- Winemaking history
- Description and Features
- Characteristics of the bush
- Vine
- Bunch
- Characteristics
- Caloric content
- Benefits and harms
- Acidity
- Productivity
- Features of cultivation
- Climate conditions
- Deadlines
- Vine training
- Standard
- Formation of four sleeves
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Diseases and pests
- Bacterial cancer
- Gray rot
- Oidium
- Grape leaf roller
- Phylloxera
- Wine quality
- False varieties
- Italian
- Grey
- Missouri
- Emerald
- Red
- Black
Riesling grapes are considered a late-ripening, industrial grape variety. This grape variety is the primary raw material for the production of dry, dessert, semi-dry, and sparkling wines and juices worldwide.
Riesling is grown in Europe, the USA, Africa, Canada, New Zealand, neighboring countries, and Russia. The taste of wines made from varietal grapes directly depends on the growing climate, care, soil fertility, the number of sunny days, and soil composition.
Winemaking history
The first mentions of the Riesling grape date back over 2,000 years. But the variety's true history began in the 15th century, when a German prince planted wild, pollinated grape vines brought from the Rhine Valley on the grounds of his castle. After the first harvest, a wine was produced and named Riesling.
The history of this variety's development didn't end there. Wines made from this grape for a long time failed to gain popularity due to their mediocre taste and aroma, until a chance coincidence revolutionized the world of winemaking.
The courier delivering the grape harvest permits got lost and was delayed for two weeks. During this time, the ripe grapes became significantly overripe and began to spoil on the vines.
But to avoid punishment, the harvested grapes were sent to the winery for processing. The drink, produced from overripe, partially spoiled, and moldy Riesling grapes, turned out to be the pinnacle of winemaking. This completely accidental result is used by winemakers around the world to this day.
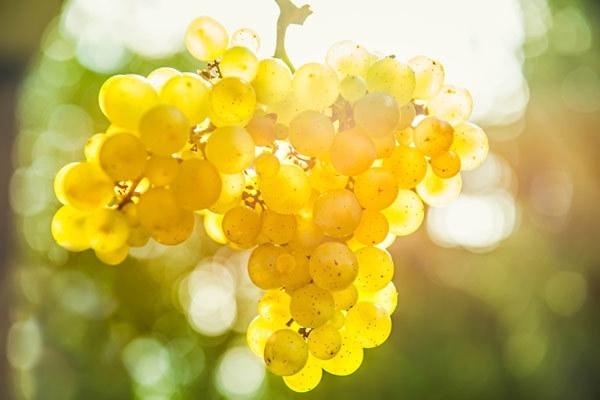

Description and Features
Riesling grapes are completely undemanding regarding growing conditions and agricultural practices. This fruit crop is grown in regions with a wide range of climates, and even in cold climates, the variety thrives and produces fruit.
Characteristics of the bush
The fruit tree's bushes are tall, branched, and feature multiple leaf blades and shoots. The leaves are large, and their color varies depending on the plant's age. Seedlings and young shoots have beautiful bronze-colored leaves, while mature bushes develop bright green leaf blades. In autumn, the grapevine's leaves turn yellow.
Young shoots are light green in color, with barely noticeable hairs; by the end of the growing season, the shoot darkens.
Flowering is late, so the bush does not suffer from spring temperature fluctuations.
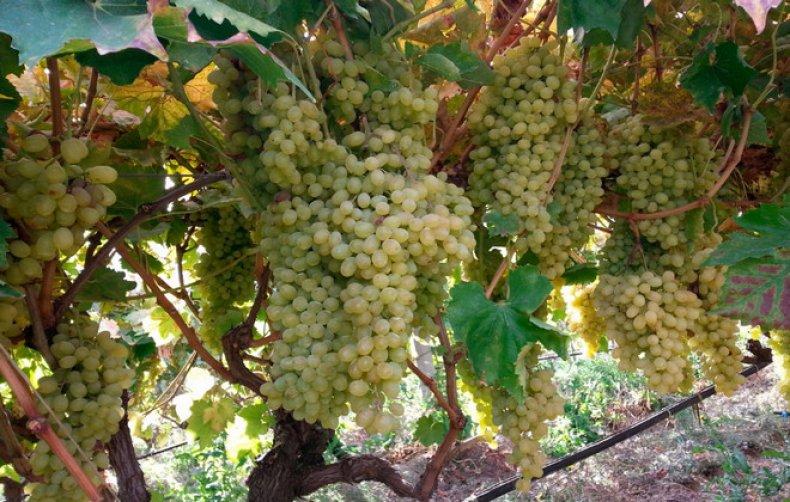

