- What is a layering?
- Conditions for the formation of the root system of grapes
- Humidity
- Nutrients
- Lack of light
- Digging depth
- Advantages and disadvantages of the method
- Methods of layering
- Underground
- Perennials
- Hilling up the bush head
- The short way
- Air method
- Propagation by lignified layering
- The Chinese way
- Kataviak
- Daldarama and Lugenda
- Seasonal features
- In summer
- In the fall
- In the spring
- Aftercare
- Watering
- Loosening and weeding
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Propagating grapes by layering, both in summer, spring, and fall, is becoming increasingly popular among gardeners who want to increase the number of vines in their plots without spending a lot of money. This process offers several effective options that not only produce new plants but also replace old, weak vines of your favorite varieties.
What is a layering?
Layers are rooted grapevines planted in the soil without being cut from the parent plant. They receive nutrients and water from the parent plant, allowing them to rapidly develop their own roots. In the fall or spring of the following year, the layers are separated from the parent plant and used as seedlings for subsequent propagation.
This is a method of vegetative propagation that ensures the preservation of the characteristics and properties of the mother plant, excellent survival rate, and rapid fruiting.
Conditions for the formation of the root system of grapes
For grapes to thrive, comfortable conditions are essential. To stimulate deep root development, factors such as humidity, nutrients, optimal planting depth, and exposure to light should be considered, as these factors determine how quickly the cuttings will root.
Humidity
Maintaining moisture is essential for root formation. For root growth, the soil must be constantly moist.
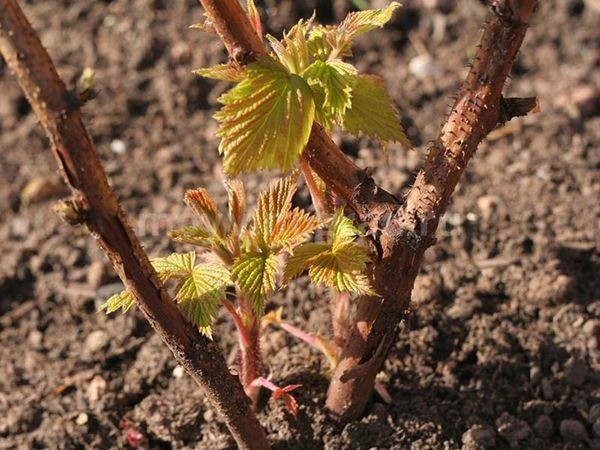

The following steps will help you achieve this:
- Water generously, keeping the soil moist not only on the surface but also in the rooting area. Water with settled, sun-warmed water, being careful not to splash it on the leaves or trunk of the plant.
- Mulch the soil in the area where the vines are buried regularly, using grass, hay, straw, or peat. This will retain moisture and reduce the need for watering.
- Shade the soil, as the section of the vine placed in the shade of the bush will root better. You can simulate shade by placing a dense material on top of the buried layer. Cardboard, sheet metal, or plastic can be used in this case.
Nutrients
The rate of root growth and its number are determined by the plant's nutrient reserves. To ensure a strong root system in new seedlings, it is recommended to apply organic and mineral fertilizers designed for grapes to the area where the shoot is buried. Growth stimulants, chemical and biochemical substances that help accelerate plant growth, can also be used.
Lack of light
Root growth is more intense in the dark. Therefore, if the cuttings are not dug deep, cover the soil with a thick material to block light from reaching the top layer of soil.
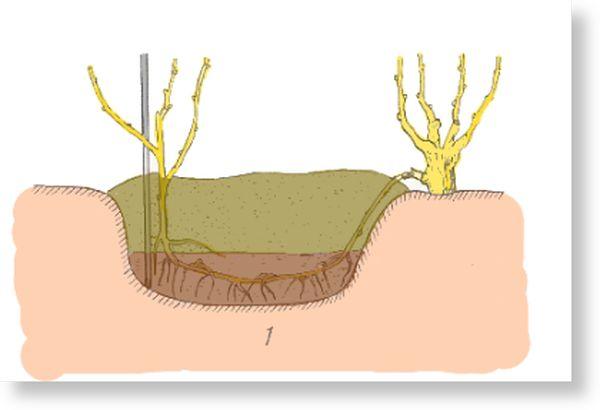
Digging depth
During the procedure, it's important to maintain the optimal planting depth, which should be between 15 and 20 cm. This will help ensure both humidity and protection from light.
Advantages and disadvantages of the method
When growing vineyards, gardeners often resort to the method of propagation by layering due to a number of advantages that allow:
- significantly increase the vineyard in a short period of time;
- reconstruct obsolete plants;
- to preserve all the characteristics and valuable qualities of the selected forms and varieties;
- ensure rapid establishment and fruiting in the first year after planting;
- get results without spending a lot of time and effort;
- use for commercial purposes to generate profit from the sale of planting material;
- create a decorative work of art.
The disadvantages of this method are the weakening of the mother bushes and the vulnerability of the plants to phylloxera.
Methods of layering
You can try propagating your favorite grape variety yourself. There are many methods for propagating grapes, each effective in its own way, but the simplest and most accessible is layering. The advantage of this method is that you can expand your vineyard without much effort, time, or expense.
There are several variations of this method.
Underground
This layering is often used when another bush of the same variety needs to be grown near the mother plant. To root, you need:
- In the spring before the growing season or in the fall after the leaves have fallen, select a green shoot of the current year, without signs of disease or mechanical damage.
- From the mother plant to the desired location, dig a trench 40 cm deep, the bottom of which is filled with a soil mixture of fertile soil, humus and granulated superphosphate.
- Place the selected shoot in the prepared hole at the bottom. If it's long, it's best to bend it into a wave or loop. Raise the top 45 cm above the soil surface, inserting a stake to secure it.
- Fill the ditch with nutrient substrate and water it.
If the steps are performed correctly, the vine will grow more than 3 m in the first year.
Perennials
To propagate grapes this way, you need to root a perennial branch containing young vines. To do this, dig a 0.5-meter-deep trench next to the mother vine and fill its bottom with organic matter mixed with soil. Then, deepen the shoot, leaving the tip with several buds above ground.

