety's advantages. Alpha can withstand winters with temperatures down to -45°C. With soil freezing down to -12 C. The bush withstands prolonged drought well and does not require additional watering.

Disease resistance
The variety is resistant to most types of fungal diseases. The plant's natural immunity can be weakened by unfavorable growing conditions:
- thickening of the vine;
- a long period of rain in a cold summer;
- incorrect choice of landing site.
Alpha is an unpretentious grape variety, not prone to diseases, and requires minimal chemical treatments when growing it.
How to plant correctly
To successfully grow this variety, you need to choose the right location for planting, prepare the soil, select viable, healthy seedlings, and organize systematic plant care.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
The Alpha grape is a frost-hardy variety that can withstand temperature fluctuations. The seedlings take root quickly and rarely get sick. The optimal planting time is spring, and plants can be planted between March and June, depending on the region's climate. Fall planting, from September to October, is also practiced.
Site selection and preparation
The main requirement for a planting site is protection from winds. Stagnant water at the roots is unacceptable for grapes; if the groundwater level exceeds 1.5 meters, drainage is recommended. The optimal location is a southwest-facing site.

How to select and prepare planting material
It's recommended to purchase grape seedlings with a closed root system from specialized stores. Before purchasing, inspect the planting material; there should be no signs of fungal diseases, swollen buds, or open leaves.
Note: The Alpha grape variety is often grown using cuttings; the plant demonstrates excellent survival and rapid fusion with the scion.
Planting diagram
Grapes are grown in various ways, with or without support, depending on the plant's intended purpose. In any case, a distance of 1.5 meters between vines is required, with a 2-meter gap between rows.
The planting hole should be 1 meter deep, and it is advisable to pour sand mixed with ash onto the bottom; the main soil should be fertilized.
Note: The deeper the planting hole for grapes, the more powerful the root system of the plant will be.
It is advisable to prepare the hole for spring planting in the fall, and for autumn planting in the spring; the soil must settle.
Care instructions
The complex of measures for vine care includes the organization of irrigation of grape plantations, disease prevention, application of fertilizers if necessary, mulching, tying and pruning of the bush.
Watering
Providing the plant with the necessary moisture is important in the first year after planting. The plant's root system and future vines are developing. Grapevines should be watered at the roots with warm water in the evening or early morning. Mature vines require up to 30 liters of water per watering.
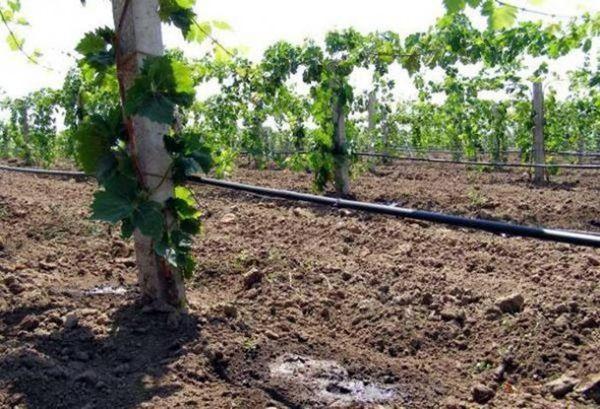

It's important to provide the plant with the necessary moisture in the spring, immediately after removing the cover. After watering, the root zone is loosened and mulched.
Top dressing
Fertilizing is an important step in plant care. From April to June, grapes need to be watered generously, preferably with a specialized liquid mineral fertilizer. Commonly used fertilizers include an infusion of bird droppings or cow dung, or a mixture of humus, wood ash, and sand.
Mulching
To maintain optimal moisture levels, it's important to mulch the root zone. Grass clippings, lawn trimmings, wood shavings, and straw are all good options. Mulching is performed after watering and loosening the soil.
Garter
From the moment of planting, the plant requires support. Grapes are tied to stakes, walls, and other surfaces. The Alpha grape produces a vigorous, spreading vine that requires staking and additional support. This grape variety is used to create hedges, arbors, and fences.
Disease prevention
The Alpha variety is genetically resistant to most types of fungal and viral diseases, but infection outbreaks may occur if not properly cared for, so preventative measures against grape diseases are recommended.
Chlorosis
It occurs when photosynthesis in the plant's leaves is disrupted. Leaf blades begin to abruptly fall and turn yellow. Grapevine growth slows significantly, new shoots fail to form, and flowers and buds die. If no measures are taken to save the vine, the vine will die by early autumn.
If signs of chlorosis are present, immediate measures must be taken to save the vine. First and foremost, it's important to review the soil composition and improve drainage. Excess organic matter, such as fresh manure, can also cause this serious disease in alkaline soils. Excess limestone must be removed from the soil.
Gardeners treat chlorosis with ferrous sulfate and fertilizing plants with manganese and zinc.

