- History of selection
- Description and Features
- Characteristics of the variety
- Frost resistance
- Drought resistance
- Productivity and fruiting
- Applications of berries
- Disease resistance
- Transportability
- Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- How to plant correctly
- Recommendations for choosing deadlines
- Site selection and preparation
- How to select and prepare planting material
- Planting diagram
- Care instructions
- Watering mode
- Top dressing
- Trimming
- Protection from birds and insects
- Preparing for winter
- Preventive spraying
- Methods of reproduction
- Cuttings
- Graft
- Layers
- Diseases and pests
- Oidium
- Mildew
- Phylloxera
- Aphid
- Thrips
- Spider mite
- Harvesting and storage
- Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
The Chocolate grape variety is considered very popular. This crop is versatile, producing high yields and boasting excellent flavor. To achieve successful cultivation, it requires proper care. Protection from diseases and pests is also crucial.
History of selection
Chocolate grapes are also known by other names: Red Maradona, Pamyati Golodrigi, and Taifi Ustoichivy. This crop is considered a hybrid, resulting from the crossing of two varieties: Antey Magarachsky and Kata-Kurgan Kirovabadsky. The plant was developed by Ukrainian breeders under the direction of P. Golodrigi.
Description and Features
This variety is characterized by vigorous bushes and bisexual inflorescences. The clusters are attractive and large. They are conical or cylindrical-conical in shape and weigh 600-1200 grams.
The fruits are large and oval, weighing 8-10 grams. The berries are characterized by a reddish-brown color and firm flesh. The outer skin is thin and tough. The fruits have a pleasant, harmonious flavor with chocolate notes. The vines ripen well, and cuttings root easily.
Characteristics of the variety
Before deciding to plant this crop, it is worth familiarizing yourself with its characteristics.
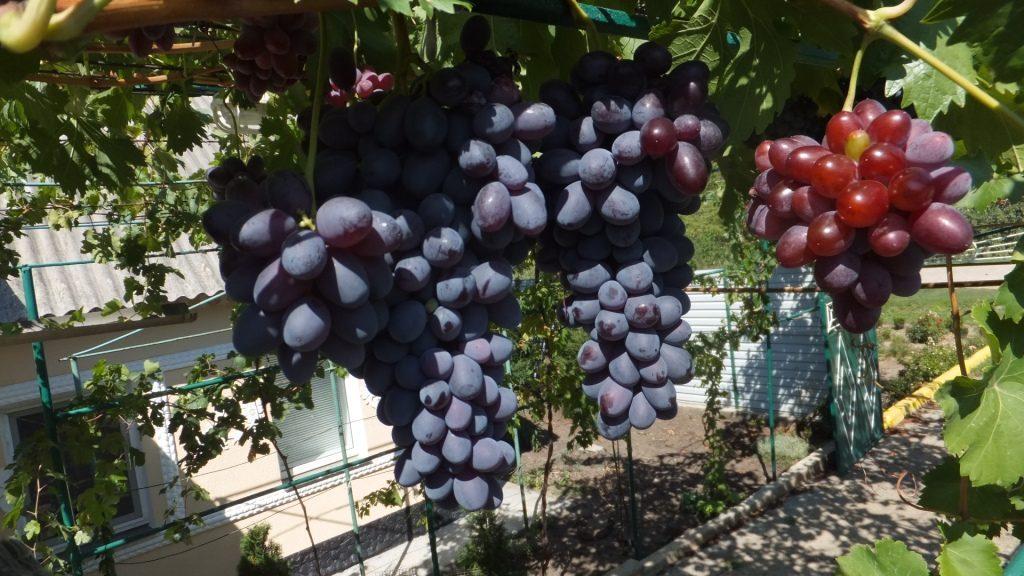