To obtain a large number of seedlings, you can place all the vines in a trench, pruning them back to 3-4 buds beforehand and pressing them down with wire. As the vines grow, add soil to the trench and moisten it. In autumn, separate the vines and transplant them from the mother plant.
Hilling up the bush head
This method of propagation is possible if you have a mother plant from which you only need to obtain planting material. To do this, prune all the vines in the spring, leaving 1-2 buds. When the shoots reach 20-25 cm in height, they should be earthed up with a layer of loose soil, keeping it moist at all times.
Although the main bush has a root system, the layers only develop roots in moist soil. In the fall, carefully loosen the mound and cut the layers as close to the ground as possible.
Important! This procedure results in severe depletion of the mother plant.
The short way
Short grapevines can also be used for propagation. Dig a 5 cm deep hole near the vine and water it thoroughly. Place a portion of the selected shoot into the hole, leaving a 15 cm gap above ground level.
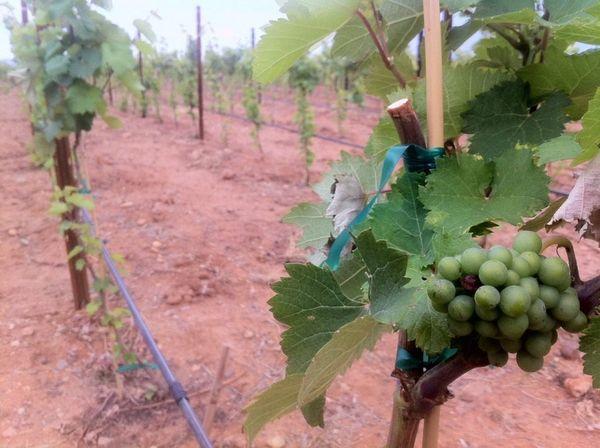

Then, fill the hole with fertile soil and compact it. Securely attach the protruding part of the cutting to a support, such as a stick or stake. This will prevent the trunk from bending or collapsing.
Air method
This method is used if there is free space near the mother plant. To do this, in the spring, when sap is flowing vigorously, pull a well-developed young stem horizontally along a wire attached to two slats. Determine a rooting area up to 8 cm long on it. Then, tie the vine tightly using copper wire and make longitudinal cuts in the bark up to 1 cm long.
Hang a container of potting soil on the shoot where it's rooted. The soil should cover the branch in the container by 2 cm and be constantly moist. Once enough roots have formed in the container, separate the cutting and its container from the parent plant. Plant the resulting seedling in the ground along with a lump of potting soil.
Propagation by lignified layering
Propagating grapes using woody cuttings should be done in the fall. This method ensures the cuttings survive thanks to double feeding.
The disadvantage is that the cuttings can be separated from the mother bush no earlier than 3 years after the procedure.

The process requires the following steps:
- Dig a hole near the bush 0.6 m deep, add organic matter mixed with fertile soil.
- Place the lower shoot in the hole, leaving the top, which should have 3 eyes above the ground surface.
New grape cuttings will delight you with a harvest within a year.
The Chinese way
The main advantage of this method is that one bush can produce up to 20 seedlings, but the disadvantage is that the mother bush is severely depleted. To do this:
- In early spring, select a shoot growing close to the ground, place it, and pin it to the soil, placing it in a trench 20-25 cm deep. Cover with a 3-5 cm layer of fertile soil, keeping it constantly moist and loose during the rooting process.
- In an exposed area, remove all the buds and tie them off with wire. This will thicken the shoot, tie it with wire, and retain all the nutrients in the vine, making the seedlings stronger and more vigorous.
- At the end of August, prune the green shoots to speed up their maturation. In the fall, cut the layers into seedlings. Plant the fully developed shoots in their permanent location, and send the weaker ones to a nursery for further growth.
Tip! The Chinese method allows you to propagate scarce varieties that are difficult to root.
Kataviak
This method involves layering the entire bush, after which the mother plant is removed.

