- History of selection
- Description and characteristics of the variety
- Main characteristics
- Appearance
- Clusters
- Berries
- Frost resistance
- Productivity
- Transportability
- Disease resistance
- Pros and cons
- How to plant correctly
- Site selection and preparation
- How to choose and prepare a seedling
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering
- Mulching
- Top dressing
- Formation
- Preventive spraying
- Protection from wasps and birds
- Shelter for the winter
- Methods of reproduction
- Seeds
- Cuttings
- Layering
- Diseases and pests
- Gray rot
- Mildew
- Oidium
- Harvesting and storage
- Applications of berries
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Saperavi is one of the most ancient Georgian red grape varieties, renowned for its wines. The primary cultivation region is Kakheti, but the plant is also cultivated in other regions of Georgia, as well as in Moldova, Kazakhstan, and Azerbaijan. The name Saperavi translates as "paint" or "color-giver." The variety received this name because it contains a high amount of tannins—substances that impart a rich color to the berries and the drinks made from them.
History of selection
The exact origin of the Saperavi variety is unknown. Georgians consider it the oldest variety and call it by various names: Kakhet Saperavi, Didi Saperavi, and Krasilshchik. In the 20th century, scientists actively used it as a source for genetic selection. The Potapenko Research Institute of Viticulture and Winemaking in Novocherkassk developed a hybrid with improved varietal properties. It was named Saperavi Severny.
This variety is recommended for cultivation in the North Caucasus and Krasnodar Krai regions. Characteristics of Northern Saperavi:
- mid-late, technical variety;
- its vegetation period is from 140 to 145 days;
- the flowers of the plant are bisexual;
- cone-shaped bunches of grapes, weighing up to 200 grams.

Description and characteristics of the variety
Saperavi is a late-ripening variety. Its highest yield in its primary growing region, Kakheti, is 110 centners per hectare. The variety grows and bears fruit in a variety of soils, with the exception of calcareous, saline, marshy, and dry soils.
Saperavi produces its best results in conditions of sufficient irrigation on well-lit and warmed, loose soils.
The variety is considered universal. It cannot be clearly classified as a table or wine grape. Saperavi vines first bear fruit four years after planting. The most abundant and high-quality harvest occurs at 15 years of age.
 Wine made from the Saperavi grape variety has a very long shelf life. Aged for over 12 years, it is considered particularly valuable and beneficial. Its alcohol content is 10-12 degrees.
Wine made from the Saperavi grape variety has a very long shelf life. Aged for over 12 years, it is considered particularly valuable and beneficial. Its alcohol content is 10-12 degrees.
Main characteristics
Saperavi bushes are vigorous, with approximately 70% of their fruit-bearing shoots growing for up to 25 years.
Appearance
The plants have rounded, five-lobed leaves with a lyrate-shaped petiole notch. Sometimes the leaf blades are entire, with curled edges. Their undersides are densely pubescent.
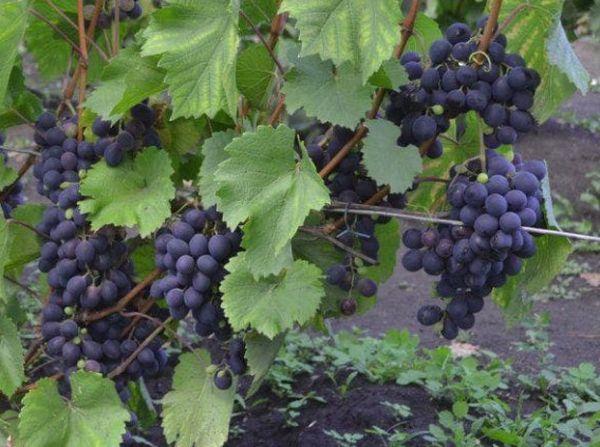

Clusters
Bunches of grapes have the following characteristics:
- weight, on average, 110 grams;
- shape – broadly conical;
- leg length 4.5 centimeters;
- branches heavily.
Berries
The berries are oval-shaped and dark blue. The skin is firm but thin. Inside are two seeds, and the pulp is juicy. The grapes taste sweet and fresh, with a pleasant aroma.

Ten kilograms of Saperavi berries yield approximately eight liters of juice. The sugar content is 19-22 grams. The juice is used to make wines, including sparkling wines. Saperavi is suitable for fine wines, as the berries are enriched with essential oils.
Frost resistance
The Saperavi Severny vine variety can withstand temperatures down to -30°C. C. Plants grown in southern regions do not require winter cover.
When cultivating the variety in the middle zone, the vines are covered before the first frost.
Productivity
Saperavi harvesting begins in September. Each fruit-bearing vine produces an average of 1.6 berry clusters. The variety's yield is high. However, it can be reduced by poor lighting, as well as a combination of unfavorable weather conditions and poor agricultural practices.
The variety is distinguished by the fact that the ripe berries do not fall off and dry out after a month.
Transportability
The grapes are transported short distances for processing into wine must. The grape clusters are not preserved in their marketable condition.