Frost resistance
This grape variety is characterized by high frost resistance. The vines can withstand temperatures as low as -25 degrees Celsius.
Drought resistance
The plant tolerates short-term drought well. However, in hot weather, periodic watering is recommended.
Productivity and fruiting
This variety is characterized by high yields. One hectare can yield 150 centners of grapes.
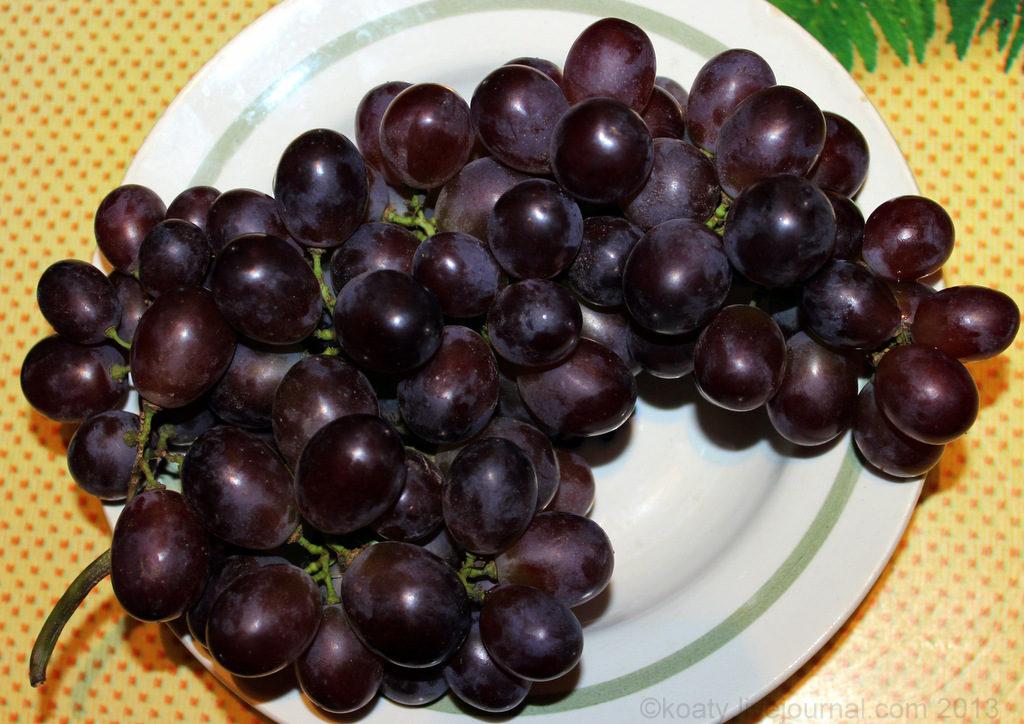

Applications of berries
The fruits of this variety are distinguished by their versatility. They can be eaten fresh. The berries are also used to make wine and various preserves.
Disease resistance
The crop is resistant to powdery mildew, downy mildew, and gray mold. Its resistance to these diseases is rated at 3 points.
Transportability
Grapes are easy to transport and suitable for long-term storage.
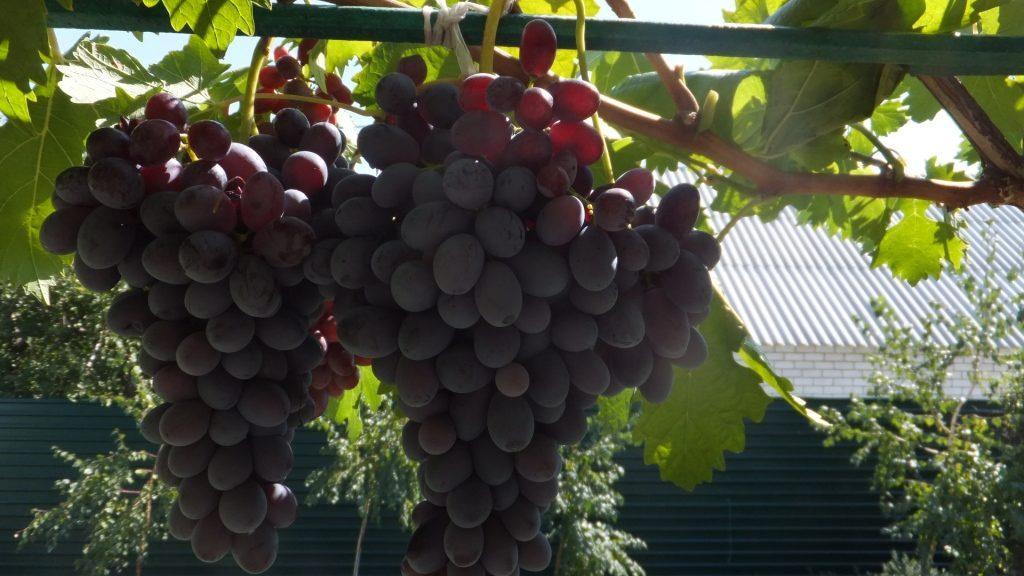

Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
The advantages of culture include the following:
- high yield parameters;
- good transportability;
- the possibility of growing in poor soil;
- resistance to dry weather;
- beneficial properties of fruits.
The crop's disadvantages include its low resistance to diseases. Furthermore, the fruit takes a long time to ripen. Therefore, it is grown primarily in the south.

How to plant correctly
To ensure proper plant development, it requires high-quality care. Strict adherence to planting recommendations is essential.
Recommendations for choosing deadlines
It's recommended to plant this grape variety in spring or fall. In colder regions, it's best to do this in the first half of May, when warm weather sets in. The short summer will give the grapes time to establish themselves and overwinter safely.
In autumn, the plant can be planted in southern regions.

Site selection and preparation
Seedlings of this variety should be planted in a sunny location. A south-facing spot is best. Shady areas will not produce the fruit well. Insufficient light will prevent the berries from remaining green.
The crop requires nutritious soil with a good drainage layer. Growing grapes in marshy areas is not recommended.
Bushes of this variety grow well near buildings or fences. Such barriers provide excellent protection from drafts and wind.
How to select and prepare planting material
You can buy a seedling of this variety at a specialty store or grow it yourself from a cutting. If you choose the former, carefully inspect the plant. When purchasing a bare-root plant, make sure it has green leaves.
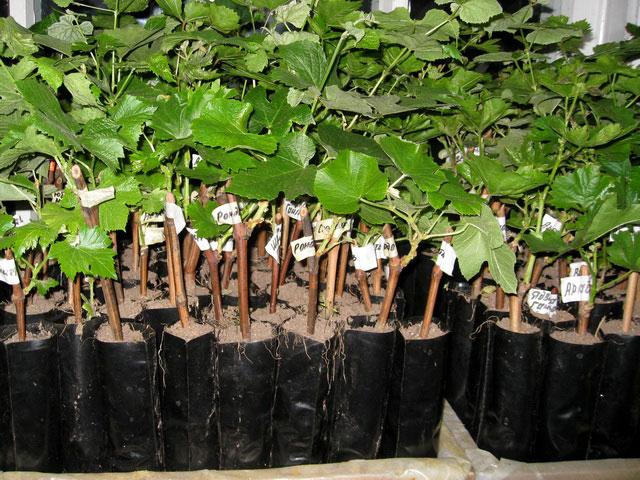

When purchasing a plant during the cold season, make sure the cutting is alive. The buds should be swelling and ready to open. A green structure should be visible when the skin is cut. There should be no rot or damage on the seedling itself.
Planting diagram
It's recommended to plant the plant in early May. The timing depends on the climate. To complete the procedure, follow these steps:
- Prepare a planting hole in advance. This should be done in the fall or at least one week beforehand. The hole should be 80 centimeters deep and in diameter.
- Fill the hole halfway with a mixture of fertile soil and compost. Add fertilizer containing potassium and phosphorus. If the soil is too heavy, add sand to loosen it. Before filling, it's recommended to add drainage material such as crushed bricks and stones.
- Remove the seedling from the pot with a lump of soil. Place it in the hole and cover with soil. Water to settle the soil. Apply a layer of peat and sawdust mulch on top.
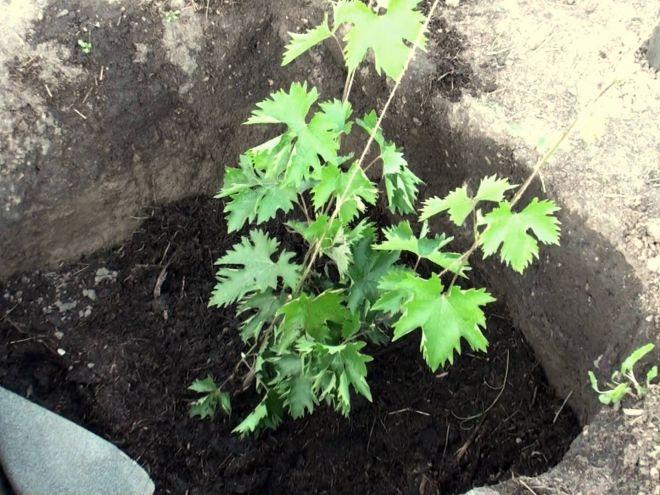