This type of propagation is used during vineyard reconstruction or renovation. The procedure is performed in late fall or winter, if climate conditions permit, before the vines begin to sap.
Daldarama and Lugenda
These methods are rarely used due to their high labor intensity and the severe depletion of the mother vine. They are used when rejuvenating and reconstructing a vineyard is necessary.
Seasonal features
Propagating grapes by layering is considered a common method for expanding a plantation or propagating a successful variety. When using this method, it's important to consider the seasonal variations, as there's much debate about whether layering is best established in spring, summer, or fall.
In summer
In summer, the procedure should begin when the grape vines reach 2.5 meters in length. This most often occurs in late July or early August. At this time, the vines are more likely to root from the layering. The method involves maintaining optimal soil moisture and applying nutrient supplements. Thanks to a stable soil temperature, the layering will begin to actively develop roots.
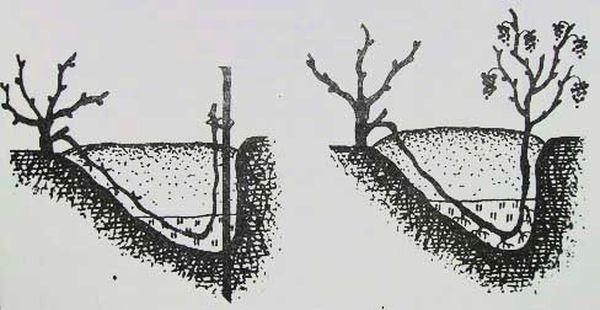
In the fall
Layering is most often done in the spring or summer. However, if you urgently need a seedling for planting, you can obtain one in the fall. To do this, regardless of the chosen propagation method, separate the young shoots from the parent plant in the fall before frost. Then plant them in a pot and store them in a basement until spring.
You can leave the cuttings in the open ground over the winter, but be sure to cover them. The thickness of the material that will protect the plants during cold weather should range from 20 to 25 cm.
In the spring
Propagating grapes in the spring is considered a simple, guaranteed method for obtaining new bushes of your favorite varieties. Hilling the head of the bush is the preferred method. This is suitable for varieties characterized by compact size and low bush formation.
When warm weather arrives, prune all shoots to leave a gap of two buds. When they reach 25 cm in length, cover them with a layer of soil and water. Throughout the season, monitor the soil moisture, watering the plants regularly to prevent them from drying out. In the fall, separate the shoots from the mother plant.
Aftercare
The strength and growth of a bush depend on proper care. Planted cuttings require favorable conditions, including maintaining soil moisture, fertilizing, loosening the soil, removing weeds, and controlling pests and diseases. This will not only increase the viability of the cuttings but also speed up the first harvest.

Watering
Immediately after planting, water the seedlings 2-3 times a week to help the roots adapt to the new growing conditions. Subsequently, water whenever the soil dries out.
Important! Excessive moisture can lead to root rot and death, as the soil doesn't have time to dry out and air doesn't reach the roots.
The soil should be watered in special furrows or directly into the holes.
Loosening and weeding
To ensure normal grape growth, loosening and weeding are essential. These activities will improve and restore the soil structure and properties, retain moisture, and ensure aeration.
After each rain, loosen the soil around the bushes. This will minimize evaporation and provide the roots with oxygen. The number of times you loosen the soil during the growing season depends on weather conditions.
It's also important to remove weeds promptly, preventing them from taking root. Weed by hand to a depth of at least 15 cm.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Before propagating grapes by layering, it is recommended to familiarize yourself with the basic intricacies of the process and follow the advice of experienced gardeners:
- Any climatic conditions are suitable for propagating the crop using this method.
- For planting, you need to give preference to a place that is well lit by the sun and also protected from drafts.
- The soil must be fertile, since when new bushes appear, the consumption of nutrients from it will increase.
- To measure the length of a young vine, you should use a centimeter.
- It is necessary to tie up grape branches using twine, ropes, and thin pieces of fabric.
- When replanting young vines, avoid rushing or fussing, as this often leads to damaged shoots and a weak root system. This is the main mistake made not only by novice winegrowers but also by experienced gardeners.
Properly followed techniques and careful consideration of all the nuances from experienced gardeners on propagating grapes by layering will allow you to obtain a beautiful, healthy plant that will delight you with a delicious harvest in its first year.