Disease resistance
In the Black Sea basin, considered ideal for growing the Saperavi variety, plants are less susceptible to diseases. The harsher the growing conditions, the lower its disease resistance. The variety exhibits moderate resistance to powdery mildew and downy mildew, but requires protection from gray mold. The plant also has strong immunity to leaf rollers.
Pros and cons
Grapes have the following advantages and disadvantages:
| Advantages of the Saperavi variety | Disadvantages of the Saperavi variety |
| It is distinguished by its frost and drought resistance. | Resistant to infection by oidium and mildew. |
| Serves as a good raw material for the preparation of various wines. | Shedding of flowers and ovaries. |
| Transported over medium distances. | Late ripening period. |
| Does not require self-pollination. | The appearance of gray mold on plants in rainy weather. |
How to plant correctly
The correct choice of location for planting a vineyard is very important, it determines the yield and taste of the fruit.
Site selection and preparation
The variety is planted in well-drained areas protected from winds. A lack of sunlight results in slow ripening and sour grapes.
Soil preparation for planting begins two weeks before planting, or in the fall. The soil must have time to settle, otherwise the plant's shoots will end up on the ground, which is unacceptable. A drainage layer of fine crushed stone or gravel is added to the holes.
How to choose and prepare a seedling
Grape seedlings are selected according to the following criteria:
- Age. Plants aged 1-2 years are considered the most viable;
- size. The height of plants should be at least 0.4 meters;
- The appearance of the trunk. Ideally, it is smooth, without damage, burrs, or thickenings;
- Root condition. They should have several main branches and numerous absorbent rootlets.
Before planting, Saperavi seedlings are soaked in water for two days. Growth stimulants are added to the water.

Recommendations for choosing deadlines
In southern regions with a mild climate, grapevines can be planted in the fall. If the soil freezes during the winter, planting should be done in March or April, when the soil has warmed up well.
Planting diagram
When planting the Saperavi variety, the optimal planting pattern is 2.5 x 1.5 meters:
- The holes are dug to a depth of 0.5 meters.
- The soil in the hole is collected into a small mound. The seedling is placed on it, spreading out the root system.
- Check that the top node of the rootstock is located 10 centimeters below the level of the planting hole.
- The hole is filled, the soil is lightly compacted and watered with several buckets of water.
- The plant is tied to a support.
Care instructions
Universal and wine grape varieties have the advantage of requiring little investment in cultivation and producing decent yields. The Saperavi variety is easy to care for and responds well to agricultural practices.

Watering
The first grape watering of the season is done immediately after removing the cover. Then, two more waterings are scheduled: 7-10 days before bud break and after flowering. As soon as the berries begin to turn blue, watering is stopped.
The last abundant watering of the season for plants to survive the winter is carried out before covering.
Bushes less than three years old are watered using buried pipes. Each plant requires four buckets of warm water.
Mulching
Mulching the soil should begin the season before planting the vineyard to ensure the young vines establish well, avoid freezing, and are resistant to disease. Mulch eliminates the need for weeding, ensures moisture absorption, and promotes good soil aeration.
The best time to apply mulch is when the buds open. The simplest method is to cover a 0.5-meter radius around the bush with organic mulch, such as straw.

Top dressing
The Saperavi variety responds well to mineral and organic fertilizers. If the grapes are fertilized during planting, the next application of fertilizer should be delayed for 3-4 years while the vines develop.
| Period | Fertilizer | Action | Quantity |
| 2 weeks before flowering | Nitrogen-containing compounds (nitrophoska, boric acid) | Active growth of green plant mass | 5 grams of boric acid and 60 grams of nitrophoska per 10 liters of water |
| When the ovaries appear | Nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium mixtures in the proportion 3:2:1 | Strengthening the growth of ovaries | 30 grams of fertilizer per 10 liters of water |
| After picking the berries | Potassium-phosphorus fertilizers | Strengthening plant immune defenses and frost resistance | According to the instructions |
Formation
The goal of bush training is to accelerate fruiting. This procedure is carried out in the first few years after planting. The permissible load on one plant is no more than 60 buds. Grapevines are pruned at 10-12 buds.
When forming a standard tree, the most vigorous shoot that has grown during the growing season is selected. It is pruned to the height of the future standard, leaving 2-3 buds at the top. The remaining shoots are removed.
Preventive spraying
The first treatment of grapes is carried out in early spring, after removing the cover, to prevent fungal and bacterial infections. Subsequent spraying times are determined based on the growing season:
- when buds appear;
- before and during flowering;
- when the berries ripen - when they are the size of a pea;
- before harvesting;
- before covering the grapes for the winter.
Various means are used to spray bushes: chemical insecticides and fungicides, biological preparations.