Vine
Every year, fruit vines grow on the grape bushes, on which clusters of berries develop.
The Riesling variety has small vines that take on a light brown hue as they ripen. Unripe vines turn reddish.
Important! The main positive characteristic of this variety is the rapid growth and maturation of the one-year-old vine.
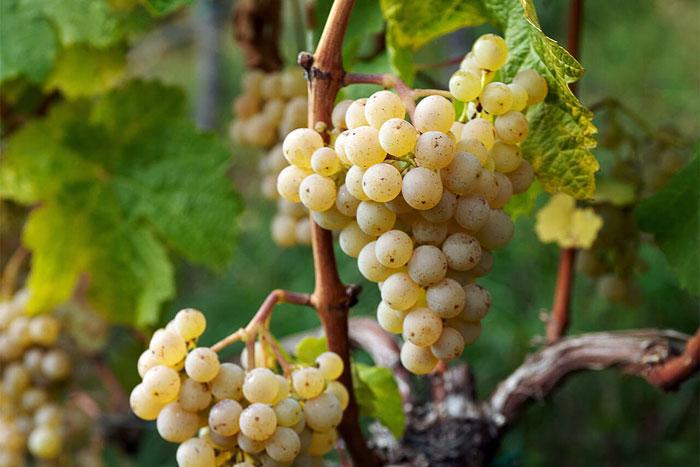
Bunch
The cluster of ripe berries is small, up to 14 cm long, cone- or cylindrical, with small, multiple green fruits. Each cluster contains 60 to 80 berries with a sweet taste and a distinctive varietal aroma.

The weight of 100 berries is only 130 g.
Characteristics
Riesling grapes contain a huge amount of vitamins, minerals, substances, and amino acids essential for proper bodily function. Therefore, the fruits of this berry crop are not only processed but also consumed fresh.
Caloric content
Grapes, due to their low calorie content—only 43 kcal per 100 g of fresh fruit—are often used in dietary regimens. Due to their high sugar and dietary fiber content, grapes quickly fill the body, keeping you full for longer.
Benefits and harms
Grapes are used to restore and strengthen the immune system, promoting healthy nervous, circulatory, and cardiovascular systems. They also support gastrointestinal function and are used in cooking and cosmetics.

To improve health and maintain proper functioning of the body, 100 to 200 g of berries per day is enough.
Those with elevated blood sugar levels or severe obesity should consume grapes with extreme caution or avoid them altogether. Riesling berries are also not recommended for those with gastrointestinal disorders or high acidity.
Acidity
The balanced acid content of up to 1% and sugar content of up to 18% in grapes allows for the production of delicious, healthy juices, nectars, dry and dessert wines after processing. The Riesling variety is also recommended for the production of sparkling wines and champagnes.

Productivity
Riesling grapes are considered self-fertile, but to ensure a high-quality and abundant harvest, pollinators are recommended. The berry ripening period ranges from 130 to 160 days, depending on the climate of the growing region.
This fruit crop variety is not distinguished by high productivity; from 1 hectare one can obtain from 7 to 9 tons of bunches with ripe berries.
The bush begins to bear fruit in the 2nd year in open ground.
Note: Under favorable weather conditions and timely agricultural practices, German farmers can yield up to 16 tons of ripe berries per hectare of land.

Features of cultivation
The Riesling grape variety is frost-resistant and undemanding of sun, which allows it to be grown in regions with different climates.
When choosing a site for planting seedlings, consider the plants' preference for limestone soil. Grape vines thrive best on gentle slopes.
Climate conditions
In southern regions, the fruit ripens early, but doesn't reach the sweetness needed for winemaking. In temperate climates, Riesling grapes ripen gradually. The longer the ripening process, the sweeter the fruit becomes.

Deadlines
Grape seedlings are planted in late autumn, 4-6 weeks before the first frost, or in early spring, before the first buds appear.
Fall planting of fruit crops is recommended for southern regions with warm, mild winters. In temperate climates, Riesling grapes are transplanted outdoors in the fall.
Preparation of the land for planting begins 1.5-2 months before planting the seedlings.
- The area is dug up, weeds are removed and the soil is loosened.
- Planting holes are dug 60-70 cm deep and wide, and a support peg is driven in.
- The distance between holes is 1.5 m, between rows 3 m.
- A drainage layer is placed at the bottom of the hole and fertile soil mixture is poured on top.
- A seedling is placed in the center of the hole and the roots are spread out evenly.
- The roots are covered with soil from above, the soil is compacted and watered.
- The plant is attached to a peg.
- The tree trunk circle is mulched with humus or dry grass.
 Important! Until the seedlings are fully rooted, water them every 8-10 days.
Important! Until the seedlings are fully rooted, water them every 8-10 days.
Vine training
Grape fruiting and yield directly depend on proper pruning. Leaving long shoots prevents the plant from developing, the vines become thin and weak, and the clusters and berries become smaller. Annual pruning of the fruiting bush is carried out until the plant reaches six years of age.
Standard
To form a standard tree, all lower branches and shoots are removed. The standard tree should be at least 1.2 m tall, with two strong main shoots and at least 6-7 fruiting vines.
When pruning in autumn, it is necessary to leave 5 to 7 buds on each shoot.
Riesling grapes grown using standard vineyards do not require any additional measures before winter dormancy.