Care instructions
Normal cultural development is impossible without high-quality and comprehensive care. This care must be comprehensive.
Watering mode
Water the plant only as needed. It's recommended to moisten the soil only when the top layer dries out. In hot weather, this should be done at least once a week. The soil shouldn't become waterlogged.
Be sure to water the plant during inflorescence formation.
The soil should also be moistened during fruit ripening and until harvest. The final watering should be done before covering the plants for the winter.
After the soil has become moist, a crust usually forms. This should be removed to provide the plant's roots with moisture and oxygen. Loosening the soil helps remove weeds. To keep the soil moist longer, apply a layer of mulch. Straw or sawdust can be used for this purpose.

Top dressing
During the first 2-3 years after planting, the plant does not require fertilizer. During this period, the fertilizers used at planting are sufficient. Older plants require complex fertilizers. Periodic application of organic matter is recommended.
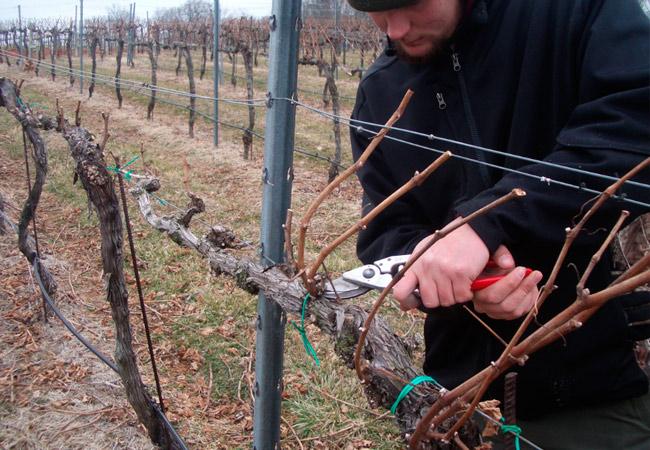
Trimming
This grape variety grows rapidly, so it requires regular pruning. This should be done in the fall and spring. In the former case, trim away excess shoots and clear the bush of dead branches.
In spring, formative pruning is performed, which gives the plant shape and stimulates abundant fruiting.
If there's sufficient space, it's recommended to train this grape variety into two branches. The bush is considered quite hardy, so a maximum of 60 buds are allowed on it. Seven to eight buds are removed from each shoot. This is considered the maximum allowable load.

Protection from birds and insects
This plant is susceptible to attacks from birds and insects. To prevent these problems, use special nets to protect the bunches.
Preparing for winter
Preparing grapes for winter is recommended only in the central or northern regions. However, in colder regions, the crop is practically not grown, as its fruits do not have time to ripen. In the south, plantings can be left uncovered.
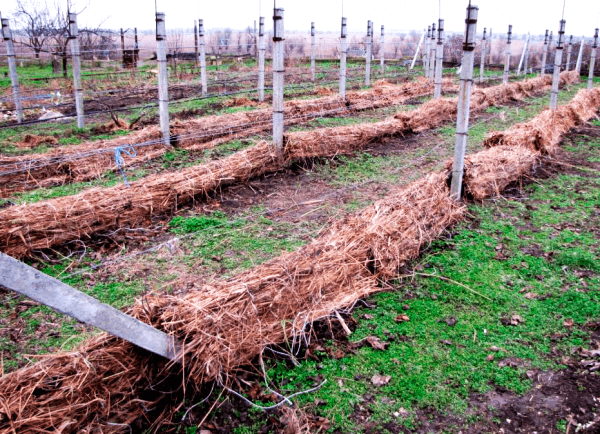