Protection from wasps and birds
One of the problems faced by winegrowers is damage to berries by wasps and birds. To combat the former, the following are used:
- traps;
- repellents and plants;
- covering fruits with various materials.
Without protection from birds, grapes can lose up to 50% of the harvest. Birds most often feast on the berries early in the morning.
Experienced gardeners recommend draping nylon nets over the vines to preserve grapes, creating a protective belt about 1.5 meters high.
Shelter for the winter
The most vulnerable part of the Saperavi bush is the root system. It should be covered with a layer of mulch before frost sets in. Young plants also require shelter. A sturdy frame is installed over them, and a plastic film is draped over it.
Methods of reproduction
Saperavi grapes are propagated by seedlings, cuttings, and layering. It is believed that vines grown from seedlings develop best and begin bearing fruit faster.

Seeds
Grapes grown from seeds differ in their properties and traits, for better or worse, from their parent plants. Seed germination is a slow process. Sow in the fall in boxes filled with garden soil and bury them in open ground. In the spring, they are transferred to a greenhouse. When 3-5 true leaves appear, the plants are transplanted to their permanent location.
Cuttings
In the fall, during grape pruning, cuttings are harvested. They are 50-60 centimeters long and about 10 millimeters thick. The cuttings are soaked in water for two days and then stored in a cellar until February. In winter, they are divided so that each cutting has two buds—one at the top and one at the bottom.
The cuttings are placed in a jar with water at the bottom and brought into a warm room. After roots appear, they are planted in cups with loose soil (a mixture of humus and sand). They are transplanted into open ground in May.
Layering
Propagation of grapes by layering Begin in the spring. Remove all leaves from a long shoot, except those at the end. Make a 5-millimeter-wide ring cut in the bark at the point that will be underground. Dig a hole, place the exposed section of the shoot at the bottom, cover it with soil, and water. Tie the end of the shoot to keep it upright.
Diseases and pests
Saperavi is not a model variety for disease resistance. It requires preventative treatment. Beginning winegrowers should closely monitor the plants, especially during adverse weather conditions.
Gray rot
Grapevine infection most often occurs under conditions of high temperature and humidity. Its symptoms include:
- drying of inflorescences;
- fluffy gray coating on the brushes;
- rotting of berries.
To combat gray mold, plants are treated with Euparen or Topsin.
Mildew
The most dangerous fungal disease. High humidity favors its development. Symptoms of mildew on vines:
- leaves are oily, yellow, and may fall off;
- the lesions are small at first, but gradually cover the entire surface of the leaf blade;
- on the underside there is a white powdery coating – mycelium;
- inflorescences and tops of shoots dry up;
- the berries darken and wrinkle.
The main means of control is Bordeaux mixture.
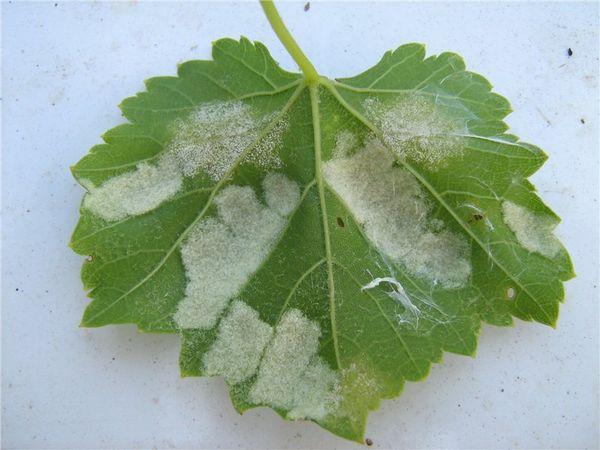

Oidium
This is a fungus that attacks grapes when the air humidity is above 80% and the temperature is above 25 C. Oidium can be recognized by the following signs:
- powdery coating on leaves;
- leaf blades curl and dry out;
- the berries crack and dry out.
The most effective means of combating the disease are sulfur preparations.
Harvesting and storage
Grapes are a vitamin-rich product. It's beneficial to eat them fresh.
The berries can be stored in a cool, ventilated area. Saperavi can be used to make wine at home. Sweet, ripe berries are best for this beverage.
Applications of berries
Saperavi grapes are used as raw material for the production of more than 40 wines.
These include table red wines, vintage red dessert wines, and fortified dessert wines. All are characterized by a tart, astringent taste, determined by their high tannin content.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
Experienced gardeners advise beginners to pay attention to the following nuances when caring for the Saperavi variety:
- It is better to plant plants in soil that does not contain salt and lime.
- It is necessary to avoid overwatering the roots, because of which the vine will bear fruit less and may die.
- Leaves growing near ripening grape clusters should be plucked off so that they do not obstruct the air supply.
- A single bush has up to 30 buds. Five buds need to be pruned short.
To ensure a good Saperavi grape harvest, it's important to monitor watering and vine health, mulch the soil, provide winter shelter, and protect the vines from fungal diseases. Saperavi wines are tart and very aromatic.