Formation of four sleeves
Let's first understand what a "sleeve" is and how to form one. A "sleeve" is a strong shoot branching off from the main trunk of a shrub.
When growing as a standard, only two shoots are left on the leader, while when forming four branches, four shoots are left from the base of the trunk. The shoot tips are removed or pinched.
Important! Grape vines are thin and flexible, requiring constant support or reinforcement. When growing grapes, remember to use supporting structures, trellises, or nets to support the plant's shoots.

Top dressing
Riesling grapes do not respond well to additional feeding and fertilizers, which affects the yield and taste of the berries.
The plant begins to be fed with wood ash in the 3rd year of growth in open ground.
Trimming
In spring and fall, fruit bushes undergo sanitary pruning, removing branches and shoots that are frozen, broken, dry, damaged, or affected by diseases or pests. Old, non-fruit-bearing shoots are also trimmed, and the cut areas are treated with garden pitch or special products.
Diseases and pests
Riesling grapes are not known for their resistance to diseases and pests. To prevent these problems, spray the fruit bushes with chemical or biological pesticides in early spring and fall.
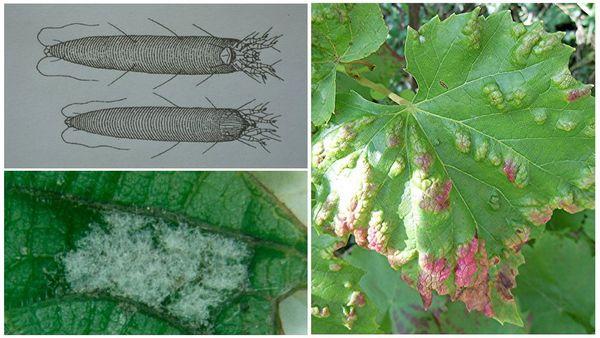
Bacterial cancer
The disease manifests itself as light or yellow growths on older branches. Unfortunately, there is no cure for bacterial canker. If the affected area is small, the branches are pruned and the bush is treated with copper sulfate. If the disease has spread to the entire plant, the bush is dug up and destroyed, and the soil is disinfected.
Gray rot
Gray mold affects the buds, leaves, fruits, and shoots of fruit crops. It appears as spots and a gray coating on the leaves and fruits. The berries rot and fall off. Spraying the bushes and soil with fungicides is used for prevention and treatment.
Oidium
Powdery mildew manifests as a white coating on leaf blades, ovaries, and berries. The fruit dries out and rots, producing an unpleasant odor.
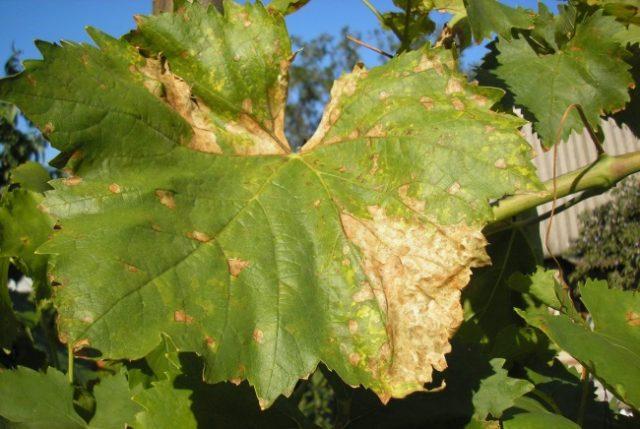

The fight against the disease involves treating the bushes with fungicide-based preparations.
Grape leaf roller
This small moth is especially dangerous in its caterpillar stage, which consumes everything in its path. For treatment and prevention, bushes and soil are sprayed with insecticides.
Phylloxera
The dangerous grape aphid attacks both the above-ground and underground parts of the plant. Grapes affected by this pest quickly dry out and die.
To prevent and control phylloxera, professional chemical preparations based on insecticides are used.

Wine quality
Every winemaker knows that the main characteristics of wine directly depend on weather conditions and proper, timely care of the grapes.
Grapes grown in temperate climates produce wine with a light apple aftertaste and acidity, while berries from southern regions impart citrus or peach notes to the wine.
Important! Riesling grapes grown in the same area can have completely different flavor characteristics each year.
False varieties
False Riesling varieties are actively cultivated throughout the world, but only a few of them have any relation to the Rhine grape variety.

Italian
This wine grape variety originated in Italy in the 19th century and subsequently quickly spread to many European countries. The Italian Riesling variety is completely unrelated to the famous Rhine grape variety.
Wines made from this variety are distinguished by their fruity aroma and high acidity.
Grey
The variety gained its fame primarily in California, but is completely unrelated to the true Rhine grape variety. It was developed in France under the name Trousseau Gris, from where it spread throughout the world.

Missouri
A hybrid fruit crop created by American breeders by crossing other grape varieties. The Missouri variety was lost for many years, but was revived in 2013 and used in wine production.
Emerald
The closest relative of the Rhine grape, bred by Californian scientists. This industrial grape variety has also found favor in Israel, where it is widely cultivated.
Red
A red-skinned hybrid variety of Riesling, widely grown in many countries around the world.
Black
Black Riesling, also a close relative of the Rhine grape, is often used to make champagne and sparkling wines.