To prepare the plant for winter, remove the vine, place it on spruce branches, and cover it with non-woven material. Special agrofibre will also work. If snow falls, add more snow to the plant.
Preventive spraying
The plant rarely experiences dangerous diseases, but it's not recommended to neglect preventative spraying. Fungicides applied before and after flowering will help prevent fungal infections. Copper-containing products also help combat this problem.

Methods of reproduction
Grapes can be propagated in a variety of ways. To achieve good results, it's important to strictly follow the procedure.
Cuttings
In this case, it is recommended to perform the following steps:
- Take the cuttings out of the basement in early February. Trim off the bottom part.
- Use a sharp knife to scratch the bark near the cut, about 2 centimeters long. This will facilitate root growth.
- Soak the cuttings in water or wrap them in moss and film.
- After roots appear, plant in a pot with soil.
It is recommended to plant the plant outdoors in early May. The exact time depends on climate conditions.

Graft
The plant can be propagated by grafting. The rootstock can be young or mature. When pruning, discard the top of the vine, as it is usually immature. The remaining shoots should be trimmed with pruning shears to obtain cuttings with 4-5 buds.
To preserve the sap, dip the cuttings in hot paraffin and wrap them in a damp cloth. Store the cuttings until spring. Then you can graft. The cleft method works best for this variety.
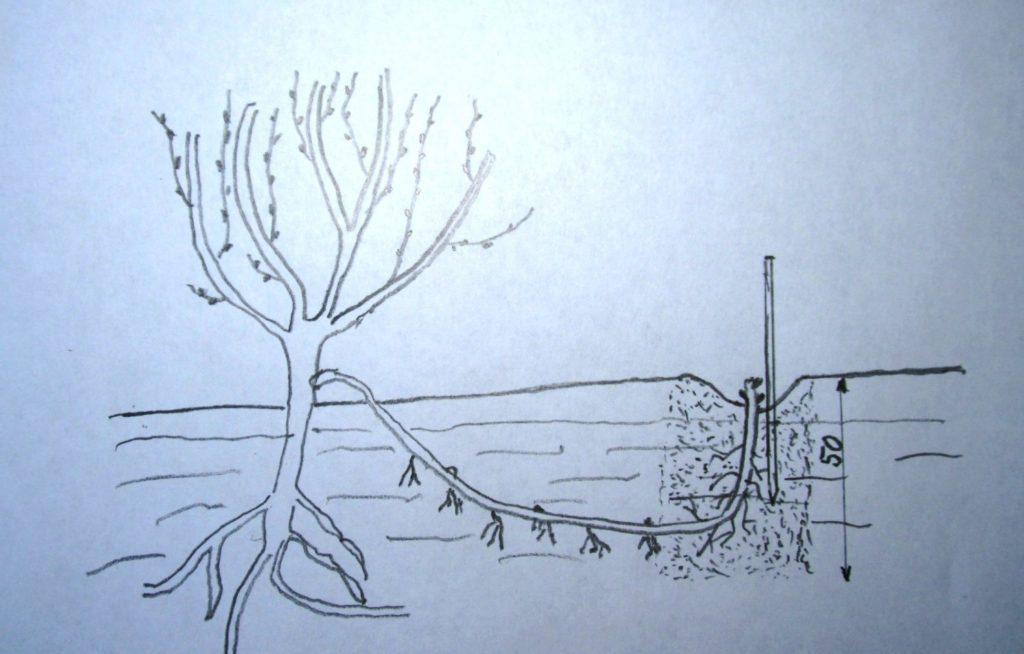
Layers
The plant can be propagated by layering. To do this, it's recommended to take a strong shoot, bend it down, and place it in a specially prepared trench. Secure it in place and cover with soil. The soil should be moistened periodically. After a while, roots will appear.
Diseases and pests
Grapes of this variety are periodically subject to attacks by harmful insects and the development of various diseases.
Oidium
This disorder causes damage to the crop. It lags in development and becomes covered with a white coating. The risk of developing the disease increases in hot and dry weather. Treating the bunches with crushed sulfur before flowering can help prevent this. Fertilizing the soil with potassium and phosphorus is recommended.
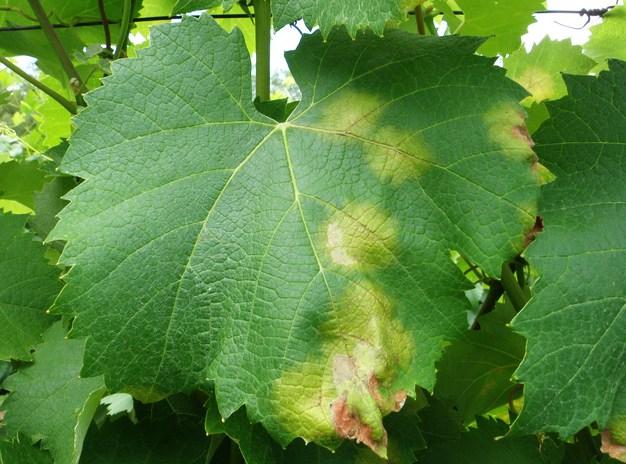
Mildew
This is one of the most dangerous diseases for grapes, occurring under conditions of high temperature and humidity. With a mild infection, the sugar content of the berries decreases, and vine ripening is disrupted. In severe cases, the plant loses leaves, and its yield decreases. When the disease progresses, Maneb or Zineb are used.