Oidium
Another name for this disease is true powdery mildew. Outbreaks most often occur in the spring. Leaves on the vines fail to open, and a grayish coating appears on the stems and leaf blades. Formed inflorescences take on the appearance of powder-covered twigs. The fungus can quickly spread to other plants, potentially destroying the entire grape crop.
To combat the disease, preventative spraying of plants with chemicals such as Horus, Skor, and Azofos is carried out. In the fall, before winter dormancy, the vines are treated with copper sulfate.
Rot
White rot and gray rot are the main fungal diseases affecting grapevines. They significantly reduce the quality of the harvest. Ripe berries dry out, burst, and acquire an unpleasant taste and aroma. These berries are unsuitable for storage and transportation. The main trigger for this disease is a cold summer with few sunny days and excessive rainfall.
For early diagnosis of the disease, spray the plants with Bordeaux mixture. If the infection is severe, use Switch, copper sulfate, or Ronilan.
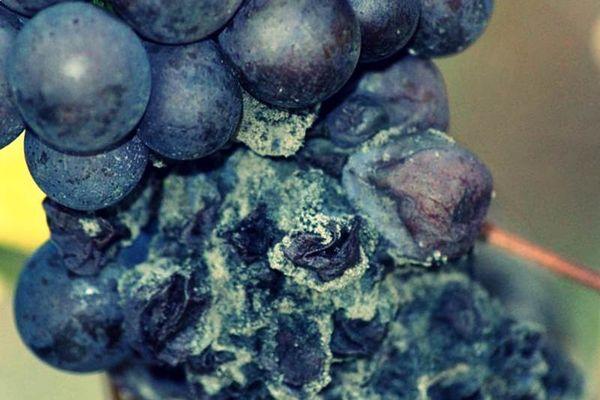

Anthracnose
Blurry brown spots appear on the leaves, which then spread to the stems and berries. Fruit rot begins. Copper-containing chemicals are used to combat the infection. Gaupsin is a biological treatment.
Bird protection
Grape yields often decline due to avian pest infestations. In this case, rustling pinwheels or scarecrows are placed near the grapes. Birds will be discouraged from approaching the delicious, juicy berries.
Methods of protection against pests
Grapes are susceptible to attack by insect pests that want to feast on the juicy foliage of plants or ripe fruits.
Grape flea beetle
A small insect that feeds on grapevine foliage. Beginning in early spring, the pest begins devouring the tasty leaves. The adult then lays eggs on the underside of the leaves, which hatch into voracious larvae. Affected grapes should be sprayed with "Karbofos."
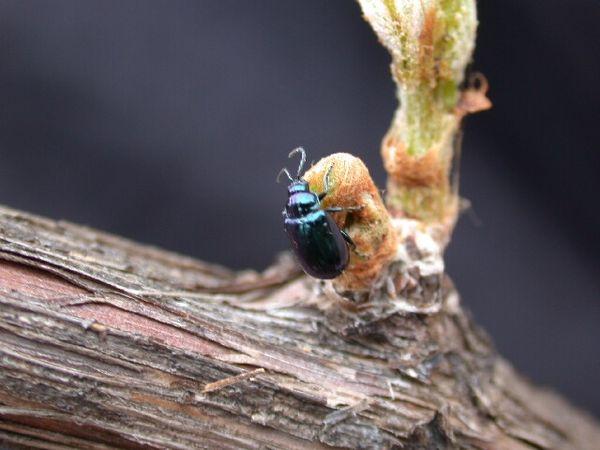