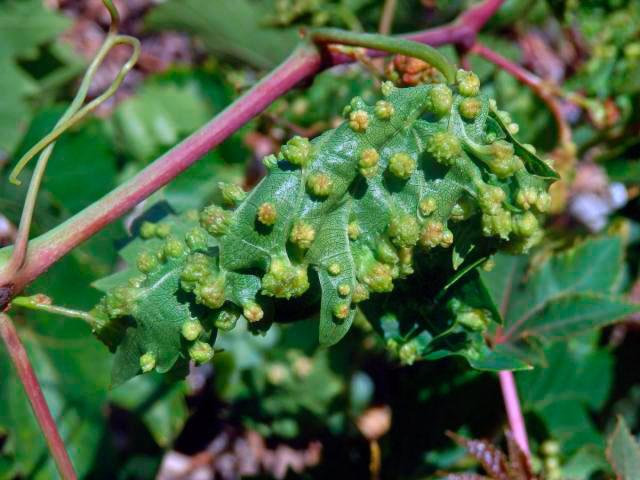
Phylloxera
This pest causes damage to leaves, roots, and cuttings. Products such as Mitak or Zolon can help control the parasites. You can also treat the bushes with Karbofos. If the root system is affected, volatile carbon disulfide is used.
Aphid
These pests attack plant leaves by absorbing their sap. Infestations with parasites significantly increase the risk of fungal diseases. Insecticides help control aphids.

Thrips
These small insects cause leaf damage and can also transmit viral infections. Insecticides are used to protect grapes.
Spider mite
These insects absorb plant juices. As a result, the crop stunts growth, loses leaves, and takes longer to mature. The product DNOC, sulfur-based products, and systemic acaricides can help combat this problem.
Harvesting and storage
The harvest should be timely. It is recommended to cut the clusters with sharp pruning shears. Ripe fruits can be stored in the refrigerator. They can also be canned, frozen, or used to make wine.

Tips and advice from experienced gardeners
To achieve success in growing the crop, you must follow these rules:
- carry out planting operations correctly;
- moisten the soil in a timely manner;
- add nutrients periodically;
- tie the plant to a support;
- perform sanitary and formative pruning;
- carry out pest and disease control.
Chocolate grapes are considered a very popular variety, grown by many gardeners. This crop is characterized by high yields and excellent taste. To achieve significant success in its cultivation, it is important to plant it correctly and strictly follow the care recommendations.