Mosquito
The pest is common in the south. It lays eggs on the underside of leaves, covering shoots with a fluffy coating. The larvae consume buds, flowers, leaves, and even plant stems. Crop losses can reach 50%. A popular method of controlling grape midges is to use parasitic parasitic wasps, which consume the larvae. In cases of severe infestation, insecticides are used.
Pillow case
A parasitic insect that feeds on plant sap. Grapes begin to significantly stunt growth, lose foliage, and may die. Control agents such as Karbofos and Isatrin are used. Cryptolaemus beetles are also popularly introduced to the grapes.
Wasps
Sweet berries attract wasps, which feast on the sweet pulp. The commercial quality of the grapes declines, the fruit spoils quickly, and cannot be transported long distances. Bunches must be protected. Gardeners often use personal protection methods, such as wrapping the bunches in gauze or netting, or using liquid smoke. Wasp repellents, such as "Sochva," can also be used.
Preparing for winter
To ensure the grapevines survive the winter with ease, the plant must be prepared. The vines are pruned and shaped, and covered with additional material for the winter.
Pruning and shaping
Prune the bush at a distance of 8-10 buds. Alpha is prone to overgrowth, so it's necessary to remove all side shoots and extra shoots with pruning shears.
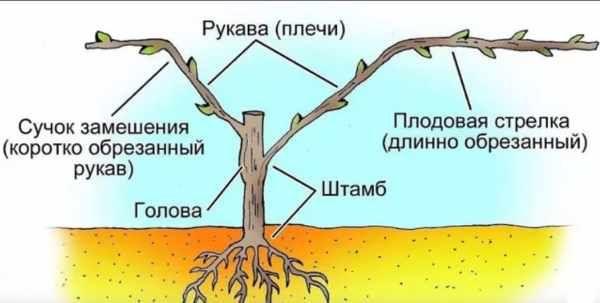
Support
Support is important for this grape variety.The vine can reach a length of 9 meters. Typically, fences, stakes, walls, nets, and sheds are used for support. Alpha cannot grow without support.
Methods of reproduction
The Alpha grape is easy to propagate indoors. Cuttings are the best method, but gardeners also use layering.
Layering
In early June, the lower branches of the vine are supported against the ground and covered with soil. Excess leaves should be removed from the layering. The point of contact with the ground should be firm. The layering should be watered generously. By the end of August, the shoot will have rooted and can be separated from the mature plant and transplanted to its permanent location.
Cuttings
In early summer, cuttings are taken from mature plants using pruning shears. The young shoot should be approximately 15-20 centimeters long and have 3-4 healthy, swollen buds. The cutting is immersed in water for several days and then planted in an individual container, covered with plastic wrap or a glass jar. By August, the cutting will have rooted and can be planted in its permanent location. Grape cuttings can also be taken in the fall; the shoot will root over the winter and be ready for replanting in the spring.

Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
Main advantages of the variety:
- Frost resistance and ability to tolerate changeable climate.
- Immunity to fungal diseases.
- Undemanding to soil and fertilization.
- Easy to propagate at home.
- Can be used as a greening agent.
The disadvantages of the Alpha grape include:
- Average taste of fruits.
- The clusters are small in size.
- Tendency to become dense, pruning is necessary.
Overall, this variety is suitable for both experienced and novice gardeners. It's important to choose the right planting location and organize proper care.
Harvesting and storage
Alpha ripens by the end of September. The bunches are hand-picked. The grapes have a long shelf life, so it's important to calibrate the harvested material, removing any diseased or overripe berries.

Grapes are best stored in fruit crates in well-ventilated areas. When harvesting grapes, care should be taken not to damage the waxy coating on the berries; this serves as a protective layer for the ripe fruit.
Obtaining wine
The Alpha grape is used to make wine, similar to the Isabella variety. The resulting wine has a rich, grape-like flavor with a slight acidity. Alpha is rarely eaten, so winemaking is the optimal way to use the ripe berries.
Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
To ensure a strong, healthy vine produces a harvest for years to come, you must believe in the success of grape growing in any region, and also adhere to all the subtleties and nuances of planting and caring for the plant.
The Alpha grape variety will complement the landscape of small garden plots and is also suitable for industrial cultivation.
Despite the variety's high frost resistance, experienced gardeners recommend covering the vines for the winter in regions with little snowfall. Covered grapes awaken more quickly in the spring and grow faster.











